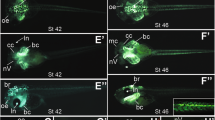
Abstract
An increasing number of genes are known to show expression in the cranial neural crest area. So far it is very difficult to analyze their effect on neural crest cell migration because of the lack of transplantation techniques. This paper presents a simple method to study the migratory behavior of cranial neural crest cells by homo- and heterotopic transplantations: Green fluorescent protein (GFP) RNA was injected into one blastomere of Xenopus laevis embryos at the 2-cell stage. The cranial neural crest area of stage 14 embryos was transplanted into the head or trunk region of an uninjected host embryo, and the migration was monitored by GFP fluorescence. The transplants were further examined by double immunostaining and confocal microscopy to trace migratory routes inside the embryo, and to exclude contaminations of grafts with foreign tissues. Our results demonstrate that we developed a highly efficient and reproducible technique to study the migratory ability of cranial neural crest cells. It offers the possibility to analyze genes involved in neural crest cell migration by coinjecting their RNA with that of GFP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 September 1999 / Accepted: 17 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borchers, A., Epperlein, HH. & Wedlich, D. An assay system to study migratory behavior of cranial neural crest cells in Xenopus . Dev Gene Evol 210, 217–222 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270050307
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270050307