Abstract
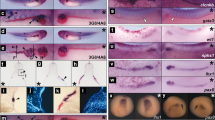
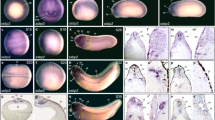
Endocytic receptors in the proximal tubule of the mammalian kidney are responsible for the reuptake of numerous ligands, including lipoproteins, sterols, vitamin-binding proteins, and hormones, and they can mediate drug-induced nephrotoxicity. In this paper, we report the first evidence indicating that the pronephric kidneys of Xenopus tadpoles are capable of endocytic transport. We establish that the Xenopus genome harbors genes for the known three endocytic receptors megalin/LRP2, cubilin, and amnionless. The Xenopus endocytic receptor genes share extensive synteny with their mammalian counterparts. In situ hybridizations demonstrated that endocytic receptor expression is highly tissue specific, primarily in the pronephric kidney, and did not occur prior to neurulation. Expression was strictly confined to proximal tubules of the pronephric kidney, which closely resembles the situation reported in mammalian kidneys. By immunohistochemistry, we demonstrated that Xenopus pronephric tubule epithelia express high amounts of the endocytic receptors megalin/lrp2 and cubilin in the apical plasma membrane. Furthermore, functional aspects of the endocytic receptors were revealed by the vesicular localization of retinol-binding protein in the proximal tubules, probably representing endocytosed protein. In summary, we provide here the first comprehensive report of endocytic receptor expression, including amnionless, in a nonmammalian species. Remarkably, renal endocytic receptor expression and function in the Xenopus pronephric kidney closely mirrors the situation in the mammalian kidney. The Xenopus pronephric kidney therefore represents a novel, simple model for physiological studies on the molecular mechanisms underlying renal tubular endocytosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saxén L (1987) Organogenesis of the kidney. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Brändli AW (1999) Towards a molecular anatomy of the Xenopus pronephric kidney. Int J Dev Biol 43:381–395
Vize PD, Seufert DW, Carroll TJ, Wallingford JB (1997) Model systems for the study of kidney development: use of the pronephros in the analysis of organ induction and patterning. Dev Biol 188:189–204
Brändli AW (2004) Prospects for the Xenopus embryo model in therapeutics technologies. Chimia 58:695–702
Jones EA (2005) Xenopus: a prince among models for pronephric kidney development. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:313–321
McLaughlin KA, Rones MS, Mercola M (2000) Notch regulates cell fate in the developing pronephros. Dev Biol 227:567–580
Reggiani L, Raciti D, Airik R, Kispert A, Brändli AW (2007) The prepattern transcription factor Irx3 directs nephron segment identity. Genes Dev 21:2358–2370
Saulnier DM, Ghanbari H, Brändli AW (2002) Essential function of Wnt-4 for tubulogenesis in the Xenopus pronephric kidney. Dev Biol 248:13–28
Tran U, Pickney LM, Ozpolat BD, Wessely O (2007) Xenopus Bicaudal-C is required for the differentiation of the amphibian pronephros. Dev Biol 307:152–164
Urban AE, Zhou X, Ungos JM, Raible DW, Altmann CR, Vize PD (2006) FGF is essential for both condensation and mesenchymal–epithelial transition stages of pronephric kidney tubule development. Dev Biol 297:103–117
Howland RB (1916) On the effect of removal of the pronephros of the amphibian embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2:231–234
Christensen EI, Birn H (2002) Megalin and cubilin: multifunctional endocytic receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:256–266
Anzenberger U, Bit-Avragim N, Rohr S, Rudolph F, Dehmel B, Willnow TE, Abdelilah-Seyfried S (2006) Elucidation of megalin/LRP2-dependent endocytic transport processes in the larval zebrafish pronephros. J Cell Sci 119:2127–2137
Christensen EI, Willnow TE (1999) Essential role of megalin in renal proximal tubule for vitamin homeostasis. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2224–2236
Nykjaer A, Dragun D, Walther D, Vorum H, Jacobsen C, Herz J, Melsen F, Christensen EI, Willnow TE (1999) An endocytic pathway essential for renal uptake and activation of the steroid 25-(OH) vitamin D3. Cell 96:507–515
Nykjaer A, Fyfe JC, Kozyraki R, Leheste JR, Jacobsen C, Nielsen MS, Verroust PJ, Aminoff M, de la Chapelle A, Moestrup SK, Ray R, Gliemann J, Willnow TE, Christensen EI (2001) Cubilin dysfunction causes abnormal metabolism of the steroid hormone 25(OH) vitamin D(3). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13895–13900
Birn H, Verroust PJ, Nexo E, Hager H, Jacobsen C, Christensen EI, Moestrup SK (1997) Characterization of an epithelial approximately 460-kDa protein that facilitates endocytosis of intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 and binds receptor-associated protein. J Biol Chem 272:26497–26504
Kozyraki R, Fyfe J, Verroust PJ, Jacobsen C, Dautry-Varsat A, Gburek J, Willnow TE, Christensen EI, Moestrup SK (2001) Megalin-dependent cubilin-mediated endocytosis is a major pathway for the apical uptake of transferrin in polarized epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12491–12496
Birn H, Vorum H, Verroust PJ, Moestrup SK, Christensen EI (2000) Receptor-associated protein is important for normal processing of megalin in kidney proximal tubules. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:191–202
Cui S, Verroust PJ, Moestrup SK, Christensen EI (1996) Megalin/gp330 mediates uptake of albumin in renal proximal tubule. Am J Physiol 271:F900–F907
Zhai XY, Nielsen R, Birn H, Drumm K, Mildenberger S, Freudinger R, Moestrup SK, Verroust PJ, Christensen EI, Gekle M (2000) Cubilin- and megalin-mediated uptake of albumin in cultured proximal tubule cells of opossum kidney. Kidney Int 58:1523–1533
Moestrup SK, Cui S, Vorum H, Bregengard C, Bjorn SE, Norris K, Gliemann J, Christensen EI (1995) Evidence that epithelial glycoprotein 330/megalin mediates uptake of polybasic drugs. J Clin Invest 96:1404–1413
Schmitz C, Hilpert J, Jacobsen C, Boensch C, Christensen EI, Luft FC, Willnow TE (2002) Megalin deficiency offers protection from renal aminoglycoside accumulation. J Biol Chem 277:618–622
Hammad SM, Barth JL, Knaak C, Argraves WS (2000) Megalin acts in concert with cubilin to mediate endocytosis of high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem 275:12003–12008
Moestrup SK, Kozyraki R, Kristiansen M, Kaysen JH, Rasmussen HH, Brault D, Pontillon F, Goda FO, Christensen EI, Hammond TG, Verroust PJ (1998) The intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor and target of teratogenic antibodies is a megalin-binding peripheral membrane protein with homology to developmental proteins. J Biol Chem 273:5235–5242
Coudroy G, Gburek J, Kozyraki R, Madsen M, Trugnan G, Moestrup SK, Verroust PJ, Maurice M (2005) Contribution of cubilin and amnionless to processing and membrane targeting of cubilin–amnionless complex. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:2330–2337
Fyfe JC, Madsen M, Hojrup P, Christensen EI, Tanner SM, de la Chapelle A, He Q, Moestrup SK (2004) The functional cobalamin (vitamin B12)-intrinsic factor receptor is a novel complex of cubilin and amnionless. Blood 103:1573–1579
He Q, Madsen M, Kilkenney A, Gregory B, Christensen EI, Vorum H, Hojrup P, Schaffer AA, Kirkness EF, Tanner SM, de la Chapelle A, Giger U, Moestrup SK, Fyfe JC (2005) Amnionless function is required for cubilin brush-border expression and intrinsic factor-cobalamin (vitamin B12) absorption in vivo. Blood 106:1447–1453
Strope S, Rivi R, Metzger T, Manova K, Lacy E (2004) Mouse amnionless, which is required for primitive streak assembly, mediates cell-surface localization and endocytic function of cubilin on visceral endoderm and kidney proximal tubules. Development 131:4787–4795
Willnow TE, Hilpert J, Armstrong SA, Rohlmann A, Hammer RE, Burns DK, Herz J (1996) Defective forebrain development in mice lacking gp330/megalin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8460–8464
Gburek J, Birn H, Verroust PJ, Goj B, Jacobsen C, Moestrup SK, Willnow TE, Christensen EI (2003) Renal uptake of myoglobin is mediated by the endocytic receptors megalin and cubilin. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F451–458
Leheste JR, Melsen F, Wellner M, Jansen P, Schlichting U, Renner-Muller I, Andreassen TT, Wolf E, Bachmann S, Nykjaer A, Willnow TE (2003) Hypocalcemia and osteopathy in mice with kidney-specific megalin gene defect. FASEB J 17:247–249
Kantarci S, Al-Gazali L, Hill RS, Donnai D, Black GC, Bieth E, Chassaing N, Lacombe D, Devriendt K, Teebi A, Loscertales M, Robson C, Liu T, MacLaughlin DT, Noonan KM, Russell MK, Walsh CA, Donahoe PK, Pober BR (2007) Mutations in LRP2, which encodes the multiligand receptor megalin, cause Donnai–Barrow and facio-oculo-acoustico-renal syndromes. Nat Genet 39:957–959
Fyfe JC, Giger U, Hall CA, Jezyk PF, Klumpp SA, Levine JS, Patterson DF (1991) Inherited selective intestinal cobalamin malabsorption and cobalamin deficiency in dogs. Pediatr Res 29:24–31
Birn H, Fyfe JC, Jacobsen C, Mounier F, Verroust PJ, Orskov H, Willnow TE, Moestrup SK, Christensen EI (2000) Cubilin is an albumin binding protein important for renal tubular albumin reabsorption. J Clin Invest 105:1353–1361
Aminoff M, Carter JE, Chadwick RB, Johnson C, Grasbeck R, Abdelaal MA, Broch H, Jenner LB, Verroust PJ, Moestrup SK, de la Chapelle A, Krahe R (1999) Mutations in CUBN, encoding the intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor, cubilin, cause hereditary megaloblastic anaemia 1. Nat Genet 21:309–313
Tanner SM, Li Z, Bisson R, Acar C, Oner C, Oner R, Cetin M, Abdelaal MA, Ismail EA, Lissens W, Krahe R, Broch H, Grasbeck R, de la Chapelle A (2004) Genetically heterogeneous selective intestinal malabsorption of vitamin B12: founder effects, consanguinity, and high clinical awareness explain aggregations in Scandinavia and the Middle East. Hum Mutat 23:327–333
Vize PD, Woolf AS, Bard JBL (2003) The kidney: from normal development to congenital disease. Academic, San Diego
Eid SR, Terrettaz A, Nagata K, Brändli AW (2002) Embryonic expression of Xenopus SGLT-1L, a novel member of the solute carrier family 5 (SLC5), is confined to tubules of the pronephric kidney. Int J Dev Biol 46:177–184
Zhou X, Vize PD (2004) Proximo-distal specialization of epithelial transport processes within the Xenopus pronephric kidney tubules. Dev Biol 271:322–338
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Brändli AW, Kirschner MW (1995) Molecular cloning of tyrosine kinases in the early Xenopus embryo: identification of Eck-related genes expressed in cranial neural crest cells of the second (hyoid) arch. Dev Dyn 203:119–140
Helbling PM, Tran CT, Brändli AW (1998) Requirement for EphA receptor signaling in the segregation of Xenopus third and fourth arch neural crest cells. Mech Dev 78:63–79
Helbling PM, Saulnier DM, Robinson V, Christiansen JH, Wilkinson DG, Brändli AW (1999) Comparative analysis of embryonic gene expression defines potential interaction sites for Xenopus EphB4 receptors with ephrin-B ligands. Dev Dyn 216:361–373
Christensen EI, Nielsen S, Moestrup SK, Borre C, Maunsbach AB, de Heer E, Ronco P, Hammond TG, Verroust P (1995) Segmental distribution of the endocytosis receptor gp330 in renal proximal tubules. Eur J Cell Biol 66:349–364
Moestrup SK, Nielsen S, Andreasen P, Jorgensen KE, Nykjaer A, Roigaard H, Gliemann J, Christensen EI (1993) Epithelial glycoprotein-330 mediates endocytosis of plasminogen activator–plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complexes. J Biol Chem 268:16564–16570
Sahali D, Mulliez N, Chatelet F, Laurent-Winter C, Citadelle D, Sabourin JC, Roux C, Ronco P, Verroust P (1993) Comparative immunochemistry and ontogeny of two closely related coated pit proteins. The 280-kD target of teratogenic antibodies and the 330-kD target of nephritogenic antibodies. Am J Pathol 142:1654–1667
Bork P, Beckmann G (1993) The CUB domain. A widespread module in developmentally regulated proteins. J Mol Biol 231:539–545
Romero A, Romao MJ, Varela PF, Kolln I, Dias JM, Carvalho AL, Sanz L, Topfer-Petersen E, Calvete JJ (1997) The crystal structures of two spermadhesins reveal the CUB domain fold. Nat Struct Biol 4:783–788
Kozyraki R, Kristiansen M, Silahtaroglu A, Hansen C, Jacobsen C, Tommerup N, Verroust PJ, Moestrup SK (1998) The human intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor, cubilin: molecular characterization and chromosomal mapping of the gene to 10p within the autosomal recessive megaloblastic anemia (MGA1) region. Blood 91:3593–3600
Hjalm G, Murray E, Crumley G, Harazim W, Lundgren S, Onyango I, Ek B, Larsson M, Juhlin C, Hellman P, Davis H, Akerstrom G, Rask L, Morse B (1996) Cloning and sequencing of human gp330, a Ca(2+)-binding receptor with potential intracellular signaling properties. Eur J Biochem 239:132–137
Saito A, Pietromonaco S, Loo AK, Farquhar MG (1994) Complete cloning and sequencing of rat gp330/“megalin,” a distinctive member of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9725–9729
Kalantry S, Manning S, Haub O, Tomihara-Newberger C, Lee HG, Fangman J, Disteche CM, Manova K, Lacy E (2001) The amnionless gene, essential for mouse gastrulation, encodes a visceral-endoderm-specific protein with an extracellular cysteine-rich domain. Nat Genet 27:412–416
Kopczynski CC, Noordermeer JN, Serano TL, Chen WY, Pendleton JD, Lewis S, Goodman CS, Rubin GM (1998) A high throughput screen to identify secreted and transmembrane proteins involved in Drosophila embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9973–9978
Hedges SB, Kumar S (2002) Genomics vertebrate genomes compared. Science 297:1283–1285
Kumar S, Hedges SB (1998) A molecular timescale for vertebrate evolution. Nature 392:917–920
Maunsbach AB, Christensen EI (1992) Functional ultrastructure of the proximal tubule. In Handbook of Physiology. Renal Physiology. Section 8 (Renal Physiology, vol. I), edited by EE Windhager. Oxford University Press, New York pp. 41–107
Christensen EI, Moskaug JO, Vorum H, Jacobsen C, Gundersen TE, Nykjaer A, Blomhoff R, Willnow TE, Moestrup SK (1999) Evidence for an essential role of megalin in transepithelial transport of retinol. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:685–695
Smith BT, Mussell JC, Fleming PA, Barth JL, Spyropoulos DD, Cooley MA, Drake CJ, Argraves WS (2006) Targeted disruption of cubilin reveals essential developmental roles in the structure and function of endoderm and in somite formation. BMC Dev Biol 6:30
Tanner SM, Aminoff M, Wright FA, Liyanarachchi S, Kuronen M, Saarinen A, Massika O, Mandel H, Broch H, de la Chapelle A (2003) Amnionless, essential for mouse gastrulation, is mutated in recessive hereditary megaloblastic anemia. Nat Genet 33:426–429
Drake CJ, Fleming PA, Larue AC, Barth JL, Chintalapudi MR, Argraves WS (2004) Differential distribution of cubilin and megalin expression in the mouse embryo. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 277:163–170
Assemat E, Chatelet F, Chandellier J, Commo F, Cases O, Verroust P, Kozyraki R (2005) Overlapping expression patterns of the multiligand endocytic receptors cubilin and megalin in the CNS, sensory organs and developing epithelia of the rodent embryo. Gene Expr Patterns 6:69–78
Kounnas MZ, Haudenschild CC, Strickland DK, Argraves WS (1994) Immunological localization of glycoprotein 330, low density lipoprotein receptor related protein and 39 kDa receptor associated protein in embryonic mouse tissues. In Vivo 8:343–351
McCarthy RA, Barth JL, Chintalapudi MR, Knaak C, Argraves WS (2002) Megalin functions as an endocytic sonic hedgehog receptor. J Biol Chem 277:25660–25667
Nieuwkoop PD, Faber J (1994) Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin): a systematical and chronological survey of the development from the fertilized egg till the end of metamorphosis. Garland, New York
Wingert RA, Selleck R, Yu J, Song HD, Chen Z, Song A, Zhou Y, Thisse B, Thisse C, McMahon AP, Davidson AJ (2007) The cdx genes and retinoic acid control the positioning and segmentation of the zebrafish pronephros. PLoS Genet 3:1922–1938
Acknowledgements
We thank Hanne Sidelmann and Inger Kristoffersen for skilful technical assistance. The work was supported in part by the Danish Medical Research Council, the University of Aarhus, the NOVO-Nordisk Foundation, and the Biomembrane Research Center to EIC, the ETH Zürich and the Swiss National Science Foundation (3100A0-101964) to AWB, and the European Community (EuReGene LSHG-CT-2004-005085) to EIC, PJV, and AWB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM
(PDF 4 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christensen, E.I., Raciti, D., Reggiani, L. et al. Gene expression analysis defines the proximal tubule as the compartment for endocytic receptor-mediated uptake in the Xenopus pronephric kidney. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 456, 1163–1176 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0488-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0488-3