Abstract
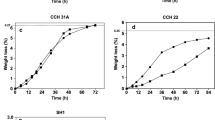
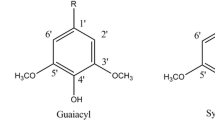
An overview of the different inhibitors formed by pre-treatment of lignocellulosic materials and their inhibition of ethanol production in yeast and bacteria is given. Different high temperature physical pre-treatment methods are available to render the carbohydrates in lignocellulose accessible for ethanol fermentation. The resulting hydrolyzsates contain substances inhibitory to fermentation—depending on both the raw material (biomass) and the pre-treatment applied. An overview of the inhibitory effect on ethanol production by yeast and bacteria is presented. Apart from furans formed by sugar degradation, phenol monomers from lignin degradation are important co-factors in hydrolysate inhibition, and inhibitory effects of these aromatic compounds on different ethanol producing microorganisms is reviewed. The furans and phenols generally inhibited growth and ethanol production rate (QEtOH) but not the ethanol yields (YEtOH) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Within the same phenol functional group (aldehyde, ketone, and acid) the inhibition of volumetric ethanol productivity was found to depend on the amount of methoxyl substituents and hence hydrophobicity (log P). Many pentose-utilizing strains Escherichia coli, Pichia stipititis, and Zymomonas mobilis produce ethanol in concentrated hemicellulose liquors but detoxification by overliming is needed. Thermoanaerobacter mathranii A3M3 can grow on pentoses and produce ethanol in hydrolysate without any need for detoxification.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahring BK, Jensen K, Nielsen P, Bjerre AB, Schmidt AS (1996) Pretreatment of wheat straw and conversion of xylose and xylan to ethanol by thermophilic anaerobic bacteria. Bioresour Technol 58:107–113
Akrida-Demertzi K, Demertzis PG, Koutinas AA (1988) pH and trace-elements content in raisin extract industrial-scale alcoholic fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 31:666–669
Alexandre H, Charpentier C (1998) Biochemical aspects of stuck and sluggish fermentation in grape must. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 20:20–27
Alén R, Sjöström E, Suominen S (1990) Application of ion-exclusion chromatography to alkaline pulping liquors; separation of hydroxy carboxylic acids from inorganic solids. J Chem Tech Biotechnol 51:225–233
Ando S, Arai I, Kiyoto K, Hanai S (1986) Identification of aromatic monomers in steam-exploded poplar and their influences on ethanol fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Technol 64:567–570
Baeza J, Freer J (1997) Chemical characterization of wood and its components. In: Hon DNS, Shirashi N (eds) Wood and cellulosic chemistry. Dekker, New York, pp 275–374
Barber AR, Hansson H, Pamment NB (2000) Acetaldehyde stimulation of the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the presence of inhibitors found in lignocellulose-to-ethanol fermentations. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 25:104–108
Bardet M, Robert DR (1985) On the reactions and degradation of the lignin during steam hydrolysis of aspen wood. Svensk Papperst 6:61–67
Barquinero E, Cruz R, Mieres G, Dominguez H (1980) Caracterizacion quimica de efluentes de pulpeoquimico a la soda de bagazo. Revista Icidca 14:28–33
Bjerre AB, Olesen AB, Fernqvist T, Plöger A, Schmidt AS (1996) Pretreatment of wheat straw using combined wet oxidation and alkaline hydrolysis resulting in convertible cellulose and hemicellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:568–577
Bobleter O (1994) Hydrothermal degradation of polymers derived from plants. Prog Polym Sci 19:797–841
Bromberg SK, Bower PA, Duncombe GR, Fehring J, Gerber L, Lau VK, Tata M (1997) Requirements for zinc, manganese, calcium and magnesium in wort. J Am Soc Brew Chem 55:123–128
Buchert J, Niemelä K, Puls J, Poutanen K (1990) Improvement in the fermentability of steamed hemicellulose hydrolysate by ion exclusion. Process Biochem Int pp 176–180
Burtscher E, Bobleter O, Schwald W, Concin R, Binder H (1987) Chromatographic analysis of biomass reaction products produced by hydrothermolysis of poplar wood. J Chromatogr 390:401–412
Campbell MM, Sederoff R (1996) Variation in lignin content and composition: mechanisms of control and implications for the genetic improvement of plants. Plant Physiol 110:3–13
Chum HL, Johnson DK, Black SK, Overend RP (1990) Pretreatment catalyst effects and the combined severity parameter. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 24/25:1–14
Clark TA, Mackie KL (1984) Fermentation inhibitors in wood hydrolysates derived from the softwood Pinus radiata. J Chem Tech Biotechnol 34B:101–110
Delgenes JP, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1996) Effects of lignocellulose degradation products on ethanol fermentations of glucose and xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Zymomonas mobilis, Pichia stipitis, and Candida shehatae. Enzyme Microb Technol 19:220–225
Dien BS, Cotta MA, Jeffries TW (2003) Bacteria engineered for fuel ethanol production: current status. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:258–266
Dierssen GA, Holtegaard K, Jensen B, Rosen K (1956) Volatile carboxylic acids in molasses and their inhibitory action on fermentation. Int Sugar J 58:35–39
Doelle M, Greenfield PF, Doelle HW (1990) Effect of mineral ions on ethanol formation during sugar cane molasses fermentation using Zymomonas mobilis ATCC 39676. Process Biochem Int: 151–156
Dunlop AP (1948) Furfural formation and behaviour. Ind Eng Chem 40:204–209
Fan LT, Lee Y-H, Gharpuray MM (1982) The nature of lignocellulosics and their pretreatments for enzymatic hydrolysis. In: Fiechter A (ed) Microbial reactions. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 157–187
Fengel D, Wegener G (1989) Wood. Chemistry, ultrastructure, reactions. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin
Fenske JJ, Griffin DA, Penner MH (1998) Comparison of aromatic monomers in lignocellulosic biomass prehydrolysates. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 20:364–368
Fenske JJ, Hashimoto AG, Penner MH (1999) Relative fermentability of lignocellulosic dilute-acid prehydrolysates: application of a Pichia stipititis-based toxicity assay. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 73:145–157
Galbe M, Zacchi G (2002) A review of the production of ethanol from softwood. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:618–628
Garrote G, Dominguez H, Parajó JC (1999) Hydrothermal processing of lignocellulosic materials. Holz Roh Werkstoff 57:191–202
Gong CS, Chen CS, Chen LF (1993) Pretreatment of sugar cane bagasse hemicellulose hydrolysate for ethanol by yeast. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 39/40:83–88
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Jeppsson H, Olsson L, Mohagheghi A (1994) An interlaboratory comparison of the performance of ethanol-producing micro-organisms in a xylose-rich acid hydrolysate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41:62–72
Herrero AA, Gomez RF (1980) Development of ethanol tolerance in Clostridium thermocellum: effect of growth temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:571–577
Holtzapple MT, Jun JH, Ashok G, Patibandla S, Dale BE (1991) The ammonia freeze explosion (AFEX) process—a practical lignocellulose pretreatment. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 28–29:59–74
Jones RP (1986) Effect of the relative concentration of ion species on yeast growth and ethanol-production. Process Biochem 21:183–187
Jones RP, Greenfield PF (1984) A review of yeast ionic nutrition. Part I. Growth and fermentation requirements. Process Biochem April:48–59
Jönsson LJ, Palmqvist E, Nilvebrant NO, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1998) Detoxification of wood hydrolysates with laccase and peroxidase from the white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:691–697
Klinke HB, Thomsen AB, Ahring BK (2001) Potential inhibitors from wet oxidation of wheat straw and their effect on growth and ethanol production by Thermoanaerobacter mathranii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:631–638
Klinke HB, Ahring BK, Schmidt AS, Thomsen AB (2002) Characterization of degradation products from alkaline wet oxidation of wheat straw. Bioresour Technol 82:15–26
Klinke HB, Olsson L, Thomsen AB, Ahring BK (2003) Potential inhibitors from wet oxidation of wheat straw and their effect on ethanol production of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: wet oxidation and fermentation by yeast. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:738–747
Larsson M, Galbe M, Zacchi G (1997) Recirculation of process water in the production of ethanol from softwood. Bioresour Technol 60:143–151
Larsson S, Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Tengborg C, Stenberg K, Zacchi G, Nilvebrant NO (1999a) The generation of fermentation inhibitors during dilute acid hydrolysis of softwood. Enzyme Microb Technol 24:151–159
Larsson S, Reimann A, Nilvebrant NO, Jönsson LJ (1999b) Comparison of different methods for the detoxification of lignocellulose hydrolyzates of spruce. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 77–79:91–103
Larsson S, Quintana-Sáinz A, Reimann A, Nilvebrant N-O, Jönsson LJ (2000) Influence of lignocellulose-derived aromatic compounds on oxygen-limited growth and ethanolic fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 84–86:617–632
Larsson S, Cassland P, Jönsson LJ (2001) Development of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with enhanced resistance to phenolic fermentation inhibitors in lignocellulosic hydrolysates by heterologous expression of laccase. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1163–1170
Lawther JM, Sun R (1996a) The fractional characterisation of polysaccharides and lignin components in alkaline treated and atmospheric refined wheat straw. Ind Crops Prod 5:87–95
Lawther JM, Sun R, Banks WB (1996b) Fractional characterization of alkali-labile lignin and alkaline-insoluble lignin from wheat straw. Ind Crops Prod 5:291–300
Lee WG, Lee JS, Shin CS, Park SC, Chang HN, Chang YK (1999) Ethanol production using concentrated oak wood hydrolysates and methods to detoxify. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 77–79:547–559
Leonard RH, Hajny GJ (1945) Fermentation of wood sugars to ethyl alcohol. Ind Eng Chem 37:390–395
Lynd LR (1989) Production of ethanol from lignocellulosic materials using thermophilic bacteria: critical evaluation of potential and review. In: Fiechter A (ed) Lignocellulosic materials. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–52
Lynd L (2001) Salt accumulation resulting from base added for pH control, and not ethanol, limits growth of Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum HG-8 at elevated feed xylose concentrations in continuous culture. Biotechnol Prog 17:118–125
Maiorella BL, Blanch HW, Wilke CR (1984) Feed component inhibition in ethanolic fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:1155–1166
Maman O, Marseille F, Guillet B, Disnar JR, Morin P (1996) Separation of phenolic aldehydes, ketones and acids from lignin degradation by capillary zone electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 755:89–97
Martin C, Jonsson LJ (2003) Comparison of the resistance of industrial and laboratory strains of Saccharomyces and Zygosaccharomyces to lignocellulose-derived fermentation inhibitors. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:386–395
Martin C, Galbe M, Nilvebrant NO, Jonsson LJ (2002a) Comparison of the fermentability of enzymatic hydrolyzates of sugarcane bagasse pretreated by steam explosion using different impregnating agents. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 98:699–716
Martin C, Galbe M, Wahlbom CF, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Jonsson LJ (2002b) Ethanol production from enzymatic hydrolysates of sugarcane bagasse using recombinant xylose-utilising Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 31:274–282
Martinez A, Rodriguez ME, Wells ML, York SW, Preston JF, Ingram LO (2001) Detoxification of dilute acid hydrolysates of lignocellulose with lime. Biotechnol Prog 17:287–293
McMillan JD (1994a) Conversion of hemicellulose hydrolyzates to ethanol. In: Himmel ME, Baker JO, Overend RP (eds) Enzymatic conversion of biomass for fuels production. ACS Symp Ser, pp 292–324
McMillan JD (1994b) Pre-treatment of lignocellulosic biomass. In: Himmel ME, Baker JO, Overend RP (eds) Enzymatic conversion of biomass for fuels production. ACS Symp Ser, pp 411–437
McMillan JD, Newman MM, Templeton DW, Mohagheghi A (1999) Simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation of dilute-acid pretreated poplar to ethanol using xylose-fermenting Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 77–79:649–665
Mikulásova M, Pekarovicová A, Vodnú S (1990) Influence of phenolics on biomass production by Candida utilis and Candida albicans. Biomass 23:149–154
Mills SC, Child JJ, Spencer JFT (1971) The utilization of aromatic compounds by yeasts. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 37:281–287
Nishikawa NK, Sutcliffe R, Saddler JN (1988) The influence of lignin degradation products on xylose fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:549–552
Olsson L, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1996) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates for ethanol production. Enzyme Microb Technol 18:312–331
Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000a) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. I. Inhibition and detoxification. Bioresour Technol 74:17–24
Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000b) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. II. Inhibitors and mechanisms of inhibition. Bioresour Technol 74:25–33
Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Galbe M, Zacchi G (1996) The effect of water-soluble inhibitors from steam-pretreated willow on enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation. Enzyme Microb Technol 19:470–476
Palmqvist E, Grage H, Meinander NQ, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1999) Main and interaction effects of acetic acid, furfural, and p-hydroxybenzoic acid on growth and ethanol productivity of yeasts. Biotechnol Bioeng 63:46–55
Ragnar M, Lindgren CT, Nilvebrant N-O (2000) pKa values of guaiacyl and syringyl phenols related to lignin. J Wood Chem Technol 20:277–305
Ranatunga TD, Jervis J, Helm RF, McMillan JD, Hatzis C (1997a) Identification of inhibitory components toxic toward Zymomonas mobilis CP4(pZB5) xylose fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 67:185–197
Ranatunga TD, Jervis J, Helm RF, McMillan JD, Hatzis C (1997b) Toxicity of hard-wood extractives toward Saccharomyces cerevisiae glucose fermentation. Biotechnol Lett 19:1125–1127
Rivard CJ, Engel RE, Hayward TK, Nagle NJ, Hatzis C, Philippidis GP (1996) Measurement of the inhibitory potential and detoxification of biomass pretreatment hydrolysate for ethanol production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 57/58:183–191
Saka S (1997) Chemical composition and distribution. In: Hon DNS, Shirashi N (eds) Wood and cellulosic chemistry. Dekker, New York, pp 51–81
Sanchez B, Bautista J (1988) Effects of furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural on the fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and biomass production from Candida guilliermondii. Enzyme Microb Technol 10:315–318
Sarkanen KV, Ludwig CH (1971) Lignins: occurrence, formation, structure and reactions. Wiley-Interscience, New York, pp 345–372
Sears KD, Beélik A, Casebier RL, Engen RJ, Hamilton JK, Hergert HL (1971) Southern pine prehydrolyzates: characterization of polysaccharides and lignin fragments. J Polym Sci, Part C 36:425–433
Shevchenko SM, Chang K, Robinson J, Saddler JN (2000) Optimization of monosaccharide recovery by post-hydrolysis of the water-soluble hemicellulose component after steam explosion of softwood chips. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 72:207–211
Sierra-Alvarez R, Lettinga G (1991) The methanogenic toxicity of wastewater lignins and lignin related compounds. J Chem Tech Biotechnol 50:443–455
von Sivers M, Zacchi G (1996) Ethanol from lignocellulosics: a review of the economy. Bioresour Technol 56:131–140
von Sivers M, Zacchi G, Olsson L, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1994) Cost ananlysis of ethanol production from willow using recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog 10:555–560
Sjöström E (1991) Carbohydrate degradation products from alkaline pretreatment of biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 1:61–64
Sommer P (1998) Conversion of hemicellulose and d-xylose into ethanol by the use of thermophilic anaerobic bacteria. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, p 64
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Taherzadeh MJ, Eklund R, Gustafsson L, Niklasson C, Lidén G (1997a) Characterization and fermentation of dilute-acid hydrolyzates from wood. Ind Eng Chem Res 36:4659–4665
Taherzadeh MJ, Niklasson C, Lidén G (1997b) Acetic acid—friend or foe in anaerobic batch conversion of glucose to ethanol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem Eng Sci 52:2653–2659
Tajima K, Yoshizumi H, Terashima Y (1966) Salt and sugar tolerances of yeast on alcoholic fermentation. I. The inhibition of fermentation by the highly concentrated salts in molasses. Jap Ferment J: 77–84
Tengborg C, Stenberg K, Galbe M, Zacchi G, Larsson S, Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1998) Comparison of SO2 and H2SO4 impregnation of softwood prior to steam pretreatment on ethanol production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 70–72:3–15
Torry-Smith M, Sommer P, Ahring BK (2003) Purification of bioethanol effluent in an UASB reactor system with simultaneous biogas formation. Biotech Bioeng 84:7–12
Torssell KBG (1997) Natural product chemistry: a mechanistic, biosynthetic and ecological approach. Apotekarsocieteten, Stockholm
Tran AV, Chambers RP (1985) Red oak wood derived inhibtors in the ethanol fermentation of xylose by Pichia stipititis CBS 5776. Biotechnol Lett 7:841–846
Tran AV, Chambers RP (1986) Lignin and extractives derived inhibitors in the 2,3-butanediol fermentation of mannose-rich prehydrolysates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:191–197
Umezawa T, Higuchi T (1991) Chemistry of lignin degradation by lignin peroxidases. In: Leatham GF, Himmel ME (eds) Enzymes in biomass conversion. ACS Symposium Series, Washington, pp 236–246
Wilkie AC, Riedesel KJ, Owens JM (2000) Stillage characterization and anaerobic treatment of ethanol stillage from conventional and cellulosic feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy 19:63–102
Wolniewicz E, Letourneau F, Villa P (1988) Comportment of S. cerevisiae in relation to ions Ca++ and Mg++ on beet molasses wort. Biotechnol Lett 10:355–360
de Wulf O, Thonart P, Gainage P, Marlier M, Paris A, Paquot M (1986) Bioconversion of vanillin to vanillyl alcohol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 17:605–616
Zaldivar J, Ingram LO (1999) Effect of organic acids on the growth and fermentation of ethanologenic Escherichia coli LY01. Biotechnol Bioeng 66:203–210
Zaldivar J, Martinez A, Ingram LO (1999) Effect of selected aldehydes on the growth and fermentation of ethanologenic Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 65:24–33
Zaldivar J, Martinez A, Ingram LO (2000) Effect of alcohol compounds found in hemicelllulose hydrolysate on the growth and fermentation of ethanologenic Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 68:524–530
Zaldivar J, Nielsen J, Olsson L (2001) Fuel ethanol production from lignocellulose: a challenge for metabolic engineering and process integration. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:17–34
Zemek J, Kosikova B, Augustin J, Joniak D (1979) Antibiotic properties of lignin components. Folia Microbiologica 24:483–486
Acknowledgments
We thank the Danish Energy Program for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klinke, H.B., Thomsen, A.B. & Ahring, B.K. Inhibition of ethanol-producing yeast and bacteria by degradation products produced during pre-treatment of biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66, 10–26 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1642-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1642-2