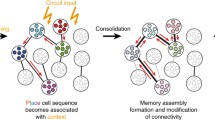
Abstract
Donald Hebb’s concept of cell assemblies is a physiology-based idea for a distributed neural representation of behaviorally relevant objects, concepts, or constellations. In the late 70s Valentino Braitenberg started the endeavor to spell out the hypothesis that the cerebral cortex is the structure where cell assemblies are formed, maintained and used, in terms of neuroanatomy (which was his main concern) and also neurophysiology. This endeavor has been carried on over the last 30 years corroborating most of his findings and interpretations. This paper summarizes the present state of cell assembly theory, realized in a network of associative memories, and of the anatomical evidence for its location in the cerebral cortex.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles M (1982) Local cortical circuits: an electrophysiological study. Springer, Berlin
Abeles M (1988) Neural codes for higher brain functions. In: Markowitsch HJ (ed) Information processing by the brain. Hans Huber Pub, Toronto, pp 225–238
Abeles M (1991) Corticonics: neural circuits of the cerebral cortex. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Abeles M, Bergman H, Gat I, Meilijson I, Seidemann E, Tishby N, Vaadia E (1995) Cortical activity flips among quasi stationary states. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8616–8620
Aertsen A (ed) (1993) Brain theory. Spatio-temporal aspects of brain function, Elsevier, Amsterdam
Amir Y, Harel M, Malach R (1993) Cortical hierarchy reflected in the organization of intrinsic connections in macaque monkey visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 334:19–46
Amit D (1989) Modeling brain function: the world of attractor neural networks. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Anderson JR et al (2004) An integrated theory of mind. Psychol Rev 111:1036–1060
Bär TH (1977) Wirkung chronischer hypoxie auf die postnatale synaptogenese im occipitalcortex der ratte. Verh Anat Ges 71:915– 924
Baillarger JGF (1840) Recherches sur la structure de la couche corticale des circonvolutions du cerveau. Mém de l’Acad royale médécine 8:149–183
Bair W, Koch C (1996) Temporal precision of spike trains in extrastriate cortex of the behaving macaque monkey. Neural Comput 8:1185–1202
Bakker R, Wachtler T, Diesmann M (2012) CoCoMac 2.0 and the future of tract-tracing databases. Front Neuroinf 6:30
Bi G, Poo MM (1998) Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: Dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type. J Neurosci 18(24):10464–10472
Bienenstock E (1995) A model of neocortex. Netw Comput Neural Syst 6:179–224
Binzegger T, Douglas RJ, Martin KAC (2004) A quantitative map of the circuit of cat primary visual cortex. J Neurosci 24(39): 8441–8453
Binzegger T, Douglas RJ, Nartin KAC (2007) Stereotypical bouton clustering of individual neurons in cat primary visual cortex. J Neurosci 27(45):12242–12254
Blakemore C, Cooper GF (1971) Modification of the visual cortex by experience. Brain Res 31:366
Bock NA, Hashim E, Janik R, Konyer NB, Weiss M, Stanisz GJ, Turner R, Geyer S (2013) Optimizing T1-weighted imaging of cortical myelin content at 3.0 T. NeuroImage 65:1–12
Bouchain DA, Palm G (2012) Neural coding in graphs of bidirectional associative memories. Brain Res 1434:189–199. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.09.050
Braitenberg V (1962) A note on myeloarchitectonics. J Comp Neurol 118:141–156
Braitenberg V (1978) Cell assemblies in the cerebral cortex. In: Heim R, Palm G (eds) Proceedings Symposium on theoretical approaches to complex systems 1977. Lecture notes in biomathematics 21, Springer, Berlin, pp 171–188
Braitenberg V, Schüz A (1991) Cortex: statistics and geometry of neuronal connectivity. Springer, Berlin
Braitenberg V, Schüz A (1998) Cortex: statistics and geometry. Revised edition of “Anatomy of the cortex: statistics and geometry” (1991) Springer, Berlin
Brodal P (2010) The central nervous system. Oxford University Press, Oxford, Structure and function
Burns B, Webb AC (1976) The spontaneous activity of neurones in the cat’s cerebral cortex. Proc R Soc London B 194:211–223
Carporale N, Dan Y (2008) Spike timing-dependent plasticity: a Hebbian learning rule. Annu Rev Neurosci 31:25–46
Cauller L (1995) Layer I of primary sensory neocortex: where top–down converges upon bottom–up. Behav Brain Res 71:163–170
Clopath C, Busing L, Vasilaki E, Gerstner W (2010) Connectivity reflects coding: a model of voltage-based STDP with homeostasis. Nature Neurosci 13(3):344–352
Colonnier M (1968) Synaptic patterns on different cell types in the different laminae of the cat visual cortex. An electron microscope study. Brain Res 9:268–287
Dantzker JL, Callaway EM (2000) Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory neurons and pyramidal neurons. Nat Neurosci 3(7):701–707
DeFelipe J, Alonso-Nanclares L, Arellano JI (2002) Microstructure of the neocortex: comparative aspects. J Neurocytol 31:299–316
Edelman GM, Tononi G (2000) A Universe of consciousness. How matter becomes imagination. Basic Books, New York
Eliasmith Ch (2013) How to build a brain: a neural architecture for biological cognition. Oxford University Press, New York
Evans EF (1968) Upper and lower levels of the auditory system: a contrast of structure and function. In: Caianiello ER (ed) Neural networks. Springer, Berlin, pp 24–33
Froemke RC, Dan Y (2002) Spike-timing-dependent synaptic modification induced by natural spike trains. Nature 416:433–438
Gennari F (1782) De peculiari structura cerebri nonnullisque ejus morbis. Parma
George D, Hawkins J (2009) Towards a mathematical theory of cortical micro-circuits. PLoS Comput Biol 5(10)
Gerstner W, Ritz R, van Hemmen JL (1993) Why spikes? Hebbian learning and retrieval of time-resolved excitation patterns. Biol Cybern 69:503–515
Girard P, Hupe JM, Bullier J (2001) Feedforward and feedback connections between areas V1 and V2 of the monkey have similar rapid conduction velocities. J Neurophysiol 85:1328–1331
Gray EG (1959) Electron microscopy of synaptic contacts on dendrite spines of the cerebral cortex. Nature 183:1592–1593
Grossberg S (1976a) Adaptive pattern classification and universal recording: I. Parallel development and coding of neural feature detectors. Biol Cybern 23:121–134
Grossberg S (1976b) Adaptive pattern classification and universal recording: II. Feedback, expectation, olfaction, and illusions. Biol Cybern 23:187–202
Grossberg S (1982) Studies of mind and brain. Reidel, Boston
Grossberg S (1999) How does the cerebral cortex work? learning, attention and grouping by the laminar cirscuits of visual cortex. Spat Vis 12:163–186
Hauser F, Palm G, Bouchain D (2009) Coexistence of cell assemblies and STDP. In: Polycerpou Ch, Panayiotou G, Ellinas G (eds) Artificial neural networks - ICANN 2009, Part I. LNCS 5768. Springer, Berlin, pp 191–197
Hauser F, Bouchain D, Palm G (2010) Simple constraints for zero-lag synchronous oscillations under STDP. In: Diamantaras K, Duch W, Iliadis LS (eds). ICANN 2010, Part I. LNCS 6352, Springer, Berlin, 311–316
Hauser F (2012) Formation and stability of spiking cell assemblies with spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Dissertation, University of Ulm
Hawkins J, Blakeslee S (2004) On intelligence. Times Books, Henry Holt and Company, New York
Hebb DO (1949) The organization of behaviour. Wiley, New York
Hecht-Nielsen R (2007) Confabulation theory. The mechanism of thought. Springer, Berlin
Hellwig B (1993) How the myelin picture of the human cortex can be computed from cytoarchitectural data. A bridge between von economo and vogt. J Hirnforsch 34:387–402
Herz A, Creutzfeldt O, Fuster J (1964) Statistische eigenschaften der neuronaktivität im ascendierenden visuellen system. Kybernetik 2:61–71
Hirsch HVB, Spinelli DN (1971) Modification of the distribution of receptive field orientation in cats by selective visual exposure during development. Exp Brain Res 13:1–43
Hopcroft JE, Ullman JD (1979) Introducion to automata theory, languages and computation. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Houser CR, Vaughan JE, Hendry SHC, Jones EG, Peters A (1984) GABA neurons in the cerebral cortex. In: Jones EG, Peters A (eds) Cerebral Cortex, vol 2., Functional properties of cortical cellsPlenum Press New York, London, pp 63–89
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1959) Receptive fields of single neurons in the cat’s striate cortex. J Physiol 148:574–591
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1965) Binocular interaction in striate cortex of kittens reared with artificial squint. J Neurophysiol 28:1041– 1059
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1974) Uniformity of monkey striate cortex: a parallel relationship between field size, scatter, and magnification factor. J Comp Neurol 158:295–306
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1977) Functional architecture of macaque monkey visual cortex. Ferrier lecture. Proc R Soc Lond B 198:1–59
Humble J, Denham S, Wennekers Th (2012) Spatio-temporal pattern recognizers using spiking neurons and spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Front Comput Neurosci 6(84). doi:10.3389/fncom.2012.00084
Huyck CR, Passmore PJ (2013) A review of cell assemblies. Biol Cybern. doi:10.1007/s00422-013-0555-5
Izhikevich E (2006) Polychronization: computation with spikes. Neural Comput 18:245–282
Izhikevich EM, Hoppensteadt FC (2009) Polychronous wavefront computations. Int J of Bifurcation and Chaos 19(5):1733–1739
Jones EG (1985) The thalamus. Plenum Press, New York
Kampa BM, Stuart GJ (2006) Calcium spikes in basal dendrites of layer 5 pyramidal neurons during action potential bursts. J Neurosci 26(28):7424–7432
Kara Kayikci Z, Palm G (2008) Word recognition and incremental learning based on neural associative memories and hidden Markov models. In: Proceedings 16th europe symposium on artificial neural networks, pp 119–124
Kenet T, Bibitchkov D, Tsodyks M, Grinvald A, Arieli A (2003) Spontaneously emerging cortical representations of visual attributes. Nature 425:954–956
Kerr JND, Denk W (2008) Imaging in vivo: watching the brain in action. Nat Rev 9:195–205
Kiefer M, Pulvermüller F (2012) Conceptual representations in mind and brain: theoretical developments, current evidence and future directions. Cortex 48:805–825
Kleene SC (1956) Representation of events in nerve nets and finite automata. In: Shannon CE, McCarthy J (eds) Automata studies. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 3–42
Knoblauch A, Palm G (2001) Pattern separation and synchronization in spiking associative memories and visual areas. Neural Netw 14:763–780
Knoblauch A, Palm G (2002a) Scene segmentation by spike synchronization in reciprocally connected visual areas. I. Local effects of cortical feedback. Biol Cybern 87:151–167
Knoblauch A, Palm G (2002b) Scene segmentation by spike synchronization in reciprocally connected visual areas. II. Global assemblies and synchronization on a larger space and time scales. Biol Cybern 87:168–184
Knoblauch A, Sommer F (2003) Synaptic plasticity, conduction delays, and inter-areal phase relations of spike activity in a model of reciprocally connected areas. Neurocomputing 52–54:301–306
Knoblauch A, Sommer F (2004) Spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity can form “zero lag” links for cortical oscillations. Neurocomputing 58–60:185–190
Knoblauch A, Fay R, Kaufmann U, Markert H, Palm G (2004) Associating words to visually recognized objects. In: Coradeschi S, Saffiotti A (eds.) Anchoring symbols to sensor data. Papers from the AAAI Workshop. Technical Report WS-04-03, AAAI Press, Menlo Park, California, pp 10–16
Knoblauch A, Palm G (2005) What is signal and what is noise in the brain? Biosystems 79(1–3):83–90
Knoblauch A, Markert, H, Palm G (2005a): An associative cortical model of language understanding and action planning. In: Mira J, Alvarez JR (eds.) Artificial Intelligence and knowledge engineering applications: A bioinspired approach. Lecture notes in computer science, LNCS 3562, Springer, Berlin, pp 405–414
Knoblauch A, Markert H, Palm G (2005b) An associative model of cortical language and action processing. In: Cangelosi A, Bugmann G, Borisyuk R (eds) Modeling language, cognition and action. Proceedings of 9th neural computation and psycholog workshop NCPW9, World Scientific, pp 79–83
Knoblauch A, Kupper R, Gewaltig MO, Körner U, Körner E (2007) A cell assembly based model for the cortical microcircuitry. Neurocomputing 70:1838–1842
Knoblauch A, Palm G, Sommer FT (2010) Memory capacities for synaptic and structural plasticity. Neural Comput 22(2):289– 341
Knoblauch A (2011) Neural associative memory with optimal Bayesian learning. Neural Computation 23:1393–1451
Knoblauch A, Hauser F, Gewaltig M, Körner E, Palm G (2012) Does spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity couple or decouple neurons firing in synchrony? Front Comput Neurosci 6, article 55. doi:10.3389/fncom.2012.00055.
Kötter R (2004) Online retrieval, processing, and visualization of primate connectivity data from the CoCoMac database. Neuroinformatics 2:127–144
Kozloski J, Cecchi G (2008) Topological effects of synaptic spike timing-dependent plasticity. http://arxiv.org/abs/0810.0029
Kozloski J, Cecchi G (2010) A theory of loop formation and elimination by spike timing-dependent plasticity. Frontiers in Neural Circuits 4(7):1–11
Krone G, Mallot H, Palm G, Schüz A (1986) Spatio-temporal receptive fields: a dynamical model derived from cortical architectonics. Proc R Soc London B 226:421–444
Lansner A (2009) Associative memory models: from the cell-assembly theory to biophysically detailed cortex simulations. J TINS 32(3):178–186. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2008.12.002
Legéndy CR (1967) On the scheme by which the human brain stores Information. Math Biosci 1:55
Legéndy CR (1975) Three principles of brain function and structure. Int J Neursci 6:237
Levitt J, Lund J (2002) Intrinsic connections in mammalian cerebral cortex. In: Schüz A, Miller R (eds) Cortical areas: unity and diversity. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 133–154
Levy N, Horn D, Meilijson I, Ruppin E (2001) Distributed synchrony in a cell assembly of spiking neurons. Neural Netw 14:815–824
Liu X, Ramirez S, Pang PT, Puryear CB, Govindarajan A, Deisseroth K, Tonegawa S (2012) Optogenetic stimulation of a hippocampal engram activates fear memory recall. Nature 484:381–387. doi:10.1038/nature11028
Lubenov E, Siapas A (2008) Decoupling through synchrony in neuronal circuits with propagation delays. Neuron 58:118–131
Markert H, Knoblauch A, Palm G (2005) Detecting sequences and understanding language with neural associative memories and cell assemblies. In: Wermter S, Palm G, Elshaw M (eds) Biomimetic neural learning for intelligent robots. LNAI 3575, Springer, Berlin, pp 107–117
Markert H, Palm G (2006) An approach to language understanding and contextual disambiguation in human-robot interaction. In: Proc. ECAI International Workshop on Neural-Symbolic Learningand Reasoning (NeSy 2006), pp 23–35.
Markert H, Knoblauch A, Palm G (2007) Modelling of syntactical processing in the cortex. BioSystems 89:300–315
Markert H, Kayikci ZK, Palm G (2008) Sentence understanding and learning of new words with large-scale neural networks. In: Prevost L, Marinai S, Schwenker F (eds) Artificial Neural Networks in Pattern Recognition (ANNPR 2008). LNAI 5064. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 217–227
Markert H, Kaufmann U, Palm G (2009) Neural associative memories for the integration of language, vision and action in an autonomous agent. Neural Netw 22:134–143
Markram H, Lübke J, Frotscher M, Sakman B (1997) Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 275:213–215
Marr D (1969) A Theory of cerebellar cortex. J Physiol 202:437
Marr D (1970) A theory of cerebellar neocortex. Proc R Soc London Ser B 176:161
Marr D (1971) Simple memory. Philos Trans R Soc London Ser B 262:23
McCulloch WS, Pitts W (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5:115
Miles R, Wong RKS (1986) Excitatory synaptic interactions between CA3 neurones in the Guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol 373:397–418
Miller R (1996) Cortico-thalamic interplay and the security of operation of neural assemblies and temporal chains in the cerebral cortex. Biol Cybern 75:263–275
Miller R (2000) Time and the brain. Taylor and Francis.
Morrison A, Aertsen A, Diesmann M (2007) Spike-timing-dependent plasticity in balanced random networks. Neural Comput 19:1437–1467
Nieuwenhuys R (2013) The myeloarchitectonic studies on the human cerebral cortex of the Vogt-Vogt school, and their significance for the interpretation of functional neuroimaging data. Brain Struct Funct 218:303–352
Palm G (1980) On associative memory. Biol Cybern 36:19–31
Palm G (1981) Towards a theory of cell assemblies. Biol Cybern 39:181–194
Palm G (1982a) Neural assemblies. An alternative approach to artificial intelligence. Springer, Berlin
Palm G (1982b) Rules for synaptic changes and their relevance for the storage of information in the brain. In: Trappl R (ed) Cybernetics and systems research. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam
Palm G, Aertsen A (eds) (1986) Brain theory. Springer, Berlin
Palm G (1987a) On associative memories. In: Caianiello ER (ed) Physics of cognitive processes. World Scientific Publishers, Singapore, pp 380–422
Palm G (1987b) Associative memory and threshold control in neural networks. In: Casti JL, Karlqvist A (eds) Real brains -artificial minds. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Palm G (1990a) Cell assemblies as a guideline for brain research. Concepts Neurosci 1:133–148
Palm G (1990b) Local learning rules and sparse coding in neural networks. In: Eckmiller R (ed) Advanced neural computers. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Palm G, Sommer FT (1992) Information capacity in recurrent McCulloch-Pitts networks with sparsely coded memory states. Network 3:177–186
Palm G (1993a) On the internal structure of cell assemblies. In: Aersten A (ed) Brain theory. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 261–270
Palm G (1993b) Cell assemblies, coherence and cortico-hippocampal interplay. Special Issue Nitsch R, Ohm TG (eds), Hippocampus 3(1):219–225
Palm G, Schwenker F, Sommer F (1994) Associative memory networks and sparse similarity preserving codes. In: Cherkassky V, Friedman JH, Wechsler H (eds) From statistics to neural networks: theory and pattern recognition applications. NATO-ASI Series F. Springer, Berlin, pp 283–302
Palm G (2013) Neural associative memories and sparse coding. Neural Netw 37:165–171. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2012.08.013
Peters A, Feldman ML (1976) The projection of the lateral geniculate nucleus to area I. General description. J Neurocytol 5: 63–84
Pfister JP, Gerstner W (2006) Triplets of spikes in a model of spike timing-dependent plasticity. J Neurosci 26(38):9673–9682
Picado-Muino D, Borgelt Ch, Berger D, Gerstein G, Grün S (2013) Finding neural assemblies with frequent item set mining. Front Neuroinf 7(9)10.3389/fninf.2013.00009
Poort J, Raudies F, Wanning A, Lamme VAF, Neumann H, Roelfsema PR (2012) Neuron 75:143–156. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.032
Potjans TC, Diesmann M (2012) The cell-type specific microcircuit: relating structure and activity in a full-scale spiking network model. Cerebral Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs358
Pulvermüller F (2002) The neuroscience of language. On brain circuits of words and serial order. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rao RP., Ballard DH (1999) Predictive coding in the visual cortex: a functional interpretation of some extra-classical receptive-field effects. Nature
Rao RP (2005) Hierarchical Bayesian inference in networks of spiking neurons. In: Saul IK, Weiss Y, Bottou L (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems.17. MIT Press, Cambridge
Raudies F, Neumann H (2010) A neural model of the temporal dynamics of figure-ground segregation in motion perception. Neural Netw 23:160–176. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2009.10.005
Renart A, de la Rocha J, Bartho P, Hollender L, Parga N, Reyes A, Harris KD (2010) The asynchronous state in cortical circuits. Science 327:587–590
Rockland KS (2004) Feedback connections: splitting the arrow. In: Kaas J, Collins EC (eds) The primate visual system. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 387–405
Rockland KS, Pandya DN (1979) Laminar origins and terminations of cortical connections of the occipital lobe in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 179:3–20
Rockland KS, Virga A (1989) Terminal arbors of individual “feedback” axons projecting from area V2 to V1 in the macaque monkey: a study using immunohistochemistry of anterogradely transported phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol 285(1):54–72
Russel SJ, Narvig P (2003) Artificial intelligence: a modern approach. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Scannell JW, Blakemore C, Young MP (1995) Analysis of connectivity in the cat cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 15(2):1463–1483
Schüz A, Palm G (1989) Density of neurons and synapses in the cerebral cortex of the mouse. J Comp Neurol 286:442–455
Schüz A, Braitenberg V (2002) The human cortical white matter: quantitative aspects of cortico-cortical long-range connectivity. In: Schüz A, Miller R (eds) Cortical areas: unity and diversity. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 377–385
Schüz A, Chaimow D, Liewald D, Dortenmann M (2006) Quantitative aspects of corticocortical connecctions: a tracer study in the mouse. Cerebral Cortex 16:1474–1486. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj085
Schultz W, Dayan P, Montague PR (1997) A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275:1593–1599
Schultz W (2002) Getting formal with dopamine and reward. Neuron 36:241–263
Schwenker F, Sommer FT, Palm G (1996) Iterative retrieval of sparsely coded associative memory patterns. Neural Netw 9(3):445–455
Sherman SM (2007) The thalamus is more than just a relay. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17:417–422
Shtyrov Y, Smith M, Horner AJ, Henson R, Nathan PJ, Bullmore ET, Pulvermüller F (2012) Attention to language: novel MEG paradigm for registering involuntary language processing in the brain. Neuropsychologia. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.07.012
Softky W (1995) Simple codes versus efficient codes. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5:239–247
Spruston N (2008) Pyramidal neurons: dendritic structure and synaptic integration. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:206–221
Spruston N (2009) Pyramidal neuron. Scholarpedia 4(5):6130
Stepanyants A, Chklovskii DB (2005) Neurogeometry and potential synaptic connectivity. TINS 28(7):387–394
Stepanyants A, Hirsch JA, Martinez LM, Kisvárday ZF, Ferecskó AS, Chklovskii DB (2008) Local potential connectivity in cat primary visual cortex. Cerebral Cortex 18:13–28. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm027
Stephan KE, Kamper L, Bozkurt A, Burns GA, Young MP, Kötter R (2001) Advanced database methodology for the collation of connectivity data on the macaque brain (CoCoMac). Philos Trans R Soc London B Biol Sci 356:1159–1186
Sutton RS, Barto AG (1998) Reinforcement learning: an introduction. The MIT Press, Cambridge
Szatmáry B, Izhikevich EM (2010) Spike-timing theory of working memory. PLoS Comput Biol 6(8):e1000879. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000879
Thomson AM, Deuschars J (1994) Temporal and spatial properties of local circuits in neocortex. TINS 17(1):119–126
Thorpe S, Fize D, Marlot C (1996) Speed of processing in the human visual system. Nature 381:520–522
Turing AM (1936) On computable numbers with an application to the Entscheidungsproblem. Proc of the London Math Soc 2, 42:230–265, 43:544–546
Uchizono K (1965) Characteristics of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the central nervous system of the cat. Nature 207:642–643
Van Rullen R, Thorpe SJ (2001) The time course of visual processing: from early perception to decision-making. J Cogn Neurosci 13(4):454–461
Voges N, Schüz A, Aertsen A, Rotter S (2010) A modeler’s view on the spatial structure of intrinsic horizontal connectivity in the neocortex. Progr in Neurobiol 92:277–292
Vogt C, Vogt O (1919) Allgemeinere Ergebnisse unserer Hirnforschung. J Psychol Neurol 25:279–468
Wallace DJ, Kerr JND (2010) Chasing the cell assembly. Curr Opin Neurobiol 20:296–305
Waydo S, Kraskov A, Quiroga R, Fried I, Koch C (2006) Sparse representation in the human medial temporal lobe. J Neurosci 26(40):10232–10234
Weidenbacher U, Neumann H (2009) Extraction of surface-related features in a recurrent model of V1–V2 interactions. PLoS ONE 4(6):e5909
Wennekers Th, Sommer FT, Palm G (1995) Iterative retrieval in associative memories by threshold control of different neural models. In: Hermann HJ (ed) Proceedings of the workshop on supercomputers in brain research. World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore
Wennekers Th, Palm G (1996) Controlling the speed of synfire chains. In: von der Malsburg C et al. (eds) Artificial neural networks - ICANN 96. Proceedings international conference, Bochum, July 1996. LNCS 1112, Springer, Berlin, pp 451–456
Wennekers Th (1998) Synfire graphs: from spike patterns to automata of spiking neurons. UIB-1998–08
Wennekers Th, Palm G (1999) How imprecise is neuronal synchronization? Neurocomputing 26–27:579–585
Wennekers Th (2006) Operational cell assemblies as a paradigm for brain-inspired future computing architectures. Neural Inf Process Lett Rev 10(4–6):135–145
Wennekers Th, Palm G (2007) Modelling generic cognitive functions with operational Hebbian cell assemblies. In: Weiss ML (ed) Neural network research horizons. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge
Wennekers Th, Palm G (2009) Syntactic sequencing in Hebbian cell assemblies. Cogn Neurodyn 3(4):429–441. doi:10.1007/s11571-009-9095-z
White EL (1989) Cortical circuits, synaptic organization of the cerebral cortex. Structure, function, and theory. Birkhäuser, Boston
Winston PH (1984) Artificial intelligence. Addison-Wesley, Boston
Wiesel TN, Hubel DH (1965) Comparison of the effects of unilateral and bilateral eye closure on cortical unit responses in kittens. J Neurophysiol 28:1029–1040
Wolff JR (1976) Quantitative analysis of topography and development of synapses in the visual cortex. Exp Brain Res Suppl 1:259–263
Yen S, Baker J, Gray C (2007) Heterogeneity in the responses of adjacent neurons to natural stimuli in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol 97:1326–1341
Young MP, Scannell JW, Burns GACP (1995) The analysis of cortical connectivity. Springer, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article forms part of a special issue of Biological Cybernetics entitled “Structural Aspects of Biological Cybernetics: Valentino Braitenberg, Neuroanatomy, and Brain Function”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palm, G., Knoblauch, A., Hauser, F. et al. Cell assemblies in the cerebral cortex. Biol Cybern 108, 559–572 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-014-0596-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-014-0596-4