Abstract
Incenp is an essential mitotic protein that, together with Aurora B, Survivin, and Borealin, forms the core of the chromosomal passenger protein complex (CPC). The CPC regulates various mitotic processes and functions to maintain genomic stability. The proper subcellular localization of the CPC and its full catalytic activity require the presence of each core subunit in the complex. We have investigated the mitotic tasks of the CPC using a function blocking antibody against Incenp microinjected into cells at different mitotic phases. This method allowed temporal analysis of CPC functions without perturbation of complex assembly or activity prior to injection. We have also studied the dynamic properties of Incenp and Aurora B using fusion protein photobleaching. We found that in early mitotic cells, Incenp and Aurora B exhibit dynamic turnover at centromeres, which is prevented by the anti-Incenp antibody. In these cells, the loss of centromeric CPC turnover is accompanied by forced mitotic exit without the execution of cytokinesis. Introduction of anti-Incenp antibody into early anaphase cells causes abnormalities in sister chromatid separation through defects in anaphase spindle functions. In summary, our data uncovers new mitotic roles for the CPC in anaphase and proposes that CPC turnover at centromeres modulates spindle assembly checkpoint signaling.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RR, Wheatley SP, Gouldsworthy AM, Kandels-Lewis SE, Carmena M, Smythe C, Gerloff DL, Earnshaw WC (2000) INCENP binds the Aurora-related kinase AIRK2 and is required to target it to chromosomes, the central spindle and cleavage furrow. Curr Biol 10:1075–1078
Adams RR, Maiato H, Earnshaw WC, Carmena M (2001) Essential roles of Drosophila inner centromere protein (INCENP) and aurora B in histone H3 phosphorylation, metaphase chromosome alignment, kinetochore disjunction, and chromosome segregation. J Cell Biol 153:865–880
Beardmore VA, Ahonen LJ, Gorbsky GJ, Kallio MJ (2004) Survivin dynamics increases at centromeres during G2/M phase transition and is regulated by microtubule-attachment and Aurora B kinase activity. J Cell Sci 117:4033–4042
Bishop JD, Schumacher JM (2002) Phosphorylation of the carboxyl terminus of inner centromere protein (INCENP) by the Aurora B Kinase stimulates Aurora B kinase activity. J Biol Chem 277:27577–27580
Bolton MA, Lan W, Powers SE, McCleland ML, Kuang J, Stukenberg PT (2002) Aurora B kinase exists in a complex with survivin and INCENP and its kinase activity is stimulated by survivin binding and phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 13:3064–3077
Brust-Mascher I, Civelekoglu-Scholey G, Kwon M, Mogilner A, Scholey JM (2004) Model for anaphase B: role of three mitotic motors in a switch from poleward flux to spindle elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15938–15943
Carvalho A, Carmena M, Sambade C, Earnshaw WC, Wheatley SP (2003) Survivin is required for stable checkpoint activation in taxol-treated HeLa cells. J Cell Sci 116:2987–2998
Cimini D, Wan X, Hirel CB, Salmon ED (2006) Aurora kinase promotes turnover of kinetochore microtubules to reduce chromosome segregation errors. Curr Biol 16:1711–1718
Cooke CA, Heck MM, Earnshaw WC (1987) The inner centromere protein (INCENP) antigens: movement from inner centromere to midbody during mitosis. J Cell Biol 105:2053–2067
Delacour-Larose M, Molla A, Skoufias DA, Margolis RL, Dimitrov S (2004) Distinct dynamics of Aurora B and Survivin during mitosis. Cell Cycle 3:1418–1426
Delacour-Larose M, Thi MN, Dimitrov S, Molla A (2007) Role of survivin phosphorylation by aurora B in mitosis. Cell Cycle 6:1878–1885
DeLuca JG, Gall WE, Ciferri C, Cimini D, Musacchio A, Salmon ED (2006) Kinetochore microtubule dynamics and attachment stability are regulated by Hec1. Cell 127:969–982
Ditchfield C, Johnson VL, Tighe A, Ellston R, Haworth C, Johnson T, Mortlock A, Keen N, Taylor SS (2003) Aurora B couples chromosome alignment with anaphase by targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to kinetochores. J Cell Biol 161:267–280
Gadea BB, Ruderman JV (2005) Aurora kinase inhibitor ZM447439 blocks chromosome-induced spindle assembly, the completion of chromosome condensation, and the establishment of the spindle integrity checkpoint in Xenopus egg extracts. Mol Biol Cell 16:1305–1318
Giet R, Glover DM (2001) Drosophila aurora B kinase is required for histone H3 phosphorylation and condensin recruitment during chromosome condensation and to organize the central spindle during cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 152:669–682
Girdler F, Gascoigne KE, Eyers PA, Hartmuth S, Crafter C, Foote KM, Keen NJ, Taylor SS (2006) Validating Aurora B as an anti-cancer drug target. J Cell Sci 119:3664–3675
Gorbsky GJ (2001) The mitotic spindle checkpoint. Curr Biol 11:R1001–1004
Guse A, Mishima M, Glotzer M (2005) Phosphorylation of ZEN-4/MKLP1 by aurora B regulates completion of cytokinesis. Curr Biol 15:778–786
Harrington EA, Bebbington D, Moore J, Rasmussen RK, Ajose-Adeogun AO, Nakayama T, Graham JA, Demur C, Hercend T, Diu-Hercend A, Su M, Golec JM, Miller KM (2004) VX-680, a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of the Aurora kinases, suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Nat Med 10:262–267
Hauf S, Cole RW, LaTerra S, Zimmer C, Schnapp G, Walter R, Heckel A, van Meel J, Rieder CL, Peters JM (2003) The small molecule Hesperadin reveals a role for Aurora B in correcting kinetochore–microtubule attachment and in maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol 161:281–294
Honda R, Korner R, Nigg EA (2003) Exploring the functional interactions between Aurora B, INCENP, and survivin in mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 14:3325–3341
Howell BJ, Moree B, Farrar EM, Stewart S, Fang G, Salmon ED (2004) Spindle checkpoint protein dynamics at kinetochores in living cells. Curr Biol 14:953–964
Jeyaprakash AA, Klein UR, Lindner D, Ebert J, Nigg EA, Conti E (2007) Structure of a Survivin-Borealin-INCENP core complex reveals how chromosomal passengers travel together. Cell 131:271–285
Kagey MH, Melhuish TA, Wotton D (2003) The polycomb protein Pc2 is a SUMO E3. Cell 113:127–137
Kaitna S, Mendoza M, Jantsch-Plunger V, Glotzer M (2000) Incenp and an aurora-like kinase form a complex essential for chromosome segregation and efficient completion of cytokinesis. Curr Biol 10:1172–1181
Kallio MJ, Beardmore VA, Weinstein J, Gorbsky GJ (2002a) Rapid microtubule-independent dynamics of Cdc20 at kinetochores and centrosomes in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 158:841–847
Kallio MJ, McCleland ML, Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ (2002b) Inhibition of aurora B kinase blocks chromosome segregation, overrides the spindle checkpoint, and perturbs microtubule dynamics in mitosis. Curr Biol 12:900–905
Katayama H, Brinkley WR, Sen S (2003) The Aurora kinases: role in cell transformation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:451–464
Klein UR, Nigg EA, Gruneberg U (2006) Centromere targeting of the chromosomal passenger complex requires a ternary subcomplex of borealin, survivin, and the N-terminal domain of INCENP. Mol Biol Cell 17:2547–2558
Kwon M, Scholey JM (2004) Spindle mechanics and dynamics during mitosis in Drosophila. Trends Cell Biol 14:194–205
Kwon M, Morales-Mulia S, Brust-Mascher I, Rogers GC, Sharp DJ, Scholey JM (2004) The chromokinesin, KLP3A, dives mitotic spindle pole separation during prometaphase and anaphase and facilitates chromatid motility. Mol Biol Cell 15:219–233
Lan W, Zhang X, Kline-Smith SL, Rosasco SE, Barrett-Wilt GA, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Walczak CE, Stukenberg PT (2004) Aurora B phosphorylates centromeric MCAK and regulates its localization and microtubule depolymerization activity. Curr Biol 14:273–286
Lens SM, Wolthuis RM, Klompmaker R, Kauw J, Agami R, Brummelkamp T, Kops G, Medema RH (2003) Survivin is required for a sustained spindle checkpoint arrest in response to lack of tension. Embo J 22:2934–2947
Mackay AM, Ainsztein AM, Eckley DM, Earnshaw WC (1998) A dominant mutant of inner centromere protein (INCENP), a chromosomal protein, disrupts prometaphase congression and cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 140:991–1002
Miyauchi K, Zhu X, Foong C, Hosoya H, Murata-Hori M (2007) Aurora B kinase activity is required to prevent polar cortical ingression during cytokinesis. Cell Cycle 6:2549–2553
Murata-Hori M, Wang YL (2002) Both midzone and astral microtubules are involved in the delivery of cytokinesis signals: insights from the mobility of aurora B. J Cell Biol 159:45–53
Murata-Hori M, Tatsuka M, Wang YL (2002) Probing the dynamics and functions of aurora B kinase in living cells during mitosis and cytokinesis. Mol Biol Cell 13:1099–1108
Musacchio A, Salmon ED (2007) The spindle-assembly checkpoint in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:379–393
Pinsky BA, Kung C, Shokat KM, Biggins S (2006) The Ipl1-Aurora protein kinase activates the spindle checkpoint by creating unattached kinetochores. Nat Cell Biol 8:78–83
Rosasco-Nitcher SE, Lan W, Khorasanizadeh S, Stukenberg PT (2008) Centromeric Aurora-B activation requires TD-60, microtubules, and substrate priming phosphorylation. Science 319:469–472
Ruchaud S, Carmena M, Earnshaw WC (2007) Chromosomal passengers: conducting cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:798–812
Sessa F, Mapelli M, Ciferri C, Tarricone C, Areces LB, Schneider TR, Stukenberg PT, Musacchio A (2005) Mechanism of Aurora B activation by INCENP and inhibition by hesperadin. Mol Cell 18:379–391
Shah JV, Botvinick E, Bonday Z, Furnari F, Berns M, Cleveland DW (2004) Dynamics of centromere and kinetochore proteins; implications for checkpoint signaling and silencing. Curr Biol 14:942–952
Sharp DJ, Rogers GC (2004) A Kin I-dependent Pacman-flux mechanism for anaphase A. Cell Cycle 3:707–710
Sharp DJ, Brown HM, Kwon M, Rogers GC, Holland G, Scholey JM (2000) Functional coordination of three mitotic motors in Drosophila embryos. Mol Biol Cell 11:241–253
Stukenberg PT, Burke DJ (2004) Analyzing the spindle checkpoint in yeast and frogs. Methods Mol Biol 280:83–98
Wheatley SP, Carvalho A, Vagnarelli P, Earnshaw WC (2001) INCENP is required for proper targeting of Survivin to the centromeres and the anaphase spindle during mitosis. Curr Biol 11:886–890
Yuen KW, Montpetit B, Hieter P (2005) The kinetochore and cancer: what’s the connection? Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:576–582
Zhang X, Lan W, Ems-McClung SC, Stukenberg PT, Walczak CE (2007) Aurora B Phosphorylates Multiple Sites on Mitotic Centromere-associated Kinesin to Spatially and Temporally Regulate Its Function. Mol Biol Cell 18:3264–3276
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants to MJK (Marie Curie EXT 002697, Academy of Finland 8206930), to PTS (R01GM063045-06), and Turku Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences. We thank Erich Nigg and Ulf Klein for sending GFP-hIncenp plasmid, David Wotton for providing pCS2 + YFP, and AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals for providing ZM447439. We thank Jouko Sandholm at the Turku Centre for Biotechnology for his kind help with the photobleaching experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: E. A. Nigg
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
412_2008_178_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
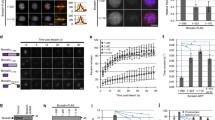
Fig. S1 a Immunofluorescence images of fixed Xeno S3 cells stained with Incenp-ab. The antibody stains inner centromeres from prophase to metaphase, spindle microtubules in anaphase, and the midbody in telophase. When injected into metaphase (b) or anaphase cells (c), the Incenp-ab binds to inner centromeres or midzone microtubules, respectively. Cells were injected, fixed, and stained for tubulin (red in the overlay, one selected focal plane is shown), Incenp-ab (green), and DNA (blue, DAPI). Insets show magnified views of the metaphase plate and the spindle midzone. (d–e) Incenp-ab-injected Xeno S3 cells undergo a forced mitotic exit despite nocodazole or taxol-induced mitotic arrest. f Incenp-ab-injected Xeno S3 cells remain arrested at M phase in the presence of proteasome inhibitor MG312. Scale bars = 10 µm (JPEG 1.73 MB)
412_2008_178_MOESM6_ESM.mov
Video 4 Recovery of photobleached GFP-xIncenp at the centromeres of a Xeno S3 cell in the presence of MG132 (MOV 1.36 MB).
412_2008_178_MOESM7_ESM.mov
Video 5 Recovery of photobleached GFP-xIncenp at the centromeres of a Xeno S3 cell after Incenp-ab injection in the presence of MG132 (MOV 1.30 MB).
412_2008_178_MOESM8_ESM.mov
Video 6 Recovery of photobleached xAurora B-YFP at the centromeres of a Xeno S3 cell in the presence of MG132 (MOV 2.70 MB).
412_2008_178_MOESM9_ESM.mov
Video 7 Recovery of photobleached xAurora B-YFP at the centromeres of a Xeno S3 cell after Incenp-ab injection in the presence of MG132 (MOV 2.08 MB).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahonen, L.J., Kukkonen, A.M., Pouwels, J. et al. Perturbation of Incenp function impedes anaphase chromatid movements and chromosomal passenger protein flux at centromeres. Chromosoma 118, 71–84 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-008-0178-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-008-0178-0