Abstract
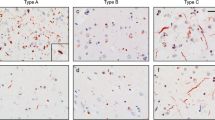
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 inclusions (FTLD-TDP) can typically be categorized into one of four distinct histopathologic patterns of TDP-43 pathology, types A to D. The strength of this histopathologic classification lies in the association between FTLD-TDP subtypes and various clinical and genetic features of disease. Seven cases of FTLD-TDP were identified here which were difficult to classify based on existing pathologic criteria. Distinct features common to these cases included TDP-43 aggregates over a wide neuroanatomic distribution comprised of granulofilamentous neuronal inclusions, abundant grains, and oligodendroglial inclusions. TDP-43 aggregates were phosphorylated and associated with loss of normal nuclear TDP-43 protein (nuclear clearance) but were negative for ubiquitin. Biochemical analysis confirmed the presence of insoluble and phosphorylated TDP-43 and also revealed a distinct pattern of TDP-43 C-terminal fragments relative to other FTLD-TDP subtypes. Finally, these cases were uniformly associated with a very rapid clinical course culminating in death within ~3 years of disease onset. We suggest that these cases may represent a unique clinicopathologic subtype of FTLD-TDP which we provisionally call “type E.” The immature appearance of TDP-43 aggregates, widespread distribution, uniform biochemical profile and rapid clinical course highlights the clinical and pathologic variability within FTLD-TDP, and raises the possibility that type E neuropathology is the sequelae of a particularly virulent strain of TDP-43 proteinopathy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brettschneider J, Arai K, Del Tredici K, Toledo JB, Robinson JL, Lee EB, Kuwabara S, Shibuya K, Irwin DJ, Fang L et al (2014) TDP-43 pathology and neuronal loss in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. Acta Neuropathol 128:423–437. doi:10.1007/s00401-014-1299-6
Brettschneider J, Del Tredici K, Irwin DJ, Grossman M, Robinson JL, Toledo JB, Lee EB, Fang L, Van Deerlin VM, Ludolph AC et al (2014) Sequential distribution of pTDP-43 pathology in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD). Acta Neuropathol 127:423–439. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1238-y
Brettschneider J, Del Tredici K, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2015) Spreading of pathology in neurodegenerative diseases: a focus on human studies. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:109–120. doi:10.1038/nrn3887
Brettschneider J, Del Tredici K, Toledo JB, Robinson JL, Irwin DJ, Grossman M, Suh E, Van Deerlin VM, Wood EM, Baek Y et al (2013) Stages of pTDP-43 pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 74:20–38. doi:10.1002/ana.23937
Cairns NJ, Bigio EH, Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Lee VM, Hatanpaa KJ, White CL 3rd, Schneider JA, Grinberg LT, Halliday G et al (2007) Neuropathologic diagnostic and nosologic criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus of the consortium for frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 114:5–22. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0237-2
Cairns NJ, Neumann M, Bigio EH, Holm IE, Troost D, Hatanpaa KJ, Foong C, White CL 3rd, Schneider JA, Kretzschmar HA et al (2007) TDP-43 in familial and sporadic frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin inclusions. Am J Pathol 171:227–240. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.070182
Davidson Y, Kelley T, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown S, Du Plessis D, Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2007) Ubiquitinated pathological lesions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration contain the TAR DNA-binding protein, TDP-43. Acta Neuropathol 113:521–533. doi:10.1007/s00401-006-0189-y
Dickson DW, Wertkin A, Kress Y, Ksiezak-Reding H, Yen SH (1990) Ubiquitin immunoreactive structures in normal human brains. Distribution and developmental aspects. Lab Invest 63:87–99
Forman MS, Mackenzie IR, Cairns NJ, Swanson E, Boyer PJ, Drachman DA, Jhaveri BS, Karlawish JH, Pestronk A, Smith TW et al (2006) Novel ubiquitin neuropathology in frontotemporal dementia with valosin-containing protein gene mutations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:571–581
Geser F, Martinez-Lage M, Robinson J, Uryu K, Neumann M, Brandmeir NJ, Xie SX, Kwong LK, Elman L, McCluskey L et al (2009) Clinical and pathological continuum of multisystem TDP-43 proteinopathies. Arch Neurol 66:180–189. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2008.558
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Quinn SM, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) Neuronal alpha-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neuron 34:521–533
Gilman S, Wenning GK, Low PA, Brooks DJ, Mathias CJ, Trojanowski JQ, Wood NW, Colosimo C, Durr A, Fowler CJ et al (2008) Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 71:670–676. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000324625.00404.15
Goldman JS, Farmer JM, Wood EM, Johnson JK, Boxer A, Neuhaus J, Lomen-Hoerth C, Wilhelmsen KC, Lee VM, Grossman M et al (2005) Comparison of family histories in FTLD subtypes and related tauopathies. Neurology 65:1817–1819. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000187068.92184.63
Guo JL, Lee VM (2014) Cell-to-cell transmission of pathogenic proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Med 20:130–138. doi:10.1038/nm.3457
Hiji M, Takahashi T, Fukuba H, Yamashita H, Kohriyama T, Matsumoto M (2008) White matter lesions in the brain with frontotemporal lobar degeneration with motor neuron disease: TDP-43-immunopositive inclusions co-localize with p62, but not ubiquitin. Acta Neuropathol 116:183–191. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0402-2
Irwin DJ, Cairns NJ, Grossman M, McMillan CT, Lee EB, Van Deerlin VM, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2015) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: defining phenotypic diversity through personalized medicine. Acta Neuropathol 129:469–491. doi:10.1007/s00401-014-1380-1
Josephs KA, Stroh A, Dugger B, Dickson DW (2009) Evaluation of subcortical pathology and clinical correlations in FTLD-U subtypes. Acta Neuropathol 118:349–358. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0547-7
Kwong LK, Irwin DJ, Walker AK, Xu Y, Riddle DM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2014) Novel monoclonal antibodies to normal and pathologically altered human TDP-43 proteins. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:33. doi:10.1186/2051-5960-2-33
Lee EB, Leng LZ, Zhang B, Kwong L, Trojanowski JQ, Abel T, Lee VM (2006) Targeting amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) oligomers by passive immunization with a conformation-selective monoclonal antibody improves learning and memory in Abeta precursor protein (APP) transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 281:4292–4299. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511018200
Lee EB, Skovronsky DM, Abtahian F, Doms RW, Lee VM (2003) Secretion and intracellular generation of truncated Abeta in beta-site amyloid-beta precursor protein-cleaving enzyme expressing human neurons. J Biol Chem 278:4458–4466. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210105200
Mackenzie IR, Baborie A, Pickering-Brown S, Du Plessis D, Jaros E, Perry RH, Neary D, Snowden JS, Mann DM (2006) Heterogeneity of ubiquitin pathology in frontotemporal lobar degeneration: classification and relation to clinical phenotype. Acta Neuropathol 112:539–549. doi:10.1007/s00401-006-0138-9
Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Baborie A, Sampathu DM, Du Plessis D, Jaros E, Perry RH, Trojanowski JQ, Mann DM, Lee VM (2011) A harmonized classification system for FTLD-TDP pathology. Acta Neuropathol 122:111–113. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0845-8
Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Alafuzoff I, Kril J, Kovacs GG, Ghetti B, Halliday G, Holm IE et al (2009) Nomenclature for neuropathologic subtypes of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus recommendations. Acta Neuropathol 117:15–18. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0460-5
McKhann GM, Albert MS, Grossman M, Miller B, Dickson D, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Clinical and pathological diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia: report of the Work Group on Frontotemporal Dementia and Pick’s Disease. Arch Neurol 58:1803–1809
Murray ME, DeJesus-Hernandez M, Rutherford NJ, Baker M, Duara R, Graff-Radford NR, Wszolek ZK, Ferman TJ, Josephs KA, Boylan KB et al (2011) Clinical and neuropathologic heterogeneity of c9FTD/ALS associated with hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72. Acta Neuropathol 122:673–690. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0907-y
Neumann M, Kwong LK, Lee EB, Kremmer E, Flatley A, Xu Y, Forman MS, Troost D, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ et al (2009) Phosphorylation of S409/410 of TDP-43 is a consistent feature in all sporadic and familial forms of TDP-43 proteinopathies. Acta Neuropathol 117:137–149. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0477-9
Neumann M, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Vanmassenhove B, Kretzschmar HA, Van Deerlin VM, Clark CM, Grossman M, Miller BL, Trojanowski JQ et al (2007) TDP-43-positive white matter pathology in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:177–183. doi:10.1097/01.jnen.0000248554.45456.58
Neumann M, Mackenzie IR, Cairns NJ, Boyer PJ, Markesbery WR, Smith CD, Taylor JP, Kretzschmar HA, Kimonis VE, Forman MS (2007) TDP-43 in the ubiquitin pathology of frontotemporal dementia with VCP gene mutations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:152–157. doi:10.1097/nen.0b013e31803020b9
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM et al (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133. doi:10.1126/science.1134108
Rohrer JD, Guerreiro R, Vandrovcova J, Uphill J, Reiman D, Beck J, Isaacs AM, Authier A, Ferrari R, Fox NC et al (2009) The heritability and genetics of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurology 73:1451–1456. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bf997a
Sampathu DM, Neumann M, Kwong LK, Chou TT, Micsenyi M, Truax A, Bruce J, Grossman M, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Pathological heterogeneity of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions delineated by ubiquitin immunohistochemistry and novel monoclonal antibodies. Am J Pathol 169:1343–1352. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.060438
Suh E, Lee EB, Neal D, Wood EM, Toledo JB, Rennert L, Irwin DJ, McMillan CT, Krock B, Elman LB et al (2015) Semi-automated quantification of C9orf72 expansion size reveals inverse correlation between hexanucleotide repeat number and disease duration in frontotemporal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 130:363–372. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1445-9
Toledo JB, Van Deerlin VM, Lee EB, Suh E, Baek Y, Robinson JL, Xie SX, McBride J, Wood EM, Schuck T et al (2014) A platform for discovery: the University of Pennsylvania Integrated Neurodegenerative Disease Biobank. Alzheimers Dement 10(477–484):e471. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2013.06.003
Trojanowski JQ, Revesz T (2007) Proposed neuropathological criteria for the post mortem diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 33:615–620. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2007.00907.x
Tsuji H, Nonaka T, Yamashita M, Masuda-Suzukake M, Kametani F, Akiyama H, Mann DM, Tamaoka A, Hasegawa M (2012) Epitope mapping of antibodies against TDP-43 and detection of protease-resistant fragments of pathological TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 417:116–121. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.066
Urwin H, Josephs KA, Rohrer JD, Mackenzie IR, Neumann M, Authier A, Seelaar H, Van Swieten JC, Brown JM, Johannsen P et al (2010) FUS pathology defines the majority of tau- and TDP-43-negative frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 120:33–41. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0698-6
Wood EM, Falcone D, Suh E, Irwin DJ, Chen-Plotkin AS, Lee EB, Xie SX, Van Deerlin VM, Grossman M (2013) Development and validation of pedigree classification criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration. JAMA Neurol 70:1411–1417. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.3956
Acknowledgements
EBL is supported by a Clinical Scientist Development Award from the Doris Duke Chartiable Foundation, and by the National Institutes of Health (R01NS095793 and R21NS097749). Additional support for this study includes National Institutes of Health Grants P30AG10124 and P01AG017586. We thank Maia A. Yoshida for her scientific illustration, and our patients and their families who made this research possible. We thank Manuela Neumann and Elisabeth Kremmer for providing the phosphorylation-specific TDP-43 antibody 1D3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, E.B., Porta, S., Michael Baer, G. et al. Expansion of the classification of FTLD-TDP: distinct pathology associated with rapidly progressive frontotemporal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 134, 65–78 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1679-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1679-9