Abstract
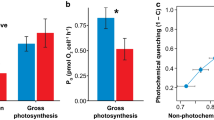
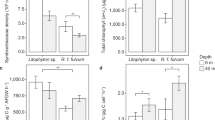
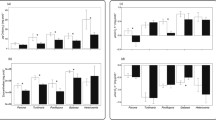
Algal endosymbionts of the genus Symbiodinium play a key role in the nutrition of reef building corals and strongly affect the thermal tolerance and growth rate of the animal host. This study reports that 14C photosynthate incorporation into juvenile coral tissues was doubled in Acropora millepora harbouring Symbiodinium C1 compared with juveniles from common parentage harbouring Symbiodinium D in a laboratory experiment. Rapid light curves performed on the same corals revealed that the relative electron transport rate of photosystem II (rETRMAX) was 87% greater in Symbiodinium C1 than in Symbiodinium D in hospite. The greater relative electron transport through photosystem II of Symbiodinium C1 is positively correlated with increased carbon delivery to the host under the applied experimental conditions (r 2 = 0.91). This may translate into a competitive advantage for juveniles harbouring Symbiodinium C1 under certain field conditions, since rapid early growth typically limits mortality. Both symbiont types exhibited severe reductions in 14C incorporation during a 10-h exposure to the electron transport blocking herbicide diuron (DCMU), confirming the link between electron transport through PSII and photosynthate incorporation within the host tissue. These findings advance the current understanding of symbiotic relationships between corals and their symbionts, providing evidence that enhanced growth rates of juvenile corals may result from greater translocation of photosynthates from Symbiodinium C1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrego D, Ulstrup KE, Willis BL, van Oppen MJH (2008) Species-specific interactions between algal endosymbionts and coral hosts define their bleaching response to heat and light stress. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 275:2273–2282
Apprill AM, Gates RD (2007) Recognizing diversity in coral symbiotic dinoflagellate communities. Mol Ecol 16:1127–1134
Baker AC (2003) Flexibility and specificity in coral-algal symbiosis: diversity, ecology, and biogeography of Symbiodinium. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 34:661–689
Baker AC, Starger CJ, McClanahan TR, Glynn PW (2004) Corals’ adaptive response to climate. Nature 430:661–689
Berkelmans R, van Oppen MJH (2006) The role of zooxanthellae in the thermal tolerance of corals: a ‘nugget of hope’ for coral reefs in an era of climate change. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 273:2305–2312
Brown BE, Ambarasari I, Warner ME, Fitt WK, Dunne RP, Gibb SW, Cummings DG (1999) Diurnal changes in photochemical efficiency and xanthophyll concentrations in shallow water reef corals: evidence for photoinhibition and photoprotection. Coral Reefs 18:99–105
Cantin NE, Negri AP, Willis BL (2007) Photoinhibition from chronic herbicide exposure reduces reproductive output of reef-building corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 344:81–93
Coffroth MA, Santos SR (2005) Genetic diversity of symbiotic dinoflagellates in the genus Symbiodinium. Protist 156:19–34
Coles SL, Brown BE (2003) Coral bleaching—capacity for acclimatization and adaptation. Adv Mar Biol 46:183–244
Crossland CJ, Barnes DJ, Borowitzka MA (1980) Diurnal lipid and mucus production in the staghorn coral Acropora acuminata. Mar Biol 60:81–90
Escoubas J, Lomas M, LaRoche J, Falkowski PG (1995) Light intensity regulation of cab gene transcription is signalled by the redox state of the plastoquinone pool. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:10237–10241
Genty B, Briantais JM, Baker NR (1989) The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta 990:87–92
Goulet TL, Cook CB, Goulet D (2005) Effect of short-term exposure to elevated temperatures and light levels on photosynthesis of different host-symbiont combinations in the Aiptasia pallida/Symbiodinium symbiosis. Limnol Oceanogr 50:1490–1498
Hoogenboom MO, Anthony KRN, Connolly SR (2006) Energetic cost of photoinhibition in corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 313:1–12
Hughes TP, Jackson JBC (1985) Population dynamics and life histories of foliaceous corals. Ecol Monogr 55:141–166
Hughes TP, Baird AH, Bellwood DR, Card M, Connolly SR, Folke C, Grosberg R, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Jackson JBC, Kleypas J, Lough JM, Marshall P, Nystrom M, Palumbi SR, Pandolfi JM, Rosen B, Roughgarden J (2003) Climate change, human impacts, and the resilience of coral reefs. Science 301:929–933
Jones RJ, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Larkum AWD, Schreiber U (1998) Temperature-induced bleaching of corals begins with impairment of the CO2 fixation mechanism in zooxanthellae. Plant Cell Environ 21:1219–1230
Jones RJ, Müller J, Haynes D, Schreiber U (2003) Effects of herbicides diuron and atrazine on corals of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 251:153–167
Jones AM, Berkelmans R, van Oppen MJH, Mieog JC, Sinclair W (2008) A community change in the algal endosymbionts of a scleractinian coral following a natural bleaching event: field evidence of acclimatization. Proc R Soc Lond B, Biol Sci 275:1359–1365
Koumandou VL, Howe CJ (2007) The copy number of chloroplast gene minicircles changes dramatically with growth phase in the dinoflagellate Amphidinium operculatum. Protist 158:89–103
LaJeunesse T (2002) Diversity and community structure of symbiotic dinoflagellates from Caribbean coral reefs. Mar Biol 141:387–400
Little AF, van Oppen MJH, Willis BL (2004) Flexibility in algal endosymbioses shapes growth in reef corals. Science 304:1492–1494
Loram JE, Trapido-Rosenthal HG, Douglas AE (2007) Functional significance of genetically different symbiotic algae Symbiodinium in a coral reef symbiosis. Mol Ecol 16:4849–4857
Masuda T, Jugen EWP, Melis A (2002) Biosynthesis and distribution of chlorophyll among the photosystems during recovery of the green alga Dunaliella salina from irradiance stress. Plant Physiol 128:603–614
Mieog JC, van Oppen MJH, Cantin NE, Stam WT, Olsen JL (2007) Real-time PCR reveals a high incidence of Symbiodinium clade D at low levels in four scleractinian corals across the Great Barrier Reef: implications for symbiont shuffling. Coral Reefs 26:449–457
Muscatine L, Falkowski PG, Porter JW, Dubinsky Z (1984) Fate of photosynthetic fixed carbon in light and shade-adapted colonies of the symbiotic coral Stylophora pistillata. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 222:181–202
Negri A, Vollhardt C, Humphrey C, Heyward A, Jones R, Eaglesham G, Fabricius K (2005) Effects of the herbicide diuron on the early life history stages of coral. Mar Pollut Bull 51:370–383
Platt T, Gallegos CL, Harrison WG (1980) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton. J Mar Res 38:687–701
Pochon X, LaJeunesse TC, Pawlowski J (2004) Biogeographic partitioning and host specialization among foraminiferan dinoflagellate symbionts (Symbiodinium; Dinophyta). Mar Biol 146:17–27
Ralph PJ, Gademann R (2005) Rapid light curves: a powerful tool to assess photosynthetic activity. Aquat Ecol 82:222–237
Ralph PJ, Gademann R, Larkum AWD, Kuhl M (2002) Spatial heterogeneity in active fluorescence and PSII activity of coral tissues. Mar Biol 141:539–646
Robison JD, Warner ME (2006) Differential impacts of photoacclimation and thermal stress on the photobiology of four different phylotypes of Symbiodinium (Pyrrhophyta). J Phycol 42:568–579
Rowan R (2004) Thermal adaptation in reef coral symbionts. Nature 430:742
Santos SR, Taylor DJ, Kinzie RAIII, Hidaka M, Sakai K, Coffroth MA (2002) Molecular phylogeny of symbiotic dinoflagellates inferred from partial chloroplast large subunit (23S)-rDNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 23:97–111
Schreiber U (2004) Pulse-amplitude-modulation (PAM) fluorometry and saturation pulse method: an overview. In: Papageorgiou G, Govindjee (eds) Chlorophyll fluorescence: a signature of photosynthesis. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 279–319
Schreiber U, Gademann R, Ralph PJ, Larkum AWD (1997) Assessment of photosynthetic performance of prochloron in Lissoclinum patella in hospite by chlorophyll fluorescence measurements. Plant Cell Physiol 38:945–951
Stat M, Morris E, Gates RD (2008) Functional diversity in coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9256–9261
Takabayashi M, Santos SR, Cook CB (2004) Mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of the symbiotic dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium, Dinophyta). J Phycol 40:160–164
Thornhill DJ, Lajeunesse TC, Kemp DW, Fitt WK, Schmidt GW (2006) Multi-year, seasonal genotypic surveys of coral-algal symbioses reveal prevalent stability or post-bleaching reversion. Mar Biol 148:711–722
Ulstrup KE, van Oppen MJH (2003) Geographic and habitat partitioning of genetically distinct zooxanthellae (Symbiodinium) in Acropora corals on the Great Barrier Reef. Mol Ecol 12:3477–3484
van Oppen MJH (2004) Mode of zooxanthella transmission does not affect zooxanthella diversity in acroporid corals. Mar Biol 144:1–7
van Oppen MJH, Palstra FP, Piquet AMT, Miller D (2001) Patterns of coral-dinoflagellate associations in Acropora: significance of local availability and physiology of Symbiodinium strains and host-symbiont selectivity. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 268:1759–1767
van Oppen MJH, Mahiny AJ, Done TD (2005) Geographic distribution of zooxanthella types in three coral species on the Great Barrier Reef sampled after the 2002 bleaching event. Coral Reefs 24:482–487
Warner ME, Lajeunesse TC, Robison JD, Thur RM (2006) The ecological distribution and comparative photobiology of symbiotic dinoflagellates from reef corals in Belize: potential implications for coral bleaching. Limnol Oceanogr 51:1887–1897
Wilson K, Yutao L, Whan K, Lehnert S, Byrne K, Moore S, Pongsomboon S, Tassanakajon A, Rosenberg G, Ballment E, Fayazi Z, Swan J, Kenway M, Benzie J (2002) Genetic mapping of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon with amplified fragment length polymorphism. Aquaculture 204:297–309
Wright SW, Jeffrey SW (1997) Phytoplankton pigments in oceanography: guidelines to modern methods. UNESCO, Paris
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Doyle and L. Peplow for technical advice, A. Baird for comments on the experimental design and P. Ralph for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant from AIMS@JCU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Biology Editor Dr. Ruth Gates
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cantin, N.E., van Oppen, M.J.H., Willis, B.L. et al. Juvenile corals can acquire more carbon from high-performance algal symbionts. Coral Reefs 28, 405–414 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-009-0478-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-009-0478-8