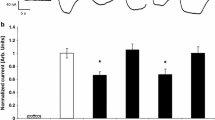
Abstract
The two-microelectrode voltage clamp technique was used to examine the kinetics and substrate specificity of the cloned renal Na+/myo-inositol cotransporter (SMIT) expressed in Xenopus oocytes. The steady-state myo-inositol-induced current was measured as a function of the applied membrane potential (V m ), the external myo-inositol concentration and the external Na+ concentration, yielding the kinetic parameters: K MI0.5 , K Na0.5 , and the Hill coefficient n. At 100 mM NaCl, K MI0.5 was about 50 μm and was independent of V m . At 0.5 mm myo-inositol, K Na0.5 ranged from 76 mm at V m =−50 mV to 40 mm at V m =−150 mV. n was voltage independent with a value of 1.9±0.2, suggesting that two Na+ ions are transported per molecule of myo-inositol. Phlorizin was an inhibitor with a voltage-dependent apparent K I of 64 μm at V m =−50 mV and 130 μm at V m = −150 mV. To examine sugar specificity, sugar-induced steady-state currents (at V m =−150 mV) were recorded for a series of sugars, each at an external concentration of 50 mm. The substrate selectivity series was myo-inositol, scyllo-inositol > l-fucose > l-xylose > l-glucose, d-glucose, α-methyl-d-glucopyranoside > d-galactose, d-fucose, 3-O-methyl-d-glucose, 2-deoxy-d-glucose > d-xylose. For comparison, oocytes were injected with cRNA for the rabbit intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1) and sugar-induced steady-state currents (at V m =−150 mV) were measured. For oocytes expressing SGLT1, the sugar selectivity was: d-glucose, α-methyl-d-glucopyranoside, d-galactose, d-fucose, 3-O-methyl-d-glucose > d-xylose, l-xylose, 2-deoxy-d-glucose > myo-inositol, l-glucose, l-fucose. The ability of SMIT to transport glucose and SGLT1 to transport myo-inositol was independently confirmed by monitoring the Na+-dependent uptake of 3H-d-glucose and 3H-myo-inositol, respectively. In common with SGLT1, SMIT gave a relaxation current in the presence of 100 mm Na+ that was abolished by phlorizin (0.5 mm). This transient current decayed with a voltage-sensitive time constant between 10 and 14 msec. The presteady-state current is apparently due to the reorientation of the cotransporter protein in the membrane in response to a change in V m . The kinetics of SMIT is accounted for by an ordered six-state nonrapid equilibrium model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birnir, B., Loo, D.D.F., Wright, E.M. 1991. Voltage-clamp studies of the Na+/glucose cotransporter cloned from rabbit small intestine. Pfluegers Arch. 418:79–85
Colman, A. 1984. Translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA in Xenopus oocytes. In: Transcription and Translation—A Practical Approach. B.D. Hames, and S.J. Higgins, editors. pp. 271–302. IRL, Oxford
Del Monte, M.A., Rabbani, R., Diaz, T.C., Lattimer, S.A., Nakamura, J., Brennan, M.C., Greene, S.A. 1991. Sorbitol, myo-inositol, and rod outer segment phagocytosis in cultured hRPE cells exposed to glucose: In vitro model of myo-inositol depletion hypothesis of diabetic complications. Diabetes 40:1335–1345
Garcia-Perez, A., Burg, M.B. 1991. Renal medullary organic osmolytes. Physiol. Rev. 71:1081–1115
Hediger, M.A., Coady, M.J., Ikeda, T.S., Wright, E.M. 1987. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Nature 330:379–381
Ikeda, T.S., Hwang, E.S., Coady, M.J., Hirayama, B.A., Hediger, M.A., Wright, E.M. 1989. Characterization of a Na+/glucose cotransporter cloned from rabbit small intestine. J. Membrane Biol. 110:87–95
Krieg, P.A., Melton, D. 1984. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned CDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 12:7057–7070
Kwon, H.M., Yamauchi, A., Uchida, S., Preston, A.S., Garcia-Perez, A., Burg, M.B., Handler, J.S. 1992. Cloning of the cDNA for a Na+/myo-inositol cotransporter, a hypertonicity stress protein. J. Biol. Chem. 267:6297–6301
LaCourse, W.R., Mead, D.A., Johnson, D.C. 1990. Anion-exchange separation of carbohydrates with pulsed amperometric detection using a pH-selective reference electrode. Anal. Chem. 62:220–224
Loo, D.D.F., Bezanilla, F., Wright, E.M. 1994. Two voltage-dependent steps are involved in the partial reactions of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. FASEB J. 8:A1992
Loo, D.D.F., Hazama, A., Supplisson, S., Turk, E., Wright, E.M. 1993. Relaxation kinetics of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5767–5771
Mager, S., Naeve, J., Quick, M., Labarca, C., Davidson, N., Lester, H.A. 1993. Steady states, charge movements, and rates for a cloned GABA transporter expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron 10:177–188
Moper, K., Schultz, C.A., Chevolot, L., Germain, C., Revuelta, R., Dawson, R. 1992. Determination of sugars in unconcentrated seawater and other natural waters by liquid chromatography and pulsed aniperometric detection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26:133–138
Pajor, A.M., Wright, E.M. 1992. Cloning and functional expression of a mammalian Na+/nucleoside cotransporter. J. Biol. Chem. 267:3557–3560
Panayotova-Heiermann, M., Loo, D.D.F., Wright, E.M. 1994, Sodium/D-Glucose cotransporter charge movements involve polar residues. J. Biol. Chem. 269:21016–21020
Parent, L., Supplisson, S., Loo, D.D.F., Wright, E.M. 1992a. Electrogenic properties of the cloned Na+/glucose cotransporter: I. Voltage-clamp studies. J. Membrane Biol. 125:49–62
Parent, L., Supplisson, S., Loo, D.D.F., Wright, E.M. 1992b. Electrogenic properties of the cloned Na+/glucose cotransporter: II. A transport model under nonrapid equilibrium conditions. J. Membrane Biol. 125:63–79
Taglialatela, M., Toro, L., Stefani, E. 1992. Novel voltage clamp to record small, fast currents from ion channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys. J. 61:78–82
Umbach, J., Coady, M.J., Wright, E.M. 1990. Intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter expressed in Xenopus oocytes is electrogenic. Biophys. J. 57:1218–1224
Yorek, M.A., Stefani, M.R., Dunlap, J.A., Ro, K.S., Davidson, E.P. 1991. Trans-hydroxyl group configuration on carbons 2 and 3 of glucose. Diabetes 40:1016–1023
Yorek, M., Stefani, M.R., Moore, S.A. 1991. Acute and chronic exposure of mouse cerebral microvessel endothelial cells to increased concentrations of glucose and galactose: effect on myo-inositol metabolism, PGE2 synthesis, and Na+/K+-ATPase transport activity. Metabolism 40:347–358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Present address: W.M. Keck Biotechnology Resource Laboratory, Boyer Center for Molecular Medicine, Rm, 305A, Yale University, 295 Congress Ave., New Haven, Connecticut 06536-0812
Present address: National Institute for Physiological Sciences, Department of Cell Physiology, Okazaka, 444, Japan
Contributed equally to this work
We thank John Welborn for the HPLC analysis of the sugar substrates. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health DK19567, DK42479 and NS25554.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hager, K., Hazama, A., Kwon, H.M. et al. Kinetics and specificity of the renal Na+/myo-inositol cotransporter expressed in Xenopus Oocytes. J. Membarin Biol. 143, 103–113 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234656
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234656