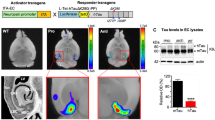
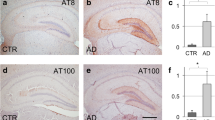
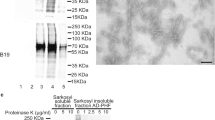
Abstract
Filamentous tau pathologies are hallmark lesions of several neurodegenerative tauopathies including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and corticobasal degeneration (CBD) which show cell type-specific and topographically distinct tau inclusions. Growing evidence supports templated transmission of tauopathies through functionally interconnected neuroanatomical pathways suggesting that different self-propagating strains of pathological tau could account for the diverse manifestations of neurodegenerative tauopathies. Here, we describe the rapid and distinct cell type-specific spread of pathological tau following intracerebral injections of CBD or AD brain extracts enriched in pathological tau (designated CBD-Tau and AD-Tau, respectively) in young human mutant P301S tau transgenic (Tg) mice (line PS19) ~6–9 months before they show onset of mutant tau transgene-induced tau pathology. At 1 month post-injection of CBD-Tau, tau inclusions developed predominantly in oligodendrocytes of the fimbria and white matter near the injection sites with infrequent intraneuronal tau aggregates. In contrast, injections of AD-Tau in young PS19 mice induced tau pathology predominantly in neuronal perikarya with little or no oligodendrocyte involvement 1 month post-injection. With longer post-injection survival intervals of up to 6 months, CBD-Tau- and AD-Tau-induced tau pathology spread to different brain regions distant from the injection sites while maintaining the cell type-specific pattern noted above. Finally, CA3 neuron loss was detected 3 months post-injection of AD-Tau but not CBD-Tau. Thus, AD-Tau and CBD-Tau represent specific pathological tau strains that spread differentially and may underlie distinct clinical and pathological features of these two tauopathies. Hence, these strains could become targets to develop disease-modifying therapies for CBD and AD.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed Z, Cooper J, Murray TK, Garn K, McNaughton E, Clarke H, Parhizkar S, Ward MA, Cavallini A, Jackson S, Bose S, Clavaguera F, Tolnay M, Lavenir I, Goedert M, Hutton ML, O’Neill MJ (2014) A novel in vivo model of tau propagation with rapid and progressive neurofibrillary tangle pathology: the pattern of spread is determined by connectivity, not proximity. Acta Neuropathol 127(5):667–683
Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(9):663–672. doi:10.1038/nrn2194
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82(4):239–259
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2011) Alzheimer’s pathogenesis: is there neuron-to-neuron propagation? Acta Neuropathol 121(5):589–595
Braak H, Thal DR, Ghebremedhin E, Del Tredici K (2011) Stages of the pathologic process in Alzheimer disease: age categories from 1 to 100 years. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70(11):960–969
Clavaguera F, Akatsu H, Fraser G, Crowther RA, Frank S, Hench J, Probst A, Winkler DT, Reichwald J, Staufenbiel M, Ghetti B, Goedert M, Tolnay M (2013) Brain homogenates from human tauopathies induce tau inclusions in mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(23):9535–9540
Clavaguera F, Bolmont T, Crowther RA, Abramowski D, Frank S, Probst A, Fraser G, Stalder AK, Beibel M, Staufenbiel M, Jucker M, Goedert M, Tolnay M (2009) Transmission and spreading of tauopathy in transgenic mouse brain. Nat Cell Biol 11(7):909–913
Cohen TJ, Guo JL, Hurtado DE, Kwong LK, Mills IP, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2011) The acetylation of tau inhibits its function and promotes pathological tau aggregation. Nat Commun 2:252
De Boni U, Crapper DR (1978) Paired helical filaments of the Alzheimer type in cultured neurones. Nature 271(5645):566–568
de Calignon A, Polydoro M, Suarez-Calvet M, William C, Adamowicz DH, Kopeikina KJ, Pitstick R, Sahara N, Ashe KH, Carlson GA, Spires-Jones TL, Hyman BT (2012) Propagation of tau pathology in a model of early Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 73(4):685–697
Forman MS, Zhukareva V, Bergeron C, Chin SSM, Grossman M, Clark C, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Signature tau neuropathology ingray and white matter of corticobasal degeneration. Am J Pathol 160(6):2045–2053. doi:10.1016/s0002-9440(10)61154-6
Frost B, Jacks RL, Diamond MI (2009) Propagation of tau misfolding from the outside to the inside of a cell. J Biol Chem 284(19):12845–12852
Guo JL, Covell DJ, Daniels JP, Iba M, Stieber A, Zhang B, Riddle DM, Kwong LK, Xu Y, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2013) Distinct alpha-synuclein strains differentially promote tau inclusions in neurons. Cell 154(1):103–117
Guo JL, Lee VM (2011) Seeding of normal tau by pathological tau conformers drives pathogenesis of Alzheimer-like tangles. J Biol Chem 286(17):15317–15331
Guo JL, Lee VM (2014) Cell-to-cell transmission of pathogenic proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Med 20(2):130–138. doi:10.1038/nm.3457
Higuchi M, Zhang B, Forman MS, Yoshiyama Y, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2005) Axonal degeneration induced by targeted expression of mutant human tau in oligodendrocytes of transgenic mice that model glial tauopathies. J Neurosci 25(41):9434–9443
Horiguchi T, Uryu K, Giasson BI, Ischiropoulos H, LightFoot R, Bellmann C, Richter-Landsberg C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2003) Nitration of tau protein is linked to neurodegeneration in tauopathies. Am J Pathol 163(3):1021–1031
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Petersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaff E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebrand M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski J, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd PR, Hayward N, Kwok JB, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann D, Lynch T, Heutink P (1998) Association of missense and 5′-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393(6686):702–705
Iba M, Guo JL, McBride JD, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2013) Synthetic tau fibrils mediate transmission of neurofibrillary tangles in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s-like tauopathy. J Neurosci 33(3):1024–1037
Irwin DJ, Cohen TJ, Grossman M, Arnold SE, McCarty-Wood E, Van Deerlin VM, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2013) Acetylated tau neuropathology in sporadic and hereditary tauopathies. Am J Pathol 183(2):344–351
Irwin DJ, Cohen TJ, Grossman M, Arnold SE, Xie SX, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2012) Acetylated tau, a novel pathological signature in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Brain 135(Pt 3):807–818
Jicha GA, Bowser R, Kazam IG, Davies P (1997) Alz-50 and MC-1, a new monoclonal antibody raised to paired helical filaments, recognize conformational epitopes on recombinant tau. J Neurosci Res 48(2):128–132
Jicha GA, Lane E, Vincent I, Otvos L Jr, Hoffmann R, Davies P (1997) A conformation- and phosphorylation-dependent antibody recognizing the paired helical filaments of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 69(5):2087–2095
Jucker M, Walker LC (2013) Self-propagation of pathogenic protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 501(7465):45–51
Kosik KS, Orecchio LD, Binder L, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Lee G (1988) Epitopes that span the tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron 1(9):817–825
Ledesma MD, Perez M, Colaco C, Avila J (1998) Tau glycation is involved in aggregation of the protein but not in the formation of filaments. Cell Mol Biol 44(7):1111–1116
Lee EB, Leng LZ, Zhang B, Kwong L, Trojanowski JQ, Abel T, Lee VM (2006) Targeting amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) oligomers by passive immunization with a conformation-selective monoclonal antibody improves learning and memory in Abeta precursor protein (APP) transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 281(7):4292–4299
Lee VM, Balin BJ, Otvos L Jr, Trojanowski JQ (1991) A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal tau. Science 251(4994):675–678
Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1121–1159
Lee VM, Page CD, Wu HL, Schlaepfer WW (1984) Monoclonal antibodies to gel-excised glial filament protein and their reactivities with other intermediate filament proteins. J Neurochem 42(1):25–32
Lee VM, Wang J, Trojanowski JQ (1999) Purification of paired helical filament tau and normal tau from human brain tissue. Methods Enzymol 309:81–89
Lippa CF, Fujiwara H, Mann DM, Giasson B, Baba M, Schmidt ML, Nee LE, O’Connell B, Pollen DA, St George-Hyslop P, Ghetti B, Nochlin D, Bird TD, Cairns NJ, Lee VM, Iwatsubo T, Trojanowski JQ (1998) Lewy bodies contain altered alpha-synuclein in brains of many familial Alzheimer’s disease patients with mutations in presenilin and amyloid precursor protein genes. Am J Pathol 153(5):1365–1370
Lippa CF, Rosso AL, Stutzbach LD, Neumann M, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2009) Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 burden in familial Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Arch Neurol 66(12):1483–1488
Lippa CF, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1999) Antibodies to alpha-synuclein detect Lewy bodies in many Down’s syndrome brains with Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 45(3):353–357
Liu L, Drouet V, Wu JW, Witter MP, Small SA, Clelland C, Duff K (2012) Trans-synaptic spread of tau pathology in vivo. PLoS One 7(2):1
Ma QL, Zuo X, Yang F, Ubeda OJ, Gant DJ, Alaverdyan M, Kiosea NC, Nazari S, Chen PP, Nothias F, Chan P, Teng E, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2014) Loss of MAP function leads to hippocampal synapse loss and deficits in the Morris Water Maze with aging. J Neurosci 34(21):7124–7136
Martin L, Latypova X, Terro F (2011) Post-translational modifications of tau protein: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 58(4):458–471
Min SW, Cho SH, Zhou Y, Schroeder S, Haroutunian V, Seeley WW, Huang EJ, Shen Y, Masliah E, Mukherjee C, Meyers D, Cole PA, Ott M, Gan L (2010) Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy. Neuron 67(6):953–966
Mott RT, Dickson DW, Trojanowski JQ, Zhukareva V, Lee VM, Forman M, Van Deerlin V, Ervin JF, Wang DS, Schmechel DE, Hulette CM (2005) Neuropathologic, biochemical, and molecular characterization of the frontotemporal dementias. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64(5):420–428
Neumann M, Kwong LK, Lee EB, Kremmer E, Flatley A, Xu Y, Forman MS, Troost D, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2009) Phosphorylation of S409/410 of TDP-43 is a consistent feature in all sporadic and familial forms of TDP-43 proteinopathies. Acta Neuropathol 117(2):137–149
Otvos L Jr, Feiner L, Lang E, Szendrei GI, Goedert M, Lee VM (1994) Monoclonal antibody PHF-1 recognizes tau protein phosphorylated at serine residues 396 and 404. J Neurosci Res 39(6):669–673
Peeraer E, Bottelbergs A, Van Kolen K, Mahieu M, Duytschaever H, Verdonck L, Torremans A, Andries L, Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Dewachter I, Kemp JA, Moechars D (2014) Intracerebral injection of tau aggregates initiates widespread tauopathy and neuronal loss in transgenic mouse brain. Neurobiol Dis 73C:83–95
Petkova AT, Leapman RD, Guo Z, Yau WM, Mattson MP, Tycko R (2005) Self-propagating, molecular-level polymorphism in Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid fibrils. Science 307(5707):262–265
Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E, Nemens E, Garruto RM, Anderson L, Andreadis A, Wiederholt WC, Raskind M, Schellenberg GD (1998) Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 43(6):815–825
Sanders DW, Kaufman SK, DeVos SL, Sharma AM, Mirbaha H, Li A, Barker SJ, Foley AC, Thorpe JR, Serpell LC, Miller TM, Grinberg LT, Seeley WW, Diamond MI (2014) Distinct tau prion strains propagate in cells and mice and define different tauopathies. Neuron 82(6):1271–1288
Schmidt ML, Schuck T, Sheridan S, Kung MP, Kung H, Zhuang ZP, Bergeron C, Lamarche JS, Skovronsky D, Giasson BI, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2001) The fluorescent Congo red derivative, (trans, trans)-1-bromo-2,5-bis-(3-hydroxycarbonyl-4-hydroxy)styrylbenzene (BSB), labels diverse beta-pleated sheet structures in postmortem human neurodegenerative disease brains. Am J Pathol 159(3):937–943
Spillantini MG, Goedert M (2013) Tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 12(6):609–622
Spillantini MG, Van Swieten JC, Goedert M (2000) Tau gene mutations in frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17). Neurogenetics 2(4):193–205
Stohr J, Condello C, Watts JC, Bloch L, Oehler A, Nick M, DeArmond SJ, Giles K, DeGrado WF, Prusiner SB (2014) Distinct synthetic Abeta prion strains producing different amyloid deposits in bigenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:10329–10334
Stohr J, Watts JC, Mensinger ZL, Oehler A, Grillo SK, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB, Giles K (2012) Purified and synthetic Alzheimer’s amyloid beta (Abeta) prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(27):11025–11030. doi:10.1073/pnas.1206555109
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2008) Specificity and regulation of casein kinase-mediated phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67(5):402–416
Yoshiyama Y, Higuchi M, Zhang B, Huang SM, Iwata N, Saido TC, Maeda J, Suhara T, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2007) Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron 53(3):337–351
Yoshiyama Y, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2013) Therapeutic strategies for tau mediated neurodegeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84(7):784–795
Zhukareva V, Joyce S, Schuck T, Van Deerlin V, Hurtig H, Albin R, Gilman S, Chin S, Miller B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Unexpected abundance of pathological tau in progressive supranuclear palsy white matter. Ann Neurol 60(3):335–345
Zhukareva V, Mann D, Pickering-Brown S, Uryu K, Shuck T, Shah K, Grossman M, Miller BL, Hulette CM, Feinstein SC, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) Sporadic Pick’s disease: a tauopathy characterized by a spectrum of pathological tau isoforms in gray and white matter. Ann Neurol 51(6):730–739
Zhukareva V, Shah K, Uryu K, Braak H, Del Tredici K, Sundarraj S, Clark C, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) Biochemical analysis of tau proteins in argyrophilic grain disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and Pick’s disease: a comparative study. Am J Pathol 161(4):1135–1141
Acknowledgments
Susana Boluda was supported by Bolsa de Ampliación de Estudios (BA11/00021) from the Spanish government, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Madrid, Spain. This work was supported by the CurePSP Foundation, NIH grant AG17586, the Marian S. Ware Alzheimer Program, the Karen Cohen Segal, the Eleanor Margaret Kurtz Endowed Fund, the Mary Rasmus Endowed Fund for Alzheimer’s Research, Mrs. Gloria J. Miller and Arthur Peck, M.D. We thank Theresa Schuck, John Robinson and Jennifer McBride for their technical assistance in immunohistochemistry, Linda Kwong for her technical assistance in biochemistry procedures and reading of this manuscript, Sue Leight for her technical assistance in mouse manipulation, Magdalena Nitla for her technical assistance in mouse injections and Young Baek and Rui Tong for data management.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boluda, S., Iba, M., Zhang, B. et al. Differential induction and spread of tau pathology in young PS19 tau transgenic mice following intracerebral injections of pathological tau from Alzheimer’s disease or corticobasal degeneration brains. Acta Neuropathol 129, 221–237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1373-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1373-0