Abstract
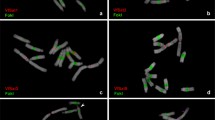
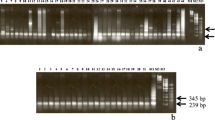
Satellite sequences of the VicTR-B family are specific for the genus Vicia (Leguminosae), but their abundance varies among the species, being the highest in Vicia sativa and Vicia grandiflora. In this study, we have sequenced multiple randomly cloned VicTR-B fragments from these two species and analyzed their sequence variability, periodicity, and chromosomal localization. We have found that V. sativa VicTR-B sequences are homogeneous with respect to their nucleotide sequences and periodicity (monomers of 38 bp), whereas V. grandiflora repeats are considerably more variable, occurring in at least four distinct sequence subfamilies. Although the periodicity of 38 bp was conserved in most of the V. grandiflora sequences, one of the subfamilies was composed of higher-order repeats of 186 bp, which originated from a pentamer of the basic repeated unit. Individual VicTR-B subfamilies were preferentially located in either intercalary or subtelomeric regions of chromosomes. Interestingly, two V. grandiflora subfamilies with the highest similarity to V. sativa VicTR-B sequences were located in intercalary heterochromatic bands, showing similar chromosomal distribution as the majority of VicTR-B repeats in V. sativa. The other two V. grandiflora subfamilies showing a considerable divergence from V. sativa sequences were found to be accumulated at subtelomeric regions of V. grandiflora chromosomes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkhimova OG, Mazurok NA, Potapova TA, Zakian SM, Heslop-Harrison JS, Vershinin AV (2004) Diverse patterns of the tandem repeats organization in rye chromosomes. Chromosoma 113:42–52
Baranczewski P, Nehls P, Rieger R, Pich U, Rajewsky MF, Schubert I (1997) Formation and repair of O6-methylguanine in recombination hot spots of plant chromosomes. Environ Mol Mutagen 29:394–399
Charlesworth B, Sniegowski P, Stephan W (1994) The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 371:215–220
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14:1188–1190
Dechyeva D, Gindullis F, Schmidt T (2003) Divergence of satellite DNA and interspersion of dispersed repeats in the genome of the wild beet Beta procumbens. Chromosome Res 11:3–21
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Dover G (1982) Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299:111–116
Dover G (2002) Molecular drive. Trends Genet 18:587–589
Elder JFE, Turner BJ (1995) Concerted evolution of repetitive DNA sequences in eukaryotes. Q Rev Biol 70:297–320
Gazdová B, Široký J, Fajkus J, Brzobohatý B, Kenton A, Parokonny A, Heslop-Harrison JS, Palme K, Bezděk M (1995) Characterization of a new family of tobacco highly repetitive DNA, GRS, specific for the Nicotiana tomentosiformis genomic component. Chromosome Res 3:245–254
Grebenstein B, Grebenstein O, Sauer W, Hemleben V (1996) Distribution and complex organization of satellite DNA sequences in Aveneae species. Genome 39:1045–1050
Hall SE, Luo S, Hall AE, Preuss D (2005) Differential rates of local and global homogenization in centromere satellites from Arabidopsis relatives. Genetics 170:1913–1927
Herzel H, Weiss O, Trifonov EN (1999) 10–11 bp periodicities in complete genomes reflect protein structure and DNA folding. Bioinformatics 15:187–193
Heslop-Harrison JS, Murata M, Ogura Y, Schwarzacher T, Motoyoshi F (1999) Polymorphisms and genomic organization of repetitive DNA from centromeric regions of Arabidopsis chromosomes. Plant Cell 11:31–42
King K, Jobst J, Hemleben V (1995) Differential homogenization and amplification of two satellite DNAs in the genus Cucurbita (Cucurbitaceae). J Mol Evol 41:996–1005
Kubis S, Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1998) Repetitive DNA elements as a major component of plant genomes. Ann Bot 82:45–55
Langdon T, Seago C, Jones RN, Ougham H, Thomas H, Forster JW, Jenkins G (2000) De novo evolution of satellite DNA on rye B chromosome. Genetics 154:869–884
Lim KY, Skalická K, Koukalová B, Volkov RA, Matyášek R, Hemleben V, Leitch AR, Kovařík A (2004) Dynamic changes in the distribution of a satellite homologous to intergenic 26-18S rDNA spacer in the evolution of Nicotiana. Genetics 166:1935–1946
Linardopoulou EV, Williams EM, Fan Y, Friedman C, Young JM, Trask BJ (2005) Human subtelomeres are hot spots of interchromosomal recombination and segmental duplication. Nature 437:94–100
Macas J, Požárková D, Navrátilová A, Nouzová M, Neumann P (2000) Two new families of tandem repeats isolated from genus Vicia using genomic self-priming PCR. Mol Gen Genet 263:741–751
Macas J, Mészáros T, Nouzová M (2002) PlantSat: a specialized database for plant satellite repeats. Bioinformatics 18:28–35
Macas J, Navrátilová A, Mészáros T (2003) Sequence subfamilies of satellite repeats related to rDNA intergenic spacer are differentially amplified on Vicia sativa chromosomes. Chromosoma 112:152–158
Matyášek R, Gazdová B, Fajkus J, Bezděk M (1997) NTRS, a new family of highly repetitive DNA specific for the T1 chromosome of tobacco. Chromosoma 106:369–379
Meyne J, Goodwin EH (1995) Direction of DNA sequences within chromatids determined using strand-specific FISH. Chromosome Res 3:375–378
Morgante M, Jurman I, Shi L, Zhu T, Keim P, Rafalski JA (1997) The STR120 satellite DNA of soybean: organization, evolution and chromosomal specificity. Chromosome Res 5:363–373
Navrátilová A, Neumann P, Macas J (2003) Karyotype analysis of four Vicia species using in situ hybridization with repetitive sequences. Ann Bot 91:921–926
Navrátilová A, Neumann P, Macas J (2005) Long-range organization of plant satellite repeats investigated using strand-specific FISH. Cytogenet Genome Res 109:58–62
Nouzová M, Kubaláková M, Doleželová M, Koblížková A, Neumann P, Doleel J, Macas J (1999) Cloning and characterization of new repetitive sequences in field bean (Vicia faba L.). Ann Bot 83:535–541
Pedrosa A, Jantsch MF, Moscone EA, Ambros PF, Schweizer D (2001) Characterization of pericentromeric and sticky intercalary heterochromatin in Ornithogalum longibracteatum (Hyacinthaceae). Chromosoma 110:203–213
Sanger F, Nicklen D, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:5463–5467
Schindelhauer D, Schwarz T (2002) Evidence for a fast, intrachromosomal conversion mechanism from mapping of nucleotide variants within a homogeneous α-satellite DNA array. Genome Res 12:1815–1826
Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1998) Genomes, genes and junk: the large-scale organization of plant chromosomes. Trends Plant Sci 3:195–199
Schneider TD, Stephens RM (1990) Sequence Logos: a new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6097–6100
Schubert I, Rieger R, Fuchs J, Pich U (1994) Sequence organization and the mechanism of interstitial deletion clustering in a plant genome (Vicia faba). Mutation Res 325:1–5
Shibata F, Hizume M, Kuroki Y (2000) Molecular cytogenetic analysis of supernumerary heterochromatic segments in Rumex acetosa. Genome 43:391–397
Skalická K, Lim KY, Matyášek R, Matzke M, Leitch AR, Kovařík A (2005) Preferential elimination of repeated DNA sequences from the parental, Nicotiana tomentosiformis genome donor of a synthetic, allotetraploid tobacco. New Phytol 166:291–303
Staden R (1996) The Staden sequence analysis package. Mol Biotechnol 5:233–241
Stephan W (1989) Tandem-repetitive noncoding DNA: forms and forces. Mol Biol Evol 6:198–212
Stephan W, Cho S (1994) Possible role of natural selection in the formation of tandem-repetitive noncoding DNA. Genetics 136:333–341
Tek A, Song J, Macas J, Jiang J (2005) Sobo, a recently amplified satellite repeat of potato, and its implications for the origin of tandemly repeated sequences. Genetics 170:1231–1238
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Ugarkovic D, Plohl M (2002) Variation in satellite DNA profiles—causes and effects. EMBO J 21:5955–5959
Vershinin AV, Heslop-Harrison JS (1998) Comparative analysis of the nucleosomal structure of rye, wheat and their relatives. Plant Mol Biol 36:149–161
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. J. Látalová and Ms. H. Štěpančíková for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by grants GA204/04/1207 from the Czech Science Foundation and AVOZ50510513 from the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic. The experiments were carried out in compliance with the current laws governing genetic experimentation in the Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by I. Schubert
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macas, J., Navrátilová, A. & Koblížková, A. Sequence homogenization and chromosomal localization of VicTR-B satellites differ between closely related Vicia species. Chromosoma 115, 437–447 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-006-0070-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-006-0070-8