Abstract
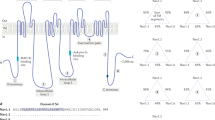
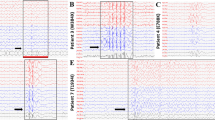
Mutations in the voltage-gated sodium channels SCN1A and SCN2A are responsible for several types of human epilepsy. Variable expressivity among family members is a common feature of these inherited epilepsies, suggesting that genetic modifiers may influence the clinical manifestation of epilepsy. The transgenic mouse model Scn2aQ54 has an epilepsy phenotype as a result of a mutation in Scn2a that slows channel inactivation. The mice display progressive epilepsy that begins with short-duration partial seizures that appear to originate in the hippocampus. The partial seizures become more frequent and of longer duration with age and often induce secondary generalized seizures. Clinical severity of the Scn2aQ54 phenotype is influenced by genetic background. Congenic C57BL/6J.Q54 mice exhibit decreased incidence of spontaneous seizures, delayed seizure onset, and longer survival in comparison with [C57BL/6J × SJL/J]F1.Q54 mice. This observation indicates that strain SJL/J carries dominant modifier alleles at one or more loci that determine the severity of the epilepsy phenotype. Genome-wide interval mapping in an N2 backcross revealed two modifier loci on Chromosomes 11 and 19 that influence the clinical severity of of this sodium channel-induced epilepsy. Modifier genes affecting clinical severity in the Scn2aQ54 mouse model may contribute to the variable expressivity seen in epilepsy patients with sodium channel mutations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Khalil B, Ge Q, Desai R, Ryther R, Bazyk A, et al. (2001) Partial and generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus and a novel SCN1A mutation. Neurology 57:2265–2272
Adamska M, MacDonald BT, Meisler MH (2003) Doubleridge, a mouse mutant with defective compaction of the apical ectodermal ridge and normal dorsal-ventral patterning of the limb. Dev Biol 255:350–362
Ayyadevara S, Ayyadevara R, Vertino A, Galecki A, Thaden JJ, et al. (2003) Genetic loci modulating fitness and life span in Caenorhabditis elegans: categorical trait interval mapping in CL2a × Bergerac-BO recombinant-inbred worms. Genetics 163:557–570
Backman SA, Stambolic V, Suzuki A, Haight J, Elia A, et al. (2001) Deletion of Pten in mouse brain causes seizures, ataxia and defects in soma size resembling Lhermitte-Duclos disease. Nat Genet 29:396–403
Buono RJ, Lohoff FW, Sander T, Sperling MR, O’Connor MJ, et al. (2004) Association between variation in the human KCNJ10 potassium ion channel gene and seizure susceptibility. Epilepsy Res 58:175–183
Chen J, Larionov S, Pitsch J, Hoerold N, Ullmann C, et al. (2005) Expression analysis of metabotropic glutamate receptors I and III in mouse strains with different susceptibility to experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Lett 375:192–197
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Escayg A, MacDonald BT, Meisler MH, Baulac S, Huberfeld G, et al. (2000) Mutations of SCN1A, encoding a neuronal sodium channel, in two families with GEFS+2. Nat Genet 24:343–345
Ferraro TN, Golden GT, Smith GG, Schork NJ, St Jean P, et al. (1997) Mapping murine loci for seizure response to kainic acid. Mamm Genome 8:200–208
Ferraro TN, Golden GT, Smith GG, St Jean P, Schork NJ, et al. (1999) Mapping loci for pentylenetetrazol-induced seizure susceptibility in mice. J Neurosci 19:6733–6739
Ferraro TN, Golden GT, Smith GG, Longman RL, Snyder RL, et al. (2001) Quantitative genetic study of maximal electroshock seizure threshold in mice: evidence for a major seizure susceptibility locus on distal chromosome 1. Genomics 75:35–42
Ferraro TN, Golden GT, Smith GG, DeMuth D, Buono RJ, et al. (2002) Mouse strain variation in maximal electroshock seizure threshold. Brain Res 936:82–86
Ferraro TN, Golden GT, Smith GG, Martin JF, Lohoff FW, et al. (2004) Fine mapping of a seizure susceptibility locus on mouse Chromosome 1: nomination of Kcnj10 as a causative gene. Mamm Genome 15:239–251
Frankel WN, Valenzuela A, Lutz CM, Johnson EW, Dietrich WF, et al.M (1995) New seizure frequency QTL and the complex genetics of epilepsy in EL mice. Mamm Genome 6:830–838
Frankel WN, Taylor L, Beyer B, Tempel BL, White HS (2001) Electroconvulsive thresholds of inbred mouse strains. Genomics 74:306–312
Galecki AT, ten Have TR, Molenberghs G (2001) A simple and fast alternative to the EM algorithm for incomplete categorical data and latent class models. Comput Stat Data Anal 35:265–281
Golden GT, Ferraro TN, Smith GG, Snyder RL, Jones NL, et al. (2001) Acute cocaine-induced seizures: differential sensitivity of six inbred mouse strains. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:291–299
Kalachikov S, Evgrafov O, Ross B, Winawer M, Barker-Cummings C, et al. (2002) Mutations in LGI1 cause autosomal-dominant partial epilepsy with auditory features. Nat Genet 30:335–341
Kearney JA, Plummer NW, Smith MR, Kapur J, Cummins TR, et al. (2001) A gain-of-function mutation in the sodium channel gene Scn2a results in seizures and behavioral abnormalities. Neuroscience 102:307–317
Kitami T, Ernest S, Gallaugher L, Friedman L, Frankel WN, et al. (2004) Genetic and phenotypic analysis of seizure susceptibility in PL/J mice. Mamm Genome 15:698–703
Kruglyak L, Lander ES (1995) A nonparametric approach for mapping quantitative trait loci. Genetics 139:1421–1428
Legare ME, Frankel WN (2000) Multiple seizure susceptibility genes on chromosome 7 in SWXL-4 congenic mouse strains. Genomics 70:62–65
Legare ME, Bartlett FS 2nd, Frankel WN (2000) A major effect QTL determined by multiple genes in epileptic EL mice. Genome Res 10:42–48
Lossin C, Wang DW, Rhodes TH, Vanoye CG, George AL Jr (2002) Molecular basis of an inherited epilepsy. Neuron 34:877–884
MacDonald BT, Adamska M, Meisler MH (2004) Hypomorphic expression of Dkk1 in the doubleridge mouse: dose dependence and compensatory interactions with Lrp6. Development 131:2543–2552
McCullagh P, Nelder JA (1989) Generalized Linear Models 2nd ed. (New York: Chapman and Hall)
Meisler MH, Kearney JA (2005) Sodium channel mutations in epilepsy and other neurological disorders. J Clin Invest 115, 2010–2017
Moulard B, Guipponi M, Chaigne D, Mouthon D, Buresi C, et al. (1999) Identification of a new locus for generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+) on chromosome 2q24-q33. Am J Hum Genet 65:1396–1400
Mukhopadhyay M, Shtrom S, Rodriguez-Esteban C, Chen L, Tsukui T, et al. (2001) Dickkopf1 is required for embryonic head induction and limb morphogenesis in the mouse. Dev Cell 1:423–434
Plummer NW, Galt J, Jones JM, Burgess DL, Sprunger LK, et al. (1998) Exon organization, coding sequence, physical mapping, and polymorphic intragenic markers for the human neuronal sodium channel gene SCN8A. Genomics 54:287–296
Preisser JS, Galecki AT, Lohman KK, Wagenknecht LE (2000) Analysis of smoking trends with incomplete repeated responses. J Am Stat Assoc 95:1021–1031
Schauwecker PE, Williams RW, Santos JB (2004) Genetic control of sensitivity to hippocampal cell death induced by kainic acid: a quantitative trait loci analysis. J Comp Neurol 477:96–107
Sebat J, Lakshmi B, Troge J, Alexander J, Young J, et al. (2004) Large-scale copy number polymorphism in the human genome. Science 305:525–528
Seyfried TN, Yu RK, Glaser GH (1980) Genetic analysis of audiogenic seizure susceptibility in C57BL/6J × DBA/2J recombinant inbred strains of mice. Genetics 94:701–718
Silver LM (1995) Mouse Genetics: Concepts and Applications (New York: Oxford University Press)
Smith MR, Goldin AL (1997) Interaction between the sodium channel inactivation linker and domain III S4–S5. Biophys J 73:1885–1895
Wallace RH, Wang DW, Singh R, Scheffer IE, George AL Jr, et al. (1998) Febrile seizures and generalized epilepsy associated with a mutation in the Na+-channel beta1 subunit gene SCN1B. Nat Genet 19:366–370
Weiss KM (2005) Cryptic causation of human disease: reading between the (germ) lines. Trends Genet 21:82–88
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Bryan MacDonald and Derek Delmonte for technical assistance. They also thank Miriam Meisler for providing the doubleridge and Dkk1 null mice, and for review of the manuscript. This work was supported by NIH research grant R21 NS046315 (JAK) and a Claude Pepper Center Grant AG024824 (AG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergren, S.K., Chen, S., Galecki, A. et al. Genetic modifiers affecting severity of epilepsy caused by mutation of sodium channelScn2a. Mamm Genome 16, 683–690 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-005-0049-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-005-0049-4