Abstract
The isolation and identification of unknown membrane proteins offers the prospect of discovering new pharmaceutical targets and identifying key biochemical receptors. However, interactions between membrane protein targets and soluble ligands are difficult to study in vitro due to the insolubility of membrane proteins in non-detergent systems. Nanodiscs, nanoscale discoidal lipid bilayers encircled by a membrane scaffold protein belt, have proven to be an effective platform to solubilize membrane proteins and have been used to study a wide variety of purified membrane proteins. This report details the incorporation of an unbiased population of membrane proteins from Escherichia coli membranes into Nanodiscs. This solubilized membrane protein library (SMPL) forms a soluble in vitro model of the membrane proteome. Since Nanodiscs contain isolated proteins or small complexes, the SMPL is an ideal platform for interactomics studies and pull-down assays of membrane proteins. Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of the protein population before and after formation of the Nanodisc library indicates that a large percentage of the proteins are incorporated into the library. Proteomic identification of several prominent bands demonstrates the successful incorporation of outer and inner membrane proteins into the Nanodisc library.

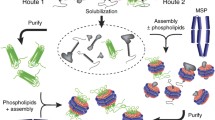
A Nanodisc-solubilized membrane protein library is formed by extracting a population of membrane proteins into detergent and then incorporating these proteins into a heterogeneous Nanodisc library, which models the membrane proteome





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCA:
-
Bicinchoninic acid
- LC-MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- MP:
-
Membrane protein
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- MSP:
-
Membrane scaffold protein
- Ni-NTA:
-
Nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid
- OG:
-
Octyl-glucoside
- POPC:
-
1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SEC:
-
Size exclusion chromatography
- SMPL:
-
Soluble membrane protein library
References
Hooker BS, Bigelow DJ, Lin C-T (2007) Methods for mapping of interaction networks involving membrane proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363(3):457–461
Piehler J (2005) New methodologies for measuring protein interactions in vivo and in vitro. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15(1):4–14
Babu M, Vlasblom J, Pu S, Guo X, Graham C, Bean BDM, Burston HE, Vizeacoumar FJ, Snider J, Phanse S, Fong V, Tam YYC, Davey M, Hnatshak O, Bajaj N, Chandran S, Punna T, Christopolous C, Wong V, Yu A, Zhong G, Li J, Stagljar I, Conibear E, Wodak SJ, Emili A, Greenblatt JF (2012) Interaction landscape of membrane-protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. doi:10.1038/nature11354
Stagljar I, Fields S (2002) Analysis of membrane protein interactions using yeast-based technologies. Trends Biochem Sci 27(11):559–563
Bayburt TH, Sligar SG (2010) Membrane protein assembly into Nanodiscs. FEBS Lett 584(9):1721–1727
Bayburt TH, Grinkova YV, Sligar SG (2002) Self-assembly of discoidal phospholipid bilayer nanoparticles with membrane scaffold proteins. Nano Lett 2(8):853–856
Leitz AJ, Bayburt TH, Barnakov AN, Springer BA, Sligar SG (2006) Functional reconstitution of β2-adrenergic receptors utilizing self-assembling nanodisc technology. BioTechniques 40 (5):601–602,604,606,608,610,612
Pandit A, Shirzad-Wasei N, Wlodarczyk LM, van Roon H, Boekema EJ, Dekker JP, de Grip WJ (2011) Assembly of the major light-harvesting complex II in lipid nanodiscs. Biophys J 101(10):2507–2515
Ham M-H, Choi JH, Boghossian AA, Jeng ES, Graff RA, Heller DA, Chang AC, Mattis A, Bayburt TH, Grinkova YV, Zeiger AS, Van Vliet KJ, Hobbie EK, Sligar SG, Wraight CA, Strano MS (2010) Photoelectrochemical complexes for solar energy conversion that chemically and autonomously regenerate. Nat Chem 2(11):929–936
Bayburt TH, Sligar SG (2003) Self-assembly of single integral membrane proteins into soluble nanoscale phospholipid bilayers. Protein Sci 12(11):2476–2481
Denisov IG, Sligar SG (2011) Cytochromes P 450 in nanodiscs. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteomics 1814(1):223–229
Bayburt TH, Leitz AJ, Xie GF, Oprian DD, Sligar SG (2007) Transducin activation by nanoscale lipid bilayers containing one and two rhodopsins. J Biol Chem 282(20):14875–14881
Grinkova YV, Denisov IG, Sligar SG (2010) Functional reconstitution of monomeric CYP3A4 with multiple cytochrome P450 reductase molecules in Nanodiscs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 398(2):194–198
Civjan NR, Bayburt TH, Schuler MA, Sligar SG (2003) Direct solubilization of heterologously expressed membrane proteins by incorporation into nanoscale lipid bilayers. Biotechniques 35(3):556–563
Borch J, Roepstorff P, Moeller-Jensen J (2011) Nanodisc-based co-immunoprecipitation for mass spectrometric identification of membrane-interacting proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics 10 (7):O110 006775, 006779 pp
Zhang XX, Chan CS, Bao H, Fang Y, Foster LJ, Duong F (2012) Nanodiscs and SILAC-based mass spectrometry to identify a membrane protein interactome. J Proteome Res 11(2):1454–1459
Arnold T, Linke D (2001) The Use of detergents to purify membrane proteins. In: Current Protocols in Protein Science. Wiley
Denisov IG, Grinkova YV, Lazarides AA, Sligar SG (2004) Directed self-assembly of monodisperse phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs with controlled size. J Am Chem Soc 126(11):3477–3487
Wessel D, Flugge UI (1984) A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem 138(1):141–143
Du P, Kibbe WA, Lin SM (2006) Improved peak detection in mass spectrum by incorporating continuous wavelet transform-based pattern matching. Bioinformatics 22(17):2059–2065
Duquesne K, Sturgis JN (2010) Membrane protein solubilization. In: Mus-Veteau I (ed) Heterologous Expression of Membrane Proteins, vol 601. Methods in Molecular Biology. Humana Press, pp 205–217
Garavito RM, Ferguson-Miller S (2001) Detergents as tools in membrane biochemistry. J Biol Chem 276(35):32403–32406
Seddon AM, Curnow P, Booth PJ (2004) Membrane proteins, lipids and detergents: not just a soap opera. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1666(1–2):105–117
Jones MN (1999) Surfactants in membrane solubilisation. Int J Pharm 177(2):137–159
Speers AE, Wu CC (2007) Proteomics of integral membrane proteins: theory and application. Chem Rev 107(8):3687–3714
Bayburt TH, Grinkova YV, Sligar SG (2006) Assembly of single bacteriorhodopsin trimers in bilayer nanodiscs. Arch Biochem Biophys 450(2):215–222
Ritchie TK, Grinkova YV, Bayburt TH, Denisov IG, Zolnerciks JK, Atkins WM, Sligar SG (2009) Reconstitution of membrane proteins in phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs. Methods Enzymol 464(Liposomes, Part F):211–231
Banerjee P, Joo JB, Buse JT, Dawson G (1995) Differential solubilization of lipids along with membrane proteins by different classes of detergents. Chem Phys Lipids 77(1):65–78
Boldog T, Grimme S, Li MS, Sligar SG, Hazelbauer GL (2006) Nanodiscs separate chemoreceptor oligomeric states and reveal their signaling properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(31):11509–11514
Denisov IG, Baas BJ, Grinkova YV, Sligar SG (2007) Cooperativity in cytochrome P450 3A4: linkages in substrate binding, spin state, uncoupling, and product formation. J Biol Chem 282(10):7066–7076
Schulz GE (2002) The structure of bacterial outer membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1565(2):308–317
Tommassen J (2010) Assembly of outer-membrane proteins in bacteria and mitochondria. Microbiology 156(9):2587–2596
Stenberg F, Chovanec P, Maslen SL, Robinson CV, Ilag LL, von Heijne G, Daley DO (2005) Protein complexes of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Biol Chem 280(41):34409–34419
Ishmukhametov R, Hornung T, Spetzler D, Frasch WD (2010) Direct observation of stepped proteolipid ring rotation in E. coli FoF1-ATP synthase. EMBO J 29(23):3911–3923
Wilcox KC, Das A, Velasco P, Marty MT, Kuhns B, Luan CH, Sligar SG, Klein WL (2012) Alzheimer’s drug discovery using Nanodisc-stabilized receptors for oligomeric Aβ. Program No. 748.014. In: New Orleans, LA: Society for Neuroscience, 2012, New Orleans, LA, 2012
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Peter Yau and the University of Illinois Urbana–Champaign Protein Science Facility for assistance in proteomic identification of bands. We thank Michelle Yoo for her assistance in preparing samples. This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01-GM31756 and R01-GM33775 to S.G.S). M.T.M. was supported by the Robert C. and Carolyn J. Springborn Endowment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marty, M.T., Wilcox, K.C., Klein, W.L. et al. Nanodisc-solubilized membrane protein library reflects the membrane proteome. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 4009–4016 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6790-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6790-8