Abstract
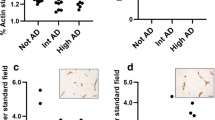
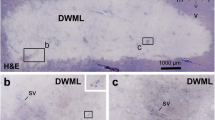
Alterations of the cerebral microvasculature have been reported in aging and in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. However, the exact role of microvascular alterations in the pathogenesis of neurodegeneration remains unknown. In the present report, the cerebral cortex microvasculature was studied by immunohistochemistry using a monoclonal antibody against vascular heparan sulfate proteoglycan protein core in normal aging controls, Alzheimer's disease, Down syndrome, Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonian dementia complex, Pick's disease and dementia pugilistica. In all dementing illnesses, increased microvascular pathology was evident compared to normal controls. Decreased microvascular density and numerous atrophic vessels were the primary abnormalities observed in all dementing disorders. These microvascular abnormalities demonstrated regional and laminar selectivity, and were primarly found in layers III and V of frontal and temporal cortex. Quantitative analysis employing computer-assisted microscopy demonstrated that the decrease in microvascular density in Alzheimer's disease was statistically significant compared to age-matched controls. In addition, extracellular heparan sulfate proteoglycan deposits were observed which colocalized with thioflavine S-positive senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease, Down syndrome and selected Guam dementia cases. In some cases, heparan sulfate proteoglycan was seen in senile plaques that appeared to be diffuse or primitive plaques that stained weakly with thioflavine. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan-containing neurons were also observed in Alzheimer's disease, as well as in Down syndrome and Guam cases. Glial staining for heparan sulfate proteoglycan was never observed. Our data support previous observations that microvascular pathology is found in aging and in Alzheimer's disease. The changes in Alzheimer's disease exceed those found in normal aging controls. We also found microvascular pathology in all other dementing disorders studied. Our studies further demonstrated that the microvascular pathology displays regional and laminar patterns which parallel patterns of neuronal loss. Finally, we also found that heparan sulfate proteoglycan is present in senile plaques and neurons not only as previously reported in Alzheimer's disease, but also in Down syndrome and Guam cases. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan in senile plaques may be derived from either the degenerating microvasculature or from degenerating neurons. Further studies are necessary to determine the role of microvascular disease in the progression of Alzheimer's disease and other dementing disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Flory J, Damasio AR, Van Hoesen GW (1991) The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Cerebral Cortex 1: 103–116
Bell MA, Ball MJ (1981) Morphometric comparison of hippocampal microvasculature in ageing and demented people: diameters and densities. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 53: 299–318
Bell MA, Ball MJ (1990) Neuritic plaques and vessels of visual cortex in aging and Alzheimer's dementia. Neurobiol Aging 11: 359–370
Buée L, Ding W, Anderson JP, Narindrasorasak S, Kisilevsky R, Greenberg B, Boyle NJ, Robakis N, Delacourte A, Fillit HM (1993) Binding of vascular heparan sulfate proteoglycan to Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein is mediated through the N-terminal region of the A4 peptide. Brain Res 627: 199–204
Buée L, Ding W, Delacourte A, Fillit HM (1993) Binding of secreted human neuroblastoma proteoglycans to the Alzheimer amyloid A4 peptide. Brain Res 601: 154–163
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science 261: 921–923
Davies DC, Hardy JA (1988) Age and neurodegenerative disease related changes in the blood brain barrier deserve more through investigation. Neurobiol Aging 9: 46–48
Davies DC, Horwood N, Isaacs SL, Mann DMA (1992) The effect of age and Alzheimer's disease on pyramidal neuron density in the individual fields of the hippocampal formation. Acta Neuropathol 83: 510–517
Davignon J, Gregg RE, Sing CF (1988) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 8: 1–21
Défossez A, Beauvillain JC, Delacourte A, Mazucca M (1988) Alzheimer's disease: new evidence for common epitopes between microtubule associated protein tau and paired helical filaments (PHF): demonstration at the electron microscopic level by a double immunogold labelling. Virchows Arch [A] 413: 141–145
Delacourte A, Flament S, Dibe EM, Hublau P, Sablonnière B, Hémon B, Scherrer V, Défossez A (1990) Pathological proteins tau 64 and 69 are specifically expressed in the somatodendritic domain of the degenerating cortical neurons during Alzheimer's disease: demonstration with a panel of antibodies against tau proteins. Acta Neuropathol 80: 111–117
Duvernoy HM (1988) The human hippocampus. Springer, New York
Duvernoy HM, Delon S, Vannson JL (1981) Cortical blood vessels of the human brain. Brain Res Bull 7: 519–579
Fillit HM, Buée L, Hof PR, Delacourte A, Morrison JH (1991) Cortical distribution of abnormal microvasculature and heparan sulfate proteoglycan positive plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Soc Neurosci [Abstr] 17: 692
Fischer VW, Siddiqui A, Yusufaly Y (1990) Altered angioarchitecture in selected areas of brains with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 79: 672–679
Fraser PE, Nguyen JT, Chin DT, Kirschner DA (1992) Effects of sulfate ions on Alzheimer β/A4 peptide assemblies: implications for amyloid fibril-proteoglycan interactions. J Neurochem 59: 1531–1540
Frederickson RCA (1992) Astroglia in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 13: 239–253
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120: 885–890
Hassler O (1965) Vascular changes in senile brains. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 5: 40–53
Hof PR, Cox K, Morrison JH (1990) Quantitative analysis of a vulnerable subset of pyramidal neurons in Alzheimer's disease. I. Superior frontal and inferior temporal cortex. J Comp Neurol 301: 44–54
Hof PR, Knabe R, Bovier P, Bouras C (1991) Neuropathological observations in a case of autism presenting with self-injury behavior. Acta Neuropathol 82: 321–326
Hof PR, Perl DP, Loerzel AJ, Morrison JH (1991) Neurofibrillary tangle distribution in the cerebral cortex of parkinsonism-dementia cases from Guam: differences with Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 564: 306–313
Hof PR, Bouras C, Buée L, Delacourte A, Perl D, Morrison JH (1992) Differential distribution of neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebral cortex of dementia pugilistica and Alzheimer's disease cases. Acta Neuropathol 85: 23–30
Hovingh P, Linker A (1974) The disaccharide repeating units of heparan sulfate. Carbohydr Res 37: 181–192
Jarrett JT, Lansbury PT Jr (1992) Amyloid fibril formation requires a chemically discriminating nucleation event: studies of an amyloidogenic sequence from the bacterial protein Osm B. Biochemistry 31: 12345–12352
Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ (1992) The seminal role of β-amyloid in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 6: 7–34
Kalaria RN (1992) The blood-brain barrier and cerebral microcirculation in Alzheimer's disease. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 4: 226–260
Karthikeyan L, Maurel P, Rauch U, Margolis RK, Margolis RU (1992) Cloning of a major heparan sulfate proteoglycan from brain and identification as the rat form of glypican. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 188: 395–401
Kemeny E, Fillit HM, Damle SP, Mahabir R, Kefalides NA, Gregory JD, Antonovych T, Sabnis S, Zabriskie JB (1988) Monoclonal antibodies to heparan sulfate proteoglycan: development and application to the study of normal tissue and pathologic human kidney biopsies. Connect Tissue Res 18: 1–12
Kisilevsky R (1990) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans in amyloidogenesis: an epiphenomenon, a unique factor, or the tip of a more fundamental process? Lab Invest 63: 589–591
LaCoste M, White CL (1993) The role of cortical connectivity in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis: a review and model system. Neurobiol Aging 14: 1–16
Lewis DA, Campbell MH, Terry RD, Morrison JH (1987) Laminar and regional distributions of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in Alzheimer's disease: a quantitative study of visual and auditory cortices. J Neurosci 7: 1799–1808
Mann DMA, Eaves NR, Marcyniuk B, Yates PO (1986) Quantitative changes in cerebral cortical microvasculature in ageing and dementia. Neurobiol Aging 7: 321–330
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 34: 939–944
Morrison JH (1993) Differential vulnerability, connectivity, and cell typology. Neurobiol Aging 14: 51–54
Narindrasorasak S, Lowery D, Gonzalez-DeWhitt P, Poorman RA, Greenberg B, Kisilevsky R (1991) High affinity interactions between the Alzheimer's β amyloid precursor proteins and the basement membrane form of heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J Biol Chem 266: 12878–12883
Perlmutter LS, Chui HC (1990) Microangiopathy, the vascular basement membrane and Alzheimer's disease: a review. Brain Res Bull 24: 677–686
Perlmutter LS, Chui HC, Saperia D, Athanikar J (1990) Microangiopathy and the colocalization of heparan sulfate proteoglycan with amyloid in senile plaques of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 508: 13–19
Perry G, Siedlak SL, Richey P, Kawai M, Cras P, Kalaria RN, Galloway PG, Scardina JM, Cordell B, Greenberg BD, Ledbetter SR, Gambetti P (1991) Association of heparan sulfate proteoglycan with the neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 11: 3679–3683
Price JL, Davis PB, Morris JC, White DL (1991) The distribution of tangles, plaques and related immunohistochemical markers in healthy aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 12: 295–312
Ravens JR (1978) Vascular changes in the human senile brain. Adv Neurol 20: 487–501
Rogers J, Morrison JH (1985) Quantitative morphology and regional and laminar distribution of senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 5: 2801–2808
Scheibel AB, Duong T (1988) On the possible relationship of cortical microvascular pathology to blood brain barrier changes in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 9: 41–42
Scheibel AB, Duong T, Tomiyasu U (1987) Denervation microangiopathy in senile dementia, Alzheimer type. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 1: 19–37
Snow AD, Wight TN (1989) Proteoglycans in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and other amyloidoses. Neurobiol Aging 10: 481–497
Snow AD, Willmer JP, Kisilevsky R (1987) Sulfated glycosaminoglycans in Alzheimer's disease. Hum Pathol 18: 506–510
Stewart PA, Hayakawa K, Akers M, Vinters HV (1992) A morphometric study of the blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer's disease. Lab Invest 67: 734–742
Su JH, Cummings BJ, Cotman CW (1992) Localization of heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan and proteoglycan protein core in aged brain and Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience 51: 801–813
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R, Hansen LA, Katzman R (1991) Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synaptic loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 30: 572–580
Tomlinson BE, Blessed S, Roth M (1970) Observations on the brains of demented old people. J Neurol Sci 11: 205–242
Vallet PG, Guntern R, Hof PR, Golaz J, Delacourte A, Robakis N, Bouras C (1992) A comparative study of histological and immunohistochemical methods for neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 83: 170–178
Weisgraber KH, Rall SC Jr, Mahley RW, Milne RW, Marcel YL, Sparrow JT (1986) Human apolipoprotein E. Determination of the heparin binding sites of apolipoprotein E3. J Biol Chem 261: 2068–2076
Willingham MC, Rutherford AV (1984) The use of osmium-thiocarbohydrazide-osmium and ferrocyanide-reduced osmium methods to enhance membrane contrast and preservation in cultured cells. J Histochem Cytochem 32: 455–460
Wisniewski T, Frangione B (1992) Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett 135: 235–238
Wisniewski HM, Wegiel J, Wang KC, Lach B (1992) Ultrastructural studies of the cells forming amyloid in the cortical vessel wall in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 84: 117–127
Zellweger H (1977) Down syndrome. Handbk Clin Neurol 31: 367–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buée, L., Hof, P.R., Bouras, C. et al. Pathological alterations of the cerebral microvasculature in Alzheimer's disease and related dementing disorders. Acta Neuropathol 87, 469–480 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294173
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294173