Summary
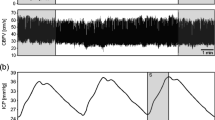
An analysis of intracranial pressure (ICP), based on an examination of the temporary correlation between the changes in amplitude of the pulse wave and the mean ICP level, is presented. The paper contains a discussion of the preliminary results of the method when applied to the analysis of ICP as monitored during infusion tests in a group of 24 children. Infusion of a certain volume of CSF is a good example of an uncompensated volume process, introduced externally into the intracranial space. Results allow an interpretation of the short term correlation coefficient RAP (correlation coefficient between ICP and variations of the amplitude of fundamental component of the pulse wave AMP), as a steady state index. According to this interpretation, the presented analysis enables the observation of a loss of equilibrium during the test. Other phenomena can also be observed, for instance a recovery to equilibrium after the test, nonlinearities of amplitude-pressure relationship, vasomotor reflexes etc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cees J, Avezaat HM, van Eijndhoven (1984) Cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and craniospinal dynamics. PhD Thesis, Academic Hospital Rotterdam and Erasmus University, Jongbloed and Zoon Publishers, The Netherlands
Czosnyka M (1985) Digital frequency analysis for intracranial pressure processing. PhD Thesis, Warsaw University of Technology, (in Polish)
Czosnyka M, Wollk-Laniewski P (1985) Intracranial pressure processing for intensive care purposes. Proc of MECOMBE '85, Sevilla, Spain, pp 75–80
Marmarou AA (1973) A theoretical and experimental evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid system. Doctor thesis, Drexel Univ
Nakamura Tet al (1983) Prognostic value of continuous ICP monitoring, computerized topography, and regional CBF in communicating hydrocephalus. In: Ishii Set al (eds) Proc of ICP V. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 696–690
Sliwka S (1985) Static and dynamic cerebrospinal elastance-clinical verification. In: Miller JDet al (eds) Proc of ICP VI. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 84–87
Sliwka S (1980) The clinical system for examination of compensatory features of intracranial space. Doctor Thesis, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw (in Polish)
Tamaki Net al (1983) Hyxdrodynamics in normal pressure hydrocephalus-correlation between the incidence of B waves, dynamics of cerebrospinal fluid circulation and cerebral blood flow. In: Ishii Set al (eds) Proc of ICP V. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 669–674
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czosnyka, M., Wollk-Laniewski, P., Batorski, L. et al. Analysis of intracranial pressure waveform during infusion test. Acta neurochir 93, 140–145 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01402897
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01402897