Abstract
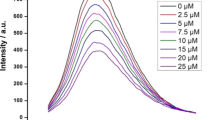
The activity of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in rheumatoid arthritis is not only due to the inhibition of the production of prostaglandins, which can even have beneficial immunosuppressive effects in chronic inflammatory processes. Since we speculated that these drugs could also act by protecting endogenous proteins against denaturation, we evaluated their effect on heat-induced denaturation human serum albumin (HSA) in comparison with several fatty acids which are known to be potent stabilizers of this protein. By the Mizushimas assay and a recently developed HPLC assay, we observed that NSAIDs were slightly less active [EC50∼10−5-10−4 M] than FA and that the HPLC method was less sensitive but more selective than the turbidimetric assay, i.e. it was capable of distinguishing true antiaggregant agents like FA and NSAIDs from substances capable of inhibiting the precipitation of denatured protein aggregates. In conclusion, this survey could be useful for the development of more effective agents in protein condensation diseases like rheumatic disorders, cataract and Alzheimers disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson, S. B. and Weissmann, G., The mechanisms of action of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs.Arthritis Rheum., 32, 1–9 (1989).
Abramson, S. B., Mechanisms of action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and therapeutic considerations.Bull. Hosp. Jt. Dis. Orthop. Inst., 50, 107–15 (1990).
Abramson, S. B., Therapy with and mechanisms of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Curr. Opin. Rheumatol., 3, 336–40 (1991).
Ballou, G. A., Boyer, P. D., Luck, J. M., and Lum, F. G., The heat coagulation of human serum albumin.J. Biol. Chem., 153, 589–605 (1944).
Benedek, G. B., Cataract as a protein condensation disease: the Proctor Lecture.Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 38, 1911–1921 (1997).
Bertelli, A. and Silvestrini, B., Current trends in the research on antiinflammatory agents.Int. J. Tissue. React., 7, 169–173 (1985).
Boyer, P. D., Lum, F. G., Ballou, G. A., Luck, J. M., and Rice, R. G., The combination of fatty acids and related compounds with serum albumin.J. Biol. Chem., 162, 181–98 (1946).
Bradford, M. M., A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem., 72, 248–254 (1976).
Bruno, M. R., Sensi, M., Cioccia, G. P., Valente, L., Negri M., Ghirlanda, G. and Pozzilli, P., Inhibition of protein non-enzymic glycation induced by Bendazac.Diabetes Res., 9, 11–14 (1988).
Carter, D. C. and Ho, J. X., Structure of serum albumin.Adv. Protein Chem., 45, 153–203 (1994).
Chen, R. F., Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment.J. Biol. Chem., 242, 173–181 (1967).
Cheng, C. Y., Mathur, P. P. and Grima, J., Structural analysis of clusterin and its subunits in ram rete testis fluid.Biochemistry, 27, 4079–4088 (1988).
Cherian, M. and Abraham, E. C., Glycation of human lens crystallins: effect of age and aspirin treatment.Ophthalmic Res., 25, 349–354 (1993).
Cioli, V., Ciarniello, M. G., Guglielmotti, A., Luparini, M. R. Durando, L., Martinelli, B., Catanese, B., Fava, L., and Silvestrini, B., A new protein antidenaturant agent, bindarit, reduces secondary phase of adjuvant arthritis in rats.J. Rheumatol., 19, 1735–1742 (1992).
Cioli, V., Corradino, C. and Scorza Barcellona P., Review of pharmacological data on benzydamine.Int. J. Tissue React., 7, 205–213 (1985).
Colaco, C. A., Ledesma, M. D., Harrington, C. R., and Avila, J., The role of the Maillard reaction in other pathologies: Alzheimer's disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant 11 (Suppl 5), 7–12 (1996).
Diaz-Gonzalez, F. and Sanchez-Madrid, F., Inhibition of leukocyte adhesion: an alternative mechanism of action for anti-inflammatory drugs.Immunol Today, 1998 Apr; 19(4): 169–72.
Gomes, I., Aspirin: a neuroprotective agent at high doses?Natl. Med. J. India., 11, 14–17 (1998).
Goodwin, J. S., Immunologic effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Am. J. Med., 77, 7–15 (1984b).
Goodwin, J. S., Mechanism of action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents.Am. J. Med., 77, 57–64 (1984a).
Harding, J. J., Pharmacological treatment strategies in age-related cataracts.Drug Aging, 2, 287–300 (1992).
Insel, P. A., Analgesic-antipyretic and antiinflammatory agents and drugs employed in the treatment of gout. In The pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, Edited by Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Molinoff PB, Ruddon RW and Goodman Gilman A, pp 617–657, McGraw Hill, New York (1996).
Kremer, J. M., Effects of modulation of inflammatory and immune parameters in patients with rheumatic and inflammatory disease receiving dietary supplementation of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids.Lipids, 31, S243-S247 (1996).
Laemmli, U. K., Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature, 227, 680–685 (1970).
Macart, M. and Gerbaut, L., An improvement of the Coomassie Blue dye binding method allowing an equal sensitivity to various proteins: application to cerebrospinal fluid.Clin. Chim. Acta., 122, 93–101 (1982).
Marques, C., Ramalho, J. S., Pereira, P. and Mota, M. C., Bendazac decreases in vitro glycation of human lens crystallins. Decrease of in vitro protein glycation by bendazac.Doc. Ophthalmol., 90, 395–404 (1995).
Mizushima, Y. and Suzuki, H., Interaction between plasma proteins and antirheumatic or new antiphlogistic drugs.Arch. Intern. Pharmacodyn., 157, 115–124 (1965).
Mizushima, Y., Inhibition of protein denaturation by anti-rheumatic or antiphlogistic agents.Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn., 149, 1–7 (1964).
Nargund, L. V., Reddy, G. R. and Hariprasad, V., Anti-inflammatory activity of substituted 1,3,4-oxadiazoles.J. Pharm. Sci., 83, 246–248 (1994).
Peters, T., Serum albumin.Adv. Prot. Chem., 37, 161–245 (1985).
Roberts, K. A. and Harding, J. J., Ibuprofen, a putative anti-cataract drug, protects the lens against cyanate and galactose.Exp. Eye. Res., 50, 157–164 (1990).
Rogers, J., Kirby, L. C., Hempelman, S. R., Berry, D. L., McGeer, P. L., Kaszniak, A. W., Zalinski, J., Cofield, M., Mansukhani, L. and Willson, P.,et al.: Clinical trial of indomethacin in Alzheimer's disease.Neurology, 43, 1609–1611 (1993).
Saso, L., Casini, M. L., Valentini, G., Mattei, E., Panzironi, C., and Silvestrini, B., Development of an HPLC assay to study the effect of endogenous and exogenous substances on heat-induced aggregation of human serum albumin.Clin. Chem. Lab. Med., 36, 155–162 (1998).
Saso, L., Silvestrini, B., Guglielmotti, A., Lahita, R., and Cheng, C. Y., Abnormal glycosylation of α2-macroglobulin, a non-acute-phase protein, in patients with auto-immune diseases.Inflammation, 17, 465–479 (1993b).
Saso, L., Silvestrini, B., Lahita, R. and Cheng, C. Y., Changes of immunoreactivity in α1-antitrypsin in patients with autoimmune diseases.Inflammation, 17, 383–400 (1993a).
Saso, L., Silvestrini, B., Zwain, I., Guglielmotti, A., Luparini, M. R., Cioli, V. and Cheng, C. Y., Abnormal glycosylation of hemopexin in arthritic rats can be blocked by bindarit.J. Rheumatol., 19, 1859–1867. (1992).
Saso, L., Valentini, G., Casini, M. L., Mattei, E., Braghiroli, L., Mazzanti, G., Panzironi, C., Grippa, E., and Silvestrini, B., Inhibition of protein denaturation by fatty acids, bile salts and other natural substances: a new hypothesis for the mechanism of action of fish oil in rheumatic diseases.Jpn. J. Pharmacol., 79, (in press) (1999).
Silvestrini, B., Catanese, B., Lisciani, R. and Alessandroni, A., Studies on the mechanism of action of bendazac (AF-983).Arzneim. Forsch., 20, 250–253 (1970).
Silvestrini, B., Cioli, V. and Burberi, S., Pharmacological properties of bendazac (AF-983), with particular reference to its topical action on some experimental inflammatory processes.Arzneim. Forsch., 19, 30–36 (1969).
Silvestrini, B., Guglielmotti, A., Saso, L. and Cheng, C. Y., Changes in concanavalin A-reactive proteins in inflammatory disorders.Clin. Chem., 35, 2207–2211 (1989).
Silvestrini, B., Primary and secondary inflammation.Panminerva. Med., 11, 587–593 (1969).
Silvestrini, B., Rationale for bendazac: In Recent Developments in the Pharmacological Treatment of Cataract, Edited by Dermo F, Ponte F And Laties AM, pp 1–9, Kugler, Amsterdam (1987).
Stevens, A., The contribution of glycation to cataract formation in diabetes.J. Am. Optom. Assoc., 69, 519–30 (1998).
Swamy, M. S. and Abraham, E. C., Inhibition of lens crystallin glycation and high molecular weight aggregate formation by aspirinin vitro andin vivo.Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 30, 1120–6 (1989).
Tallarida, R. J. and Murray, R. B., Manual of Pharmacologic Calculations with Computer Programs. New York, Springer-Verlag, (1986).
van der Tempel, H., Tulleken, J. E., Limburg, P. C., Muskiet, F. A. and van Rijswijk, M. H., Effects of fish oil supplementation in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann. Rheum. Dis., 49, 76–80 (1990).
Vane, J. R., Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs.Nature (New Biol), 231, 232–235 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saso, L., Valentini, G., Casini, M.L. et al. Inhibition of heat-induced denaturation of albumin by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Pharmacological implications. Arch. Pharm. Res. 24, 150–158 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976483
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976483