Abstract
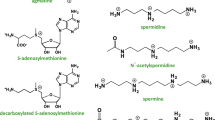
Diamine oxidase catalyzes the oxidative deamination of short chain aliphatic diamines, like putrescine, and histamine. The enzyme is rate-limiting in the terminal catabolism of polyamines, which are endogenous polycations important for cell growth and differentiation. This review examines the behavior of diamine oxidase in mammalian tissues in relation to diamine and polyamine metabolism under physiological and pathological conditions. The role of diamine oxidase in the control of putrescine levels in growing tissues and the known mechanisms responsible for the enzyme expression are also described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. A. Zeller,Diamine oxidases. InThe Enzymes, Vol. 8. (Ed. P. D. Boyer, H. Lardy and K. Myrbäck) 2nd Edition, pp. 313–335, Academic Press, New York 1963.
F. Buffoni,Histaminase and related amine oxidases. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 1163–1199 (1966).
U. Bachrach,Copper amine oxidases and amines as regulators of cellular processes. InStructure and Functions of Amine Oxidases. (Ed. B. Mondovi) pp. 5–20, CRC Press, Boca Raton 1985.
R. Kapeller-Adler,Amine Oxidases and Methods for Their Study. Wiley-Interscience, New York 1970.
C. Maśliński,Histamine and its metabolism in mammals. Agents and Actions5, 89–107, 183–225 (1975).
C. Maśliński and W. A. Fogel,Catabolism of histamine. InHistamine and Histamine Antagonists. (Ed. B. Uvnäs) Handbook Exp. Pharmacol. Vol. 97, 165–189, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg 1991.
A. E. Pegg,Recent advances in the biochemistry of polyamines in eukaryotes. Biochem. J.234, 249–262 (1986).
O. Heby and L. Persson,Molecular genetics of polyamine synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Trends Biochem. Sci.15, 153–158 (1990).
J. Jänne, L. Alhonen and P. Leinonen,Polyamines: From molecular biology to clinical applications, Ann. Med.23, 241–259 (1991).
T. L. Sourkes and K. Missala,Histamine metabolism. Putrescine metabolism and the study of diamine oxidase activity in vivo. Agents and Actions11, 20–27 (1981).
N. Seiler and B. Eichentopf,4-Aminobutyrate in mammalian putrescine catabolism. Biochem. J.152, 201–210 (1975).
T. Okuyama and Y. Kobayashi,Determination of diamine oxidase activity by liquid scintillation counting. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.95, 242–250 (1961).
K. Missala and T. L. Sourkes,Putrescine catabolism in rats given heparin or aminoguanidine. Eur. J. Pharmacol.64, 307–311 (1980).
J. Kusche, H. Richter, J. Schmidt, R. Hesterberg, A. Friedrich and W. Lorenz,Diamine oxidase in rabbit small intestine: Separation from a soluble monoamine oxidase, properties and pathophysiological significance in intestinal ischemia. Agents and Actions5, 431–439 (1975).
J. Kusche, J. Schmidt, A. Schmidt and W. Lorenz,Diamine oxidases in the small intestine of rabbits, dogs and pigs: Separation from soluble monoamine oxidases and substrate specificity of the enzyme. Agents and Actions5, 440–441 (1975).
T. Biegański, J. Kusche, W. Lorenz, R. Hesterberg, C.-D. Stahlknecht and K.-D. Feussner,Distribution and properties of human intestinal diamine oxidase and its relevance for histamine catabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta756, 196–203 (1983).
F. Sánchez-Jiménez, J. M. Matés, J. L. Urdiales, M. A. Medina, E. Viguera, M. Garcia-Caballero and I. N. De Castro,Does histamine behave as a growth-related polyamine? InHistamine in normal and cancer cell proliferation. (Eds. M. Garcia-Caballero, L. J. Brandes and S. Hosoda) pp. 43–70, Pergamon Press, Oxford 1993.
R. Hesterberg, J. Sattler, W. Lorenz, C.-D. Stahlknecht, H. Barth and M. Crombach,1. Distribution and metabolism of histamine. Histamine content, diamine oxidase activity and histamine methyltransferase activity in human tissues: Fact or fiction? Agents and Actions14, 325–334 (1984).
R. E. Shaff and M. A. Beaven,Turnover and synthesis of diamine oxidase (DAO) in rat tissues. Studies with heparin and cycloheximide. Biochem. Pharmacol.25, 1057–1062 (1976).
K. S. Kim, B. Backus, N. Harris and P. Rourke,Distribution of diamine oxidase and imidazole N-methyltransferase along the gastrointestinal tract. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.31, 137–145 (1969).
J. Kusche, W. Lorenz, C.-D. Stahlknecht,Diamine oxidase activity in gastric and duodenal mucosa of man and other mammals with special reference to the pyloric junction. Agents and Actions8, 366–371 (1978).
T. Biegański,Biochemical, physiological and pathophysiological aspects of intestinal diamine oxidase. Acta Physiol. Pol.34, 139–153 (1983).
L. D'Agostino, G. D'Argenio, C. Ciacci, B. Daniele, V. Macchia and G. Mazzacca,Diamine oxidase in rat small bowel: Distribution in different segments and cellular location. Enzyme31, 217–220 (1984).
J. Kusche, J. R. Izbicki, R. Mennigen, A. Curt and J. V. Parkin,The effect of experimental carcinogenesis on intestinal diamine oxidase, a polyamine deaminating enzyme. Cancer Detect. Prev.9, 17–29 (1986).
W. A. Fogel,Mucosal mono- and polyamine oxidase activities in digestive tract are distributed complementary to diamine oxidase. J. Neural Transm. (Suppl.)32, 345–349 (1990).
S. B. Baylin, S. A. Stevens and K. M. M. Shakir,Association of diamine oxidase and ornithine decarboxylase with maturing cells in rapidly proliferating epithelium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta541, 415–419 (1978).
K. M. M. Shakir, S. Margolis and S. B. Baylin,Localization of histaminase (diamine oxidase) in rat small intestinal mucosa: Site of release by heparin. Biochem. Pharmacol.26, 2343–2347 (1977).
A. Robertson-White, S. B. Baylin, T. Olivecrona and M. A. Beaven,Binding of diamine oxidase activity to rat and guine pig microvascular endothelial cells. J. Clin. Invest.76, 93–100 (1986).
L. D'Agostino, S. Pignata, B. Daniele, R. Ventriglia, G. Ferrari, C. Ferraro, S. Spagnuolo, P. E. Lucchelli and G. Mazzacca,Release of diamine oxidase into plasma by glycosaminoglycans in rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta993, 228–232 (1989).
A. Wollin, H. Navert and G. Bounous,Effect of intestinal ischemia on diamine oxidase activity in rat intestinal tissue and blood. Gastroenterology80, 349–355 (1981).
G. D. Luk, W. P. Vaughan, P. J. Burke and S. B. Baylin,Diamine oxidase as a plasma marker of rat intestinal mucosal injury and regeneration after administration of 1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine. Cancer Res.41, 2334–2337 (1981).
D. V. Maudsley, J. Leif and Y. Kobayashi,Ornithine decarboxylase in rat small intestine: Stimulation with food or insulin. Am. J. Physiol.231, 1557–1561 (1976).
G. D. Luk, L. J. Marton and S. B. Baylin,Ornithine decarboxylase is important in intestinal mucosal maturation and recovery from injury in rats. Science210, 195–198 (1980).
G. D. Luk and S. B. Baylin,Polyamines and intestinal growth. Increased polyamine biosynthesis after jejunectomy. Am. J. Physiol.245, G656-G660 (1983).
P. Moore and M. E. Swenseid,Dietary regulation of the activities of ornithine decarboxylase and S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase in rats. J. Nutr.113, 1927–1935 (1983).
G. D. Luk and S. B. Baylin,Inhibition of intestinal epithelial DNA synthesis and adaptive hyperplasia after jejunectomy in the rat by suppression of polyamine biosynthesis. J. Clin. Invest.74, 698–704 (1984).
E. R. Seidel, M. K. Haddox and L. R. Johnson,Polyamines in response to intestinal obstruction. Am. J. Physiol.246, G649-G653 (1984).
G. D. Luk and P. Yang,Distribution of polyamines and their biosynthetic enzymes in intestinal adaptation. Am. J. Physiol.254, G194-G200 (1988).
B. Daniele and A. Quaroni,Polarized secretion of diamine oxidase by intestinal epithelial cells and its stimulation by heparin. Gastroenterology99, 1675–1687 (1990).
T. Rokkas, S. Vaja, P. Taylor, G. M. Murphy and R. H. Dowling,Effect of intestinal diamine oxidase (DAO) depletion by heparin on mucosal polyamine metabolism. Digestion46, 378–382 (1990).
M. Pinto, S. Robine-Leon, M. D. Appay, M. Kedinger, N. Triadou, E. Dussaulx, B. Lacroix, P. Simon-Assmann, K. Haffen, J. Fongh and A. Zweibaum,Enterocyte-like differentiation and polarization of the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture. Biol. Cell47, 323–330 (1983).
L. D'Agostino, B. Daniele, S. Pignata, R. Gentile, P. Tagliaferri, A. Contegiacomo, G. Silvestro, C. Polistina, A. R. Bianco and G. Mazzacca,Ornithine decarboxylase and diamine oxidase in human colon carcinoma cell line CaCo-2 in culture. Gastroenterology97, 888–894 (1989).
B. Daniele and A. Quaroni,Effects of epidermal growth factor on diamine oxidase expression and cell growth in Caco-2 cells. Am. J. Physiol.261, G669-G676 (1991).
A. Quaroni,Crypt cell antigen expression in human tumor colonic cell lines: analysis with a panel of monoclonal antibodies to CaCo-2 luminal membrane components. J. Natl. Cancer Inst.76, 571–585 (1986).
T. Bamba, S. Vaja, G. M. Murphy and R. H. Dowling,Effect of fasting and feeding on polyamines and related enzymes along the villus: crypt axis. Digestion46, 424–429 (1990).
S. H. Erdman,Effects of starvation and difluoromethyl-ornithine (DFMO) on diamine oxidase activity in rat ileum. Digestion46, 396–402 (1990).
L. D'Agostino, B. Daniele, S. Pignata, M. V. Barone, G. D'Argenio and G. Mazzacca,Modification in ornithine decarboxylase and diamine oxidase in small bowel mucosa of starved and refed rats. Gut28, S1, 135–138 (1987).
J. Kusche, W. Lorenz, C.-D. Stahlknecht, H. Richter, R. Hesterberg, A. Schmal, E. Hinterlang, D. Weber and C. Ohmann,Intestinal diamine oxidase and histamine release in rabbit mesenteric ischemia. Gastroenterology80, 980–987 (1981).
L. E. Bragg, J. S. Thompson and W. W. West,Intestinal diamine oxidase levels reflect ischemic injury. J. Surg. Res.50, 228–233 (1991).
S. Koshi, M. Inoue, H. Obayashi and Y. Miyauchi,Inhibition of post-ischemic reperfusion injury of the small intestine by diamine oxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1075, 231–236 (1991).
S. H. Erdman, J. H. Y. Park, J. S. Thompson, C. J. Grandjean, M. H. Hart and J. A. Vanderhoof,Suppression of diamine oxidase activity enhances post-resection ileal proliferation. Gastroenterology96, 1533–1538 (1989).
G. D. Luk, T. M. Bayless and S. B. Baylin,Diamine oxidase (histaminase). A circulating marker for rat intestinal mucosal maturation and integrity. J. Clin. Invest.66, 66–70 (1980).
J. Kusche, C.-D. Stahlknecht, W. Lorenz, G. Reichert and H. Richter,Diamine oxidase activity and histamine release in dogs following acute mesenteric artery occlusion. Agents and Actions7, 81–84 (1977).
M. Boros, J. Kaszaki and S. Nagy,Oxygen free radical-induced histamine release during intestinal ischemia and reperfusion. Eur. Surg. Res.21, 297–304 (1989).
J. Fujisaki, K. Fujimoto, A. Oohara, T. Sakata, M. Hirano, T. Ohyama, R. Iwakiri and M. Yamaguchi,Roles of histamine and diamine oxidase in mucosa of rat small intestine after ischemia-reperfusion. Dig. Dis. Sci.38, 1195–1200 (1993).
F. Hahn, W. Schmutzler, G. Seseke, H. Giertz and W. Bernauer,Histaminase-freisetzung durch heparin and protamin beim meerschweinchen. Biochem. Pharmacol.15, 155–160 (1966).
S. B. Baylin, M. A. Beaven, R. M. Krauss and H. R. Keiser,Response of plasma histaminase activity to small doses of heparin in normal subjects and patients with hyperlipoproteinemia. J. Clin. Invest.52, 1985–1993 (1973).
V. Gäng, W. Gaubiz and U. Gunzer,Postheparin-diamine oxidase (histaminase) in anaphylaxis. Klin. Wschr.53, 285–287 (1975).
V. Gäng, G. Gehring and J. Schönborn,Combined decrease of postheparin-diamine oxidase (histaminase) and postheparin-lipoproteinlipase in inflammatory diseases. Klin. Wschr.55, 169–173 (1977).
G. D. Luk, T. M. Bayless and S. B. Baylin,Plasma postheparin diamine oxidase. Sensitive provocative test for quantitating length of acute intestinal mucosal injury in the rat. J. Clin. Invest.71, 1308–1315 (1983).
L. D'Agostino, B. Daniele, S. Pignata, M. V. Barone, C. Ciacci, R. Sollazzo and G. Mazzacca,Postheparin plasma diamine oxidase increases in patients with celiac disease during gluten-free diet. Gut28, S1, 131–134 (1987).
L. D'Agostino, C. Ciacci, B. Daniele, M. V. Barone, R. Sollazzo, and G. Mazzacca,Postheparin plasma diamine oxidase in subjects with small bowel mucosa atrophy. Dig. Dis. Sci.32, 313–317 (1987).
G. R. Corazza, A. Falasca, A. Strocchi, C. A. Rossi and G. Gasbarrini,Decreased plasma postheparin diamine oxidase levels in celiac disease. Dig. Dis. Sci.33, 956–961 (1988).
G. R. Corazza, L. Ginaldi, A. Falasca, A. Strocchi, C. A. Rossi, D. Quaglino and G. Gasbarrini,Diamine oxidase plasma activities after treatment with heparin and jejunal morphometry in untreated coeliac disease. J. Clin. Pathol.42, 1136–1139 (1989).
L. D'Agostino, A. Contegiacomo, S. Pignata, N. Zilembo, B. Daniele, C. Ferraro, G. D'Adamo, G. Petrelli, A. R. Bianco and G. Mazzacca,Plasma postheparin diamine oxidase in patients with small intestinal lymphoma. Cancer67, 511–515 (1991).
W. U. Schmidt, J. Sattler, R. Hesterberg, H. D. Röher, Th. Zoedler, H. Sitter and W. Lorenz,Human intestinal diamine oxidase (DAO) activity in Crohn's disease: A new marker for disease assessment? Agents and Actions30, 267–270 (1990).
L. D'Agostino, S. Pignata, B. Daniele, M. Visconti, C. Ferraro, G. D'Adamo, G. Tritto, G. Ambrogio and G. Mazzacca,Postheparin plasma diamine oxidase values in the follow-up of patients with small bowel Crohn's disease. Gut32, 932–935 (1991).
R. Hesterberg, J. Kusche, C.-D. Stahlknecht and K.-D. Feussner,The start of a programme for measuring diamine oxidase activity in biopsy specimens of human rectal mucosa. Agents and Actions11, 33–37 (1981).
R. Mennigen, J. Kusche, C. Streffer and B. Krakamp,Diamine oxidase activities in the large bowel mucosa of ulcerative colitis patients. Agents and Actions30, 264–266 (1990).
M. Raithel, A. M. Hörauf, M. Matek and H. W. Baenkler,Kinetics of histamine released from rectal mucosa. Agents and Actions28, 164–167 (1989).
R. Mennigen, J. Kusche, B. Krakamp, A. Elbers, B. Amoei, M. Kessebohm and H. Sommer,Large bowel tumors and diamine oxidase (DAO) activity in patients: A new approach for risk group identification. Agents and Actions23, 351–353 (1988).
S. B. Baylin and G. D. Luk,Diamine oxidase (histaminase) activity in human disease. InPolyamines in Biology and Medicine. (Eds. D. R. Morris and L. J. Marton) pp. 377–388, Marcel Dekker, New York, Basel 1981.
A. Sessa, M. A. Desiderio, M. Baizini and A. Perin,Diamine oxidase activity in regenerating rat liver and in 4-dimethylaminoazobenzene-induced and Yoshida AH 130 hepatomas. Cancer Res.41, 1929–1934 (1981).
S. B. Baylin and G. D. Luk,Diamine oxidase activity in human tumors: Clinical and biologic significance. InStructure and Functions of Amine Oxidases. (Ed. B. Mondovi) pp. 187–194, CRC Press, Boca Raton 1985.
A. Sessa, M. A. Desiderio and A. Perin,Diamine oxidase activity in a model of multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.51, 75–78 (1990).
A. Sessa, E. Broglia, M. R. Terreni and A. Perin,Diamine oxidase activity in rat brain carcinogenesis and in gliomas. Cancer Lett.71, 183–187 (1993).
J. Kusche, R. Mennigen, L. Leisten and B. Krakamp,Large bowel tumor promotion by diamine oxidase inhibition: Animal model and clinical aspects. InProgress in Polyamine Research. (Eds. V. Zappia, A. E. Pegg) pp. 745–752. Plenum Press, New York, London 1988.
J. Kusche, R. Mennigen and L. Leisten,Early alterations of rat intestinal diamine oxidase activity by azoxymethane, an intestinal carcinogen. Agents and Actions27, 218–220 (1989).
J. Kusche, A. Horn and R. Mennigen,Large bowel tumor promotion in rats by diamine oxidase inhibition. InPolyamines in the gastrointestinal tract. (Eds. R. H. Dowling, U. R. Fölsch and Chr. Löser) pp. 347–359. Kluwer, Dordrecht 1992.
J. Kusche, T. Bieganski, R. Hesterberg, C.-D. Stahlknecht, K.-D. Feussner, J. Stahlenberg and W. Lorenz,The influence of carcinoma growth on diamine oxidase activity in human gastrointestinal tract. Agents and Actions10, 110–113 (1980).
N. Seiler,Polyamine metabolism and elimination by the vertebrate organism. InPolyamines in the Gastrointestinal Tract. (Eds. R. H. Dowling, U. R. Fölsch, Chr. Löser) pp. 65–85, Kluwer, Dordrecht 1992.
S. K. Guha and J. Jänne,The synthesis and accumulation of polyamines in reproductive organs of the rat during pregnancy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta437, 244–252 (1976).
D. V. Maudsley and Y. Kobayashi,Biosynthesis and metabolism of putrescine in the rat placenta. Biochem. Pharmacol.26, 121–124 (1977).
A. C. Andersson, S. Henningsson and E. Rosengren,Increased formation of diamines and polyamines in the pregnant rat. J. Physiol.285, 311–324 (1978).
A. C. Andersson, S. Henningsson and E. Rosengren,Formation of cadaverine in the pregnant rat. Acta Physiol. Scand.105, 508–512 (1979).
M. A. Desiderio, A. Sessa and A. Perin,Polyamines and diamine oxidase activity in maternal, embryonal, and fetal tissues of rat after chronic ethanol consumption. Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun.142, 843–848 (1987).
A. Sessa, M. A. Desiderio and A. Perin,Ethanol and polyamine metabolism in adult and fetal tissues: Possible implication in fetus damage. InAdvances in Alcohol and Substance Abuse. (Ed. B. Stimmel) pp. 73–85. Haworth Press, New York 1987.
W. A. Fogel, C. Chmielecki, M. Gralek and C. Maśliński,Histamine metabolism in diabetic rats. Agents and Actions30, 243–246 (1990).
H. Barth, W. Lorenz and I. Niemeyer,Inhibition and activation of histamine methyltransferase by methylated histamine. Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem.354, 1021–1026 (1973).
J. Sattler, D. Häfner, H.-J. Klotter, W. Lorenz and P. K. Wagner,Food-induced histaminosis as an epidemiological problem: Plasma histamine elevation and haemodynamic alterations after oral histamine administration and blockade of diamine oxidase (DAO). Agents and Actions23, 361–365 (1988).
J. Sattler, W. Lorenz, K. Kubo, A. Schmal, S. Sauer and L. Lüben,Food-induced histaminosis under diamine oxidase (DAO) blockade in pigs: Further evidence of the key role of elevated plasma histamine levels as demonstrated by successful prophylaxis with antihistamines. Agents and Actions27, 212–214 (1989).
J. Sattler and W. Lorenz,Intestinal diamine oxidases and enteral-induced histaminosis: Studies on three prognostic variables in an epidemiological model. J. Neuronal Transm. (Suppl.)32, 291–314 (1990).
J. Sattler, W. Lorenz, R. Lindlar and U. Schäfer,Histamine in duodenal ulcer, stress-induced lesions, and upper gastrointestinal bledding: Causality analysis. InHistamine and Histamine Antagonists. (Ed. B. Uvnäs) Handbook Exp. Pharmacol. Vol.97, pp. 441–472, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg 1991.
J. Sattler, R. Hesterberg, W. Lorenz, M. Ennis, C.-D., Stahlknecht and J. Kusche,Pathophysiological functions of diamine oxidase: An evaluation in animal studies using a probabilistic model with several types of causal relationship. InStructure and Functions of Amine Oxidases. (Ed. B. Mondovi) pp. 167–178, CRC Press, Boca Raton 1985.
A. Sessa, M. A. Desiderio and A. Perin,Effect of acute ethanol administration on diamine oxidase activity in the upper gastrointestinal tract of rat. Alcoholism: Clin. Exp. Res.8, 185–190 (1984).
A. Perin, G. Scalabrino, A. Sessa and A. Arnaboldi,In vitro inhibition of protein synthesis in rat liver as a consequence of ethanol metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta366, 101–108 (1974).
A. Sessa, M. A. Desiderio and A. Perin,Stimulation of hepatic and renal diamine oxidase activity after acute ethanol administration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta801, 285–289 (1984).
M. Piacentini, C. Sartori, S. Beninati, A. Barqaqli and M. P. Cerù-Argento,Ornithine decarboxylase, transglutaminase, diamine oxidase and total diamines and polyamines in maternal liver and kidney throughout rat pregnancy. Biochem. J.234, 435–440 (1986).
A. Sessa, M. A. Desiderio and A. Perin,Effect of acute ethanol administration on diamine oxidase activity in maternal, embryonal and fetal tissues. Agents and Actions21, 49–53 (1987).
N. C. R. Räihä, M. Koskinen and P. Pikkarainen,Developmental changes in alcohol-dehydrogenase activity in rat and guinea pig liver. Biochem. J.103, 623–626 (1967).
A. Sessa and A. Perin,Diamine oxidase activity and related substrates in rat liver after chronic ethanol feeding. Agents and Actions37, 107–110 (1992).
C. S. Lieber,Mechanism of ethanol induced hepatic injury. Pharmac. Ther.46, 1–41 (1990).
A. Sessa and A. Perin,Chronic ethanol feeding and diamine oxidase activity in rat brain and liver. J. Neural Transm. (Suppl.)32, 319–322 (1990).
A. Perin and A. Sessa,Relationship between diamine oxidase activity and ethanol-induced gastric damage. InPolyamines in the Gastrointestinal Tract. (Eds. R. H. Dowling, U. R. Fölsch and Chr. Löser) pp. 269–273, Kluwer, Dordrecht 1992.
M. A. Desiderio, A. Sessa and A. Perin,Induction of diamin oxidase activity in rat kidney during compensatory hypertrophy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta714, 243–249 (1982).
A. Perin, A. Sessa and M. A. Desiderio,Polyamine levels and diamine oxidase activity in hypertrophic heart of spontaneously hypertensive rats and of rats treated with isoproterenol, Biochim. Biophys. Acta755, 344–351 (1983).
A. Sessa, M. A. Desiderio and A. Perin,Diamine oxidase activity induction in regenerating rat liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta698, 11–14 (1982).
M. A. Desiderio, I. Zini, P. Davalli, M. Zoli, A. Corti, K. Fuxe and L. F. Agnati,Polyamines, ornithine decarboxylase, and diamine oxidase in the substantia nigra and striatum of the male rat after hemitransection. J. Neurochem.51, 25–31 (1988).
M. A. Desiderio, A. Sessa and A. Perin,Diamine oxidase activity inhibition and putrescine levels in renal hypertrophy. InAdvances in Polyamines in Biomedical Science. (Eds. C. M. Caldarera and U. Bachrach) pp. 141–144, CLUEB, Bologna 1984.
P. E. Duffy and L. T. Kremzner,Ornithine decarboxylase activity and polyamines in relation to aging of human fibroblasts. Exp. Cell Res.108, 435–440 (1977).
J. E. Kay and V. J. Lindsay,Control of ornithine decarboxylase activity in stimulated human lymphocytes by putrescine and spermidine. Biochem. J.132, 791–796 (1973).
W. F. Fong, J. S. Heller and E. S. Canellakis,The appearance of an ornithine decarboxylase inhibitory protein upon the addition of putrescine to cell culture. Biochim. Biophys. Acta428, 456–465 (1976).
I. Holm, L. Persson, L. Stjernborg, L. Thorsson and O. Heby,Feedback control of ornithine decarboxylase expression by polyamines. Biochim. J.258, 343–350 (1989).
R. H. Dowling,Polyamines in intestinal adaptation and disease. Digestion46 (Suppl. 2) 331–344 (1990).
P. S. Sunkara, S. Ramakrishna, K. Nishioka and P. N. Rao,The relationship between levels and rates of synthesis of polyamines during mammalian cell cycle. Life Sci.28, 1497–1506 (1981).
M. A. Desiderio, A. Sessa and A. Perin,Regulation of diamine oxidase expression by β 2-adrenoceptors in normal and hypertrophic rat kidney. Biochim. Biophys. Acta845, 463–468 (1985).
M. A. Desiderio, A. Sessa and A. Perin,Involvement of beta 2 adrenoceptors in the regulation of diamine oxidase activity in the heart of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertension4, S139-S140 (1986).
J. D. Veldhuis, T. S. Harrison and J. M. Hammond, β2-adrenergicstimulation of ornithine decarboxylase activity in porcine granulosa cells in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta627, 123–130 (1980).
J. Bartolome, J. Huguenard and T. A. Slotkin,Role of ornithine decarboxylase in cardiac growth and hypertrophy. Science210, 793–794 (1980).
W. B. Karp, A. F. Robertson and W. P. Kanto, Jr.,The effect of hydrocortisone, thyroxine, and phenobarbital on diamine oxidase activity in newborn rat intestine. Pediatr. Res.21, 368–370 (1987).
A. Sessa, M. A. Desiderio and A. Perin,Estrogenic regulation of diamine oxidase activity in rat uterus. Agents and Actions29, 162–166 (1990).
W. A. Fogel,Diamine oxidase (DAO) and female sex hormones. Agents and Actions18, 44–45 (1986).
E. V. O'Loughlin, M. Chung, M. Hollemberg, J. Hayden, I. Zahavi and D. G. Gall,Effect of epidermal growth factor on ontogeny of the gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol.249, G674-G678 (1985).
I. J. Hidalgo, A. Kato and R. T. Borchardt,Binding of epidermal growth factor by human colon carcinoma cell (Caco-2) monolayers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.160, 317–324 (1989).
L. R. Fitzpatrick, P. Wang and L. R. Johnson,Effect of epidermal growth factor on polyamine-synthesizing enzymes in rat enterocytes. Am. J. Physiol.252, G209-G214 (1987).
A. Perin, A. Sessa and M. A. Desiderio,Response of tissue diamine oxidase activity to polyamine administration. Biochem. J.234, 119–123 (1986).
L. D'Agostino, S. Pignata, B. Daniele, C. Ferraro, G. D'Adamo, G. Tritto and G. Mazzacca,Regulation of diamine oxidase expression by ornithine decarboxylase in isolated rat small bowel enterocytes. Digestion46, 403–409 (1990).
A. Perin, A. Sessa and M. A. Desiderio,Diamine oxidase in regenerating and hypertrophic tissues. InStructure and Functions of Amine Oxidases. (Ed. B. Mondovi) pp. 179–186, CRC Press, Boca Raton 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sessa, A., Perin, A. Diamine oxidase in relation to diamine and polyamine metabolism. Agents and Actions 43, 69–77 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02005768
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02005768