Abstract
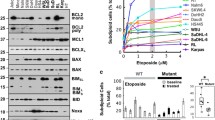
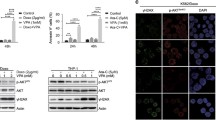
The molecular basis of the antitumor selectivity of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDIs) remains unclear. Centrosomal Aurora-A kinase regulates chromosomal segregation during mitosis. The overexpression or amplification of Aurora-A leads to genetic instability, and its inhibition has shown significant antitumor effects. In this paper, we report that structurally related hydroxamate LAQ824 and SK-7068 induce tumor-selective mitotic defects by depleting Aurora-A. We found that HDI-treated cancer cells, unlike nontransformed cells, exhibit defective mitotic spindles. After HDI, Aurora-A was selectively downregulated in cancer cells, whereas Aurora-B remained unchanged in both cancer and nontransformed cells. LAQ824 or SK-7068 treatment inhibited histone deacetylase (HDAC) 6 present in Aurora-A/heat shock protein (Hsp) 90 complex. Inhibition of HDAC6 acetylated Hsp90 and resulted in dissociation of acetylated Hsp90 from Aurora-A. As a result, Hsp70 binding to Aurora-A was enhanced in cancer cells, leading to proteasomal degradation of Aurora-A. Overall, these provide a novel molecular basis of tumor selectivity of HDI. LAQ824 and SK-7068 might be more effective HDIs in cancer cells with Aurora-A overexpression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnstone RW (2002) Histone-deacetylase inhibitors: novel drugs for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:287–299
Marks P, Rifkind RA, Richon VM, Breslow R, Miller T, Kelly WK (2001) Histone deacetylases and cancer: causes and therapies. Nat Rev Cancer 1:194–202
Insinga A, Monestiroli S, Ronzoni S, Gelmetti V, Marchesi F, Viale A, Altucci L, Nervi C, Minucci S, Pelicci PG (2005) Inhibitors of histone deacetylases induce tumor-selective apoptosis through activation of the death receptor pathway. Nat Med 11:71–76
Nebbioso A, Clarke N, Voltz E, Germain E, Ambrosino C, Bontempo P, Alvarez R, Schiavone EM, Ferrara F, Bresciani F, Weisz A, de Lera AR, Gronemeyer H, Altucci L (2005) Tumor-selective action of HDAC inhibitors involves TRAIL induction in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Nat Med 11:77–84
Xu WS, Perez G, Ngo L, Gui CY, Marks PA (2005) Induction of polyploidy by histone deacetylase inhibitor: a pathway for antitumor effects. Cancer Res 65:7832–7839
Byrd JC, Marcucci G, Parthun MR, Xiao JJ, Klisovic RB, Moran M, Lin TS, Liu S, Sklenar AR, Davis ME, Lucas DM, Fischer B, Shank R, Tejaswi SL, Binkley P, Wright J, Chan KK, Grever MR (2005) A phase 1 and pharmacodynamic study of depsipeptide (FK228) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 105:959–967
Kelly WK, O’Connor OA, Krug LM, Chiao JH, Heaney M, Curley T, MacGregore-Cortelli B, Tong W, Secrist JP, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Chu E, Olgac S, Marks PA, Scher H, Richon VM (2005) Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:3923–3931
Johnstone RW, Licht JD (2003) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy: is transcription the primary target? Cancer Cell 4:13–18
Warrener R, Beamish H, Burgess A, Waterhouse NJ, Giles N, Fairlie D, Gabrielli B (2003) Tumor cell-selective cytotoxicity by targeting cell cycle checkpoints. FASEB J 17:1550–1552
Krebs JE, Fry CJ, Samuels ML, Peterson CL (2000) Global role for chromatin remodeling enzymes in mitotic gene expression. Cell 102:587–598
Blagosklonny MV, Robey R, Sackett DL, Du L, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z, Fojo T, Bates SE (2002) Histone deacetylase inhibitors all induce p21 but differentially cause tubulin acetylation, mitotic arrest, and cytotoxicity. Mol Cancer Ther 1:937–941
Dowling M, Voong KR, Kim M, Keutmann MK, Harris E, Kao GD (2005) Mitotic spindle checkpoint inactivation by trichostatin A defines a mechanism for increasing cancer cell killing by microtubule-disrupting agents. Cancer Biol Ther 4:197–206
Matsuyama A, Shimazu T, Sumida Y, Saito A, Yshimatsu Y, Seigneurin-Berny D, Osada H, Komatsu Y, Nishino N, Khochbin S, Horinouchi S, Yoshida M (2002) In vivo destabilization of dynamic microtubules by HDAC6-mediated deacetylation. EMBO J 21:6820–6831
Cimini D, Mattiuzzo M, Torosantucci L, Degrassi F (2003) Histone hyperacetylation in mitosis prevents sister chromatid separation and produces chromosome segregation defects. Mol Biol Cell 14:3821–3833
Maison C, Almouzni G (2004) HP1 and the dynamics of heterochromatin maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:296–304
Taddei A, Maison C, Roche D, Almouzni G (2001) Reversible disruption of pericentric heterochromatin and centromere function by inhibiting deacetylases. Nat Cell Biol 3:114–120
Park JH, Jung Y, Kim TY, Kim SG, Jong HS, Lee JW, Kim DK, Lee JS, Kim NK, Kim TY, Bang YJ (2004) Class I histone deacetylase-selective novel synthetic inhibitors potently inhibit human tumor proliferation. Clin Cancer Res 10:5271–5281
Jung M, Brosch G, Kolle D, Scherf H, Gerhauser C, Loidl P (1999) Amide analogues of trichostatin A as inhibitors of histone deacetylase and inducers of terminal cell differentiation. J Med Chem 42:4669–4679
Sternson SM, Wong JC, Grozinger CM, Schreiber SL (2001) Synthesis of 7200 small molecules based on a substructural analysis of the histone deacetylase inhibitors trichostatin and trapoxin. Org Lett 3:4239–4242
Remiszewski SW, Sambucetti LC, Bair KW, Bontempo J, Cesarz D, Chandramouli N, Chen R, Cheung M, Cornell-Kennon S, Dean K, Diamantidis G, France D, Green MA, Howell KL, Kashi R, Kwon P, Lassota P, Martin MS, Mou Y, Perez LB, Sharma S, Smith T, Sorensen E, Taplin F, Trogani N, Versace R, Walker H, Weltchek-Engler S, Wood A, Wu A, Atadja P (2003) N-Hydroxy-3-phenyl-2-propenamides as novel inhibitors of human histone deacetylase with in vivo antitumor activity: discovery of (2E)-N-hydroxy-3-(4-(((2-hydroxyethyl)(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)amino)methyl)phenyl)-2-propenamide (NVP-LAQ824). J Med Chem 46:4609–4624
Shin HJ, Baek KH, Jeon AH, Kim SJ, Jang KL, Sung YC, Kim CM, Lee CW (2003) Inhibition of histone deacetylase activity increases chromosomal instability by the aberrant regulation of mitotic checkpoint activation. Oncogene 22:3853–3858
Blagden SP, Glover DM (2003) Polar expeditions—provisioning the centrosome for mitosis. Nat Cell Biol 5:505–511
Yu X, Guo ZS, Marcu MG, Neckers L, Nguyen DM, Chen GA, Schrump DS (2002) Modulation of p53, ErbB1, ErbB2, and Raf-1 expression in lung cancer cells by depsipeptide FR901228. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:504–513
Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M, Fiskus W, Guo F, Rocha K, Kumaraswamy S, Boyapalle S, Atadja P, Seto E, Bhalla K (2005) Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 280:26729–26734
Harrington EA, Bebbington D, Moore J, Rasmussen RK, Ajose-Adeogun AO, Nakayama T, Graham JA, Demur C, Hercend T, Diu-Hercend A, Su M, Golec JM, Miller KM (2004) VX-680, a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of the Aurora kinases, suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Nat Med 10:262–267
Emanuel S, Rugg CA, Gruninger RH, Lin R, Fuentes-Pesquera A, Connolly PJ, Wetter SK, Hollister B, Kruger WW, Napier C, Jolliffe L, Middleton SA (2005) The in vitro and in vivo effects of JNJ-7706621: a dual inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases and aurora kinases. Cancer Res 65:9038–9046
Robbins AR, Jablonski SA, Yen TJ, Yoda K, Robey R, Bates SE, Sackett DL (2005) Inhibitors of histone deacetylases alter kinetochore assembly by disrupting pericentromeric heterochromatin. Cell Cycle 4:717–726
Ke YW, Dou Z, Zhang J, Yao XB (2003) Function and regulation of Aurora/Ipl1p kinase family in cell division. Cell Res 13:69–81
Warner SL, Bearss DJ, Han H, Von Hoff DD (2003) Targeting Aurora-2 kinase in cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2:589–595
Keen N, Taylor S (2004) Aurora-kinase inhibitors as anticancer agents. Nat Rev Cancer 4:927–936
Hata T, Furukawa T, Sunamura M, Egawa S, Motoi F, Ohmura N, Marumoto T, Saya H, Horii A (2005) RNA interference targeting aurora kinase a suppresses tumor growth and enhances the taxane chemosensitivity in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 65:2899–2905
Gennaro ED, Bruzzese F, Caraglia M, Abruzzese A, Budillon A (2004) Acetylation of proteins as novel target for antitumor therapy: review article. Amino Acids 26:435–441
Kovacs JJ, Murphy PJ, Gaillard S, Zhao X, Wu JT, Nicchitta CV, Yoshida M, Toft DO, Pratt WB, Yao TP (2005) HDAC6 regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell 18:601–607
Fuino L, Bali P, Wittmann S, Donapaty S, Guo F, Yamaguchi H, Wang HG, Atadja P, Bhalla K (2003) Histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824 down-regulates Her-2 and sensitizes human breast cancer cells to trastuzumab, taxotere, gemcitabine, and epothilone B. Mol Cancer Ther 2:971–984
Chen L, Meng S, Wang H, Bali P, Bai W, Li B, Atadja P, Bhalla KN, Wu J (2005) Chemical ablation of androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells by the histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824. Mol Cancer Ther 4:1311–1319
Acknowledgments
We thank Kyung-Sun Kang for the M13SV1 cells and Keith Robertson for reviewing this manuscript. We also thank the members of Dr. Bang’s laboratory for helpful discussion. This work was supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and Technology through the National Research Laboratory Program for Cancer Epigenetics and in part by the Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine (Grant no. CRI-03-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figures
(PPT 2.10 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JH., Jong, HS., Kim, S.G. et al. Inhibitors of histone deacetylases induce tumor-selective cytotoxicity through modulating Aurora-A kinase. J Mol Med 86, 117–128 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0260-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0260-8