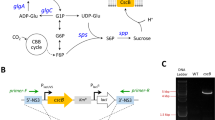
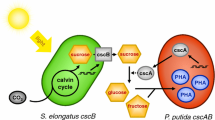
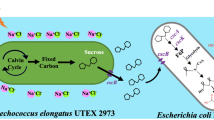
Abstract
It is important to obtain abundant sugar feedstocks economically and sustainably for bio-fermentation industry, especially for producing cheap biofuels and biochemicals. Besides plant biomass, photosynthetic cyanobacteria have also been considered to be potential microbe candidates for sustainable production of carbohydrate feedstocks. As the fastest growing cyanobacterium reported so far, Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973 (Syn2973) might have huge potential for bioproduction. In this study, we explored the potentials of this strain as photo-bioreactors for sucrose and glycogen production. Under nitrogen-replete condition, Syn2973 could accumulate glycogen with a rate of 0.75 g L−1 day−1 at the exponential phase and reach a glycogen content as high as 51 % of the dry cell weight (DCW) at the stationary phase. By introducing a sucrose transporter CscB, Syn2973 was endowed with an ability to secrete over 94 % sucrose out of cells under salt stress condition. The highest extracellular sucrose productivity reached 35.5 mg L−1 h−1 for the Syn2973 strain expressing cscB, which contained the similar amounts of intracellular glycogen with the wild type. Potassium chloride was firstly proved to induce sucrose accumulation as well as sodium chloride in Syn2973. By semi-continuous culturing, 8.7 g L−1 sucrose was produced by the cscB-expressing strain of Syn2973 in 21 days. These results support that Syn2973 is a promising candidate with great potential for production of sugars.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikawa S, Joseph A, Yamada R, Izumi Y, Yamagishi T, Matsuda F, Kawai H, Chang JS, Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2013) Direct conversion of Spirulina to ethanol without pretreatment or enzymatic hydrolysis processes. Energ Environ Sci 6(6):1844–1849. doi:10.1039/c3ee40305j
Aikawa S, Nishida A, Ho SH, Chang JS, Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2014) Glycogen production for biofuels by the euryhaline cyanobacteria Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002 from an oceanic environment. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:88. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-7-88
Allen MM (1984) Cyanobacterial cell inclusions. Ann Rev Microbiol 38(1):1–25. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.000245
Angermayr SA, Rovira AG, Hellingwerf KJ (2015) Metabolic engineering of cyanobacteria for the synthesis of commodity products. Trends Biotechnol 33(6):352–361. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.03.009
Balat M, Balat H (2009) Recent trends in global production and utilization of bio-ethanol fuel. Appl Energ 86(11):2273–2282. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.03.015
Berry S, Esper B, Karandashova I, Teuber M, Elanskaya I, Rogner M, Hagemann M (2003) Potassium uptake in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 mainly depends on a Ktr-like system encoded by slr1509 (ntpJ). FEBS Lett 548(1–3):53–58. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00729-4
Carrieri D, Paddock T, Maness PC, Seibert M, Yu JP (2012) Photo-catalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to organic acids by a recombinant cyanobacterium incapable of glycogen storage. Energ Environ Sci 5(11):9457–9461. doi:10.1039/c2ee23181f
Desplats P, Folco E, Salerno GL (2005) Sucrose may play an additional role to that of an osmolyte in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 salt-shocked cells. Plant Physiol Biochem 43(2):133–138. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2005.01.008
Du W, Liang F, Duan Y, Tan X, Lu X (2013) Exploring the photosynthetic production capacity of sucrose by cyanobacteria. Metab Eng 19:17–25. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2013.05.001
Ducat DC, Avelar-Rivas JA, Way JC, Silver PA (2012) Rerouting carbon flux to enhance photosynthetic productivity. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(8):2660–2668. doi:10.1128/aem.07901-11
E4tech, RE-CORD, WUR (2015) From the Sugar Platform to biofuels and biochemicals. Final report for the European Commission:contract No. ENER/C2/423–2012/SI2012.673791.
Elhai J, Wolk CP (1988) Conjugal transfer of DNA to cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol 167:747–754
Graham-Rowe D (2011) Agriculture: beyond food versus fuel. Nature 474(7352):S6–S8. doi:10.1038/474S06a
Grundel M, Scheunemann R, Lockau W, Zilliges Y (2012) Impaired glycogen synthesis causes metabolic overflow reactions and affects stress responses in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Microbiology 158(12):3032–3043. doi:10.1099/mic.0.062950-0
Gupta V, Ratha SK, Sood A, Chaudhary V, Prasanna R (2013) New insights into the biodiversity and applications of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae)—prospects and challenges. Algal Res 2(2):79–97. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2013.01.006
Hagemann M (2011) Molecular biology of cyanobacterial salt acclimation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35(1):87–123. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00234.x
Hara KY, Araki M, Okai N, Wakai S, Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2014) Development of bio-based fine chemical production through synthetic bioengineering. Microb Cell Factories 13(1):1–19. doi:10.1186/s12934-014-0173-5
Hays SG, Ducat DC (2015) Engineering cyanobacteria as photosynthetic feedstock factories. Photosynthesis Res 123(3):285–295. doi:10.1007/s11120-014-9980-0
Hernandez-Prieto MA, Semeniuk TA, Futschik ME (2014) Toward a systems-level understanding of gene regulatory, protein interaction, and metabolic networks in cyanobacteria. Front Genet 5:191. doi:10.3389/fgene.2014.00191
Hickman JW, Kotovic KM, Miller C, Warrener P, Kaiser B, Jurista T, Budde M, Cross F, Roberts JM, Carleton M (2013) Glycogen synthesis is a required component of the nitrogen stress response in Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942. Algal Res 2(2):98–106. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2013.01.008
Karandashova IV, Elanskaya IV (2005) Genetic control and mechanisms of salt and hyperosmotic stress resistance in cyanobacteria. Russ J Genet 41(12):1311–1321. doi:10.1007/s11177-006-0001-z
Klotz A, Reinhold E, Doello S, Forchhammer K (2015) Nitrogen starvation acclimation in Synechococcus elongatus: redox-control and the role of nitrate reduction as an electron sink. Life 5(1):888. doi:10.3390/life5010888
Lau N-S, Matsui M, Abdullah AA-A (2015) Cyanobacteria: photoautotrophic microbial factories for the sustainable synthesis of industrial products. Biomed Res Int 2015:9. doi:10.1155/2015/754934
Niederholtmeyer H, Wolfstadter BT, Savage DF, Silver PA, Way JC (2010) Engineering cyanobacteria to synthesize and export hydrophilic products. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(11):3462–3466. doi:10.1128/AEM.00202-10
Okuhara H, Matsumura T, Fujita Y, Hase T (1999) Cloning and inactivation of genes encoding ferredoxin- and nadh-dependent glutamate synthases in the cyanobacterium Plectonema boryanum. Imbalances in nitrogen and carbon assimilations caused by deficiency of the ferredoxin-dependent enzyme. Plant Physiol 120(1):33–42
Peralta-Yahya PP, Zhang F, del Cardayre SB, Keasling JD (2012) Microbial engineering for the production of advanced biofuels. Nature 488(7411):320–328. doi:10.1038/nature11478
Sarkar D, Shimizu K (2015) An overview on biofuel and biochemical production by photosynthetic microorganisms with understanding of the metabolism and by metabolic engineering together with efficient cultivation and downstream processing. Bioresour Bioprocess 2(1):17. doi:10.1186/s40643-015-0045-9
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35(2):171–205
Suzuki E, Ohkawa H, Moriya K, Matsubara T, Nagaike Y, Iwasaki I, Fujiwara S, Tsuzuki M, Nakamura Y (2010) Carbohydrate metabolism in mutants of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 defective in glycogen synthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(10):3153–3159. doi:10.1128/aem.00397-08
Tan X, Du W, Lu X (2015) Photosynthetic and extracellular production of glucosylglycerol by genetically engineered and gel-encapsulated cyanobacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(5):2147–2154. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-6273-7
Wolk CP, Ernst A, Elhai J (1994) Heterocyst metabolism and development. In: Bryant AD (ed) The molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Springer, Netherlands, pp. 769–823
Xu Y, Guerra LT, Li Z, Ludwig M, Dismukes GC, Bryant DA (2013) Altered carbohydrate metabolism in glycogen synthase mutants of Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002: cell factories for soluble sugars. Metab Eng 16:56–67. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2012.12.002
Yu J, Liberton M, Cliften PF, Head RD, Jacobs JM, Smith RD, Koppenaal DW, Brand JJ, Pakrasi HB (2015) Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973, a fast growing cyanobacterial chassis for biosynthesis using light and CO(2). Sci Rep 5:8132. doi:10.1038/srep08132
Zhou J, Li Y (2010) Engineering cyanobacteria for fuels and chemicals production. Protein Cell 1(3):207–210. doi:10.1007/s13238-010-0043-9
Ziolkowska JR (2014) Prospective technologies, feedstocks and market innovations for ethanol and biodiesel production in the US. Biotechnol Rep 4:94–98. doi:10.1016/j.btre.2014.09.001
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Cheng Li, Quan Luo, and Yangkai Duan for valuable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (31525002 to X. Lu), the Excellent Youth Award of the Shandong Natural Science Foundation (JQ201306 to X. Lu), the Shandong Taishan Scholarship (X. Lu), the National Science Foundation of China (31301018 to X. Tan), the State Oceanic Administration (SOA) Global Change and Air-Sea Interaction Program (GASI-03-01-02-05 to X. Tan), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association (X. Tan).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Electronic Supplementary Materials
ESM 1
(PDF 275 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, K., Tan, X., Liang, Y. et al. The potential of Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973 for sugar feedstock production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 7865–7875 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7510-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7510-z