Abstract
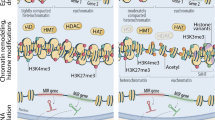
Epigenetics refers to phenotypic changes caused by mechanisms that are unrelated to changes in the underlying DNA sequence, most notably chromatin remodeling driven by histone modifications, and DNA methylation. Such variation is transmitted by cell division, but generally not passed on through the germ line. An increasing body of evidence supports a role for epigenetic changes in the etiology of aging and its associated disease sequelae. Here, we review the role of epigenetics in aging and longevity with a focus on DNA methylation. Increased understanding of those aging-related processes that are driven by epigenetic mechanisms will allow for the development of novel epigenetic-based diagnostic, preventive, and therapeutic strategies for age-related diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anway MD, Cupp AS, Uzumcu M, Skinner MK (2005) Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and male fertility. Science 308:1466–1469
Bahar R, Hartmann CH, Rodriguez KA, Denny AD, Busuttil RA, Dollé ME, Calder RB, Chisholm GB, Pollock BH, Klein CA, Vijg J (2006) Increased cell-to-cell variation in gene expression in ageing mouse heart. Nature 441:1011–1014
Barbot W, Dupressoir A, Lazar V, Heidmann T (2002) Epigenetic regulation of an IAP retrotransposon in the aging mouse: progressive demethylation and de-silencing of the element by its repetitive induction. Nucleic Acids Res 30:2365–2373
Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K, Pistell PJ, Poosala S, Becker KG, Boss O, Gwinn D, Wang M, Ramaswamy S, Fishbein KW, Spencer RG, Lakatta EG, Le Couteur D, Shaw RJ, Navas P, Puigserver P, Ingram DK, de Cabo R, Sinclair DA (2006) Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 444:337–342
Baylin SB, Herman JG (2001) Promoter hypermethylation—can this change alone ever designate true tumor suppressor gene function? J Natl Cancer Inst 93:664–665
Baylin SB, Herman JG (2000) DNA hypermethylation in tumorigenesis: epigenetics joins genetics. Trends Genet 16:168–174
Bennett-Baker PE, Wilkowski J, Burke DT (2003) Age-associated activation of epigenetically repressed genes in the mouse. Genetics 165:2055–2062
Bjornsson HT, Sigurdsson MI, Fallin MD, Irizarry RA, Aspelund T, Cui H, Yu W, Rongione MA, Ekstrom TJ, Harris TB, Launer LJ, Eiriksdottir G, Leppert MF, Sapienza C, Gudnason V, Feinberg AP (2008) Intra-individual change over time in DNA methylation with familial clustering. JAMA 299:2877–2883
Boyes J, Bird A (1991) DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell 64:1123–1134
Buck MJ, Lieb JD (2004) ChIP-chip: considerations for the design, analysis, and application of genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments. Genomics 83:349–360
Buiting K, Gross S, Lich C, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, el-Maarri O, Horsthemke B (2003) Epimutations in Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes: a molecular study of 136 patients with an imprinting defect. Am J Hum Genet 72:571–577
Busuttil R, Bahar R, Vijg J (2007) Genome dynamics and transcriptional deregulation in aging. Neuroscience 145:1341–1347
Campisi J (2000) Cancer, aging and cellular senescence. In Vivo 14:183–188
Campisi J (2005) Senescent cells, tumor suppression, and organismal aging: good citizens, bad neighbors. Cell 120:513–522
Campisi J, d'Adda di Fagagna F (2007) Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:729–740
Campisi J, Kim SH, Lim CS, Rubio M (2001) Cellular senescence, cancer and aging: the telomere connection. Exp Gerontol 36:1619–1637
Campisi J, Vijg J (2009) Does damage to DNA and other macromolecules play a role in aging? If so, how? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64:175–178
Chandler VL, Stam M (2004) Chromatin conversations: mechanisms and implications of paramutation. Nat Rev Genet 5:532–544
Clayton AL, Hazzalin CA, Mahadevan LC (2006) Enhanced histone acetylation and transcription: a dynamic perspective. Mol Cell 23:289–296
Coppe JP, Patil CK, Rodier F, Sun Y, Munoz DP, Goldstein J, Nelson PS, Desprez PY, Campisi J (2008) Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biol 6:2853–2868
DeBusk FL (1972) The Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Report of 4 cases and review of the literature. J Pediatr 80:697–724
Di Micco R, Fumagalli M, Cicalese A, Piccinin S, Gasparini P, Luise C, Schurra C, Garre M, Nuciforo PG, Bensimon A, Maestro R, Pelicci PG, d'Adda di Fagagna F (2006) Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper-replication. Nature 444:638–642
Dillon N, Festenstein R (2002) Unravelling heterochromatin: competition between positive and negative factors regulates accessibility. Trends Genet 18:252–258
Dolinoy DC, Weidman JR, Waterland RA, Jirtle RL (2006) Maternal genistein alters coat color and protects Avy mouse offspring from obesity by modifying the fetal epigenome. Environ Health Perspect 114:567–572
Dollé ME, Giese H, van Steeg H, Vijg J (2000) Mutation accumulation in vivo and the importance of genome stability in aging and cancer. Results Probl Cell Differ 29:165–180
Eden A, Gaudet F, Waghmare A, Jaenisch R (2003) Chromosomal instability and tumors promoted by DNA hypomethylation. Science 300:455
Ehrich M, Nelson MR, Stanssens P, Zabeau M, Liloglou T, Xinarianos G, Cantor CR, Field JK, van den Boom D (2005) Quantitative high-throughput analysis of DNA methylation patterns by base-specific cleavage and mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15785–15790
Feinberg AP (2008) Epigenetics at the epicenter of modern medicine. JAMA 299:1345–1350
Feinberg AP, Ohlsson R, Henikoff S (2006) The epigenetic progenitor origin of human cancer. Nat Rev Genet 7:21–33
Ferguson-Smith AC, Surani MA (2001) Imprinting and the epigenetic asymmetry between parental genomes. Science 293:1086–1089
Fischle W, Wang Y, Jacobs SA, Kim Y, Allis CD, Khorasanizadeh S (2003) Molecular basis for the discrimination of repressive methyl-lysine marks in histone H3 by Polycomb and HP1 chromodomains. Genes Dev 17:1870–1881
Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Paz MF, Ropero S, Setien F, Ballestar ML, Heine-Suner D, Cigudosa JC, Urioste M, Benitez J, Boix-Chornet M, Sanchez-Aguilera A, Ling C, Carlsson E, Poulsen P, Vaag A, Stephan Z, Spector TD, Wu YZ, Plass C, Esteller M (2005) Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10604–10609
Friso S, Choi SW (2002) Gene–nutrient interactions and DNA methylation. J Nutr 132:2382S–2387S
Fu VX, Dobosy JR, Desotelle JA, Almassi N, Ewald JA, Srinivasan R, Berres M, Svaren J, Weindruch R, Jarrard DF (2008) Aging and cancer-related loss of insulin-like growth factor 2 imprinting in the mouse and human prostate. Cancer Res 68:6797–6802
Fuks F, Burgers WA, Godin N, Kasai M, Kouzarides T (2001) Dnmt3a binds deacetylases and is recruited by a sequence-specific repressor to silence transcription. EMBO J 20:2536–2544
Gaudet F, Hodgson JG, Eden A, Jackson-Grusby L, Dausman J, Gray JW, Leonhardt H, Jaenisch R (2003) Induction of tumors in mice by genomic hypomethylation. Science 300:489–492
Giese H, Snyder WK, van Oostrom C, van Steeg H, Dollé ME, Vijg J (2002) Age-related mutation accumulation at a lacZ reporter locus in normal and tumor tissues of Trp53-deficient mice. Mutat Res 514:153–163
Glasspool RM, Teodoridis JM, Brown R (2006) Epigenetics as a mechanism driving polygenic clinical drug resistance. Br J Cancer 94:1087–1092
Gray MD, Jesch SA, Stein GH (1991) 5-Azacytidine-induced demethylation of DNA to senescent level does not block proliferation of human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 149:477–484
Grewal SI, Elgin SC (2002) Heterochromatin: new possibilities for the inheritance of structure. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:178–187
Grewal SI, Klar AJ (1996) Chromosomal inheritance of epigenetic states in fission yeast during mitosis and meiosis. Cell 86:95–101
Guarente L (1999) Diverse and dynamic functions of the Sir silencing complex. Nat Genet 23:281–285
Haigis MC, Guarente LP (2006) Mammalian sirtuins—emerging roles in physiology, aging, and calorie restriction. Genes Dev 20:2913–2921
Harley CB, Futcher AB, Greider CW (1990) Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature 345:458–460
Hayflick L (1965) The limited in vitro lifetime of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res 37:614–636
Hegele RA (2003) Drawing the line in progeria syndromes. Lancet 362:416–417
Herbig U, Jobling WA, Chen BP, Chen DJ, Sedivy JM (2004) Telomere shortening triggers senescence of human cells through a pathway involving ATM, p53, and p21(CIP1), but not p16(INK4a). Mol Cell 14:501–513
Holliday R (1987) The inheritance of epigenetic defects. Science 238:163–170
Issa JP (1999) Aging, DNA methylation and cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 32:31–43
Itahana K, Campisi J, Dimri GP (2007) Methods to detect biomarkers of cellular senescence: the senescence-associated beta-galactosidase assay. Methods Mol Biol 371:21–31
Jablonka E, Lamb MJ (1989) The inheritance of acquired epigenetic variations. J Theor Biol 139:69–83
Jacob RA (1999) Evidence that diet modification reduces in vivo oxidant damage. Nutr Rev 57:255–258
Jones PA (2002) DNA methylation and cancer. Oncogene 21:5358–5360
Jones PA, Laird PW (1999) Cancer epigenetics comes of age. Nat Genet 21:163–167
Kaeberlein M, McVey M, Guarente L (1999) The SIR2/3/4 complex and SIR2 alone promote longevity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by two different mechanisms. Genes Dev 13:2570–2580
Kanungo A, Chandi SM (1994) Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of the epididymis. A case report. Indian J Cancer 31:138–140
Kator K, Cristofalo V, Charpentier R, Cutler RG (1985) Dysdifferentiative nature of aging: passage number dependency of globin gene expression in normal human diploid cells grown in tissue culture. Gerontology 31:355–361
Khulan B, Thompson RF, Ye K, Fazzari MJ, Suzuki M, Stasiek E, Figueroa ME, Glass JL, Chen Q, Montagna C, Hatchwell E, Selzer RR, Richmond TA, Green RD, Melnick A, Greally JM (2006) Comparative isoschizomer profiling of cytosine methylation: the HELP assay. Genome Res 16:1046–1055
Krtolica A, Parrinello S, Lockett S, Desprez PY, Campisi J (2001) Senescent fibroblasts promote epithelial cell growth and tumorigenesis: a link between cancer and aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12072–12077
Kudlow BA, Kennedy BK, Monnat RJ Jr (2007) Werner and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndromes: mechanistic basis of human progeroid diseases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:394–404
Laird CD, Pleasant ND, Clark AD, Sneeden JL, Hassan KM, Manley NC, Vary JC Jr, Morgan T, Hansen RS, Stoger R (2004) Hairpin-bisulfite PCR: assessing epigenetic methylation patterns on complementary strands of individual DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:204–209
Lane N, Dean W, Erhardt S, Hajkova P, Surani A, Walter J, Reik W (2003) Resistance of IAPs to methylation reprogramming may provide a mechanism for epigenetic inheritance in the mouse. Genesis 35:88–93
Liu B, Wang J, Chan KM, Tjia WM, Deng W, Guan X, Huang JD, Li KM, Chau PY, Chen DJ, Pei D, Pendas AM, Cadinanos J, Lopez-Otin C, Tse HF, Hutchison C, Chen J, Cao Y, Cheah KS, Tryggvason K, Zhou Z (2005) Genomic instability in laminopathy-based premature aging. Nat Med 11:780–785
Lumey LH, Stein AD (1997) In utero exposure to famine and subsequent fertility: The Dutch Famine Birth Cohort Study. Am J Public Health 87:1962–1966
Marks PA, Breslow R (2007) Dimethyl sulfoxide to vorinostat: development of this histone deacetylase inhibitor as an anticancer drug. Nat Biotechnol 25:84–90
Martin GM (2005) Epigenetic drift in aging identical twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10413–10414
Martin SL, Hopkins CL, Naumer A, Dolle ME, Vijg J (2001) Mutation frequency and type during ageing in mouse seminiferous tubules. Mech Ageing Dev 122:1321–1331
Menendez L, Benigno BB, McDonald JF (2004) L1 and HERV-W retrotransposons are hypomethylated in human ovarian carcinomas. Mol Cancer 3:12
Minamino T, Komuro I (2007) Vascular cell senescence: contribution to atherosclerosis. Circ Res 100:15–26
Morgan HD, Sutherland HG, Martin DI, Whitelaw E (1999) Epigenetic inheritance at the agouti locus in the mouse. Nat Genet 23:314–318
Morley R (2006) Fetal origins of adult disease. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 11:73–78
Muller HJ, Altenburg E (1930) The frequency of translocations produced by x-rays in drosophila. Genetics 15:283–311
Nan X, Campoy FJ, Bird A (1997) MeCP2 is a transcriptional repressor with abundant binding sites in genomic chromatin. Cell 88:471–481
Narita M, Nunez S, Heard E, Lin AW, Hearn SA, Spector DL, Hannon GJ, Lowe SW (2003) Rb-mediated heterochromatin formation and silencing of E2F target genes during cellular senescence. Cell 113:703–716
Oberdoerffer P, Michan S, McVay M, Mostoslavsky R, Vann J, Park SK, Hartlerode A, Stegmuller J, Hafner A, Loerch P, Wright SM, Mills KD, Bonni A, Yankner BA, Scully R, Prolla TA, Alt FW, Sinclair DA (2008) SIRT1 redistribution on chromatin promotes genomic stability but alters gene expression during aging. Cell 135:907–918
Okamoto I, Otte AP, Allis CD, Reinberg D, Heard E (2004) Epigenetic dynamics of imprinted X inactivation during early mouse development. Science 303:644–649
Okano M, Takebayashi S, Okumura K, Li E (1999) Assignment of cytosine-5 DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b to mouse chromosome bands 12A2–A3 and 2H1 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 86:333–334
Ono T, Dean RG, Chattopadhyay SK, Cutler RG (1985) Dysdifferentiative nature of aging: age-dependent expression of MuLV and globin genes in thymus, liver and brain in the AKR mouse strain. Gerontology 31:362–372
Park PJ (2008) Epigenetics meets next-generation sequencing. Epigenetics 3:318–321
Pembrey ME, Bygren LO, Kaati G, Edvinsson S, Northstone K, Sjostrom M, Golding J (2006) Sex-specific, male-line transgenerational responses in humans. Eur J Hum Genet 14:159–166
Rakyan VK, Chong S, Champ ME, Cuthbert PC, Morgan HD, Luu KV, Whitelaw E (2003) Transgenerational inheritance of epigenetic states at the murine Axin(Fu) allele occurs after maternal and paternal transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2538–2543
Reik W, Dean W, Walter J (2001) Epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian development. Science 293:1089–1093
Robertson KD (2001) DNA methylation, methyltransferases, and cancer. Oncogene 20:3139–3155
Rodenhiser D, Mann M (2006) Epigenetics and human disease: translating basic biology into clinical applications. CMAJ 174:341–348
Rogina B, Helfand SL (2004) Sir2 mediates longevity in the fly through a pathway related to calorie restriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15998–16003
Romanov GA, Vaniushin BF (1980) Intragenomic specificity of DNA methylation in animals. Qualitative differences in tissues and changes in methylation of repeating sequences during aging, carcinogenesis and hormonal induction. Mol Biol (Mosk) 14:357–368
Rountree MR, Bachman KE, Baylin SB (2000) DNMT1 binds HDAC2 and a new co-repressor, DMAP1, to form a complex at replication foci. Nat Genet 25:269–277
Santos F, Hendrich B, Reik W, Dean W (2002) Dynamic reprogramming of DNA methylation in the early mouse embryo. Dev Biol 241:172–182
Scaffidi P, Misteli T (2005) Reversal of the cellular phenotype in the premature aging disease Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Nat Med 11:440–445
Scaffidi P, Misteli T (2006) Lamin A-dependent nuclear defects in human aging. Science 312:1059–1063
Schmid M, Haaf T, Grunert D (1984) 5-Azacytidine-induced undercondensations in human chromosomes. Hum Genet 67:257–263
Schumacher A, Petronis A (2006) Epigenetics of complex diseases: from general theory to laboratory experiments. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 310:81–115
Shay JW, Roninson IB (2004) Hallmarks of senescence in carcinogenesis and cancer therapy. Oncogene 23:2919–2933
Shumaker DK, Dechat T, Kohlmaier A, Adam SA, Bozovsky MR, Erdos MR, Eriksson M, Goldman AE, Khuon S, Collins FS, Jenuwein T, Goldman RD (2006) Mutant nuclear lamin A leads to progressive alterations of epigenetic control in premature aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:8703–8708
Siegmund KD, Connor CM, Campan M, Long TI, Weisenberger DJ, Biniszkiewicz D, Jaenisch R, Laird PW, Akbarian S (2007) DNA methylation in the human cerebral cortex is dynamically regulated throughout the life span and involves differentiated neurons. PLoS ONE 2:e895
Sims RJ 3rd, Reinberg D (2009) Processing the H3K36me3 signature. Nat Genet 41:270–271
Sinclair DA, Guarente L (1997) Extrachromosomal rDNA circles—a cause of aging in yeast. Cell 91:1033–1042
Sommer M, Poliak N, Upadhyay S, Ratovitski E, Nelkin BD, Donehower LA, Sidransky D (2006) DeltaNp63alpha overexpression induces downregulation of Sirt1 and an accelerated aging phenotype in the mouse. Cell Cycle 5:2005–2011
Thompson RF, Suzuki M, Lau KW, Greally JM (2009) A pipeline for the quantitative analysis of CG dinucleotide methylation using mass spectrometry. Bioinformatics Resource Number
Tra J, Kondo T, Lu Q, Kuick R, Hanash S, Richardson B (2002) Infrequent occurrence of age-dependent changes in CpG island methylation as detected by restriction landmark genome scanning. Mech Ageing Dev 123:1487–1503
Vidal DO, Paixao VA, Brait M, Souto EX, Caballero OL, Lopes LF, Vettore AL (2007) Aberrant methylation in pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Res 31:175–181
Vijg J, Dollé ME (2002) Large genome rearrangements as a primary cause of aging. Mech Ageing Dev 123:907–915
Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (1993) The multistep nature of cancer. Trends Genet 9:138–141
Wang H, Cao R, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Borchers C, Tempst P, Zhang Y (2001) Purification and functional characterization of a histone H3-lysine 4-specific methyltransferase. Mol Cell 8:1207–1217
Wang SC, Oelze B, Schumacher A (2008) Age-specific epigenetic drift in late-onset Alzheimer's disease. PLoS ONE 3:e2698
Wareham KA, Lyon MF, Glenister PH, Williams ED (1987) Age related reactivation of an X-linked gene. Nature 327:725–727
Waterland RA, Lin JR, Smith CA, Jirtle RL (2006) Post-weaning diet affects genomic imprinting at the insulin-like growth factor 2 (Igf2) locus. Hum Mol Genet 15:705–716
Watt F, Molloy PL (1988) Cytosine methylation prevents binding to DNA of a HeLa cell transcription factor required for optimal expression of the adenovirus major late promoter. Genes Dev 2:1136–1143
Weaver IC, Diorio J, Seckl JR, Szyf M, Meaney MJ (2004) Early environmental regulation of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor gene expression: characterization of intracellular mediators and potential genomic target sites. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1024:182–212
Wiemann SU, Satyanarayana A, Tsahuridu M, Tillmann HL, Zender L, Klempnauer J, Flemming P, Franco S, Blasco MA, Manns MP, Rudolph KL (2002) Hepatocyte telomere shortening and senescence are general markers of human liver cirrhosis. FASEB J 16:935–942
Wilson VL, Smith RA, Ma S, Cutler RG (1987) Genomic 5-methyldeoxycytidine decreases with age. J Biol Chem 262:9948–9951
Wright WE, Shay JW (1992) Telomere positional effects and the regulation of cellular senescence. Trends Genet 8:193–197
Young J, Smith JR (2000) Epigenetic aspects of cellular senescence. Exp Gerontol 35:23–32
Young JI, Smith JR (2001) DNA methyltransferase inhibition in normal human fibroblasts induces a p21-dependent cell cycle withdrawal. J Biol Chem 276:19610–19616
Acknowledgements
We thank the SENS Foundation, the National Institute on Aging, and the Ellison Medical Foundation for supporting the research of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gravina, S., Vijg, J. Epigenetic factors in aging and longevity. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 459, 247–258 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0730-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0730-7