Abstract
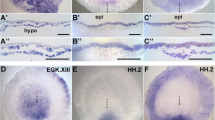
Gastrulation in higher vertebrate species classically commences with the generation of mesoderm cells in the primitive streak by epithelio-mesenchymal transformation of epiblast cells. However, the primitive streak also marks, with its longitudinal orientation in the posterior part of the conceptus, the anterior-posterior (or head-tail) axis of the embryo. Results obtained in chick and mouse suggest that signals secreted by the hypoblast (or visceral endoderm), the extraembryonic tissue covering the epiblast ventrally, antagonise the mesoderm induction cascade in the anterior part of the epiblast and thereby restrict streak development to the posterior pole (and possibly initiate head development anteriorly). In this paper we took advantage of the disc-shape morphology of the rabbit gastrula for defining the expression compartments of the signalling molecules Cerberus and Dickkopf at pre-gastrulation and early gastrulation stages in a mammal other than the mouse. The two molecules are expressed in novel expression compartments in a complementary fashion both in the hypoblast and in the emerging primitive streak. In loss-of-function experiments, carried out in a New-type culturing system, hypoblast was removed prior to culture at defined stages before and at the beginning of gastrulation. The epiblast shows a stage-dependent and topographically restricted susceptibility to express Brachyury, a T-box gene pivotal for mesoderm formation, and to transform into (histologically proven) mesoderm. These results confirm for the mammalian embryo that the anterior-posterior axis of the conceptus is formed first as a molecular prepattern in the hypoblast and then irrevocably fixed, under the control of signals secreted from the hypoblast, by epithelio-mesenchymal transformation (primitive streak formation) in the epiblast.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang SL, Wierda A, Wong D, Stevens KA, Cascio S, Rossant J, Zaret KS (1993). The formation and maintenance of the definitive endoderm lineage in the mouse—involvement of HNF3/forkhead proteins. Development 119:1301–1315
Arnold SJ, Stappert J, Bauer A, Kispert A, Herrmann BG Kemler R (2000) Brachyury is a target gene of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mech Dev 91:249–258
Barnes JD, Crosby JL, Jones CM, Wright CVE, Hogan BLM (1994) Embryonic expression of lim-1, the mouse homolog of Xenopus XLim-1, suggests a role in lateral mesoderm differentiation and neurogenesis. Dev Biol 161:168–178
Beddington RS, Robertson EJ (1998) Anterior patterning in mouse. Trends Genet 14:277–284
Beddington RS, Robertson EJ (1999) Axis development and early asymmetry in mammals. Cell 96:195–209
Bellairs R (1986) The primitive streak. Anat Embryol 174:1–14
Belo JA, Bouwmeester T, Leyns L, Kertesz N, Gallo M, Follettie M, De Robertis EM (1997) Cerberus-like is a secreted factor with neutralizing activity expressed in the anterior primitive endoderm of the mouse gastrula. Mech Dev 68:45–57
Belo JA, Bachiller D, Agius E, Kemp C, Borges AC, Marques S, Piccolo S, De Robertis EM (2000) Cerberus-like is a secreted BMP and nodal antagonist not essential for mouse development. Genesis 26:265–270
Bertocchini F, Stern CD (2002) The hypoblast of the chick embryo positions the primitive streak by antagonizing nodal signaling. Dev Cell 3:735–744
Biben C, Stanley E, Fabri L, Kotecha S, Rhinn M, Drinkwater C, Lah M, Wang CC, Nash A, Hilton D, Ang SL, Mohun T, Harvey RP (1998) Murine cerberus homologue mCer-1: a candidate anterior patterning molecule. Dev Biol 194:135–151
Blum M, Gaunt SJ, Cho KWY, Blumberg B, Steinbeisser H, Bittner D, De Robertis EM (1992) Gastrulation in the mouse: the role of the homeobox gene goosecoid. Cell 69:1097–1106
Bouwmeester T, Kim SH, Sasai Y, Lu B, De Robertis EM (1996) Cerberus is a head-inducing secreted factor expressed in the anterior endoderm of Spemann’s organizer. Nature 382:595–601
Callebaut M., Van Nueten E, Bortier H, Harrisson F (2003) Positional information by Rauber’s sickle and a new look at the mechanisms of primitive streak initiation in avian blastoderms. J Morphol 255:315–327
Chapman SC, Schubert FR, Schoenwolf GC, Lumsden A (2002). Analysis of spatial and temporal gene expression patterns in blastula and gastrula stage chick embryos. Dev Biol 245:187–199
Conlon FL, Lyons KM, Takaesu N, Barth KS, Kispert A, Herrmann B, Robertson EJ (1994) A primary requirement for nodal in the formation and maintenance of the primitive streak in the mouse. Development 120:1919–1928
Filosa S, Rivera-Perez JA, Gomez AP, Gansmuller A, Sasaki H, Behringer RR, Ang SL (1997) Goosecoid and HNF-3beta genetically interact to regulate neural tube patterning during mouse embryogenesis. Development 124:2843–2854
Fischer A, Viebahn C, Blum M (2002) FGF8 acts as a right determinant during establishment of the left-right axis in the rabbit. Curr Biol 12:1807–1816
Foley AC, Skromne I, Stern CD (2000) Reconciling different models of forebrain induction and patterning: a dual role for the hypoblast. Development 127:3839–3854
Glinka A, Wu W, Delius H, Monaghan AP, Blumenstock C, Niehrs C (1998) Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature 391:357–362
Hay ED (1995) An overview of epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat 154:8–20
Huber O, Bierkamp C, Kemler R (1996) Cadherins and catenins in development. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8:685–691
Idkowiak J, Weisheit G, Viebahn C (2004) Polarity in the rabbit embryo. Semin Cell Dev Biol 15:607–617
Kazanskaya O, Glinka A, Niehrs C (2000) The role of Xenopus dickkopf1 in prechordal plate specification and neural patterning. Development 127:4981–4992
Kimura C, Yoshinaga K, Tian E, Suzuki M, Aizawa S, Matsuo I (2000) Visceral endoderm mediates forebrain development by suppressing posteriorizing signals. Dev Biol 225:304–321
King T, Brown NA (1999) Developmental biology. Antagonists on the left flank. Nature 401:222–223
Knoetgen H, Teichmann U, Wittler L, Viebahn C, Kessel M (2000) Anterior neural induction by nodes from rabbits and mice. Dev Biol 225:370–380
Krupnik VE, Sharp JD, Jiang C, Robison K, Chickering TW, Amaravadi L, Brown DE, Guyot D, Mays G, Leiby K, Chang B, Duong T, Goodearl AD, Gearing DP, Sokol SY, McCarthy SA (1999) Functional and structural diversity of the human Dickkopf gene family. Nature 401:243–251
Liu P, Wakamiya M, Shea MJ, Albrecht U, Behringer RR, Bradley A (1999) Requirement for Wnt3 in vertebrate axis formation. Nat Genet 22:361–365
Lowe LA, Supp DM, Sampath K, Yokoyama T, Wright CVE, Potter SS, Overbeek P, Kuehn MR (1996) Conserved left-right asymmetry of nodal expression and alterations in murine situs inversus. Nature 381:158–161
Meno C, Saijoh Y, Fujii H, Ikeda M, Yokoyama T, Yokoyama M, Toyoda Y, Hamada H (1996) Left-right asymmetric expression of the TGF beta-family member lefty in mouse embryos. Nature 381:151–155
Monaghan AP, Kaestner KH, Grau E, Schütz G (1993) Postimplantation expression patterns indicate a role for the mouse forkhead/hnf-3 alpha, beta and gamma genes in determination of the definitive endoderm, chordamesoderm and neuroectoderm. Development 119:567–578
New DAT (1955) A new technique for the cultivation of the chick embryo in vitro. J Embryol Exp Morphol 3:326–331
Oulad-Abdelghani M, Chazaud C, Bouillet P, Mattei MG, Dolle P, Chambon P (1998) Stra3/lefty, a retinoic acid-inducible novel member of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. Int J Dev Biol 42:23–32
Pearce JJ, Penny G, Rossant J (1999) A mouse cerberus/Dan-related gene family. Dev Biol 209:98–110
Perea-Gomez A, Lawson KA, Rhinn M, Zakin L, Brulet P, Mazan S, Ang SL (2001a) Otx2 is required for visceral endoderm movement and for the restriction of posterior signals in the epiblast of the mouse embryo. Development 128:753–765
Perea-Gomez A, Rhinn M, Ang SL (2001b) Role of the anterior visceral endoderm in restricting posterior signals in the mouse embryo. Int J Dev Biol 45:311–320
Perea-Gomez A, Vella FD, Shawlot W, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Chazaud C, Meno C, Pfister V, Chen L, Robertson E, Hamada H, Behringer RR, Ang SL (2002) Nodal antagonists in the anterior visceral endoderm prevent the formation of multiple primitive streaks. Dev Cell 3:745–756
Perea-Gomez A, Camus A, Moreau A, Grieve K, Moneron G, Dubois A, Cibert C, Collignon J (2004) Initiation of gastrulation in the mouse embryo is preceded by an apparent shift in the orientation of the anterior-posterior axis. Curr Biol 14:197–207
Pöpperl H, Schmidt C, Wilson V, Hume CR, Dodd J, Krumlauf R, Beddington RSP (1997) Misexpression of Cwnt8C in the mouse induces an ectopic embryonic axis and causes a truncation of the anterior neuroectoderm. Development 124:2997–3005
Rivera-Perez JA, Mager J, Magnuson T (2003) Dynamic morphogenetic events characterize the mouse visceral endoderm. Dev Biol 261:470–487
de Robertis EM, Larrain J, Oelgeschlager M, Wessely O (2000) The establishment of Spemann’s organizer and patterning of the vertebrate embryo. Nat Rev Genet 1:171–181
Rodriguez-Esteban C, Capdevila J, Economides AN, Pascual J, Ortiz A, Izpisua Belmonte JC (1999) The novel Cer-like protein Caronte mediates the establishment of embryonic left-right asymmetry. Nature 401:243–251
Sasaki H, Hogan BLM (1993) Differential expression of multiple fork head related genes during gastrulation and axial pattern formation in the mouse embryo. Development 118:47–59
Schier AF, Shen MM (2000) Nodal signalling in vertebrate development. Nature 403:385–389
Seher TC, Leptin M (2000) Tribbles, a cell-cycle brake that coordinates proliferation and morphogenesis during Drosophila gastrulation. Curr Biol 10:623–629
Shawlot W, Behringer RR (1995) Requirement for lim1 in head-organizer function. Nature 374:425–430
Shawlot W, Deng JM, Behringer RR (1998) Expression of the mouse cerberus-related gene, Cerr1, suggests a role in anterior neural induction and somitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6198–6203
Skromne I, Stern CD (2001) Interactions between Wnt and Vg1 signalling pathways initiate primitive streak formation in the chick embryo. Development 128(15):2915–2927
Skromne I, Stern CD (2002) A hierarchy of gene expression accompanying induction of the primitive streak by Vg1 in the chick embryo. Mech Dev 114:115–118
Stanley EG, Biben C, Allison J, Hartley L, Wicks IP, Campbell IK, McKinley M, Barnett L, Koentgen F, Robb L, Harvey RP (2000) Targeted insertion of a lacZ reporter gene into the mouse Cer1 locus reveals complex and dynamic expression during embryogenesis. Genesis 26:259–264
Tam PPL, Gad JM (2004) Gastrulation in the mouse. In: Stern CD (ed) Gastrulation. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor (in press)
Thomas PQ, Beddington RSP (1996) Anterior primitive endoderm may be responsible for patterning the anterior neural plate in the mouse embryo. Curr Biol 6:1487–1496
Thomas PQ, Brown A, Beddington RSP (1998). Hex: a homeobox gene revealing peri-implantation asymmetry in the mouse embryo and an early transient marker of endothelial cell precursors. Development 125:85–94
Varlet I, Collignon J, Robertson EJ (1997) nodal expression in the primitive endoderm is required for specification of the anterior axis during mouse gastrulation. Development 124:1033–1044
Viebahn C (1995) Epithelio-mesenchymal transformation during formation of the mesoderm in the mammalian embryo. Acta Anat 154:79–97
Viebahn C, Mayer B, Miething A (1995) Morphology of incipient mesoderm formation in the rabbit embryo: a light- and retrospective electron-microscopic study. Acta Anat 154:99–110
Viebahn C, Stortz C, Mitchell SM, Blum M (2002) Low proliferative and high migratory activity in the area of Brachyury expressing mesoderm progenitor cells in the gastrulating rabbit embryo. Development 129:2355–2365
Waddington CH (1933) Induction by the primitive streak and its derivatives in the chick. J Exp Biol 10:38–46
Weinstein DC, Hemmati-Brivanlou A (1999) Neural induction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:411–433
Weisheit G, Mertz KD, Schilling K, Viebahn C (2002) An efficient in situ hybridization protocol for multiple tissues sections and probes on miniaturized slides. Dev Genes Evol 212:403–406
Wodarz A, Hinz U, Engelbert M, Knust E (1995) Expression of crumbs confers apical character on plasma membrane domains of ectodermal epithelia of Drosophila. Cell 82:67–76
Wu W, Glinka A, Delius H, Niehrs C (2000) Mutual antagonism between dickkopf1 and dickkopf2 regulates Wnt/beta- catenin signalling. Curr Biol 10:1611–1614
Yamamoto M, Saijoh Y, Perea-Gomez A, Shawlot W, Behringer RR, Ang SL, Hamada H, Meno C (2004) Nodal antagonists regulate formation of the anteroposterior axis of the mouse embryo. Nature 428:387–392
Yokouchi Y, Vogan KJ, Pearse RV, Tabin CJ (1999) Antagonistic signaling by Caronte, a novel Cerberus-related gene, establishes left-right asymmetric gene expression. Cell 98:573–583
Acknowledgements
The technical help of Rosemarie Rappold, Elke Bernhard (both Halle), Heike Faust and Irmgard Weiß (both Göttingen) is gratefully acknowledged. Many thanks to Bernd Püschel for fruitful discussions. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Vi 151/3-4 and Vi 151/6-2) and by the Deutsche Akademischer Austauschdienst (Procope programme D/9910412).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by D. Tautz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Idkowiak, J., Weisheit, G., Plitzner, J. et al. Hypoblast controls mesoderm generation and axial patterning in the gastrulating rabbit embryo. Dev Genes Evol 214, 591–605 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-004-0436-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-004-0436-y