Abstract
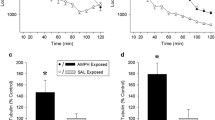
Two experiments were designed to assess the effect of a “novel” environment on the development of sensitization to the psychomotor activating effects ofd-amphetamine. In the first experiment, rats with a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the mesostriatal dopamine system received ten daily injections of amphetamine (2 mg/kg), either in their home cages or in novel test cages. The home and novel cages were physically identical (cylindrical transparent buckets), but one group lived and were tested in these cages, whereas the other group was transported from the stainless steel hanging cages where they lived to these novel test cages, for each test session. The first injection of amphetamine produced significantly more rotational behavior in animals tested in a novel environment than in animals tested at home. In addition, animals tested in a novel environment showed greater sensitization than animals tested at home, so the difference between the two groups was even more pronounced following the last injection. In a second experiment, locomotor activity was quantified in rats that received ten injections of either saline or 1.5 mg/kg amphetamine, in their home cages or in a physically identical novel environment. Again, there was a significantly greater locomotor response to the first injection of amphetamine, and greater sensitization, in animals tested in a novel environment than in animals tested at home. These data indicate that environmental factors can exert a large effect on the susceptibility to sensitization, and mechanisms by which this may occur are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie ED, Keefe KA, Di Frischia DS, Zigmond MJ (1989) Differential effect of stress on in vivo dopamine release in striatum, nucleus accumbens, and medial frontal cortex. J Neurochem 52:1655–1658
Anagnostaras S, Badiani A, Robinson TE (1993) Context-dependent amphetamine sensitization. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19:1241
Anisman H, Hahn B, Hoffman D, Zacharko RM (1985) Stressor invoked exacerbation of amphetamine-elicited perseveration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:173–183
Antelman SM, Eichler AJ, Black CA, Kocan D (1980) Interchangeability of stress and amphetamine in sensitization. Science 207:329–331
Badiani A, Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S (1992) Chronic stress induces strain-dependent sensitization to the behavioral effects of amphetamine in the mouse. Pharmacol biochem Behav 43:53–60
Bardo MT, Bowling SL, Pierce RC (1990) Changes in locomotion and dopamine neurotrasmission following amphetamine, haloperidol, and exposure to novel environmental stimuli. Psychopharmacology 101:338–343
Beck CHM, Chow HL, Cooper SJ (1986) Initial environment influences amphetamine-induced stereotypy: subsequently environment change has little effect. Behav Neural Biol 46:383–397
Breese GR, Traylor TD (1971) Depletion of brain noradrenaline and dopamine by 6-hydroxydopamine. Br J Pharmacol 42:88–99
Cador M, Dulluc J, Mormede P (1993a) Modulation of the locomotor response to amphetamine by corticosterone. Neuroscience 56:981–988
Cador M, Cole BJ, Koob GF, Stinus L, Le Moal M (1993b) Central administration of corticotropin releasing factor induces longterm sensitization tod-amphetamine. Brain Res 606:181–186
Cole BJ, Koob GF (1989) Low doses of corticotropin-releasing factor potentiate amphetamine-induced stereotyped behavior. Psychopharmacology 1989:27–33
Cools AR, Van den Bos R, Ploeger G, Ellenbroek BA (1991) Gating function of noradrenaline in the ventral striatum: its role in behavioural responses to environmental and pharmacological challenges. In: Willner P, Scheel-Krüger J (eds) The mesolimbic dopamine system: from motivation to action, Wiley, Chichester, pp 141–173
Deroche V, Piazza PV, Casolini P, Maccari S, Le Moal M, Simon H (1992a) Stress-induced sensitization to amphetamine and morphine psychomotor effects depend on stress-induced corticosterone secretion. Brain Res 598:343–348
Deroche V, Piazza PV, Maccari S, Le Moal M, Simon H (1992b) Repeated corticosterone administration sensitizes the locomotor response to amphetamine. Brain Res 584:309–313
Einat H, Szechtman H (1993) Environmental modulation of both locomotor response and locomotor sensitization to the dopamine agonist quinpirole. Behav Pharmacol 4:399–403
Ellinwood EHJ (1971) “Accidental conditioning” with chronic metamphetamine intoxication: implication for a theory of drug habituation. Psychopharmacologia 21:131–138
Ellinwood EHJ, Kilbey MM (1975) Amphetamine stereotypy: the influence of environmental factors and prepotent behavioral patterns on its topography and development. Biol Psychiat 10:3–16
Friedman SB, Ader R (1967) Adrenocortical response to novelty and noxious stimulation. Neuroendocrinology 2:209–212
Hefti F, Melamed E, Sahakian BJ, Wurtman RJ (1980a) Circling behavior in rats with partial, unilateral nigro-striatal lesions: effect of amphetamine, apomorphine, and DOPA. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:185–188
Hefti F, Melamed E, Wurtman RJ (1980b) Partial lesions of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal system in rat brain: biochemical characterization. Brain Res 195:123–137
Hennessy MB (1991) Sensitization of the plasma corticosterone response to novel environments. Physiol Behav 50:1175–1179
Hennessy MB, Levine S (1977) Effects of various habituation procedures on pituitary-adrenal responsiveness in the mouse. Physiol Behav 18:799–802
Hennessy JW, Levin R, Levine S (1977) Influence of experiential factors and gonadal hormones on pituitary-adrenal response of the mouse to novelty and electric shock. J Comp Physiol Psychol 91:770–777
Hinson RE, Poulos CX (1981) Sensitization to the behavioral effects of cocaine: modification by Pavlovian conditioning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:559–562
Hirabayashi M, Alam MR (1981) Enhancing effect of methamphetamine on ambulatory activity produced by repeated administration in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:925–932
Hoffman DC, Wise RA (1992) Locomotor activating effects of the D2 agonist bromocriptine show environment-specific sensitization following repeated injections. Psychopharmacology 107:277–284
Kalivas PW, Stewart J (1991) Dopamine transmission in the initiation and expression of drug- and stress-induced sensitization of motor activity. Brain Res Rev 16:223–244
Kiyatkin EA (1992) State-dependent peculiarities of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization and their possible reasons. Int J Neurosci 67:93–103
Marinelli M, Piazza PV, Deroche V, Maccari S, Le Moal M, Simon H (1994) Corticosterone circadian secretion differentially facilitates dopamine-mediated psychomotor effect of cocaine and morphine. J Neurosci 14:2724–2731
Mattingly BA, Gotsick JE (1989) Conditioning and experiential factors affecting the development of sensitization to apomorphine. Behav Neurosci 103:1311–1317
Mazurski EJ, Beninger RJ (1987) Environment-specific conditioning and sensitization with (+)-amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 27:61–65
Morimoto A, Nakamori T, Morimoto K, Tan N, Murakami N (1993) The central role of corticotrophin-releasing factor (CRF-41) in psychological stress in rats. J Physiol 460:221–229
Pauly JR, Robinson SF, Collins AC (1993) Chronic corticosterone administration enhances behavioral sensitization to amphetamine in mice. Brain Res 620:195–202
Piazza PV, Deminière JM, Le Moal M, Simon H (1989) Factors that predict individual vulnerability to amphetamine self-administration. Science 245:1511–1513
Post RM, Lockfeld A, Squillace KM, Contel NR (1981) Drug-environment interaction: context dependency of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization. Life Sci 28:755–760
Rivet JM, Stinus L, Le Moal M, Mormede P (1989) Behavioral sensitization to amphetamine is dependent on corticosteroid receptor activation. Brain Res 498:149–153
Robinson TE (1984) Behavioral sensitization: characterization of enduring changes in rotational behavior produced by intermittent injections of amphetamine in male and female rats. Psychopharmacology 84:466–475
Robinson TE (1988) Stimulant drugs and stress: factors influencing individual differences in the susceptibility to sensitization. In: Kalivas PW, Barnes C (eds) Sensitization in the nervous System, Telford Press, Caldwell, N.J., pp 145–173
Robinson TE, Becker JB (1986) Enduring changes in brain and behavior produced by chronic amphetamine administration: a review and evaluation of animal models of amphetamine psychosis. Brain Res Rev 396:157–198
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Robinson TE, Angus AL, Becker JB (1985) Sensitization to stress: the enduring effects of prior stress on amphetamine-induced rotational behavior. Life Sci 37:1039–1042
Russel RL, Pihl RO (1978) The effect of dose, novelty, and exploration on amphetamine-produced stereotyped behavior. Psychopharmacology 60:93–100
Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW, Morgan MJ, Iversen SD (1975) The effects of psychomotor stimulants on stereotypy and locomotor activity in socially-deprived and control rats. Brain Res 84:195–205
Schallert T, De Ryck M, Teitelbaum P (1980) Atropine stereotypy as a behavioral trap: a movement subsystem and electroencephalographic analysis. J Comp Physiol Psychol 94:1–24
Schiff SR (1982) Conditioned dopaminergic activity. Biol Psychiatry 17:135–154
Segal DS, Schuckit MA (1983) Animal models of stimulant-induced psychosis. In: Creese I (ed) Stimulants: neurochemical, behavioral and clinical perspectives. Raven Press, New York, pp 131–167
Stewart J, Badiani A (1993) Tolerance and sensitization to the behavioral effects of drugs. Behav Pharmacol 4:289–312
Stewart J, Vezina P (1987) Environment-specific enhancement of the hyperactivity induced by systemic or intra-VTA morphine injections in rats preexposed to amphetamine. Psychobiology 15:144–153
Stewart J, Vezina P (1988) Conditioning and behavioral sensitization. In: Kalivas PW, Barnes CD (eds) Sensitization in the nervous system. Telford Press, Caldwell, N.J., pp 207–224
Stewart J, Vezina P (1991) Extinction procedures abolish conditioned stimulus control but spare sensitized responding to amphetamine. Behav Pharmacol 2:65–71
Sullivan R, Dogaru C, Szechtman H (1992) Constriction of environmental space and the behavioral response to the dopamine agonist quinpirole. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:1217–1219
Terlouw EMC, De Rosa G, Lawrence AB, Illius AW, Ladewig J (1992) Behavioural responses to amphetamine and apomorphine in pigs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:329–340
Thierry AM, Tassin JP, Blanc G, Glowinski J (1976) Selective activation of the mesocortical DA system by stress. Nature 263:242–243
Tilson HA, Rech RA (1973) Conditioned drug effects and absence of tolerance tod-amphetamine induced motor activity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1:149–153
Ungerstedt U, Arbuthnott GW (1970) Quantitative recording of rotational behavior in rats after 6-hydroxy-dopamine lesions of the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Res 24:485–493
Vezina P, Stewart J (1984) Conditioning and place-specific sensitization of increases in activity induced by morphine in the VTA. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:925–934
Weiss SR, Post RM, Pert A, Woodward R, Murman D (1989) Context-dependent cocaine sensitization: differential effect of haloperidol on development versus expression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:655–661
Wilcox RA, Robinson TE, Becker JB (1986) Enduring enhancement in amphetamine-stimulated striatal dopamine release in vitro produced by prior exposure to amphetamine or stress in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 124:375–376
Williams JL, Barber RG (1989) Effects of cat exposure and cat odors on subsequent amphetamine-induced stereotypy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 36:375–380
Willner P, Papp M, Cheeta S, Muscat R (1992) Environmental influences on behavioural sensitization to the dopamine agonist quinpirole. Behav Pharmacol 3:43–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badiani, A., Anagnostaras, S.G. & Robinson, T.E. The development of sensitization to the psychomotor stimulant effects of amphetamine is enhanced in a novel environment. Psychopharmacology 117, 443–452 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246217
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246217