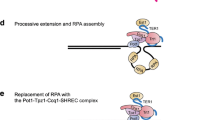
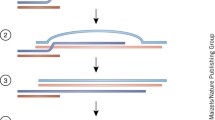
Abstract
Telomeres constitute the ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes. Due to the conventional mode of DNA replication, telomeric DNA erodes at each cell division. To counteract this, a specialized reverse transcriptase, telomerase, can elongate chromosome ends to maintain them at a constant average length. Because of their similarity to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), telomeres might be expected to induce a DNA damage response, which would lead to repair reactions and the generation of translocations or fusions. Many proteins present at telomeres prevent this by protecting (capping) the chromosome termini. Conversely, a DSB occurring in other regions of the genome, due, for instance, to a stalled replication fork or genotoxic agents, must be repaired by homologous recombination or end-joining to ensure genome stability. Interestingly, telomerase is able to generate a telomere de novo at an accidental DSB, with potentially lethal consequences in haploid cells and, at a minimum, loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in diploid cells. Recent data suggest that telomerase is systematically recruited to DSBs but is prevented from acting in the absence of a minimal stretch of flanking telomere-repeat sequences. In this review, we will focus on the mechanisms that regulate telomere addition to DSBs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anbalagan S, Bonetti D, Lucchini G, Longhese MP (2011) Rif1 supports the function of the CST complex in yeast telomere capping. PLoS Genet 7(3):e1002024
Andaluz E, Bellido A, Gomez-Raja J, Selmecki A, Bouchonville K, Calderone R, Berman J, Larriba G (2011) Rad52 function prevents chromosome loss and truncation in Candida albicans. Mol Microbiol 79(6):1462–1482
Arneric M, Lingner J (2007) Tel1 kinase and subtelomere-bound Tbf1 mediate preferential elongation of short telomeres by telomerase in yeast. EMBO Rep 8(11):1080–1085
Artandi SE, DePinho RA (2010) Telomeres and telomerase in cancer. Carcinogenesis 31(1):9–18
Baroin A, Prat A, Caron F (1987) Telomeric site position heterogeneity in macronuclear DNA of Paramecium primaurelia. Nucleic Acids Res 15(4):1717–1728
Beaucher M, Zheng XF, Amariei F, Rong YS (2012) Multiple pathways suppress telomere addition to DNA breaks in the Drosophila germline. Genetics 191(2):407–417
Bianchi A, Negrini S, Shore D (2004) Delivery of yeast telomerase to a DNA break depends on the recruitment functions of Cdc13 and Est1. Mol Cell 16(1):139–146
Bianchi A, Shore D (2007) Increased association of telomerase with short telomeres in yeast. Genes Dev 21(14):1726–1730
Biessmann H, Mason JM, Ferry K, d’Hulst M, Valgeirsdottir K, Traverse KL, Pardue ML (1990) Addition of telomere-associated HeT DNA sequences “heals” broken chromosome ends in Drosophila. Cell 61(4):663–673
Bochman ML, Sabouri N, Zakian VA (2010) Unwinding the functions of the Pif1 family helicases. DNA Repair (Amst) 9(3):237–249
Bonetti D, Clerici M, Anbalagan S, Martina M, Lucchini G, Longhese MP (2010a) Shelterin-like proteins and Yku inhibit nucleolytic processing of Saccharomyces cerevisiae telomeres. PLoS Genet 6(5):e1000966
Bonetti D, Clerici M, Manfrini N, Lucchini G, Longhese MP (2010b) The MRX complex plays multiple functions in resection of Yku- and Rif2-protected DNA ends. PLoS One 5(11):e14142
Bonetti D, Martina M, Clerici M, Lucchini G, Longhese MP (2009) Multiple pathways regulate 3′ overhang generation at S. cerevisiae telomeres. Molecular cell 35(1):70–81
Bottius E, Bakhsis N, Scherf A (1998) Plasmodium falciparum telomerase: de novo telomere addition to telomeric and nontelomeric sequences and role in chromosome healing. Mol Cell Biol 18(2):919–925
Boule JB, Vega LR, Zakian VA (2005) The yeast Pif1p helicase removes telomerase from telomeric DNA. Nature 438(7064):57–61
Boule JB, Zakian VA (2007) The yeast Pif1p DNA helicase preferentially unwinds RNA DNA substrates. Nucleic Acids Res 35(17):5809–5818
Brigati C, Kurtz S, Balderes D, Vidali G, Shore D (1993) An essential yeast gene encoding a TTAGGG repeat-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol 13(2):1306–1314
Cappai R, van Schravendijk MR, Anders RF, Peterson MG, Thomas LM, Cowman AF, Kemp DJ (1989) Expression of the RESA gene in Plasmodium falciparum isolate FCR3 is prevented by a subtelomeric deletion. Mol Cell Biol 9(8):3584–3587
Cesare AJ, Kaul Z, Cohen SB, Napier CE, Pickett HA, Neumann AA, Reddel RR (2009) Spontaneous occurrence of telomeric DNA damage response in the absence of chromosome fusions. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16(12):1244–1251
Chen C, Kolodner RD (1999) Gross chromosomal rearrangements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae replication and recombination defective mutants. Nat Genet 23(1):81–85
Chung WH, Zhu Z, Papusha A, Malkova A, Ira G (2010) Defective resection at DNA double-strand breaks leads to de novo telomere formation and enhances gene targeting. PLoS Genet 6(5):e1000948
Cullen JK, Hussey SP, Walker C, Prudden J, Wee BY, Dave A, Findlay JS, Savory AP, Humphrey TC (2007) Break-induced loss of heterozygosity in fission yeast: dual roles for homologous recombination in promoting translocations and preventing de novo telomere addition. Mol Cell Biol 27(21):7745–7757
Dehe PM, Rog O, Ferreira MG, Greenwood J, Cooper JP (2012) Taz1 enforces cell-cycle regulation of telomere synthesis. Mol Cell 46(6):797–808
Dejardin J, Kingston RE (2009) Purification of proteins associated with specific genomic Loci. Cell 136(1):175–186
Diede SJ, Gottschling DE (1999) Telomerase-mediated telomere addition in vivo requires DNA primase and DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Cell 99(7):723–733
Diede SJ, Gottschling DE (2001) Exonuclease activity is required for sequence addition and Cdc13p loading at a de novo telomere. Curr Biol 11(17):1336–1340
Evans SK, Lundblad V (1999) Est1 and Cdc13 as comediators of telomerase access. Science 286(5437):117–120
Fisher TS, Taggart AKP, Zakian VA (2004) Cell cycle-dependent regulation of yeast telomerase by Ku. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11(12):1198–1205
Flint J, Craddock CF, Villegas A, Bentley DP, Williams HJ, Galanello R, Cao A, Wood WG, Ayyub H, Higgs DR (1994) Healing of broken human chromosomes by the addition of telomeric repeats. Am J Hum Genet 55(3):505–512
Forney JD, Blackburn EH (1988) Developmentally controlled telomere addition in wild-type and mutant paramecia. Mol Cell Biol 8(1):251–258
Frank CJ, Hyde M, Greider CW (2006) Regulation of telomere elongation by the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK1. Mol Cell 24(3):423–432
Fukunaga K, Hirano Y, Sugimoto K (2012) Subtelomere-binding protein Tbf1 and telomere-binding protein Rap1 collaborate to inhibit localization of the Mre11 complex to DNA ends in budding yeast. Mol Biol Cell 23(2):347–359
Gallardo F, Laterreur N, Cusanelli E, Ouenzar F, Querido E, Wellinger RJ, Chartrand P (2011) Live cell imaging of telomerase RNA dynamics reveals cell cycle-dependent clustering of telomerase at elongating telomeres. Mol Cell 44(5):819–827
Gao Q, Reynolds GE, Wilcox A, Miller D, Cheung P, Artandi SE, Murnane JP (2008) Telomerase-dependent and -independent chromosome healing in mouse embryonic stem cells. DNA Repair (Amst) 7(8):1233–1249
Garvik B, Carson M, Hartwell L (1995) Single-stranded DNA arising at telomeres in cdc13 mutants may constitute a specific signal for the RAD9 checkpoint. Mol Cell Biol 15(11):6128–6138
Greider CW, Blackburn EH (1985) Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell 43(2):405–413
Greider CW, Blackburn EH (1987) The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell 51(6):887–898
Greider CW, Blackburn EH (1989) A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature 337(6205):331–337
Hannes F, Van Houdt J, Quarrell OW, Poot M, Hochstenbach R, Fryns JP, Vermeesch JR (2010) Telomere healing following DNA polymerase arrest-induced breakages is likely the main mechanism generating chromosome 4p terminal deletions. Hum Mutat 31(12):1343–1351
Henning KA, Moskowitz N, Ashlock MA, Liu PP (1998) Humanizing the yeast telomerase template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(10):5667–5671
Hirano Y, Fukunaga K, Sugimoto K (2009) Rif1 and rif2 inhibit localization of tel1 to DNA ends. Mol Cell 33(3):312–322
Hirano Y, Sugimoto K (2007) Cdc13 telomere capping decreases Mec1 association but does not affect Tel1 association with DNA ends. Mol Biol Cell 18(6):2026–2036
Honma M, Sakuraba M, Koizumi T, Takashima Y, Sakamoto H, Hayashi M (2007) Non-homologous end-joining for repairing I-SceI-induced DNA double strand breaks in human cells. DNA Repair (Amst) 6(6):781–788
Kaul Z, Cesare AJ, Huschtscha LI, Neumann AA, Reddel RR (2012) Five dysfunctional telomeres predict onset of senescence in human cells. EMBO Rep 13(1):52–59
Kramer KM, Haber JE (1993) New telomeres in yeast are initiated with a highly selected subset of TG1-3 repeats. Genes Dev 7(12A):2345–2356
Kulkarni A, Zschenker O, Reynolds G, Miller D, Murnane JP (2010) Effect of telomere proximity on telomere position effect, chromosome healing, and sensitivity to DNA double-strand breaks in a human tumor cell line. Mol Cell Biol 30(3):578–589
Lahaye A, Stahl H, Thines-Sempoux D, Foury F (1991) PIF1: a DNA helicase in yeast mitochondria. EMBO J 10(4):997–1007
Lamb J, Wilkie AO, Harris PC, Buckle VJ, Lindenbaum RH, Barton NJ, Reeders ST, Weatherall DJ, Higgs DR (1989) Detection of breakpoints in submicroscopic chromosomal translocation, illustrating an important mechanism for genetic disease. Lancet 2(8667):819–824
Latre L, Genesca A, Martin M, Ribas M, Egozcue J, Blasco MA, Tusell L (2004) Repair of DNA broken ends is similar in embryonic fibroblasts with and without telomerase. Radiat Res 162(2):136–142
Lingner J, Cooper JP, Cech TR (1995) Telomerase and DNA end replication: no longer a lagging strand problem? Science 269(5230):1533–1534
Luciano P, Coulon S, Faure V, Corda Y, Bos J, Brill SJ, Gilson E, Simon MN, Geli V (2012) RPA facilitates telomerase activity at chromosome ends in budding and fission yeasts. EMBO J 31(8):2034–2046
Lustig AJ, Petes TD (1986) Identification of yeast mutants with altered telomere structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83(5):1398–1402
Lydeard JR, Lipkin-Moore Z, Jain S, Eapen VV, Haber JE (2010) Sgs1 and exo1 redundantly inhibit break-induced replication and de novo telomere addition at broken chromosome ends. PLoS Genet 6(5):e1000973
Magnenat L, Tobler H, Muller F (1999) Developmentally regulated telomerase activity is correlated with chromosomal healing during chromatin diminution in Ascaris suum. Mol Cell Biol 19(5):3457–3465
Makovets S, Blackburn EH (2009) DNA damage signalling prevents deleterious telomere addition at DNA breaks. Nat Cell Biol 11(11):1383–1386
Mangahas JL, Alexander MK, Sandell LL, Zakian VA (2001) Repair of chromosome ends after telomere loss in Saccharomyces. Mol Biol Cell 12(12):4078–4089
Maringele L, Lydall D (2002) EXO1-dependent single-stranded DNA at telomeres activates subsets of DNA damage and spindle checkpoint pathways in budding yeast yku70Delta mutants. Genes Dev 16(15):1919–1933
Martina M, Clerici M, Baldo V, Bonetti D, Lucchini G, Longhese MP (2012) A balance between Tel1 and Rif2 activities regulates nucleolytic processing and elongation at telomeres. Mol Cell Biol 32(9):1604–1617
McGee JS, Phillips JA, Chan A, Sabourin M, Paeschke K, Zakian VA (2010) Reduced Rif2 and lack of Mec1 target short telomeres for elongation rather than double-strand break repair. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17(12):1438–1445
Melek M, Shippen DE (1996) Chromosome healing: spontaneous and programmed de novo telomere formation by telomerase. BioEssays 18(4):301–308
Michelson RJ, Rosenstein S, Weinert T (2005) A telomeric repeat sequence adjacent to a DNA double-stranded break produces an anticheckpoint. Genes Dev 19(21):2546–2559
Miller KM, Rog O, Cooper JP (2006) Semi-conservative DNA replication through telomeres requires Taz1. Nature 440(7085):824–828
Mimitou EP, Symington LS (2008) Sae2, Exo1 and Sgs1 collaborate in DNA double-strand break processing. Nature 455(7214):770–774
Muller F, Wicky C, Spicher A, Tobler H (1991) New telomere formation after developmentally regulated chromosomal breakage during the process of chromatin diminution in Ascaris lumbricoides. Cell 67(4):815–822
Murnane JP (2012) Telomere dysfunction and chromosome instability. Mutat Res 730(1–2):28–36
Myung K, Chen C, Kolodner RD (2001) Multiple pathways cooperate in the suppression of genome instability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 411(6841):1073–1076
Myung K, Kolodner RD (2003) Induction of genome instability by DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA Repair (Amst) 2(3):243–258
Nakada D, Matsumoto K, Sugimoto K (2003) ATM-related Tel1 associates with double-strand breaks through an Xrs2-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev 17(16):1957–1962
Negrini S, Ribaud V, Bianchi A, Shore D (2007) DNA breaks are masked by multiple Rap1 binding in yeast: implications for telomere capping and telomerase regulation. Genes Dev 21(3):292–302
Nugent CI, Hughes TR, Lue NF, Lundblad V (1996) Cdc13p: a single-strand telomeric DNA-binding protein with a dual role in yeast telomere maintenance. Science 274(5285):249–252
Oza P, Jaspersen SL, Miele A, Dekker J, Peterson CL (2009) Mechanisms that regulate localization of a DNA double-strand break to the nuclear periphery. Genes Dev 23(8):912–927
Pennaneach V, Putnam CD, Kolodner RD (2006) Chromosome healing by de novo telomere addition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 59(5):1357–1368
Pfingsten JS, Goodrich KJ, Taabazuing C, Ouenzar F, Chartrand P, Cech TR (2012) Mutually exclusive binding of telomerase RNA and DNA by Ku alters telomerase recruitment model. Cell 148(5):922–932
Piazza A, Serero A, Boule JB, Legoix-Ne P, Lopes J, Nicolas A (2012) Stimulation of gross chromosomal rearrangements by the human CEB1 and CEB25 minisatellites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends on G-quadruplexes or Cdc13. PLoS Genet 8(11):e1003033
Pologe LG, Ravetch JV (1988) Large deletions result from breakage and healing of P. falciparum chromosomes. Cell 55(5):869–874
Putnam CD, Pennaneach V, Kolodner RD (2004) Chromosome healing through terminal deletions generated by de novo telomere additions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(36):13262–13267
Rebuzzini P, Khoriauli L, Azzalin CM, Magnani E, Mondello C, Giulotto E (2005) New mammalian cellular systems to study mutations introduced at the break site by non-homologous end-joining. DNA Repair (Amst) 4(5):546–555
Reynolds GE, Gao Q, Miller D, Snow BE, Harrington LA, Murnane JP (2011) PIF1 disruption or NBS1 hypomorphism does not affect chromosome healing or fusion resulting from double-strand breaks near telomeres in murine embryonic stem cells. DNA Repair (Amst) 10(11):1164–1173
Ribaud V, Ribeyre C, Damay P, Shore D (2012) DNA-end capping by the budding yeast transcription factor and subtelomeric binding protein Tbf1. EMBO J 31(1):138–149
Ribeyre C, Lopes J, Boule JB, Piazza A, Guedin A, Zakian VA, Mergny JL, Nicolas A (2009) The yeast Pif1 helicase prevents genomic instability caused by G-quadruplex-forming CEB1 sequences in vivo. PLoS Genet 5(5):e1000475
Ribeyre C, Shore D (2012) Anticheckpoint pathways at telomeres in yeast. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19(3):307–313
Ricchetti M, Dujon B, Fairhead C (2003) Distance from the chromosome end determines the efficiency of double strand break repair in subtelomeres of haploid yeast. J Mol Biol 328(4):847–862
Rooms L, Reyniers E, Kooy RF (2007) Diverse chromosome breakage mechanisms underlie subtelomeric rearrangements, a common cause of mental retardation. Hum Mutat 28(2):177–182
Sabourin M, Tuzon CT, Zakian VA (2007) Telomerase and Tel1p preferentially associate with short telomeres in S. cerevisiae. Mol Cell 27(4):550–561
Sandell LL, Zakian VA (1993) Loss of a yeast telomere: arrest, recovery, and chromosome loss. Cell 75(4):729–739
Schramke V, Luciano P, Brevet V, Guillot S, Corda Y, Longhese MP, Gilson E, Geli V (2004) RPA regulates telomerase action by providing Est1p access to chromosome ends. Nat Genet 36(1):46–54
Schulz VP, Zakian VA (1994) The Saccharomyces PIF1 DNA helicase inhibits telomere elongation and de novo telomere formation. Cell 76(1):145–155
Snow BE, Mateyak M, Paderova J, Wakeham A, Iorio C, Zakian V, Squire J, Harrington L (2007) Murine Pif1 interacts with telomerase and is dispensable for telomere function in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 27(3):1017–1026
Spangler EA, Ryan T, Blackburn EH (1988) Developmentally regulated telomere addition in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res 16(12):5569–5585
Sprung CN, Reynolds GE, Jasin M, Murnane JP (1999) Chromosome healing in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(12):6781–6786
Stellwagen AE, Haimberger ZW, Veatch JR, Gottschling DE (2003) Ku interacts with telomerase RNA to promote telomere addition at native and broken chromosome ends. Genes Dev 17(19):2384–2395
Stracker TH, Petrini JH (2011) The MRE11 complex: starting from the ends. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12(2):90–103
Varga T, Aplan PD (2005) Chromosomal aberrations induced by double strand DNA breaks. DNA Repair (Amst) 4(9):1038–1046
Varley H, Di S, Scherer SW, Royle NJ (2000) Characterization of terminal deletions at 7q32 and 22q13.3 healed by de novo telomere addition. Am J Hum Genet 67(3):610–622
Vodenicharov MD, Laterreur N, Wellinger RJ (2010) Telomere capping in non-dividing yeast cells requires Yku and Rap1. EMBO J 29(17):3007–3019
Wellinger RJ (2010) When the caps fall off: responses to telomere uncapping in yeast. FEBS Lett 584(17):3734–3740
Wilkie AO, Lamb J, Harris PC, Finney RD, Higgs DR (1990) A truncated human chromosome 16 associated with alpha thalassaemia is stabilized by addition of telomeric repeat (TTAGGG)n. Nature 346(6287):868–871
Wong AC, Ning Y, Flint J, Clark K, Dumanski JP, Ledbetter DH, McDermid HE (1997) Molecular characterization of a 130-kb terminal microdeletion at 22q in a child with mild mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 60(1):113–120
Wotton D, Shore D (1997) A novel Rap1p-interacting factor, Rif2p, cooperates with Rif1p to regulate telomere length in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev 11(6):748–760
Xue Y, Rushton MD, Maringele L (2011) A novel checkpoint and RPA inhibitory pathway regulated by Rif1. PLoS Genet 7(12):e1002417
Zhang DH, Zhou B, Huang Y, Xu LX, Zhou JQ (2006) The human Pif1 helicase, a potential Escherichia coli RecD homologue, inhibits telomerase activity. Nucleic Acids Res 34(5):1393–1404
Zhang W, Durocher D (2010) De novo telomere formation is suppressed by the Mec1-dependent inhibition of Cdc13 accumulation at DNA breaks. Genes Dev 24(5):502–515
Zhou J, Monson EK, Teng S, Schulz VP, Zakian VA (2000) Pif1p helicase, a catalytic inhibitor of telomerase in yeast. Science 289(5480):771–774
Zhou JQ, Qi H, Schulz VP, Mateyak MK, Monson EK, Zakian VA (2002) Schizosaccharomyces pombe pfh1+ encodes an essential 5′ to 3′ DNA helicase that is a member of the PIF1 subfamily of DNA helicases. Mol Biol Cell 13(6):2180–2191
Zhu Z, Chung WH, Shim EY, Lee SE, Ira G (2008) Sgs1 helicase and two nucleases Dna2 and Exo1 resect DNA double-strand break ends. Cell 134(6):981–994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeyre, C., Shore, D. Regulation of telomere addition at DNA double-strand breaks. Chromosoma 122, 159–173 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-013-0404-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-013-0404-2