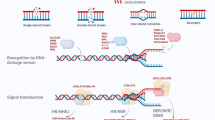
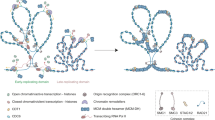
Abstract
DNA double-strand breaks arise accidentally upon exposure of DNA to radiation and chemicals or result from faulty DNA metabolic processes. DNA breaks can also be introduced in a programmed manner, such as during the maturation of the immune system, meiosis, or cancer chemo- or radiotherapy. Cells have developed a variety of repair pathways, which are fine-tuned to the specific needs of a cell. Accordingly, vegetative cells employ mechanisms that restore the integrity of broken DNA with the highest efficiency at the lowest cost of mutagenesis. In contrast, meiotic cells or developing lymphocytes exploit DNA breakage to generate diversity. Here, we review the main pathways of eukaryotic DNA double-strand break repair with the focus on homologous recombination and its various subpathways. We highlight the differences between homologous recombination and end-joining mechanisms including non-homologous end-joining and microhomology-mediated end-joining and offer insights into how these pathways are regulated. Finally, we introduce noncanonical functions of the recombination proteins, in particular during DNA replication stress.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akamatsu Y, Jasin M (2010) Role for the mammalian Swi5-Sfr1 complex in DNA strand break repair through homologous recombination. PLoS Genet 6:e1001160
Allers T, Lichten M (2001) Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell 106:47–57
Anand R, Beach A, Li K, Haber J (2017) Rad51-mediated double-strand break repair and mismatch correction of divergent substrates. Nature 544:377–380
Anand R, Ranjha L, Cannavo E, Cejka P (2016) Phosphorylated CtIP functions as a co-factor of the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 endonuclease in DNA end resection. Mol Cell 64:940–950
Arakawa H, Hauschild J, Buerstedde JM (2002) Requirement of the activation-induced deaminase (AID) gene for immunoglobulin gene conversion. Science 295:1301–1306
Arya R, Bassing CH (2017) V(D)J recombination exploits DNA damage responses to promote immunity. Trends Genet 33:479–489
Audebert M, Salles B, Calsou P (2004) Involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and XRCC1/DNA ligase III in an alternative route for DNA double-strand breaks rejoining. J Biol Chem 279:55117–55126
Bae SH, Choi E, Lee KH, Park JS, Lee SH, Seo YS (1998) Dna2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae possesses a single-stranded DNA-specific endonuclease activity that is able to act on double-stranded DNA in the presence of ATP. J Biol Chem 273:26880–26890
Barber LJ, Youds JL, Ward JD, McIlwraith MJ, O’Neil NJ, Petalcorin MI, Martin JS, Collis SJ, Cantor SB, Auclair M et al (2008) RTEL1 maintains genomic stability by suppressing homologous recombination. Cell 135:261–271
Bardwell AJ, Bardwell L, Tomkinson AE, Friedberg EC (1994) Specific cleavage of model recombination and repair intermediates by the yeast Rad1-Rad10 DNA endonuclease. Science 265:2082–2085
Baskar R, Dai J, Wenlong N, Yeo R, Yeoh KW (2014) Biological response of cancer cells to radiation treatment. Front Mol Biosci 1:24
Baudat F, Manova K, Yuen JP, Jasin M, Keeney S (2000) Chromosome synapsis defects and sexually dimorphic meiotic progression in mice lacking Spo11. Mol Cell 6:989–998
Baumann P, Benson FE, West SC (1996) Human Rad51 protein promotes ATP-dependent homologous pairing and strand transfer reactions in vitro. Cell 87:757–766
Bebenek K, Pedersen LC, Kunkel TA (2014) Structure-function studies of DNA polymerase lambda. Biochemistry 53:2781–2792
Bedell VM, Wang Y, Campbell JM, Poshusta TL, Starker CG, Krug RG 2nd, Tan W, Penheiter SG, Ma AC, Leung AY et al (2012) In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system. Nature 491:114–118
Bennardo N, Cheng A, Huang N, Stark JM (2008) Alternative-NHEJ is a mechanistically distinct pathway of mammalian chromosome break repair. PLoS Genet 4:e1000110
Benson FE, Baumann P, West SC (1998) Synergistic actions of Rad51 and Rad52 in recombination and DNA repair. Nature 391:401–404
Benson FE, Stasiak A, West SC (1994) Purification and characterization of the human Rad51 protein, an analogue of E. coli RecA. EMBO J 13:5764–5771
Berti M, Ray Chaudhuri A, Thangavel S, Gomathinayagam S, Kenig S, Vujanovic M, Odreman F, Glatter T, Graziano S, Mendoza-Maldonado R et al (2013) Human RECQ1 promotes restart of replication forks reversed by DNA topoisomerase I inhibition. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20:347–354
Betous R, Mason AC, Rambo RP, Bansbach CE, Badu-Nkansah A, Sirbu BM, Eichman BF, Cortez D (2012) SMARCAL1 catalyzes fork regression and Holliday junction migration to maintain genome stability during DNA replication. Genes Dev 26:151–162
Bhargava R, Onyango DO, Stark JM (2016) Regulation of single-strand annealing and its role in genome maintenance. Trends Genet 32:566–575
Bhat KP, Betous R, Cortez D (2015) High-affinity DNA-binding domains of replication protein A (RPA) direct SMARCAL1-dependent replication fork remodeling. J Biol Chem 290:4110–4117
Bianchi J, Rudd SG, Jozwiakowski SK, Bailey LJ, Soura V, Taylor E, Stevanovic I, Green AJ, Stracker TH, Lindsay HD et al (2013) PrimPol bypasses UV photoproducts during eukaryotic chromosomal DNA replication. Mol Cell 52:566–573
Biehs R, Steinlage M, Barton O, Juhasz S, Kunzel J, Spies J, Shibata A, Jeggo PA, Lobrich M (2017) DNA double-strand break resection occurs during non-homologous end joining in G1 but is distinct from resection during homologous recombination. Mol Cell 65:671–684 e675
Bishop DK, Park D, Xu L, Kleckner N (1992) DMC1: a meiosis-specific yeast homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation, and cell cycle progression. Cell 69:439–456
Bishop DK, Zickler D (2004) Early decision; meiotic crossover interference prior to stable strand exchange and synapsis. Cell 117:9–15
Blanco MG, Matos J, West SC (2014) Dual control of Yen1 nuclease activity and cellular localization by Cdk and Cdc14 prevents genome instability. Mol Cell 54:94–106
Bocquet N, Bizard AH, Abdulrahman W, Larsen NB, Faty M, Cavadini S, Bunker RD, Kowalczykowski SC, Cejka P, Hickson ID et al (2014) Structural and mechanistic insight into Holliday-junction dissolution by topoisomerase IIIalpha and RMI1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:261–268
Boddy MN, Gaillard PH, McDonald WH, Shanahan P, Yates JR 3rd, Russell P (2001) Mus81-Eme1 are essential components of a Holliday junction resolvase. Cell 107:537–548
Bonetti D, Clerici M, Manfrini N, Lucchini G, Longhese MP (2010) The MRX complex plays multiple functions in resection of Yku- and Rif2-protected DNA ends. PLoS One 5:e14142
Borde V, Lin W, Novikov E, Petrini JH, Lichten M, Nicolas A (2004) Association of Mre11p with double-strand break sites during yeast meiosis. Mol Cell 13:389–401
Branzei D, Szakal B (2016) DNA damage tolerance by recombination: molecular pathways and DNA structures. DNA Repair (Amst) 44:68–75
Branzei D, Szakal B (2017) Building up and breaking down: mechanisms controlling recombination during replication. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 52:381–394
Bregenhorn S, Kallenberger L, Artola-Boran M, Pena-Diaz J, Jiricny J (2016) Non-canonical uracil processing in DNA gives rise to double-strand breaks and deletions: relevance to class switch recombination. Nucleic Acids Res 44:2691–2705
Broderick R, Nieminuszczy J, Baddock HT, Deshpande RA, Gileadi O, Paull TT, McHugh PJ, Niedzwiedz W (2016) EXD2 promotes homologous recombination by facilitating DNA end resection. Nat Cell Biol 18:271–280
Brosh RM, Li JL, Kenny MK, Karow JK, Cooper MP, Kureekattil RP, Hickson ID, Bohr VA (2000) Replication protein A physically interacts with the Bloom’s syndrome protein and stimulates its helicase activity. J Biol Chem 275:23500–23508
Bugreev DV, Brosh RM Jr, Mazin AV (2008) RECQ1 possesses DNA branch migration activity. J Biol Chem 283:20231–20242
Bugreev DV, Hanaoka F, Mazin AV (2007a) Rad54 dissociates homologous recombination intermediates by branch migration. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:746–753
Bugreev DV, Rossi MJ, Mazin AV (2011) Cooperation of RAD51 and RAD54 in regression of a model replication fork. Nucleic Acids Res 39:2153–2164
Bugreev DV, Yu X, Egelman EH, Mazin AV (2007b) Novel pro- and anti-recombination activities of the Bloom’s syndrome helicase. Genes Dev 21:3085–3094
Buisson R, Dion-Cote AM, Coulombe Y, Launay H, Cai H, Stasiak AZ, Stasiak A, Xia B, Masson JY (2010) Cooperation of breast cancer proteins PALB2 and piccolo BRCA2 in stimulating homologous recombination. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1247–1254
Canela A, Maman Y, Jung S, Wong N, Callen E, Day A, Kieffer-Kwon KR, Pekowska A, Zhang H, Rao SSP et al (2017) Genome organization drives chromosome fragility. Cell 170:507–521 e518
Cannavo E, Cejka P (2014) Sae2 promotes dsDNA endonuclease activity within Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 to resect DNA breaks. Nature 514:122–125
Carballo JA, Johnson AL, Sedgwick SG, Cha RS (2008) Phosphorylation of the axial element protein Hop1 by Mec1/Tel1 ensures meiotic interhomolog recombination. Cell 132:758–770
Carreira A, Hilario J, Amitani I, Baskin RJ, Shivji MK, Venkitaraman AR, Kowalczykowski SC (2009) The BRC repeats of BRCA2 modulate the DNA-binding selectivity of RAD51. Cell 136:1032–1043
Carson CT, Schwartz RA, Stracker TH, Lilley CE, Lee DV, Weitzman MD (2003) The Mre11 complex is required for ATM activation and the G2/M checkpoint. EMBO J 22:6610–6620
Casellas R, Nussenzweig A, Wuerffel R, Pelanda R, Reichlin A, Suh H, Qin XF, Besmer E, Kenter A, Rajewsky K et al (1998) Ku80 is required for immunoglobulin isotype switching. EMBO J 17:2404–2411
Castor D, Nair N, Declais AC, Lachaud C, Toth R, Macartney TJ, Lilley DM, Arthur JS, Rouse J (2013) Cooperative control of Holliday junction resolution and DNA repair by the SLX1 and MUS81-EME1 nucleases. Mol Cell 52:221–233
Ceballos SJ, Heyer WD (2011) Functions of the Snf2/Swi2 family Rad54 motor protein in homologous recombination. Biochim Biophys Acta 1809:509–523
Cejka P (2015) DNA end resection: nucleases team up with the right partners to initiate homologous recombination. J Biol Chem 290(38):22931–22938
Cejka P, Cannavo E, Polaczek P, Masuda-Sasa T, Pokharel S, Campbell JL, Kowalczykowski SC (2010a) DNA end resection by Dna2-Sgs1-RPA and its stimulation by Top3-Rmi1 and Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2. Nature 467:112–116
Cejka P, Plank JL, Bachrati CZ, Hickson ID, Kowalczykowski SC (2010b) Rmi1 stimulates decatenation of double Holliday junctions during dissolution by Sgs1-Top3. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1377–1382
Cejka P, Plank JL, Dombrowski CC, Kowalczykowski SC (2012) Decatenation of DNA by the S. cerevisiae Sgs1-Top3-Rmi1 and RPA complex: a mechanism for disentangling chromosomes. Mol Cell 47:886–896
Chaganti RS, Schonberg S, German J (1974) A manyfold increase in sister chromatid exchanges in Bloom’s syndrome lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 71:4508–4512
Chan YW, West SC (2014) Spatial control of the GEN1 Holliday junction resolvase ensures genome stability. Nat Commun 5:4844
Chang HHY, Pannunzio NR, Adachi N, Lieber MR (2017) Non-homologous DNA end joining and alternative pathways to double-strand break repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18:495–506
Chanut P, Britton S, Coates J, Jackson SP, Calsou P (2016) Coordinated nuclease activities counteract Ku at single-ended DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Commun 7:12889
Chapman JR, Taylor MR, Boulton SJ (2012) Playing the end game: DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Mol Cell 47:497–510
Chappell C, Hanakahi LA, Karimi-Busheri F, Weinfeld M, West SC (2002) Involvement of human polynucleotide kinase in double-strand break repair by non-homologous end joining. EMBO J 21:2827–2832
Chen L, Trujillo K, Ramos W, Sung P, Tomkinson AE (2001) Promotion of Dnl4-catalyzed DNA end-joining by the Rad50/Mre11/Xrs2 and Hdf1/Hdf2 complexes. Mol Cell 8:1105–1115
Chen SH, Plank JL, Willcox S, Griffith JD, Hsieh TS (2014) Top3alpha is required during the convergent migration step of double Holliday junction dissolution. PLoS One 9:e83582
Chi P, San Filippo J, Sehorn MG, Petukhova GV, Sung P (2007) Bipartite stimulatory action of the Hop2-Mnd1 complex on the Rad51 recombinase. Genes Dev 21:1747–1757
Chiolo I, Minoda A, Colmenares SU, Polyzos A, Costes SV, Karpen GH (2011) Double-strand breaks in heterochromatin move outside of a dynamic HP1a domain to complete recombinational repair. Cell 144:732–744
Chu VT, Weber T, Wefers B, Wurst W, Sander S, Rajewsky K, Kuhn R (2015) Increasing the efficiency of homology-directed repair for CRISPR-Cas9-induced precise gene editing in mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol 33:543–548
Ciccia A, Elledge SJ (2010) The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell 40:179–204
Ciccia A, Nimonkar AV, Hu Y, Hajdu I, Achar YJ, Izhar L, Petit SA, Adamson B, Yoon JC, Kowalczykowski SC et al (2012) Polyubiquitinated PCNA recruits the ZRANB3 translocase to maintain genomic integrity after replication stress. Mol Cell 47:396–409
Cloud V, Chan YL, Grubb J, Budke B, Bishop DK (2012) Rad51 is an accessory factor for Dmc1-mediated joint molecule formation during meiosis. Science 337:1222–1225
Daley JM, Niu H, Sung P (2013) Roles of DNA helicases in the mediation and regulation of homologous recombination. Adv Exp Med Biol 767:185–202
de los Santos T, Hunter N, Lee C, Larkin B, Loidl J, Hollingsworth NM (2003) The Mus81/Mms4 endonuclease acts independently of double-Holliday junction resolution to promote a distinct subset of crossovers during meiosis in budding yeast. Genetics 164:81–94
Dehe PM, Gaillard PH (2017) Control of structure-specific endonucleases to maintain genome stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18:315–330
Deng SK, Gibb B, de Almeida MJ, Greene EC, Symington LS (2014) RPA antagonizes microhomology-mediated repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:405–412
Deshpande RA, Lee JH, Arora S, Paull TT (2016) Nbs1 converts the human Mre11/Rad50 nuclease complex into an endo/exonuclease machine specific for protein-DNA adducts. Mol Cell 64:593–606
Dinkelmann M, Spehalski E, Stoneham T, Buis J, Wu Y, Sekiguchi JM, Ferguson DO (2009) Multiple functions of MRN in end-joining pathways during isotype class switching. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:808–813
Dion V, Kalck V, Horigome C, Towbin BD, Gasser SM (2012) Increased mobility of double-strand breaks requires Mec1, Rad9 and the homologous recombination machinery. Nat Cell Biol 14:502–509
Donnianni RA, Symington LS (2013) Break-induced replication occurs by conservative DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:13475–13480
Duckett DR, Murchie AI, Diekmann S, von Kitzing E, Kemper B, Lilley DM (1988) The structure of the Holliday junction, and its resolution. Cell 55:79–89
Dunderdale HJ, Benson FE, Parsons CA, Sharples GJ, Lloyd RG, West SC (1991) Formation and resolution of recombination intermediates by E. coli RecA and RuvC proteins. Nature 354:506–510
Dungrawala H, Bhat KP, Le Meur R, Chazin WJ, Ding X, Sharan SK, Wessel SR, Sathe AA, Zhao R, Cortez D (2017) RADX promotes genome stability and modulates chemosensitivity by regulating RAD51 at replication forks. Mol Cell 67:374–386 e375
Eggler AL, Inman RB, Cox MM (2002) The Rad51-dependent pairing of long DNA substrates is stabilized by replication protein A. J Biol Chem 277:39280–39288
Ehmsen KT, Heyer WD (2008) Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mus81-Mms4 is a catalytic, DNA structure-selective endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res 36:2182–2195
Ehrenstein MR, Neuberger MS (1999) Deficiency in Msh2 affects the efficiency and local sequence specificity of immunoglobulin class-switch recombination: parallels with somatic hypermutation. EMBO J 18:3484–3490
Fasching CL, Cejka P, Kowalczykowski SC, Heyer WD (2015) Top3-Rmi1 dissolve Rad51-mediated D loops by a topoisomerase-based mechanism. Mol Cell 57:595–606
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B (1990) A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 61:759–767
Fekairi S, Scaglione S, Chahwan C, Taylor ER, Tissier A, Coulon S, Dong MQ, Ruse C, Yates JR 3rd, Russell P et al (2009) Human SLX4 is a Holliday junction resolvase subunit that binds multiple DNA repair/recombination endonucleases. Cell 138:78–89
Feng W, Jasin M (2017) BRCA2 suppresses replication stress-induced mitotic and G1 abnormalities through homologous recombination. Nat Commun 8:525
Feng Z, Scott SP, Bussen W, Sharma GG, Guo G, Pandita TK, Powell SN (2011) Rad52 inactivation is synthetically lethal with BRCA2 deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:686–691
Forget AL, Kowalczykowski SC (2012) Single-molecule imaging of DNA pairing by RecA reveals a three-dimensional homology search. Nature 482:423–427
Fricke WM, Brill SJ (2003) Slx1-Slx4 is a second structure-specific endonuclease functionally redundant with Sgs1-Top3. Genes Dev 17:1768–1778
Fugger K, Mistrik M, Danielsen JR, Dinant C, Falck J, Bartek J, Lukas J, Mailand N (2009) Human Fbh1 helicase contributes to genome maintenance via pro- and anti-recombinase activities. J Cell Biol 186:655–663
Fugger K, Mistrik M, Neelsen KJ, Yao Q, Zellweger R, Kousholt AN, Haahr P, Chu WK, Bartek J, Lopes M et al (2015) FBH1 catalyzes regression of stalled replication forks. Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.028
Gaillard PHL, Noguchi E, Shanahan P, Russell P (2003) The endogenous Mus81-Eme1 complex resolves Holliday junctions by a nick and counternick mechanism. Mol Cell 12:747–759
Gaines WA, Godin SK, Kabbinavar FF, Rao T, VanDemark AP, Sung P, Bernstein KA (2015) Promotion of presynaptic filament assembly by the ensemble of S. cerevisiae Rad51 paralogues with Rad52. Nat Commun 6:7834
Garcia V, Gray S, Allison RM, Cooper TJ, Neale MJ (2015) Tel1(ATM)-mediated interference suppresses clustered meiotic double-strand-break formation. Nature 520:114–118
Garcia V, Phelps SE, Gray S, Neale MJ (2011) Bidirectional resection of DNA double-strand breaks by Mre11 and Exo1. Nature 479:241–244
Garcia-Gomez S, Reyes A, Martinez-Jimenez MI, Chocron ES, Mouron S, Terrados G, Powell C, Salido E, Mendez J, Holt IJ et al (2013) PrimPol, an archaic primase/polymerase operating in human cells. Mol Cell 52:541–553
Gari K, Decaillet C, Delannoy M, Wu L, Constantinou A (2008) Remodeling of DNA replication structures by the branch point translocase FANCM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16107–16112
Gottlieb TM, Jackson SP (1993) The DNA-dependent protein kinase: requirement for DNA ends and association with Ku antigen. Cell 72:131–142
Gravel S, Chapman JR, Magill C, Jackson SP (2008) DNA helicases Sgs1 and BLM promote DNA double-strand break resection. Genes Dev 22:2767–2772
Guilliam TA, Doherty AJ (2017) PrimPol—prime time to reprime. Genes (Basel) 8(1):20
Gupta S, Yeeles JT, Marians KJ (2014) Regression of replication forks stalled by leading-strand template damage: I. Both RecG and RuvAB catalyze regression, but RuvC cleaves the holliday junctions formed by RecG preferentially. J Biol Chem 289:28376–28387
Hasham MG, Donghia NM, Coffey E, Maynard J, Snow KJ, Ames J, Wilpan RY, He Y, King BL, Mills KD (2010) Widespread genomic breaks generated by activation-induced cytidine deaminase are prevented by homologous recombination. Nat Immunol 11:820–826
Hashimoto Y, Ray Chaudhuri A, Lopes M, Costanzo V (2010) Rad51 protects nascent DNA from Mre11-dependent degradation and promotes continuous DNA synthesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1305–1311
Helmink BA, Bredemeyer AL, Lee BS, Huang CY, Sharma GG, Walker LM, Bednarski JJ, Lee WL, Pandita TK, Bassing CH et al (2009) MRN complex function in the repair of chromosomal Rag-mediated DNA double-strand breaks. J Exp Med 206:669–679
Heyer WD (2015) Regulation of recombination and genomic maintenance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a016501
Hicks WM, Kim M, Haber JE (2010) Increased mutagenesis and unique mutation signature associated with mitotic gene conversion. Science 329:82–85
Hickson ID, Mankouri HW (2011) Processing of homologous recombination repair intermediates by the Sgs1-Top3-Rmi1 and Mus81-Mms4 complexes. Cell Cycle 10:3078–3085
Higgins NP, Kato K, Strauss B (1976) A model for replication repair in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol 101:417–425
Hinz JM (2010) Role of homologous recombination in DNA interstrand crosslink repair. Environ Mol Mutagen 51:582–603
Holm C, Covey JM, Kerrigan D, Pommier Y (1989) Differential requirement of DNA replication for the cytotoxicity of DNA topoisomerase I and II inhibitors in Chinese hamster DC3F cells. Cancer Res 49:6365–6368
Horigome C, Oma Y, Konishi T, Schmid R, Marcomini I, Hauer MH, Dion V, Harata M, Gasser SM (2014) SWR1 and INO80 chromatin remodelers contribute to DNA double-strand break perinuclear anchorage site choice. Mol Cell 55:626–639
Howard SM, Yanez DA, Stark JM (2015) DNA damage response factors from diverse pathways, including DNA crosslink repair, mediate alternative end joining. PLoS Genet 11:e1004943
Hu J, Sun L, Shen F, Chen Y, Hua Y, Liu Y, Zhang M, Hu Y, Wang Q, Xu W et al (2012) The intra-S phase checkpoint targets Dna2 to prevent stalled replication forks from reversing. Cell 149:1221–1232
Hu Y, Raynard S, Sehorn MG, Lu X, Bussen W, Zheng L, Stark JM, Barnes EL, Chi P, Janscak P et al (2007) RECQL5/Recql5 helicase regulates homologous recombination and suppresses tumor formation via disruption of Rad51 presynaptic filaments. Genes Dev 21:3073–3084
Huang J, Dynan WS (2002) Reconstitution of the mammalian DNA double-strand break end-joining reaction reveals a requirement for an Mre11/Rad50/NBS1-containing fraction. Nucleic Acids Res 30:667–674
Huertas P, Cortes-Ledesma F, Sartori AA, Aguilera A, Jackson SP (2008) CDK targets Sae2 to control DNA-end resection and homologous recombination. Nature 455:689–692
Huertas P, Jackson SP (2009) Human CtIP mediates cell cycle control of DNA end resection and double strand break repair. J Biol Chem 284:9558–9565
Hunter N (2015) Meiotic recombination: the essence of heredity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7
Hunter N, Kleckner N (2001) The single-end invasion: an asymmetric intermediate at the double-strand break to double-Holliday junction transition of meiotic recombination. Cell 106:59–70
Imai K, Slupphaug G, Lee WI, Revy P, Nonoyama S, Catalan N, Yel L, Forveille M, Kavli B, Krokan HE et al (2003) Human uracil-DNA glycosylase deficiency associated with profoundly impaired immunoglobulin class-switch recombination. Nat Immunol 4:1023–1028
Ip SC, Rass U, Blanco MG, Flynn HR, Skehel JM, West SC (2008) Identification of Holliday junction resolvases from humans and yeast. Nature 456:357–361
Ira G, Pellicioli A, Balijja A, Wang X, Fiorani S, Carotenuto W, Liberi G, Bressan D, Wan L, Hollingsworth NM et al (2004) DNA end resection, homologous recombination and DNA damage checkpoint activation require CDK1. Nature 431:1011–1017
Ivanov EL, Sugawara N, Fishman-Lobell J, Haber JE (1996) Genetic requirements for the single-strand annealing pathway of double-strand break repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 142:693–704
Jackson SP, Bartek J (2009) The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 461:1071–1078
Jensen RB, Carreira A, Kowalczykowski SC (2010) Purified human BRCA2 stimulates RAD51-mediated recombination. Nature 467:678–683
Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337:816–821
Johzuka K, Ogawa H (1995) Interaction of Mre11 and Rad50: two proteins required for DNA repair and meiosis-specific double-strand break formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 139:1521–1532
Kanagaraj R, Saydam N, Garcia PL, Zheng L, Janscak P (2006) Human RECQ5beta helicase promotes strand exchange on synthetic DNA structures resembling a stalled replication fork. Nucleic Acids Res 34:5217–5231
Kawamoto T, Araki K, Sonoda E, Yamashita YM, Harada K, Kikuchi K, Masutani C, Hanaoka F, Nozaki K, Hashimoto N et al (2005) Dual roles for DNA polymerase eta in homologous DNA recombination and translesion DNA synthesis. Mol Cell 20:793–799
Keeney S (2008) Spo11 and the formation of DNA double-strand breaks in meiosis. Genome Dyn Stab 2:81–123
Keeney S, Giroux CN, Kleckner N (1997) Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by Spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell 88:375–384
Keeney S, Kleckner N (1995) Covalent protein-DNA complexes at the 5′ strand termini of meiosis-specific double-strand breaks in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:11274–11278
Keeney S, Lange J, Mohibullah N (2014) Self-organization of meiotic recombination initiation: general principles and molecular pathways. Annu Rev Genet 48:187–214
Kile AC, Chavez DA, Bacal J, Eldirany S, Korzhnev DM, Bezsonova I, Eichman BF, Cimprich KA (2015) HLTF’s ancient HIRAN domain binds 3′ DNA ends to drive replication fork reversal. Mol Cell 58:1090–1100
Kim JH, Grosbart M, Anand R, Wyman C, Cejka P, Petrini JH (2017) The Mre11-Nbs1 interface is essential for viability and tumor suppression. Cell Rep 18:496–507
Kim KP, Weiner BM, Zhang L, Jordan A, Dekker J, Kleckner N (2010) Sister cohesion and structural axis components mediate homolog bias of meiotic recombination. Cell 143:924–937
Kolinjivadi AM, Sannino V, De Antoni A, Zadorozhny K, Kilkenny M, Techer H, Baldi G, Shen R, Ciccia A, Pellegrini L et al (2017) Smarcal1-mediated fork reversal triggers Mre11-dependent degradation of nascent DNA in the absence of Brca2 and stable Rad51 nucleofilaments. Mol Cell 67:867–881
Kosugi S, Hasebe M, Tomita M, Yanagawa H (2009) Systematic identification of cell cycle-dependent yeast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins by prediction of composite motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:10171–10176
Kowalczykowski SC (2015) An overview of the molecular mechanisms of recombinational DNA repair. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7
Krejci L, Van Komen S, Li Y, Villemain J, Reddy MS, Klein H, Ellenberger T, Sung P (2003) DNA helicase Srs2 disrupts the Rad51 presynaptic filament. Nature 423:305–309
Lam I, Keeney S (2014) Mechanism and regulation of meiotic recombination initiation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a016634
Lange J, Yamada S, Tischfield SE, Pan J, Kim S, Zhu X, Socci ND, Jasin M, Keeney S (2016) The landscape of mouse meiotic double-strand break formation, processing, and repair. Cell 167:695–708 e616
Langerak P, Mejia-Ramirez E, Limbo O, Russell P (2011) Release of Ku and MRN from DNA ends by Mre11 nuclease activity and Ctp1 is required for homologous recombination repair of double-strand breaks. PLoS Genet 7:e1002271
Lavery PE, Kowalczykowski SC (1992) A postsynaptic role for single-stranded DNA-binding protein in recA protein-promoted DNA strand exchange. J Biol Chem 267:9315–9320
Lee JH, Paull TT (2004) Direct activation of the ATM protein kinase by the Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex. Science 304:93–96
Lee JH, Paull TT (2005) ATM activation by DNA double-strand breaks through the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex. Science 308:551–554
Lee-Theilen M, Matthews AJ, Kelly D, Zheng S, Chaudhuri J (2011) CtIP promotes microhomology-mediated alternative end joining during class-switch recombination. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:75–79
Lemacon D, Jackson J, Quinet A, Brickner JR, Li S, Yazinski S, You Z, Ira G, Zou L, Mosammaparast N et al (2017) MRE11 and EXO1 nucleases degrade reversed forks and elicit MUS81-dependent fork rescue in BRCA2-deficient cells. Nat Commun 8:860
Lengsfeld BM, Rattray AJ, Bhaskara V, Ghirlando R, Paull TT (2007) Sae2 is an endonuclease that processes hairpin DNA cooperatively with the Mre11/Rad50/Xrs2 complex. Mol Cell 28:638–651
Leu JY, Chua PR, Roeder GS (1998) The meiosis-specific Hop2 protein of S. cerevisiae ensures synapsis between homologous chromosomes. Cell 94:375–386
Levikova M, Klaue D, Seidel R, Cejka P (2013) Nuclease activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Dna2 inhibits its potent DNA helicase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:E1992–E2001
Levikova M, Pinto C, Cejka P (2017) The motor activity of DNA2 functions as an ssDNA translocase to promote DNA end resection. Genes Dev 31:493–502
Li X, Stith CM, Burgers PM, Heyer WD (2009) PCNA is required for initiation of recombination-associated DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase delta. Mol Cell 36:704–713
Li Z, Otevrel T, Gao Y, Cheng HL, Seed B, Stamato TD, Taccioli GE, Alt FW (1995) The XRCC4 gene encodes a novel protein involved in DNA double-strand break repair and V(D)J recombination. Cell 83:1079–1089
Lipkin SM, Moens PB, Wang V, Lenzi M, Shanmugarajah D, Gilgeous A, Thomas J, Cheng J, Touchman JW, Green ED et al (2002) Meiotic arrest and aneuploidy in MLH3-deficient mice. Nat Genet 31:385–390
Liu J, Doty T, Gibson B, Heyer WD (2010) Human BRCA2 protein promotes RAD51 filament formation on RPA-covered single-stranded DNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1260–1262
Liu J, Renault L, Veaute X, Fabre F, Stahlberg H, Heyer WD (2011a) Rad51 paralogues Rad55-Rad57 balance the antirecombinase Srs2 in Rad51 filament formation. Nature 479:245–248
Liu T, Wan L, Wu Y, Chen J, Huang J (2011b) hSWS1.SWSAP1 is an evolutionarily conserved complex required for efficient homologous recombination repair. J Biol Chem 286:41758–41766
Llorente B, Smith CE, Symington LS (2008) Break-induced replication: what is it and what is it for? Cell Cycle 7:859–864
Lobrich M, Jeggo P (2017) A process of resection-dependent nonhomologous end joining involving the goddess Artemis. Trends Biochem Sci 42(9):690–701
Lombardo A, Genovese P, Beausejour CM, Colleoni S, Lee YL, Kim KA, Ando D, Urnov FD, Galli C, Gregory PD et al (2007) Gene editing in human stem cells using zinc finger nucleases and integrase-defective lentiviral vector delivery. Nat Biotechnol 25:1298–1306
Lopes M, Cotta-Ramusino C, Pellicioli A, Liberi G, Plevani P, Muzi-Falconi M, Newlon CS, Foiani M (2001) The DNA replication checkpoint response stabilizes stalled replication forks. Nature 412:557–561
Lynn A, Soucek R, Borner GV (2007) ZMM proteins during meiosis: crossover artists at work. Chromosom Res 15:591–605
Ma Y, Pannicke U, Schwarz K, Lieber MR (2002) Hairpin opening and overhang processing by an Artemis/DNA-dependent protein kinase complex in nonhomologous end joining and V(D)J recombination. Cell 108:781–794
Mahadevaiah SK, Turner JM, Baudat F, Rogakou EP, de Boer P, Blanco-Rodriguez J, Jasin M, Keeney S, Bonner WM, Burgoyne PS (2001) Recombinational DNA double-strand breaks in mice precede synapsis. Nat Genet 27:271–276
Makharashvili N, Tubbs AT, Yang SH, Wang H, Barton O, Zhou Y, Deshpande RA, Lee JH, Lobrich M, Sleckman BP et al (2014) Catalytic and noncatalytic roles of the CtIP endonuclease in double-strand break end resection. Mol Cell 54:1022–1033
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM, Aach J, Guell M, DiCarlo JE, Norville JE, Church GM (2013) RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 339:823–826
Martin V, Chahwan C, Gao H, Blais V, Wohlschlegel J, Yates JR 3rd, McGowan CH, Russell P (2006) Sws1 is a conserved regulator of homologous recombination in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J 25:2564–2574
Mason JM, Dusad K, Wright WD, Grubb J, Budke B, Heyer WD, Connell PP, Weichselbaum RR, Bishop DK (2015) RAD54 family translocases counter genotoxic effects of RAD51 in human tumor cells. Nucleic Acids Res 43:3180–3196
Masson JY, Tarsounas MC, Stasiak AZ, Stasiak A, Shah R, McIlwraith MJ, Benson FE, West SC (2001) Identification and purification of two distinct complexes containing the five RAD51 paralogs. Genes Dev 15:3296–3307
Mateos-Gomez PA, Gong F, Nair N, Miller KM, Lazzerini-Denchi E, Sfeir A (2015) Mammalian polymerase theta promotes alternative NHEJ and suppresses recombination. Nature 518:254–257
Mateos-Gomez PA, Kent T, Deng SK, McDevitt S, Kashkina E, Hoang TM, Pomerantz RT, Sfeir A (2017) The helicase domain of Poltheta counteracts RPA to promote alt-NHEJ. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24(12):1116–1123
Matos J, Blanco MG, Maslen S, Skehel JM, West SC (2011) Regulatory control of the resolution of DNA recombination intermediates during meiosis and mitosis. Cell 147:158–172
Matos J, Blanco MG, West SC (2013) Cell-cycle kinases coordinate the resolution of recombination intermediates with chromosome segregation. Cell Rep 4:76–86
Matos J, West SC (2014) Holliday junction resolution: regulation in space and time. DNA Repair (Amst) 19:176–181
Mazina OM, Mazin AV, Nakagawa T, Kolodner RD, Kowalczykowski SC (2004) Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mer3 helicase stimulates 3′-5′ heteroduplex extension by Rad51; implications for crossover control in meiotic recombination. Cell 117:47–56
McBlane JF, van Gent DC, Ramsden DA, Romeo C, Cuomo CA, Gellert M, Oettinger MA (1995) Cleavage at a V(D)J recombination signal requires only RAG1 and RAG2 proteins and occurs in two steps. Cell 83:387–395
McGlynn P, Lloyd RG (2001) Rescue of stalled replication forks by RecG: simultaneous translocation on the leading and lagging strand templates supports an active DNA unwinding model of fork reversal and Holliday junction formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:8227–8234
McIlwraith MJ, Vaisman A, Liu Y, Fanning E, Woodgate R, West SC (2005) Human DNA polymerase eta promotes DNA synthesis from strand invasion intermediates of homologous recombination. Mol Cell 20:783–792
McIlwraith MJ, West SC (2008) DNA repair synthesis facilitates RAD52-mediated second-end capture during DSB repair. Mol Cell 29:510–516
Methot SP, Di Noia JM (2017) Molecular mechanisms of somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination. Adv Immunol 133:37–87
Mijic S, Zellweger R, Chappidi N, Berti M, Jacobs K, Mutreja K, Ursich S, Ray Chaudhuri A, Nussenzweig A, Janscak P et al (2017) Replication fork reversal triggers fork degradation in BRCA2-defective cells. Nat Commun 8:859
Miller AS, Daley JM, Pham NT, Niu H, Xue X, Ira G, Sung P (2017) A novel role of the Dna2 translocase function in DNA break resection. Genes Dev 31:503–510
Mimitou EP, Symington LS (2008) Sae2, Exo1 and Sgs1 collaborate in DNA double-strand break processing. Nature 455:770–774
Mimitou EP, Symington LS (2010) Ku prevents Exo1 and Sgs1-dependent resection of DNA ends in the absence of a functional MRX complex or Sae2. EMBO J 29:3358–3369
Mimitou EP, Yamada S, Keeney S (2017) A global view of meiotic double-strand break end resection. Science 355:40–45
Mine-Hattab J, Rothstein R (2012) Increased chromosome mobility facilitates homology search during recombination. Nat Cell Biol 14:510–517
Mitchel K, Lehner K, Jinks-Robertson S (2013) Heteroduplex DNA position defines the roles of the Sgs1, Srs2, and Mph1 helicases in promoting distinct recombination outcomes. PLoS Genet 9:e1003340
Moldovan GL, Dejsuphong D, Petalcorin MI, Hofmann K, Takeda S, Boulton SJ, D'Andrea AD (2012) Inhibition of homologous recombination by the PCNA-interacting protein PARI. Mol Cell 45:75–86
Moon AF, Pryor JM, Ramsden DA, Kunkel TA, Bebenek K, Pedersen LC (2014) Sustained active site rigidity during synthesis by human DNA polymerase mu. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:253–260
Mortensen UH, Bendixen C, Sunjevaric I, Rothstein R (1996) DNA strand annealing is promoted by the yeast Rad52 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:10729–10734
Mouron S, Rodriguez-Acebes S, Martinez-Jimenez MI, Garcia-Gomez S, Chocron S, Blanco L, Mendez J (2013) Repriming of DNA synthesis at stalled replication forks by human PrimPol. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20:1383–1389
Muramatsu M, Kinoshita K, Fagarasan S, Yamada S, Shinkai Y, Honjo T (2000) Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell 102:553–563
Neale MJ, Pan J, Keeney S (2005) Endonucleolytic processing of covalent protein-linked DNA double-strand breaks. Nature 436:1053–1057
Neelsen KJ, Lopes M (2015) Replication fork reversal in eukaryotes: from dead end to dynamic response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16:207–220
Nicolette ML, Lee K, Guo Z, Rani M, Chow JM, Lee SE, Paull TT (2010) Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 and Sae2 promote 5′ strand resection of DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1478–1485
Nimonkar AV, Genschel J, Kinoshita E, Polaczek P, Campbell JL, Wyman C, Modrich P, Kowalczykowski SC (2011) BLM-DNA2-RPA-MRN and EXO1-BLM-RPA-MRN constitute two DNA end resection machineries for human DNA break repair. Genes Dev 25:350–362
Nimonkar AV, Sica RA, Kowalczykowski SC (2009) Rad52 promotes second-end DNA capture in double-stranded break repair to form complement-stabilized joint molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:3077–3082
Nishant KT, Plys AJ, Alani E (2008) A mutation in the putative MLH3 endonuclease domain confers a defect in both mismatch repair and meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 179:747–755
Niu H, Chung WH, Zhu Z, Kwon Y, Zhao W, Chi P, Prakash R, Seong C, Liu D, Lu L et al (2010) Mechanism of the ATP-dependent DNA end-resection machinery from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 467:108–111
Niu H, Wan L, Baumgartner B, Schaefer D, Loidl J, Hollingsworth NM (2005) Partner choice during meiosis is regulated by Hop1-promoted dimerization of Mek1. Mol Biol Cell 16:5804–5818
Oh J, Al-Zain A, Cannavo E, Cejka P, Symington LS (2016) Xrs2 dependent and independent functions of the Mre11-Rad50 complex. Mol Cell 64:405–415
Olive PL (1998) The role of DNA single- and double-strand breaks in cell killing by ionizing radiation. Radiat Res 150:S42–S51
Olive PL, Banath JP, Durand RE (1990) Heterogeneity in radiation-induced DNA damage and repair in tumor and normal cells measured using the “comet” assay. Radiat Res 122:86–94
Orthwein A, Noordermeer SM, Wilson MD, Landry S, Enchev RI, Sherker A, Munro M, Pinder J, Salsman J, Dellaire G et al (2015) A mechanism for the suppression of homologous recombination in G1 cells. Nature 528:422–426
Oza P, Jaspersen SL, Miele A, Dekker J, Peterson CL (2009) Mechanisms that regulate localization of a DNA double-strand break to the nuclear periphery. Genes Dev 23:912–927
Papavasiliou FN, Schatz DG (2000) Cell-cycle-regulated DNA double-stranded breaks in somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes. Nature 408:216–221
Patel DS, Misenko SM, Her J, Bunting SF (2017) BLM helicase regulates DNA repair by counteracting RAD51 loading at DNA double-strand break sites. J Cell Biol 216(11):3521–3534
Paull TT, Gellert M (1998) The 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity of Mre 11 facilitates repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Mol Cell 1:969–979
Peoples TL, Dean E, Gonzalez O, Lambourne L, Burgess SM (2002) Close, stable homolog juxtaposition during meiosis in budding yeast is dependent on meiotic recombination, occurs independently of synapsis, and is distinct from DSB-independent pairing contacts. Genes Dev 16:1682–1695
Pepe A, West SC (2014a) MUS81-EME2 promotes replication fork restart. Cell Rep 7:1048–1055
Pepe A, West SC (2014b) Substrate specificity of the MUS81-EME2 structure selective endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res 42:3833–3845
Petalcorin MI, Galkin VE, Yu X, Egelman EH, Boulton SJ (2007) Stabilization of RAD-51-DNA filaments via an interaction domain in Caenorhabditis elegans BRCA2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:8299–8304
Petersen-Mahrt SK, Harris RS, Neuberger MS (2002) AID mutates E. coli suggesting a DNA deamination mechanism for antibody diversification. Nature 418:99–103
Petukhova GV, Pezza RJ, Vanevski F, Ploquin M, Masson JY, Camerini-Otero RD (2005) The Hop2 and Mnd1 proteins act in concert with Rad51 and Dmc1 in meiotic recombination. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:449–453
Pezza RJ, Voloshin ON, Vanevski F, Camerini-Otero RD (2007) Hop2/Mnd1 acts on two critical steps in Dmc1-promoted homologous pairing. Genes Dev 21:1758–1766
Pham P, Bransteitter R, Petruska J, Goodman MF (2003) Processive AID-catalysed cytosine deamination on single-stranded DNA simulates somatic hypermutation. Nature 424:103–107
Pieper K, Tan J, Piccoli L, Foglierini M, Barbieri S, Chen Y, Silacci-Fregni C, Wolf T, Jarrossay D, Anderle M et al (2017) Public antibodies to malaria antigens generated by two LAIR1 insertion modalities. Nature 548:597–601
Pinto C, Kasaciunaite K, Seidel R, Cejka P (2016) Human DNA2 possesses a cryptic DNA unwinding activity that functionally integrates with BLM or WRN helicases. Elife 5. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18574
Piwko W, Mlejnkova LJ, Mutreja K, Ranjha L, Stafa D, Smirnov A, Brodersen MM, Zellweger R, Sturzenegger A, Janscak P et al (2016) The MMS22L-TONSL heterodimer directly promotes RAD51-dependent recombination upon replication stress. EMBO J 35:2584–2601
Plank JL, Wu J, Hsieh TS (2006) Topoisomerase IIIalpha and Bloom’s helicase can resolve a mobile double Holliday junction substrate through convergent branch migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:11118–11123
Prakash R, Satory D, Dray E, Papusha A, Scheller J, Kramer W, Krejci L, Klein H, Haber JE, Sung P et al (2009) Yeast Mph1 helicase dissociates Rad51-made D-loops: implications for crossover control in mitotic recombination. Genes Dev 23:67–79
Prakash R, Zhang Y, Feng W, Jasin M (2015) Homologous recombination and human health: the roles of BRCA1, BRCA2, and associated proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a016600
Qi Z, Redding S, Lee JY, Gibb B, Kwon Y, Niu H, Gaines WA, Sung P, Greene EC (2015) DNA sequence alignment by microhomology sampling during homologous recombination. Cell 160:856–869
Qing Y, Yamazoe M, Hirota K, Dejsuphong D, Sakai W, Yamamoto KN, Bishop DK, Wu X, Takeda S (2011) The epistatic relationship between BRCA2 and the other RAD51 mediators in homologous recombination. PLoS Genet 7:e1002148
Rada C, Williams GT, Nilsen H, Barnes DE, Lindahl T, Neuberger MS (2002) Immunoglobulin isotype switching is inhibited and somatic hypermutation perturbed in UNG-deficient mice. Curr Biol 12:1748–1755
Ramsden DA, Gellert M (1998) Ku protein stimulates DNA end joining by mammalian DNA ligases: a direct role for Ku in repair of DNA double-strand breaks. EMBO J 17:609–614
Ranjha L, Anand R, Cejka P (2014) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mlh1-Mlh3 heterodimer is an endonuclease that preferentially binds to Holliday junctions. J Biol Chem 289:5674–5686
Rao HB, Qiao H, Bhatt SK, Bailey LR, Tran HD, Bourne SL, Qiu W, Deshpande A, Sharma AN, Beebout CJ et al (2017) A SUMO-ubiquitin relay recruits proteasomes to chromosome axes to regulate meiotic recombination. Science 355:403–407
Rass E, Grabarz A, Plo I, Gautier J, Bertrand P, Lopez BS (2009) Role of Mre11 in chromosomal nonhomologous end joining in mammalian cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:819–824
Rass U, Compton SA, Matos J, Singleton MR, Ip SC, Blanco MG, Griffith JD, West SC (2010) Mechanism of Holliday junction resolution by the human GEN1 protein. Genes Dev 24:1559–1569
Ray Chaudhuri A, Callen E, Ding X, Gogola E, Duarte AA, Lee JE, Wong N, Lafarga V, Calvo JA, Panzarino NJ et al (2016) Replication fork stability confers chemoresistance in BRCA-deficient cells. Nature 535:382–387
Ray Chaudhuri A, Hashimoto Y, Herrador R, Neelsen KJ, Fachinetti D, Bermejo R, Cocito A, Costanzo V, Lopes M (2012) Topoisomerase I poisoning results in PARP-mediated replication fork reversal. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:417–423
Renkawitz J, Lademann CA, Jentsch S (2014) Mechanisms and principles of homology search during recombination. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:369–383
Reynolds A, Qiao H, Yang Y, Chen JK, Jackson N, Biswas K, Holloway JK, Baudat F, de Massy B, Wang J et al (2013) RNF212 is a dosage-sensitive regulator of crossing-over during mammalian meiosis. Nat Genet 45:269–278
Robert T, Nore A, Brun C, Maffre C, Crimi B, Bourbon HM, de Massy B (2016) The TopoVIB-like protein family is required for meiotic DNA double-strand break formation. Science 351:943–949
Rogacheva MV, Manhart CM, Chen C, Guarne A, Surtees J, Alani E (2014) Mlh1-Mlh3, a meiotic crossover and DNA mismatch repair factor, is a Msh2-Msh3-stimulated endonuclease. J Biol Chem 289:5664–5673
Rossi MJ, Bugreev DV, Mazina OM, Mazin AV (2011) The RecA/RAD51 protein drives migration of Holliday junctions via polymerization on DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:6432–6437
Ryu T, Spatola B, Delabaere L, Bowlin K, Hopp H, Kunitake R, Karpen GH, Chiolo I (2015) Heterochromatic breaks move to the nuclear periphery to continue recombinational repair. Nat Cell Biol 17:1401–1411
Sakofsky CJ, Malkova A (2017) Break induced replication in eukaryotes: mechanisms, functions, and consequences. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 52:395–413
Sartori AA, Lukas C, Coates J, Mistrik M, Fu S, Bartek J, Baer R, Lukas J, Jackson SP (2007) Human CtIP promotes DNA end resection. Nature 450:509–514
Schatz DG, Swanson PC (2011) V(D)J recombination: mechanisms of initiation. Annu Rev Genet 45:167–202
Schimmel J, Kool H, van Schendel R, Tijsterman M (2017) Mutational signatures of non-homologous and polymerase theta-mediated end-joining in embryonic stem cells. EMBO J 36:3634–3649
Schlacher K, Christ N, Siaud N, Egashira A, Wu H, Jasin M (2011) Double-strand break repair-independent role for BRCA2 in blocking stalled replication fork degradation by MRE11. Cell 145:529–542
Schlacher K, Wu H, Jasin M (2012) A distinct replication fork protection pathway connects Fanconi anemia tumor suppressors to RAD51-BRCA1/2. Cancer Cell 22:106–116
Schrader CE, Guikema JE, Linehan EK, Selsing E, Stavnezer J (2007) Activation-induced cytidine deaminase-dependent DNA breaks in class switch recombination occur during G1 phase of the cell cycle and depend upon mismatch repair. J Immunol 179:6064–6071
Schrader CE, Linehan EK, Mochegova SN, Woodland RT, Stavnezer J (2005) Inducible DNA breaks in Ig S regions are dependent on AID and UNG. J Exp Med 202:561–568
Schwacha A, Kleckner N (1994) Identification of joint molecules that form frequently between homologs but rarely between sister chromatids during yeast meiosis. Cell 76:51–63
Schwacha A, Kleckner N (1997) Interhomolog bias during meiotic recombination: meiotic functions promote a highly differentiated interhomolog-only pathway. Cell 90:1123–1135
Schwendener S, Raynard S, Paliwal S, Cheng A, Kanagaraj R, Shevelev I, Stark JM, Sung P, Janscak P (2010) Physical interaction of RECQ5 helicase with RAD51 facilitates its anti-recombinase activity. J Biol Chem 285:15739–15745
Seigneur M, Bidnenko V, Ehrlich SD, Michel B (1998) RuvAB acts at arrested replication forks. Cell 95:419–430
Seol JH, Shim EY, Lee SE (2017) Microhomology-mediated end joining: good, bad and ugly. Mutat Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.07.002
Sfeir A, Symington LS (2015) Microhomology-mediated end joining: a back-up survival mechanism or dedicated pathway? Trends Biochem Sci 40:701–714
Shah Punatar R, Martin MJ, Wyatt HD, Chan YW, West SC (2017) Resolution of single and double Holliday junction recombination intermediates by GEN1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:443–450
Shibata A (2017) Regulation of repair pathway choice at two-ended DNA double-strand breaks. Mutat Res 803–805:51–55
Shibata A, Moiani D, Arvai AS, Perry J, Harding SM, Genois MM, Maity R, van Rossum-Fikkert S, Kertokalio A, Romoli F et al (2014) DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice is directed by distinct MRE11 nuclease activities. Mol Cell 53:7–18
Shinohara A, Shinohara M, Ohta T, Matsuda S, Ogawa T (1998) Rad52 forms ring structures and co-operates with RPA in single-strand DNA annealing. Genes Cells 3:145–156
Shinohara M, Oh SD, Hunter N, Shinohara A (2008) Crossover assurance and crossover interference are distinctly regulated by the ZMM proteins during yeast meiosis. Nat Genet 40:299–309
Sigurdsson S, Van Komen S, Bussen W, Schild D, Albala JS, Sung P (2001) Mediator function of the human Rad51B-Rad51C complex in Rad51/RPA-catalyzed DNA strand exchange. Genes Dev 15:3308–3318
Simsek D, Brunet E, Wong SY, Katyal S, Gao Y, McKinnon PJ, Lou J, Zhang L, Li J, Rebar EJ et al (2011) DNA ligase III promotes alternative nonhomologous end-joining during chromosomal translocation formation. PLoS Genet 7:e1002080
Simsek D, Jasin M (2010) Alternative end-joining is suppressed by the canonical NHEJ component Xrcc4-ligase IV during chromosomal translocation formation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:410–416
Singh TR, Ali AM, Busygina V, Raynard S, Fan Q, Du CH, Andreassen PR, Sung P, Meetei AR (2008) BLAP18/RMI2, a novel OB-fold-containing protein, is an essential component of the Bloom helicase-double Holliday junction dissolvasome. Genes Dev 22:2856–2868
Snowden T, Acharya S, Butz C, Berardini M, Fishel R (2004) hMSH4-hMSH5 recognizes Holliday junctions and forms a meiosis-specific sliding clamp that embraces homologous chromosomes. Mol Cell 15:437–451
Sogo JM, Lopes M, Foiani M (2002) Fork reversal and ssDNA accumulation at stalled replication forks owing to checkpoint defects. Science 297:599–602
Solinger JA, Kiianitsa K, Heyer WD (2002) Rad54, a Swi2/Snf2-like recombinational repair protein, disassembles Rad51:dsDNA filaments. Mol Cell 10:1175–1188
Song B, Sung P (2000) Functional interactions among yeast Rad51 recombinase, Rad52 mediator, and replication protein A in DNA strand exchange. J Biol Chem 275:15895–15904
Sourirajan A, Lichten M (2008) Polo-like kinase Cdc5 drives exit from pachytene during budding yeast meiosis. Genes Dev 22:2627–2632
Stephens PJ, McBride DJ, Lin ML, Varela I, Pleasance ED, Simpson JT, Stebbings LA, Leroy C, Edkins S, Mudie LJ et al (2009) Complex landscapes of somatic rearrangement in human breast cancer genomes. Nature 462:1005–1010
Sturzenegger A, Burdova K, Kanagaraj R, Levikova M, Pinto C, Cejka P, Janscak P (2014) DNA2 cooperates with the WRN and BLM RecQ helicases to mediate long-range DNA end resection in human cells. J Biol Chem 289:27314–27326
Sugiyama T, Zaitseva EM, Kowalczykowski SC (1997) A single-stranded DNA-binding protein is needed for efficient presynaptic complex formation by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51 protein. J Biol Chem 272:7940–7945
Sun H, Treco D, Schultes NP, Szostak JW (1989) Double-strand breaks at an initiation site for meiotic gene conversion. Nature 338:87–90
Sun H, Treco D, Szostak JW (1991) Extensive 3′-overhanging, single-stranded DNA associated with the meiosis-specific double-strand breaks at the ARG4 recombination initiation site. Cell 64:1155–1161
Sung P (1994) Catalysis of ATP-dependent homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange by yeast RAD51 protein. Science 265:1241–1243
Sung P (1997) Yeast Rad55 and Rad57 proteins form a heterodimer that functions with replication protein A to promote DNA strand exchange by Rad51 recombinase. Genes Dev 11:1111–1121
Svendsen JM, Smogorzewska A, Sowa ME, O'Connell BC, Gygi SP, Elledge SJ, Harper JW (2009) Mammalian BTBD12/SLX4 assembles a Holliday junction resolvase and is required for DNA repair. Cell 138:63–77
Sy SM, Huen MS, Chen J (2009) PALB2 is an integral component of the BRCA complex required for homologous recombination repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:7155–7160
Sym M, Roeder GS (1994) Crossover interference is abolished in the absence of a synaptonemal complex protein. Cell 79:283–292
Symington LS, Gautier J (2011) Double-strand break end resection and repair pathway choice. Annu Rev Genet 45:247–271
Szostak JW, Orr-Weaver TL, Rothstein RJ, Stahl FW (1983) The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell 33:25–35
Taglialatela A, Alvarez S, Leuzzi G, Sannino V, Ranjha L, Huang JW, Madubata C, Anand R, Levy B, Rabadan R et al (2017) Restoration of replication fork stability in BRCA1- and BRCA2-deficient cells by inactivation of SNF2-family fork remodelers. Mol Cell 68:414–430
Tan J, Pieper K, Piccoli L, Abdi A, Perez MF, Geiger R, Tully CM, Jarrossay D, Maina Ndungu F, Wambua J et al (2016) A LAIR1 insertion generates broadly reactive antibodies against malaria variant antigens. Nature 529:105–109
Taylor MR, Spirek M, Chaurasiya KR, Ward JD, Carzaniga R, Yu X, Egelman EH, Collinson LM, Rueda D, Krejci L et al (2015) Rad51 paralogs remodel pre-synaptic Rad51 filaments to stimulate homologous recombination. Cell 162:271–286
Taylor MR, Spirek M, Jian Ma C, Carzaniga R, Takaki T, Collinson LM, Greene EC, Krejci L, Boulton SJ (2016) A polar and nucleotide-dependent mechanism of action for RAD51 paralogs in RAD51 filament remodeling. Mol Cell 64:926–939
Thangavel S, Berti M, Levikova M, Pinto C, Gomathinayagam S, Vujanovic M, Zellweger R, Moore H, Lee EH, Hendrickson EA et al (2015) DNA2 drives processing and restart of reversed replication forks in human cells. J Cell Biol 208:545–562
Thorslund T, McIlwraith MJ, Compton SA, Lekomtsev S, Petronczki M, Griffith JD, West SC (2010) The breast cancer tumor suppressor BRCA2 promotes the specific targeting of RAD51 to single-stranded DNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1263–1265
Tran PT, Erdeniz N, Dudley S, Liskay RM (2002) Characterization of nuclease-dependent functions of Exo1p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA Repair (Amst) 1:895–912
Tsai SP, Su GC, Lin SW, Chung CI, Xue X, Dunlop MH, Akamatsu Y, Jasin M, Sung P, Chi P (2012) Rad51 presynaptic filament stabilization function of the mouse Swi5-Sfr1 heterodimeric complex. Nucleic Acids Res 40:6558–6569
Tse YC, Kirkegaard K, Wang JC (1980) Covalent bonds between protein and DNA. Formation of phosphotyrosine linkage between certain DNA topoisomerases and DNA. J Biol Chem 255:5560–5565
Tubbs A, Nussenzweig A (2017) Endogenous DNA damage as a source of genomic instability in cancer. Cell 168:644–656
Uziel T, Lerenthal Y, Moyal L, Andegeko Y, Mittelman L, Shiloh Y (2003) Requirement of the MRN complex for ATM activation by DNA damage. EMBO J 22:5612–5621
Vaisman A, Woodgate R (2017) Translesion DNA polymerases in eukaryotes: what makes them tick? Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 52:274–303
van Mameren J, Modesti M, Kanaar R, Wyman C, Peterman EJ, Wuite GJ (2009) Counting RAD51 proteins disassembling from nucleoprotein filaments under tension. Nature 457:745–748
Veaute X, Jeusset J, Soustelle C, Kowalczykowski SC, Le Cam E, Fabre F (2003) The Srs2 helicase prevents recombination by disrupting Rad51 nucleoprotein filaments. Nature 423:309–312
Vujanovic M, Krietsch J, Raso MC, Terraneo N, Zellweger R, Schmid JA, Taglialatela A, Huang JW, Holland CL, Zwicky K et al (2017) Replication fork slowing and reversal upon DNA damage require PCNA polyubiquitination and ZRANB3 DNA translocase activity. Mol Cell 67:882–890 e885
Wang H, Li Y, Truong LN, Shi LZ, Hwang PY, He J, Do J, Cho MJ, Li H, Negrete A et al (2014) CtIP maintains stability at common fragile sites and inverted repeats by end resection-independent endonuclease activity. Mol Cell 54:1012–1021
Wang M, Wu W, Wu W, Rosidi B, Zhang L, Wang H, Iliakis G (2006) PARP-1 and Ku compete for repair of DNA double strand breaks by distinct NHEJ pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 34:6170–6182
Ward JF (1988) DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: identities, mechanisms of formation, and reparability. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 35:95–125
Wechsler T, Newman S, West SC (2011) Aberrant chromosome morphology in human cells defective for Holliday junction resolution. Nature 471:642–646
Wei K, Clark AB, Wong E, Kane MF, Mazur DJ, Parris T, Kolas NK, Russell R, Hou H Jr, Kneitz B et al (2003) Inactivation of exonuclease 1 in mice results in DNA mismatch repair defects, increased cancer susceptibility, and male and female sterility. Genes Dev 17:603–614
Wilson MA, Kwon Y, Xu Y, Chung WH, Chi P, Niu H, Mayle R, Chen X, Malkova A, Sung P et al (2013) Pif1 helicase and Poldelta promote recombination-coupled DNA synthesis via bubble migration. Nature 502:393–396
Wold MS (1997) Replication protein A: a heterotrimeric, single-stranded DNA-binding protein required for eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem 66:61–92
Wolner B, Peterson CL (2005) ATP-dependent and ATP-independent roles for the Rad54 chromatin remodeling enzyme during recombinational repair of a DNA double strand break. J Biol Chem 280:10855–10860
Wright WD, Heyer WD (2014) Rad54 functions as a heteroduplex DNA pump modulated by its DNA substrates and Rad51 during D loop formation. Mol Cell 53:420–432
Wu L, Hickson ID (2003) The Bloom’s syndrome helicase suppresses crossing over during homologous recombination. Nature 426:870–874
Wyatt HD, Laister RC, Martin SR, Arrowsmith CH, West SC (2017) The SMX DNA repair tri-nuclease. Mol Cell 65:848–860 e811
Wyatt HD, Sarbajna S, Matos J, West SC (2013) Coordinated actions of SLX1-SLX4 and MUS81-EME1 for Holliday junction resolution in human cells. Mol Cell 52:234–247
Xie A, Kwok A, Scully R (2009) Role of mammalian Mre11 in classical and alternative nonhomologous end joining. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:814–818
Xue X, Raynard S, Busygina V, Singh AK, Sung P (2013) Role of replication protein A in double holliday junction dissolution mediated by the BLM-Topo IIIalpha-RMI1-RMI2 protein complex. J Biol Chem 288:14221–14227
Yabuki M, Fujii MM, Maizels N (2005) The MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex accelerates somatic hypermutation and gene conversion of immunoglobulin variable regions. Nat Immunol 6:730–736
Yang H, Jeffrey PD, Miller J, Kinnucan E, Sun Y, Thoma NH, Zheng N, Chen PL, Lee WH, Pavletich NP (2002) BRCA2 function in DNA binding and recombination from a BRCA2-DSS1-ssDNA structure. Science 297:1837–1848
Yang H, Li Q, Fan J, Holloman WK, Pavletich NP (2005) The BRCA2 homologue Brh2 nucleates RAD51 filament formation at a dsDNA-ssDNA junction. Nature 433:653–657
Yildiz O, Majumder S, Kramer B, Sekelsky JJ (2002) Drosophila MUS312 interacts with the nucleotide excision repair endonuclease MEI-9 to generate meiotic crossovers. Mol Cell 10:1503–1509
Yuan SS, Lee SY, Chen G, Song M, Tomlinson GE, Lee EY (1999) BRCA2 is required for ionizing radiation-induced assembly of Rad51 complex in vivo. Cancer Res 59:3547–3551
Zadorozhny K, Sannino V, Belan O, Mlcouskova J, Spirek M, Costanzo V, Krejci L (2017) Fanconi-anemia-associated mutations destabilize RAD51 filaments and impair replication fork protection. Cell Rep 21:333–340
Zahn A, Eranki AK, Patenaude AM, Methot SP, Fifield H, Cortizas EM, Foster P, Imai K, Durandy A, Larijani M et al (2014) Activation induced deaminase C-terminal domain links DNA breaks to end protection and repair during class switch recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E988–E997
Zaitseva EM, Zaitsev EN, Kowalczykowski SC (1999) The DNA binding properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51 protein. J Biol Chem 274:2907–2915
Zakharyevich K, Ma Y, Tang S, Hwang PY, Boiteux S, Hunter N (2010) Temporally and biochemically distinct activities of Exo1 during meiosis: double-strand break resection and resolution of double Holliday junctions. Mol Cell 40:1001–1015
Zakharyevich K, Tang S, Ma Y, Hunter N (2012) Delineation of joint molecule resolution pathways in meiosis identifies a crossover-specific resolvase. Cell 149:334–347
Zan H, Wu X, Komori A, Holloman WK, Casali P (2003) AID-dependent generation of resected double-strand DNA breaks and recruitment of Rad52/Rad51 in somatic hypermutation. Immunity 18:727–738
Zelensky AN, Schimmel J, Kool H, Kanaar R, Tijsterman M (2017) Inactivation of Pol theta and C-NHEJ eliminates off-target integration of exogenous DNA. Nat Commun 8:66
Zellweger R, Dalcher D, Mutreja K, Berti M, Schmid JA, Herrador R, Vindigni A, Lopes M (2015) Rad51-mediated replication fork reversal is a global response to genotoxic treatments in human cells. J Cell Biol 208:563–579
Zhang L, Wang S, Yin S, Hong S, Kim KP, Kleckner N (2014) Topoisomerase II mediates meiotic crossover interference. Nature 511:551–556
Zhang Y, Hefferin ML, Chen L, Shim EY, Tseng HM, Kwon Y, Sung P, Lee SE, Tomkinson AE (2007) Role of Dnl4-Lif1 in nonhomologous end-joining repair complex assembly and suppression of homologous recombination. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:639–646
Zhang Y, Jasin M (2011) An essential role for CtIP in chromosomal translocation formation through an alternative end-joining pathway. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:80–84
Zhao W, Steinfeld JB, Liang F, Chen X, Maranon DG, Jian Ma C, Kwon Y, Rao T, Wang W, Sheng C et al (2017) BRCA1-BARD1 promotes RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing. Nature 550:360–365
Zhao W, Vaithiyalingam S, San Filippo J, Maranon DG, Jimenez-Sainz J, Fontenay GV, Kwon Y, Leung SG, Lu L, Jensen RB et al (2015) Promotion of BRCA2-dependent homologous recombination by DSS1 via RPA targeting and DNA mimicry. Mol Cell 59:176–187
Zhu Z, Chung WH, Shim EY, Lee SE, Ira G (2008) Sgs1 helicase and two nucleases Dna2 and Exo1 resect DNA double-strand break ends. Cell 134:981–994
Zou L, Elledge SJ (2003) Sensing DNA damage through ATRIP recognition of RPA-ssDNA complexes. Science 300:1542–1548
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the members of the Cejka Laboratory (IRB Bellinzona), Massimo Lopes (University of Zurich), and Kathrin Pieper (Lanzavecchia Laboratory, IRB Bellinzona) for comments on the manuscript. We apologize to colleagues whose work could not be cited due to length constraint.
Funding
The work was supported by grants from the European Research Council (681630) and the Swiss National Science Foundation (31003A_175444) to P.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain studies involving animals or human participants by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjha, L., Howard, S. & Cejka, P. Main steps in DNA double-strand break repair: an introduction to homologous recombination and related processes. Chromosoma 127, 187–214 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-017-0658-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-017-0658-1