Abstract
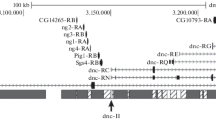
In situ hybridisation to mitotic chromosomes shows that sequences homologous to different Drosophila melanogaster transposable elements are widely distributed not only in beta but also in alpha-heterochromatin. Clusters of these sequences are detected in most proximal positions. They colocalise with known satellite sequences in several regions, but are also located in places where no known sequence has been mapped so far. The pattern of hybridisation is dinstinctive and specific for each element, and presents constant features in six different D. melanogaster strains studied. The entirely heterochromatic Y chromosome contains large amounts of these sequences. Additionally, some of these sequences appear to be present in substantial quantities in the smallest minichromosome of Drosophila, Dp(1;f)1187.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad JP, Carmena M, Baars S, Saunders RDC, Glover DM, Ludena P, Sentis C, Tyler-Smith C, Villasante A (1992) Dodecasatellite: a conserved G+C rich satellite from the centromeric heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4663–4667
Ananiev EV, Barsky VE, Ilyin UV, Ryzic MV (1984) The arrangement of transposable elements in the polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 90:366–377
Biessmann H, Carter SB, Mason JM (1990) Chromosome ends in Drosophila without telomeric DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1758–1761
Bonaccorsi S, Lohe A (1991) Fine mapping of satellite DNA sequences along the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster: relationships between satellite sequences and fertility factors. Genetics 129:177–189
Bucheton A, Paro R, Sang HM, Pelisson A, Finnegan DJ (1984) The molecular basis of I-R dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Identification, cloning and properties of the I factor. Cell 38:153–163
Caizzi R, Caggese C, Pimpinelli S (1993) Bari-1, a new transposon-like family of Drosophila melanogaster with a unique heterochromatic organization. Genetics 133:335–341
Carlson M, Brutlag DL (1978) One of the copia genes is adjacent to satellite DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 15:733–742
Carmena M, Abad JP, Villasante A, Gonzalez C (1993) The Drosophila melanogaster dodecasatellite sequence is closely linked to the centromere and can form connections between sister chromatids during mitosis. J Cell Sci 105:41–50
Cherkassova VA, Surkov SN, Ilyin YV (1991) Leader region of mdg1 Drosophila retrotransposon RNA contains 3′-end processing sites. Nucleic Acids Res 19:3212–3219
Danilevskaya O, Lofsky A, Kurenove EV, Pardue M-L (1993) The Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster contains a distinctive subclass of Het-A related repeats. Genetics 134:531–543
Devlin RH, Bingham B, Wakimoto BT (1990) The organization and expression of the light gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 125:129–140
Dorer DR, Henikoff S (1994) Expansions of transgene repeats cause heterochromatin formation and gene silencing in Drosophila. Cell 77:993–1002
Finnegan DJ (1989) Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution. Trends Genet 5:103–107
Gatti M, Pimpinelli S (1992) Functional elements in Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin. Annu Rev Genet 26:239–275
Gonzalez C, Casal J, Ripoll P, Sunkel S (1991) The spindle is required for the process of sister chromatid separation in Drosophila neuroblasts. Exp Cell Res 192:10–15
Hawley RS, Irick H, Zitron AE, Haddox DA, Lohe A, New C, Whitley MD, Arbel T, Jang J, McKim K, Childs G (1993) There are two mechanisms of achiasmate segregation in Drosophila, one of which requires heterochromatic homology. Dev Genet 13:440–467
Hennig W (1993) Conventional protein coding genes in the Drosophila Y chromosome: is the puzzle of the fertility gene function solved? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10904–10906
Hilliker AJ, Appels R, Schalet A (1980) The genetic analysis of D. melanogaster heterochromatin. Cell 21:607–619
Hochstenbach R, Potgens A, Meijer H, Dijkhof R, Knops M, Schouren K, Hennig W (1993) Partial reconstruction of the lampbrush loop pair Nooses on the Y chromosome of Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma 102:526–545
Huijser P, Kirchhoff C, Lankenau D-H, Hennig W (1988) Retrotransposon-like sequences are expressed in Y chromosomal lampbrush loops of Drosophila hydei. J Mol Biol 203:689–697
Inouye S, Yuki S, Saigo K (1984) Sequence-specific insertion of the Drosophila transposable element 17.6. Nature 310:332–333
John B (1988) The biology of heterochromatin. In: Verma RS (ed) Heterochromatin: molecular and structural aspects. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–147
Karpen G (1994) Position effect variegation and the new biology of heterochromatin. Curr Opin Genet Dev 4:281–291
Lica L, Narayanswami S, Hamkalo B (1986) Mouse satellite DNA, centromere structure, and sister chromatid pairing. J Cell Biol 103:1145–1151
Lindsley DL, Zimm GG (1992) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Academic Press, San Diego, London
Lohe AR, Brutlag DL (1987) Adjacent satellite DNA segments in Drosophila. Structure of junctions. J Mol Biol 194:171–179
Lohe AR, Hilliker AJ, Roberts PA (1993) Mapping simple repeated DNA sequences in heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 134:1149–1174
Novitski E (1977) Compound autosomes. In: Ashburner M, Novitski E (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, vol. 1b. Academic Press, London New York San Francisco, pp 562–568
O'Hare K, Alley MRK, Cullingford TE, Driver A, Sanderson MJ (1990) DNA sequence of the Doc retroposon in the white-one mutant of Drosophila melanogaster and of secondary insertions in the phenotypically altered derivatives white-honey and white-eosin. Mol Gen Genet 225:17–24
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Spathas DH, Ferguson-Smith MA (1993) A simplified one-step procedure for enhanced detection of biotinylated probes with fluorescein conjugates. TIG 9:262
Steinemann M, Steinemann S, Lottspeich F (1993) How Y chromosomes become genetically inert. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5737–5741
Streck RD, MacGaffey JE, Beckendorf SK (1986) The structure of hobo transposable elements and their insertion sites. EMBO J 5:3615–3623
Tchurikov NA, Ilyin YV, Skryabin KG, Ananiev EV, Bayev AAJr, Krayev AS, Zelentsova ES, Kulguskin VV, Lyubomirskaya NV, Georgiev GP (1980) General properties of mobile dispersed genetic elements in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 14:655–665
Truett M, Jones RS, Potter SS (1981) Unusual structure of the FB family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Cell 24: 753–763
Vaury C, Bucheton A, Pelisson A (1989) The beta-heterochromatic sequences flanking the I elements are themselves defective transposable elements. Chromosoma 98:215–224
Yamamoto MT, Mitchelson A, Tudor M, O'Hare K, Davies JA, Miklos GL (1990) Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of the heterochromatin-euchromatin junction region of the Drosophila melanogaster X chromosome using cloned DNA sequences. Genetics 125:821–832
Young BS, Pession A, Traverse KL, French C, Pardue ML (1983) Telomere regions in Drosophila share complex DNA sequences with pericentric heterochromatin. Cell 34:85–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carmena, M., González, C. Transposable elements map in a conserved pattern of distribution extending from beta-heterochromatin to centromeres in Drosophila melanogaster . Chromosoma 103, 676–684 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344228
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344228