Abstract
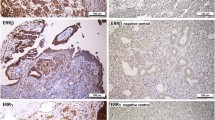
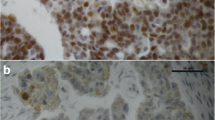
A subfamily of orphan receptors, estrogen receptor-related receptors (ERRs), has been demonstrated to modulate the transcription of some estrogen responsive genes via variant estrogen response elements (EREs). This study was conducted to determine whether human ERRα, ERRβ, and ERRγ might be involved in the tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer. RT-PCR was performed to analyze the expression of hERRα, hERRβ, hERRβ-2, and hERRγ mRNA in five ovarian cancer cell lines as well as 33 samples of ovarian cancer and 12 samples of normal ovary. Serum CA-125 levels were also analyzed in all samples by ELISA. Progression-free survival and overall survival of patients with different expression of ERRs were analyzed by the Kaplan–Meier method. To analyze the subcellular localization of ERRα, a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-reporter plasmid of hERRα was constructed and transfected into the ovarian cancer cell line OVCAR-3. Expression of hERRα-GFP fusion protein was observed in the nucleus of OVCAR-3 ovarian cancer cell lines. We observed increased expression of hERRα mRNA (P=0.020) and hERRγ mRNA (P=0.045) in ovarian cancers compared to normal ovaries. In contrast, hERRβ was only observed in 9.1% of ovarian cancers. We found a positive correlation between the serum CA-125 levels and hERRα expression (P=0.012), but not hERRβ and hERRγ expression. Survival analysis showed that the hERRα-positive group has a reduced overall survival (P=0.015), and the ERRγ-positive group has a longer progression-free survival (P=0.020). In multivariate analysis, expression of hERRα was an independent prognostic factor for poor survival (relative risk, 3.032; 95% CI, 1.27–6.06). Based on our results, ERRs may play an important role in ovarian cancer. hERRα may represent a biomarker of poor prognosis, and hERRγ may be a new therapeutic target in ovarian cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landis SH, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA (1999) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 49:8–31
Sehouli J, Akdogan Z, Heinze T, Konsgen D, Stengel D, Mustea A, Lichtenegger W (2003) Preoperative determination of CASA and CA-125 for the discrimination between benign and malignant pelvic tumor mass: a prospective study. Anticancer Res 23:1115–1118
Muramatsu M, Inoue S (2000) Estrogens receptors: how do they control reproductive and nonreproductive functions? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:1–10
Clinton GM, Hua W (1997) Estrogen action in human ovarian cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 25:1–9
Brandenberger AW, Tee MK, Jaffe RB (1998) Estrogen receptor alpha and beta mRNAs in normal ovary, ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma and ovarian cancer cell lines: down-regulation of ER-β in neoplastic tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:1025–1028
Lau KM, Mok SC, Ho SM (1999) Expression of human estrogen receptor-α and -β, progesterone receptor and androgen receptor mRNA in normal and malignant ovarian epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5722–5727
Giguere V, Yang N, Segui P, Evans RM (1988) Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature 331:91–94
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M, Chambon P (1995) The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell 83:835–839
Giguere V (1999) Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocr Rev 20:689–725
Horard B, Vanacker JM (2003) Estrogen receptor-related receptors: orphan receptors desperately seeking a ligand. J Mol Endocrinol 31:349–357
Giguere V (2002) To ERR in the estrogen pathway. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:220–225
Chen S, Itoh T, Wu K, Zhou D, Yang C (2002) Transcriptional regulation of aromatase expression in human breast tissue. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 83:93–99
Lu D, Kiriyama Y, Lee KY, Giguere V (2001) Transcriptional regulation of the estrogen-inducible pS2 breast cancer marker gene by the ERR family of orphan nuclear receptors. Cancer Res 61: 6755–6761
Hong H, Yang L, Stallcup MR (1999) Hormone-independent transcriptional activation and coactivator binding by novel orphan nuclear receptor ERR3. J Biol Chem 274:22618–22626
Vanacker JM, Bonnelye E, Chopin-Delannoy S, Delmarre C, Cavailles V, Laudet V (1999) Transcriptional activities of the orphan nuclear receptor ERR alpha (estrogen receptor-related receptor-α). Mol Endocrinol 13:764–773
Vanacker JM, Pettersson K, Gustafsson JA, Laudet V (1999) Transcriptional targets shared by estrogen receptor-related receptors (ERRs) and estrogen receptor (ER) alpha but not by ER beta. EMBO J 18:4270–4279
Zhang Z, Teng CT (2000) Estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha-1 interacts with coactivator and constitutively activates the estrogen response elements of the human lactoferrin gene. J Biol Chem 275:20837–20846
Bonnelye E, Merdad L, Kung V, Aubin JE (2001) The orphan nuclear estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha (ERR alpha) is expressed throughout osteoblast differentiation and regulates bone formation in vitro. J Cell Biol 153:971–984
Yang N, Shigeta H, Shi H, Teng CT (1996) Estrogen-related receptor, hERR1, modulates estrogen receptor-mediated response of human lactoferrin gene promoter. J Biol Chem 271:5795–5804
Yang C, Zhou D, Chen S (1998) Modulation of aromatase expression in the breast tissue by ERR alpha-1 orphan nuclear receptor. Cancer Res 58:5695–5700
Rollerova E, Urbancikova M (2000) Intracellular estrogen receptors, their characterization and function. Endocr Regul 34:203–218
Sanchez R, Nguyen D, Rocha W, White JH, Mader S (2002) Diversity in the mechanisms of gene regulation by estrogen receptors. BioEssays 24:244–254
Zhang Z, Teng CT (2001) Estrogen receptor α and estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha1 compete for binding and coactivator. Mol Cell Endocrinol 172:223–233
Akahira J, Suzuki T, Ito K, Kaneko C, Darnel AD, Moriya T, Okamura K, Yaegashi N, Sasano H (2002) Differential expression of progesterone receptor isoforms A and B in the normal ovary, and in benign, borderline, and malignant ovarian tumors. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:807–815
Kyo S, Kanaya T, Takakura M, Tanaka M, Yamashita A, Inoue H, Inoue M (1999) Expression of human telomerase subunits in ovarian malignant, borderline and benign tumors. Int J Cancer 80:804–809
Johnston SD, Liu X, Zuo F, Eisenbraun TL, Wiley SR, Kraus RJ, Mertz JE (1997) Estrogen-related receptor alpha1 functionally binds as a monomer to extended half-site sequence including ones contained within estrogen-response elements. Mol Endocrinol 11:342–352
Xie W, Hong H, Yang NN, Lin RJ, Simon CM, Stallcup MR, Evans RM (1999) Constitutive activation of transcription and binding of coactivator by estrogen-related receptors 1 and 2. Mol Endocrinol 13:2151–2162
Kraus RJ, Ariazi EA, Farrell ML, Mertz JE (2002) Estrogen-related receptor α-1 actively antagonizes estrogen receptor-regulated transcription in MCF-7 mammary cells. J Biol Chem 277:24826–24834
Coward P, Lee D, Hull MV, Lehmann JM (2001) 4-Hydroxytamoxifen binds to and deactivates the estrogen-related receptor gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:8880–8884
Tremblay GB, Bergeron D, Giguere V (2001) 4-Hydroxytamoxifen is an isoform-specific inhibitor of orphan estrogen-receptor-related (ERR) nuclear receptors beta and gamma. Endocrinology 142:4572–4575
Ariazi EA, Clark GM, Mertz JE (2002) Estrogen-related receptor alpha and estrogen-relate receptor gamma associated with unfavorable and favorable biomarkers, respectively, in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 62:6510–6518
Pettersson K, Svensson K, Mattsson R, Carlsson B, Ohlsson B, Berkenstam A (1996) Expression of a novel member of estrogen response element-binding nuclear receptors is restricted to the early stages of chorion formation during mouse embryogenesis. Mech Dev 54:211–223
Tremblay GB, Kunath T, Bergeron D, Lapointe L, Champigny C, Bader JA, Rossant J, Giguere V (2001) Diethylstilbestrol regulates trophoblast stem cell differentiation as a ligand of orphan nuclear receptor ERR beta. Genes Dev 15:833–838
Luo J, Sladek R, Bader JA, Matthyssen A, Rossant J, Giguere V (1997) Placental abnormalities in mouse embryos lacking the orphan nuclear receptor ERR-beta. Nature 388:778–782
Russo J, Hu YF, Yang X, Russo IH (2000) Developmental, cellular and molecular basis of human breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 27:17–37
Chen S, Zhou D, Yang C, Sherman M (2001) Molecular basis for the constitutive activity of estrogen-related receptor alpha-1. J Biol Chem 276:28465–28470
Yang C, Chen S (1999) Two organochlorine pesticides, toxaphene and chlordane, are antagonists for estrogen-related receptor alpha-1 orphan receptor. Cancer Res 59:4519–4524
Papadimitriou CA, Markaki S, Siapkaras J, Vlachos G, Efstathiou E, Grimani I, Hamilos G, Zorzou M, Dimopoulos MA (2004) Hormonal therapy with letrozole for relapsed epithelial ovarian cancer long-term results of a phase II study. Oncology 66:112–117
Williams CJ, Simera I (2004) Tamoxifen for relapse of ovarian cancer. The Cochrane Library, 3rd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Acknowledgements
Pengming Sun was a scholarship holder of the Gottlieb–Daimler Benz Foundation (Serial No.17/05-03). This research was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Serial No. 30371477). We thank Prof. Jean Marc Vanacker for plasmids pSG-hERRα, pSG-mERRβ, pSG-mERRγ, and comments on the manuscript. We thank Dr. Eckardt Treuter for the GFP-reporter plasmid. We thank Dr. Michel R. Stallcup for the HA-tag-hERRγ plasmid. We thank Miss Cristina Pirvulescu for her excellent follow-up work. We also thank Dr. Wilko Weichert, Mrs. Elisabeth Glanz, and Mrs. Beate Pesche for their great support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, P., Sehouli, J., Denkert, C. et al. Expression of estrogen receptor-related receptors, a subfamily of orphan nuclear receptors, as new tumor biomarkers in ovarian cancer cells. J Mol Med 83, 457–467 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-005-0639-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-005-0639-3