Abstract
A new stereotaxic brain atlas of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus), an important animal model in neurosciences, is presented. It combines high-quality histological material for identification of brain structures with reliable stereotaxic coordinates. The atlas consists of high-resolution images of frontal sections alternately stained for cell bodies (Nissl) and myelinated fibers (Gallyas) of 62 rostro-caudal levels at intervals of 350 μm. Brain structures were named according to the Paxinos nomenclature for rodents. The accuracy of the stereotaxic coordinate system was improved substantially by comparing and matching the series of histological sections to in vivo brain images of the gerbil obtained by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The skull outlines corresponding to the MR images were acquired using X-ray computerized tomography (CT) and were used to establish the relationship between coordinates of brain structures and skull. Landmarks such as lambda, bregma, ear canals and occipital crest can be used to line up skull and brain in standard atlas coordinates. An easily reproducible protocol allows sectioning of experimental brains in the standard frontal plane of the atlas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
During the last decades, the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus, Thomas 1908) has emerged as an important animal model in neuroscience. It is a versatile and advantageous laboratory animal because of its robustness, its ease of handling and its reliable breeding under laboratory conditions.
Virtually all sensory systems, especially the auditory system, are being intensively studied in gerbils, involving a wide range of neuroanatomical and neurophysiological approaches. Topics include development and plasticity as well as effects of aging. Research in the motor system and investigations of behavioral mechanisms, learning and memory and of transmitter systems use gerbils as model organism as well. Due to a peculiarity of the cerebral arteries (circle of Willis) in Mongolian gerbils, cerebral infarction can be induced in a controllable way and has made it a widely used model for cerebral ischemia. It is also a model animal for inherited epilepsy, hippocampal seizure and pathogenesis of CNS infections.
Despite a large body of literature related to the investigation of the gerbil brain, the availability of brain atlases published for this animal species is limited. To date, there are two stereotaxic atlases of the gerbil’s brain. The ‘Stereotaxic Atlas of the Mongolian Gerbil Brain’ (Loskota et al. 1974) includes photographic montages of corresponding hemispheres of adjacent sections stained for myelinated fibers (Weil) and cell bodies (Nissl). Brain structures are outlined and labeled separately, while the neocortex is represented without subdivisions. The heavy shrinkage of the brain caused by the celloidin embedding technique was not corrected in the stereotaxic coordinates.
The brains used for the ‘Stereotaxic Atlas of the Gerbil Brain’ by Thiessen and Yahr (1977) were frozen and cut in a cryostat, which causes only little shrinkage and thus more reliably reproduces stereotaxic coordinates. This atlas incorporates the earlier ‘Stereotaxic Atlas of the Hypothalamus’ by Thiessen and Goar (1970). The atlas presents only schematic outlines of structures and does not provide illustrative material of the underlying Nissl-stained histological sections. In addition, the sectioning plane deviates from the conventional frontal plane in rodents perpendicular to the axis of the brain stem in both atlases.
Thus, the need for a new stereotaxic atlas of the gerbil brain that combines high-quality histological material to identify brain structures with reliable stereotaxic coordinates is evident. Brain sections are inevitably subject to distortions during tissue fixation and subsequent histological procedures (embedding, sectioning, staining and section mounting). Here, we improved the accuracy of the stereotaxic coordinate system substantially by comparing and matching the series of histological sections to in vivo brain images of the gerbil obtained by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Moreover, X-ray computerized tomography (CT) yielded the outlines of the skull corresponding to the MR images, which helped to establish the relationship between coordinates of brain structures and skull coordinates. This is essential for any stereotaxic procedure using landmarks on the skull to reliably target brain structures for recording, imaging, tracer or virus applications. The atlas can also be used effectively as a common reference base to collect and compare positional data from any kind of research in the gerbil brain.
Methods
Animals
Twenty-one young adult male Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus) at the age of 4 months and weighing between 80 and 100 g were used for this study. Out of them, brains of seven animals were processed for cyto- and myeloarchitectonic features. Six other brains were additionally processed for chemo- and immunoarchitecture to support identification of anatomical structures. This material is not included in the atlas and will be published separately. Overall 10 CT scans of skulls and a total of 13 MR brain scans were performed in various combinations.
All experiments were in agreement with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (2011) and the guidelines of the European Communities Council Directive (86/609/EEC) and approved by the animal care committee of Sachsen-Anhalt, Germany.
CT imaging
Animals were scanned under isoflurane anesthesia (1.0–1.5 % in 2:1 O2:N2O volume ratio) with the CT functionality of a NanoSPECT/CT scanner (Mediso Ltd., Budapest, Hungary). CT scans were made at 45 kVp, 1.77 μA, with 180 projections, 500 ms per projection and 96 μm pixel size. Images were reconstructed with the InVivoScope (vs.1.43) at isotropic voxel sizes of 100 μm and analyzed with the DICOM viewers Osirix (Pixmeo SARL, Bernex, Switzerland, v.5.1.7 64-bit) and the open source program AMIDE: A Medical Imaging Data Examiner (amide.exe 1.0.4, ©Andreas Loening, http://amide.sourceforge.net/; GNU GPL).
MR imaging
Animals were anesthetized with isoflurane (1.0–1.5 % in 1:1 O2:N2 volume ratio) and fixed with bite bars in a head-holder to reduce motion artifacts. MR scans were performed on a Bruker Biospec 47/20 scanner (Bruker Biospin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany) at 4.7 T (free bore of 20 cm) equipped with a BGA 09 (400 mT/m) gradient system. A 35 mm Litzcage small animal imaging system (DotyScientific Inc., Colombus, SC, USA) was used for radio frequency (RF) excitation and signal reception. Two days before MRI measurements, animals were injected subcutaneously with an aqueous solution containing 1 μmol/g MnCl2 (manganese enhanced MRI: ME-MRI). A data set of T1-weighted images was obtained using a 3D MDEFT (modified driven equilibrium Fourier transform) pulse sequence with the following parameters: repetition time 13.6 ms; echo time 4.3 ms; flip angle 20°; field of view 30 × 30 mm2; matrix 256 × 256 (yielding a nominal in plane resolution of 117 × 117 µm2); standard frontal orientation; slice thickness 350 µm; 20 averages. Images were reconstructed using Bruker ParaVision 4.0 (Bruker Biospin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany) and exported as raw images as well as in DICOM format. The open source program AMIDE (amide.exe 1.0.4, ©Andreas Loening, http://amide.sourceforge.net/) was used to align CT and MR scans and to extract images shown in the atlas.
Histology
Animals were anesthetized with a lethal dose of ketamine (40 mg/100 g body weight, i.p.) and xylazine (2 mg/100 g body weight, i.p.). When a deep anesthetic state marked by a complete loss of the flexor reflex at all limbs was reached, animals were perfused transcardially with 20 mL of phosphate buffered saline (0.1 M PBS, pH 7.4) supplemented with 0.1 % heparin followed by 200 mL of 4 % PFA (in 0.05 M PBS, pH 7.4). The brains were postfixed in the skull with 4 % PFA (in 0.05 M PBS, pH 7.4) at 4 °C for at least 7 days before removal to best preserve the brain shape.
Brains were cryo-protected in 22.5 % sucrose in PBS (0.05 M, pH 7.4) overnight and cut in a cryostat (LEICA CM 3050S) into four series of 40 µm thick frontal sections. The sections were directly mounted on gelatine-coated slides and dried overnight. Alternating section series were stained on-slide either for cells (Nissl) or for myelin (Gallyas 1979). The brains additionally processed for chemo- and immunoarchitecture were stained for cytochrome oxidase, acetylcholine-esterase (AChE), NADPH-diaphorase, calcium-binding proteins (parvalbumin, calbindin and calretinin) and neurofilament protein (SMI-32) in various combinations. Sections were imaged with a virtual slide microscope (VS120 S1, Olympus BX61VST, Olympus-Deutschland, Hamburg, Germany) at 10× magnification using the proprietary software dotSlide® (Olympus).
Atlas coordinate system
The coordinate system of the brain atlas is based on the conventional definition of anatomical sectioning planes in rodents. Frontal sections are perpendicular to the brainstem axis, which in the Mongolian gerbil is also parallel to the plane defined by the most dorsal points of cerebrum and cerebellum (Fig. 1). This plane is therefore chosen as origin for the dorsoventral dimension with negative values in ventral direction. The lateral dimension is zeroed to the midsagittal plane with negative values towards the right and positive values towards the left side. The anterior to posterior coordinates of the atlas are given for different origins (bregma, lambda, interaural line and occipital crest as skull landmarks) and are valid for the skull in standard atlas orientation.
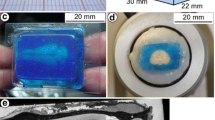
View of fixed gerbil brain positioned for embedding. In the lower part of the figure, the brain is shown in the acrylic glass box used for embedding (rectangular block volume indicated by fine dotted lines). The brain is positioned on three pins (one is hidden by the left front pin) protruding from the base so that the plane defined by the most dorsal elevation of cerebrum and cerebellum (cc) as well as the brainstem axis (bs) are aligned parallel to the base. The anterior and posterior surfaces of the embedding block define the frontal sectioning plane (sp) perpendicular to cc and bs. A pin protruding from a bracket over the side walls of the box (only partly shown) prevents the brain from being washed off when the embedding medium is poured into the box
The frontal sectioning plane was implemented by a standardized embedding procedure using an acrylic glass box (Fig. 1). Each brain was oriented within the box so that the brainstem axis (Fig. 1 bs) was parallel to the base of the box and the midsagittal plane lined up with the long axis of the box. Note that in this orientation the plane through the highest point of cerebellum and cerebrum (Fig. 1 cc) is parallel to the base of the box and can therefore also be used to align the brain. The brain was stabilized in this orientation by adjustable supporting needles protruding from the bottom and from a bracket on top of the box. The volume around the brain was filled with embedding medium, namely a freshly prepared mixture of gelatin–albumin–glutaraldehyde. After 2–3 min, this mixture had hardened and the block was taken out of the box. Subsequently, the block was shock frozen in dry ice and mounted with its hind surface on the cutting platform of the cryostat. Due to the prior orientation within the box, the sectioning plane was now perpendicular to the long axis of the block and therefore also perpendicular to the brainstem axis and the horizontal plane through the highest cerebellar and cerebral points.
Stereotaxic reference system
In rats and mice, the connecting line through lambda and bregma coincides with that through lambda and occipital crest and is used as a horizontal guideline to align the in vivo brain in the classical planes (Paxinos and Watson 2007; Paxinos and Franklin 2001). In the Mongolian gerbil, the line linking lambda and bregma deviates from that linking lambda and occipital crest (Fig. 2, lower panel) and should, therefore, not be used as horizontal guideline to position the gerbil skull and brain in the atlas coordinate system. A horizontal adjustment of the skull along the line between lambda and occipital crest (Fig. 2, horizontal solid line) results in the best approximation to the atlas orientation (Fig. 2, dotted line) and is recommended as standard orientation.
Atlas coordinate system and stereotaxic reference system. Upper panel landmarks bregma, lambda and occipital crest (encircled) on the skull of a Mongolian gerbil in a top view. They are defined by the intersection of lines (dotted lines) approximating the course of the bone sutures. Lower panel montage of CT skull image and MR brain image at a parasagittal distance of 1 mm in standard orientation of the atlas. The solid line corresponds to the horizontal plane through lambda and occipital crest, which is parallel to the plane through the highest points of cerebrum and cerebellum (dotted line)
Selection of atlas series
The atlas series of histological sections was selected according to the following criteria:
-
the entire series, alternately stained for cell bodies (Nissl) and myelin (Gallyas), had to show good staining quality and tissue preservation
-
the atlas series had to match the MR scan of an average-sized brain, and relative distances of indicative structures of the brain had to show congruency with the distances in the available MR scans.
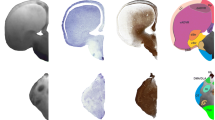
The following structures that could clearly be determined both in histological sections and in MR slices were used as ‘indicative structures’ (Fig. 3): the rostral beginning of neocortex (1), the crossing of the anterior commissure (2), the distinct appearance of the medial habenular nucleus (3), the end of the superior colliculus concurrent with the middle of the inferior colliculus (4) and the end of the cerebellum (5). To judge brain size and to probe the consistency of individual histology series, the distances between indicative brain structures and the rostral pole of neocortex were evaluated and compared to the corresponding median distances in 13 MR scans (Fig. 3; Table 1).
Indicative structures in histological and MRI brain series. The following structures were used (from rostral to caudal): beginning of neocortex (1), midline crossing of anterior commissure (2), distinct appearance of medial habenular nucleus (3), end of the superior colliculus (concurrent with the middle of the inferior colliculus) and (4) end of the cerebellum (5). Montages combine CT and MR scans and half of the corresponding Nissl-stained section. The anterior–posterior location of the corresponding atlas plates is indicated by dotted lines and respective numbers in the central brain image
The MR series that corresponded best to the median values was chosen as ‘ATLAS MRI’. The same distance measurements were performed in seven high-quality histological series. The series that corresponded best to the atlas MRI median values was designated as ‘ATLAS histology series’. Table 1 shows the conformance of the atlas histology series with the atlas MR scan and the median values of MRI series.
CT scans of the skull provide the interface to the brain coordinate system in vivo. Therefore, the available CT scans were overlaid to the atlas MRI. The CT scan matching best was chosen as ‘ATLAS CT’ series. For all CT scans the distances between bregma and the skull landmarks lambda, interaural line and occipital crest were calculated (Table 2). The comparison across animals corresponded well to the values of the atlas CT scan.
Preparation of images and plates
For each 350 µm thick slice of the atlas MR series a corresponding Nissl-stained section of the atlas series was selected and grouped with the adjacent myelin-stained section to represent one of the 62 rostro-caudal levels (Fig. 4). Usually, every forth Nissl-stained section fitted best to the subsequent MR slice, which corresponded to a distance of 320 µm between the matching Nissl-stained sections. The 30 µm difference between the MR slices and the Nissl-stained sections can be explained by the shrinkage of the atlas brain due to histological processing, mainly fixation. This shrinkage is in the range of 8–10 % generally observed for cryo-protected frozen-cut brains with PFA fixation (4 %). Contrast and brightness of the images of the sections were corrected with Photoshop (CS6, Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA, USA), and distortions due to histological processing were compensated by slightly transforming the sections to optimize the congruency of anatomical structures between histological sections and MR images. Images were arranged in the atlas coordinate frame using CorelDraw graphics suite version X6 or X7 (Corel Corporation, Ottawa, ON, Canada). MR and CT images were adjusted according to the definition of the atlas coordinate system in 62 plates and reflect the in vivo orientation of the brain and skull. The images of cell- and myelin-stained sections were inserted in line with the corresponding MR image. The anterior–posterior coordinates of the plates are indicated relative to bregma, lambda, interaural line and the occipital crest. All outlines were drawn in CorelDraw on the base of the Nissl-stained section of each atlas plate. The structural boundaries seen in the corresponding myelin-stained section generally correlate well with these outlines.
Anatomical structures, nomenclature and abbreviations
Anatomical structures were identified on the basis of cyto- and myeloarchitecture and their relative location. For comparison we mainly used the published atlases of the Mongolian gerbil brain (Loskota et al. 1974; Thiessen and Yahr 1977), the atlases and books for rat brain of Paxinos, Swanson and Zilles (Paxinos 1995, 2004; Paxinos and Watson 2007; Paxinos et al. 2009; Swanson 1992, 2004; Zilles 1985) and for mouse brain (Paxinos and Franklin 2001; Dong 2008; Franklin and Paxinos 2008; Watson and Paxinos 2010; Watson et al. 2012). Brain series stained for chemoarchitectonic markers were consulted to support the structural identification. Unfortunately, no unified neuroanatomical nomenclature exists to date (Swanson 2015). Therefore, we decided to use the widely accepted Paxinos nomenclature and abbreviations for naming structures. Auditory midbrain and brainstem nuclei for which gerbil specific terms were already established (Budinger et al. 2000, 2013; Mylius et al. 2013; Radtke-Schuller et al. 2015) were labeled according to these studies.
Practical hints
Sectioning in atlas coordinates: It is also possible to section the brain in the standard atlas plane without the above described embedding procedure. In this case, the brain is positioned upside down on a flat surface so that it is seated with the cerebellum and cerebrum on the base. Then, part of the brain is cut off perpendicular to the base to create a surface for mounting the brain’s portion of interest on the cryostat platform. By subsequent sectioning of the brain parallel to this cutting surface the resulting sections correspond best to the frontal plane of the atlas.
Stereotaxic procedure: In addition to traditional landmarks and reference points such as lambda, bregma and interaural line, we recommend the occipital crest (Fig. 2) for anterior–posterior reference and adjustment of the skull in vivo. The traditional landmarks are often difficult to discern, show individual variations and cannot be accessed in some experimental approaches (e.g., interaural coordinates in auditory research where ear bars are avoided). In general, a higher precision of in vivo positioning of the skull can be achieved by using the specific pattern of skull profiles instead of single reference points [for profile oriented stereotaxic procedure see Schuller et al. (1986)].
Index of structures
The structures are listed in alphabetical order followed by their abbreviation and the plate number(s) of occurrence
1st cerebellar lobule (lingula) | 1Cb | 46–48 |
2nd cerebellar lobule | 2Cb | 43–46 |
3rd cerebellar lobule | 3Cb | 43–49 |
3rd ventricle | 3V | 23–34 |
4th cerebellar lobule | 4Cb | 41–49 |
4th ventricle | 4V | 43–54 |
5th cerebellar lobule | 5Cb | 42–50 |
6th cerebellar lobule | 6Cb | 46–54 |
7th cerebellar lobule | 7Cb | 51–56 |
8th cerebellar lobule | 8Cb | 51–58 |
9th cerebellar lobule | 9Cb | 50–51 |
9th cerebellar lobule, a | 9aCb | 52–59 |
9th cerebellar lobule, b | 9bCb | 52–59 |
9th cerebellar lobule, c | 9cCb | 52–59 |
10th cerebellar lobule (nodule) | 10Cb | 50–55 |
A | ||
A11 dopamine cells | A11 | 30–31 |
A13 dopamine cells | A13 | 28–29 |
A5 noradrenaline cells | A5 | 44–47 |
abducens nerve | 6n | 46–47 |
abducens nucleus | 6N | 47 |
accessory nerve nucleus | 11N | 60–62 |
accessory neurosecretory nuclei | ANS | 27–28 |
accumbens nucleus, core | AcbC | 16–21 |
accumbens nucleus, shell | AcbSh | 16–21 |
agranular insular cortex | AI | 11–27 |
alveus of the hippocampus | alv | 27–38 |
ambiguus nucleus, compact part | AmbC | 52 |
ambiguus nucleus, loose part | AmbL | 55 |
ambiguus nucleus, subcompact part | AmbSC | 53–54 |
amygdalohippocampal area | AHi | 29–33 |
amygdaloid fissure | af | 31–32 |
amygdaloid intramedullary gray | IMG | 27–28 |
amygdalopiriform transition area | APir | 30–35 |
amygdalostriatal transition area | ASt | 26–30 |
angular thalamic nucleus | AngT | 28–28 |
ansoparamedian fissure | apmf | 52–55 |
anterior amygdaloid area | AA | 24–26 |
anterior auditory field | AAF | 28–29 |
anterior cerebral artery | acer | 23 |
anterior commissure, anterior part | aca | 11–24 |
anterior commissure, intrabulbar part | aci | 1–10 |
anterior commissure, posterior part | acp | 23–25 |
anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus | ACo | 24–28 |
anterior hypothalamic area, anterior part | AHA | 25–26 |
anterior hypothalamic area, central part | AHC | 27–28 |
anterior hypothalamic area, posterior part | AHP | 28 |
anterior olfactory nucleus, dorsal part | AOD | 8–12 |
anterior olfactory nucleus, external part | AOE | 6–10 |
anterior olfactory nucleus, lateral part | AOL | 6–12 |
anterior olfactory nucleus, medial part | AOM | 9–13 |
anterior olfactory nucleus, posterior part | AOP | 14–16 |
anterior olfactory nucleus, ventral part | AOV | 8–11 |
anterior olfactory nucleus, ventroposterior part | AOVP | 11–15 |
anterior pretectal nucleus | APT | 35 |
anterior pretectal nucleus, dorsal part | APTD | 31–34 |
anterior pretectal nucleus, ventral part | APTV | 32–34 |
anterior tegmental nucleus | ATg | 40–41 |
anterodorsal thalamic nucleus | AD | 26–27 |
anterolateral periolivary nucleus | ALPO | 44 |
anteromedial thalamic nucleus | AM | 25–28 |
anteromedial thalamic nucleus, ventral part | AMV | 27 |
anterovent thalamic nucleus, dorsomedial part | AVDM | 26–28 |
anteroventral periventricular nucleus | AVPe | 23 |
anteroventral thalamic nucleus | AV | 25 |
anteroventral thalamic nucleus, ventrolateral part | AVVL | 26–27 |
aqueduct | Aq | 35–42 |
arcuate hypothalamic nucleus | Arc | 27–33 |
area postrema | AP | 55–56 |
ascending fibers of the facial nerve | asc7 | 48 |
B | ||
Barrington’s nucleus | Bar | 43–44 |
basal nucleus (Meynert) | B | 24–29 |
basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, anterior part | BLA | 25–29 |
basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, posterior part | BLP | 27–32 |
basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventral part | BLV | 25–27 |
basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, anterior part | BMA | 25–27 |
basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, posterior part | BMP | 28–31 |
bed nucleus of stria terminalis, fusiform part | Fu | 23 |
bed nucleus of the accessory olfactory tract | BAOT | 27 |
bed nucleus of the anterior commissure | BAC | 24 |
bed nucleus of the stria terminalis | ST | 22 |
bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, intraamygdaloid division | STIA | 28–29 |
bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division, intermediate part | STLI | 24 |
bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division, posterior part | STLP | 23–24 |
bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division, ventral part | STLV | 23–24 |
bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division, anterior part | STMA | 23–24 |
bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division, posterior part | STMP | 25–26 |
bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division, ventral part | STMV | 23–24 |
blood vessel | BV | 21 |
Bötzinger complex | Bo | 52 |
brachium of the inferior colliculus | bic | 36–40 |
brachium of the superior colliculus | bsc | 33–35 |
C | ||
caudal linear nucleus of the raphe | CLi | 37–39 |
caudal periolivary nucleus | CPO | 48 |
caudate putamen (striatum) | CPu | 17–30 |
caudomedial entothinal cortex | CEnt | 35–41 |
caudoventrolateral reticular nucleus | CVL | 52–53 |
cell bridges of the ventral striatum | CB | 20–22 |
central amygdaloid nucleus, capsular part | CeC | 26–29 |
central amygdaloid nucleus, lateral division | CeL | 27–28 |
central amygdaloid nucleus, medial division | CeM | 25–29 |
central canal | CC | 55–62 |
central cervical nucleus of the spinal cord | CeCv | 56–62 |
central gray | CG | 43 |
central gray of the pons | CGPn | 45 |
central gray, alpha part | CGA | 44–46 |
central gray, beta part | CGB | 44–45 |
central gray, gamma part | CGG | 46 |
central gray, nucleus O | CGO | 44–45 |
central medial thalamic nucleus | CM | 26–31 |
central nucleus of the inferior colliculus | CIC | 39–42 |
centrolateral thalamic nucleus | CL | 28–31 |
cerebellar white matter | cbw | 43–57 |
cerebral peduncle | cp | 28–39 |
choroid plexus | chp | 24–54 |
cingulate cortex, area 1 | Cg1 | 10–27 |
cingulate cortex, area 2 | Cg2 | 19–27 |
cingulum | cg | 17–34 |
claustrum | Cl | 12–27 |
commissural stria terminalis | cst | 26–27 |
commissure of the inferior colliculus | cic | 42–43 |
commissure of the lateral lemniscus | cll | 41–42 |
commissure of the superior colliculus | csc | 34–36 |
copula of the pyramis | Cop | 49–57 |
corpus callosum | cc | 20–30 |
cortex-amygdala transition zone | CxA | 24–26 |
crus 1 of the ansiform lobule | Crus1 | 43–54 |
crus 2 of the ansiform lobule | Crus2 | 49–55 |
cuneate fasciculus | cu | 53–62 |
cuneate nucleus | Cu | 52–62 |
cuneate nucleus, rotundus part | CuR | 55–56 |
cuneiform nucleus | CnF | 41–43 |
D | ||
decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle | xscp | 39–41 |
decussation of the trapezoid body | tzx | 44–47 |
deep cerebral white matter | dcw | 29–39 |
deep gray layer of the superior colliculus | DpG | 33–41 |
deep white layer of the superior colliculus | DpWh | 34–41 |
dentate gyrus | DG | 30 |
dorsal acoustic stria | das | 49–50 |
dorsal cochlear nucleus, deep core | DCDp | 49–50 |
dorsal cochlear nucleus, fusiform layer | DCFu | 48–50 |
dorsal cochlear nucleus, molecular layer | DCMo | 48–50 |
dorsal cortex of the inferior colliculus | DCIC | 40–43 |
dorsal corticospinal tract | dcs | 60–62 |
dorsal endopiriform nucleus | DEn | 12–32 |
dorsal fornix | df | 26–27 |
dorsal hippocampal commissure | dhc | 28–38 |
dorsal hypothalamic area | DA | 29–30 |
dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus | DLG | 29–33 |
dorsal lateral olfactory tract | dlo | 5–12 |
dorsal motor nucleus of vagus | 10N | 53–58 |
dorsal nucleus of the lateral lemniscus | DNLL | 41–42 |
dorsal paragigantocellular nucleus | DPGi | 48–51 |
dorsal part of claustrum | DCl | 16–26 |
dorsal peduncular cortex | DP | 12–18 |
dorsal periolivary nucleus | DPO | 45–47 |
dorsal raphe nucleus | DR | 37–38 |
dorsal raphe nucleus, caudal part | DRC | 43–44 |
dorsal raphe nucleus, dorsal part | DRD | 39–42 |
dorsal raphe nucleus, lateral part | DRL | 39–41 |
dorsal raphe nucleus, ventral part | DRV | 39–42 |
dorsal spinocerebellar tract | dsc | 52–62 |
dorsal subiculum | DS | 33–36 |
dorsal tegmental decussation | dtgx | 36–37 |
dorsal tegmental nucleus | DTg | 44 |
dorsal tegmental nucleus, central part | DTgC | 43 |
dorsal tegmental nucleus, pericentral part | DTgP | 43 |
dorsal tenia tecta | DTT | 11–18 |
dorsal transition zone | Dtr | 12–15 |
dorsolateral orbital cortex | DLO | 9–12 |
dorsolateral periaqueductal gray | DLPAG | 36–42 |
dorsolateral periolivary nucleus | DLPO | 44–47 |
dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus | DM | 29–32 |
dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, compact part | DMC | 31 |
dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, dorsal part | DMD | 31 |
dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, ventral part | DMV | 31 |
dorsomedial nucleus of the inferior colliculus | DMIC | 41–43 |
dorsomedial periaqueductal gray | DMPAG | 35–42 |
dorsomedial spinal trigeminal nucleus | DMSp5 | 48–54 |
dorsomedial tegmental area | DMTg | 43–45 |
dysgranular insular cortex | DI | 13–27 |
E | ||
ectorhinal cortex | Ect | 28–42 |
Edinger–Westphal nucleus | EW | 36–38 |
entopeduncular nucleus | EP | 27–28 |
entorhinal cortex | Ent | 42 |
ependyma and subependymal layer | E | 1–23 |
ethmoid thalamic nucleus | Eth | 32 |
external capsule | ec | 19–30 |
external cortex of the inferior colliculus | ECIC | 38–44 |
external cuneate nucleus | ECu | 52–56 |
external medullary lamina | eml | 28–30 |
external plexiform layer of the accessory olfactory bulb | EPlA | 5–9 |
external plexiform layer of the olfactory bulb | EPl | 1–9 |
F | ||
F cell group of the vestibular complex | FVe | 52 |
facial nerve | 7n | 45–47 |
facial nucleus, dorsal intermediate subnucleus | 7DI | 48–50 |
facial nucleus, dorsolateral subnucleus | 7DL | 48–50 |
facial nucleus, dorsomedial subnucleus | 7DM | 48–50 |
facial nucleus, lateral subnucleus | 7L | 49–51 |
facial nucleus, ventral intermediate subnucleus | 7VI | 48–50 |
facial nucleus, ventromedial subnucleus | 7VM | 48–50 |
fasciculus retroflexus | fr | 27–36 |
fasciola cinereum | FC | 29–33 |
field CA1 of the hippocampus | CA1 | 28–36 |
field CA2 of the hippocampus | CA2 | 28–32 |
field CA3 of the hippocampus | CA3 | 27–34 |
fimbria of the hippocampus | fi | 22–30 |
flocculus | Fl | 43–48 |
forceps major of the corpus callosum | fmj | 34–39 |
forceps minor of the corpus callosum | fmi | 13–18 |
fornix | f | 23–32 |
frontal association cortex | FrA | 7–9 |
frontal cortex, area 3 | Fr3 | 11–17 |
G | ||
gelatinous layer of the caudal spinal trigeminal nucleus | Ge5 | 57–62 |
genu of the corpus callosum | gcc | 19 |
genu of the facial nerve | g7 | 46–48 |
gigantocellular reticular nucleus | Gi | 47–54 |
gigantocellular reticular nucleus, alpha part | GiA | 48–51 |
gigantocellular reticular nucleus, ventral part | GiV | 51–52 |
globular cell area, ventral cochlear nucleus | Gca | 46–49 |
globus pallidus | GP | 24–29 |
glomerular layer of the accessory olfactory bulb | GlA | 5–10 |
glomerular layer of the olfactory bulb | Gl | 1–11 |
glossopharyngeal nerve nucleus | 9N | 62 |
gracile fasciculus | gr | 54–62 |
gracile nucleus | Gr | 54–62 |
granular cell layer of the olfactory bulb | GrO | 1–10 |
granular insular cortex | GI | 13–27 |
granular layer of the dentate gyrus | GrDG | 27–36 |
granule cell layer of cochlear nuclei | GrC | 43–50 |
granule cell layer of the accessory olfactory bulb | GrA | 3–10 |
H | ||
habenular commissure | hbc | 31–32 |
hippocampal fissure | hif | 30–34 |
hypoglossal nerve | 12n | 53–58 |
hypoglossal nucleus | 12N | 51–58 |
hypoglossal nucleus, geniohyoid part | 12GH | 57–58 |
I | ||
indusium griseum | IG | 18–33 |
inferior cerebellar peduncle (restiform body) | icp | 46–53 |
inferior olive, beta subnucleus | IOBe | 56–58 |
inferior olive, cap of Kooy of the medial nucleus | IOK | 56–57 |
inferior olive, dorsal nucleus | IOD | 52–56 |
inferior olive, dorsomedial cell group | IODM | 52–55 |
inferior olive, medial nucleus | IOM | 52–55 |
inferior olive, principal nucleus | IOPr | 52–56 |
inferior olive, subnucleus A of medial nucleus | IOA | 57–58 |
inferior olive, subnucleus B of medial nucleus | IOB | 56–58 |
inferior olive, subnucleus C of medial nucleus | IOC | 56–58 |
infralimbic cortex | IL | 14–18 |
interanterodorsal thalamic nucleus | IAD | 26–27 |
interanteromedial thalamic nucleus | IAM | 27 |
intercalated amygdaloid nucleus, main part | IM | 26 |
intercalated nuclei of the amygdala | I | 23–29 |
intercrural fissure | icf | 49–54 |
interfascicular nucleus | IF | 35–38 |
intermediate endopiriform nucleus | IEn | 12–24 |
intermediate gray layer of the superior colliculus | InG | 33–41 |
intermediate nucleus of the lateral lemniscus | INLL | 40–42 |
intermediate reticular nucleus | IRt | 46–62 |
intermediate white layer of the superior colliculus | InWh | 33–41 |
intermediodorsal thalamic nucleus | IMD | 28–30 |
intermedioventral thalamic commissure | imvc | 29–30 |
internal capsule | ic | 23–30 |
internal medullary lamina | iml | 26 |
internal plexiform layer of the olfactory bulb | IPl | 1–10 |
interpeduncular fossa | IPF | 36 |
interpeduncular nucleus, caudal subnucleus | IPC | 37–40 |
interpeduncular nucleus, dorsal subnucleus | IPD | 38 |
interpeduncular nucleus, intermediate subnucleus | IPI | 38–39 |
interpeduncular nucleus, lateral subnucleus | IPL | 37–39 |
interpeduncular nucleus, rostral subnucleus | IPR | 37–38 |
interposed cerebellar nucleus, anterior part | IntA | 47–49 |
interposed cerebellar nucleus, dorsolateral hump | IntDL | 47–50 |
interposed cerebellar nucleus, dorsomedial crest | IntDM | 48–50 |
interposed cerebellar nucleus, posterior part | IntP | 49–50 |
interposed cerebellar nucleus, posterior parvicellular part | IntPPC | 49–50 |
interstitial nucleus of Cajal | InC | 33–38 |
interstitial nucleus of the medulla | IB | 57–62 |
interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure | IPAC | 22–25 |
interventricular foramen | IVF | 25– |
islands of Calleja | ICj | 16–22 |
islands of Calleja, major island | ICjM | 20–21 |
isthmic reticular formation | isRt | 39–42 |
K | ||
Kölliker–Fuse nucleus | KF | 43–44 |
L | ||
lacunosum moleculare layer of the hippocampus | LMol | 29–36 |
lambdoid septal zone | Ld | 19–21 |
lateral accumbens shell | LAcbSh | 19–21 |
lateral amygdaloid nucleus | La | 26–31 |
lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal part | LaD | 27–30 |
lateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventral part | LaV | 27–30 |
lateral (dentate) cerebellar nucleus | Lat | 46–49 |
lateral cerebellar nucleus, parvicellular part | LatPC | 46–48 |
lateral entorhinal cortex | LEnt | 29–41 |
lateral habenular nucleus | LHb | 28–31 |
lateral habenular nucleus, lateral part | LHbL | 29–30 |
lateral habenular nucleus, medial part | LHbM | 29–30 |
lateral lemniscus | ll | 39–43 |
lateral mammillary nucleus | LM | 33–35 |
lateral nucleus of the trapezoid body | LNTB | 44–47 |
lateral olfactory tract | lo | 5–25 |
lateral orbital cortex | LO | 8–16 |
lateral parabrachial nucleus | LPB | 45 |
lateral parabrachial nucleus, central part | LPBC | 43–44 |
lateral parabrachial nucleus, crescent part | LPBCr | 44 |
lateral parabrachial nucleus, internal part | LPBI | 43–45 |
lateral paragigantocellular nucleus | LPGi | 51–53 |
lateral paragigantocellular nucleus, alpha part | LPGiA | 48–50 |
lateral paragigantocellular nucleus, external part | LPGiE | 48–50 |
lateral parietal association cortex | LPtA | 28–30 |
lateral periaqueductal gray | LPAG | 35–42 |
lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, laterocaudal part | LPLC | 32–33 |
lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, laterorostral part | LPLR | 29–31 |
lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, mediocaudal part | LPMC | 32–34 |
lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, mediorostral part | LPMR | 29–32 |
lateral preoptic area | LPO | 22–25 |
lateral recess of the 4th ventricle | LR4V | 45–51 |
lateral reticular nucleus | LRt | 54–59 |
lateral reticular nucleus, parvicellular part | LRtPC | 56–58 |
lateral reticular nucleus, subtrigeminal part | LRtS5 | 55–56 |
lateral septal nucleus, dorsal part | LSD | 19–25 |
lateral septal nucleus, intermediate part | LSI | 18–23 |
lateral septal nucleus, ventral part | LSV | 19–23 |
lateral stripe of the striatum | LSS | 21–23 |
lateral superior olive | LSO | 45–47 |
lateral terminal nucleus of the accessory optic tract | LT | 33 |
lateral ventricle | LV | 17–32 |
lateral vestibular nucleus | LVe | 47–49 |
lateroanterior hypothalamic nucleus | LA | 25–26 |
laterodorsal tegmental nucleus | LDTg | 42–44 |
laterodorsal tegmental nucleus, ventral part | LDTgV | 43 |
laterodorsal thalamic nucleus, dorsomedial part | LDDM | 27–28 |
laterodorsal thalamic nucleus, ventrolateral part | LDVL | 27–29 |
lateroventral periolivary nucleus | LVPO | 44–47 |
layer 1 of cortex | 1 | 11–33 |
layer 2 of cortex | 2 | 11–33 |
layer 3 of cortex | 3 | 11–33 |
layer 4 of cortex | 4 | 14–16 |
lemina terminalis | LTer | 24 |
linear nucleus of the medulla | Li | 51–53 |
lithoid nucleus | Lth | 33 |
locus coeruleus | LC | 44–45 |
longitudinal fasciculus of the pons | lfp | 40–43 |
M | ||
magnocellular nucleus of the lateral hypothalamus | MCLH | 29 |
magnocellular nucleus of the posterior commissure | MCPC | 33–34 |
magnocellular preoptic nucleus | MCPO | 23–25 |
mammillary peduncle | mp | 35–36 |
mammillary recess of the 3rd ventricle | MRe | 34 |
mammillotegmental tract | mtg | 33 |
mammillothalamic tract | mt | 27–33 |
marginal zone of the medial geniculate | MZMG | 33–35 |
matrix region of the medulla | Mx | 50–59 |
medial (fastigial) cerebellar nucleus | Med | 47–50 |
medial accessory oculomotor nucleus | MA3 | 34–35 |
medial amygdaloid nucleus, anterodorsal part | MeAD | 26–27 |
medial amygdaloid nucleus, anteroventral part | MeAV | 27 |
medial amygdaloid nucleus, posterodorsal part | MePD | 27–29 |
medial amygdaloid nucleus, posteroventral part | MePV | 28–29 |
medial cerebellar nucleus, dorsolateral protuberance | MedDL | 49–50 |
medial cerebellar nucleus, lateral part | MedL | 49–50 |
medial corticohypothalamic tract | mch | 25 |
medial entorhinal cortex | MEnt | 34–41 |
medial forebrain bundle | mfb | 19–32 |
medial geniculate nucleus, dorsal part | MGD | 33–36 |
medial geniculate nucleus, medial part | MGM | 33–36 |
medial geniculate nucleus, ventral part | MGV | 33–36 |
medial habenular nucleus | MHb | 27–31 |
medial lemniscus | ml | 28–54 |
medial lemniscal decussation | mlx | 56 |
medial longitudinal fasciculus | mlf | 37–62 |
medial mammillary nucleus, lateral part | ML | 34–36 |
medial mammillary nucleus, medial part | MM | 34–35 |
medial mammillary nucleus, median part | MnM | 34– |
medial nucleus of the trapezoid body | MNTB | 43–47 |
medial orbital cortex | MO | 8–14 |
medial parabrachial nucleus | MPB | 43–45 |
medial parabrachial nucleus, external part | MPBE | 44 |
medial parietal association cortex | MPtA | 28–30 |
medial preoptic area | MPA | 22–25 |
medial preoptic nucleus | MPO | 24–25 |
medial pretectal nucleus | MPT | 32 |
medial septal nucleus | MS | 19–23 |
medial superior olive | MSO | 44–47 |
medial terminal nucleus of the accessory optic tract | MT | 35 |
medial tuberal nucleus | MTu | 29–31 |
medial vestibular nucleus | MVe | 53 |
medial vestibular nucleus, magnocellular part | MVeMC | 46–52 |
medial vestibular nucleus, parvicellular part | MVePC | 46–52 |
median accessory nucleus of the medulla | MnA | 59–62 |
median eminence | ME | 30–32 |
median preoptic nucleus | MnPO | 22–24 |
median raphe nucleus | MnR | 39–43 |
mediodorsal thalamic nucleus | MD | 27 |
mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, central part | MDC | 28–30 |
mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, lateral part | MDL | 28–30 |
mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, medial part | MDM | 28–30 |
medioventral periolivary nucleus | MVPO | 44–47 |
medullary reticular nucleus, dorsal part | MdD | 55–62 |
medullary reticular nucleus, ventral part | MdV | 55–62 |
mesencehalic reticular formation | mRt | 36–38 |
mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus | Me5 | 38–45 |
mesencephalic trigeminal tract | me5 | 43–45 |
microcellular tegmental nucleus | MiTg | 38–39 |
middle cerebellar peduncle | mcp | 40–46 |
middle cerebral artery | mcer | 23 |
mitral cell layer of the accessory olfactory bulb | MiA | 5–9 |
mitral cell layer of the olfactory bulb | Mi | 1–10 |
molecular layer of the dentate gyrus | MoDG | 27–37 |
molecular layer of the subiculum | MoS | 37 |
motor root of the trigeminal nerve | m5 | 43–45 |
motor trigeminal nucleus | 5N | 44–45 |
motor trigeminal nucleus, anterior digastric part | 5ADi | 45–46 |
motor trigeminal nucleus, tensor tympani part | 5TT | 43–44 |
N | ||
navicular nucleus of the basal forebrain | Nv | 17–18 |
nigrostriatal bundle | ns | 27–33 |
nucleus of Darkschewitsch | Dk | 33–35 |
nucleus of origin of efferents of the vestibular nerve | EVe | 47 |
nucleus of Roller | Ro | 52–56 |
nucleus of the brachium of the inferior colliculus | BIC | 36–37 |
nucleus of the central acoustic tract | CAT | 43– |
nucleus of the fields of Forel | F | 32–34 |
nucleus of the horizontal limb of the diagonal band | HDB | 20–25 |
nucleus of the lateral olfactory tract | LOT | 25–26 |
nucleus of the optic tract | OT | 32–35 |
nucleus of the posterior commissure | PCom | 33–34 |
nucleus of the solitary tract | Sol | 49–50 |
nucleus of the solitary tract, commissural part | SolC | 55–62 |
nucleus of the solitary tract, medial part | SolM | 55–59 |
nucleus of the solitary tract, ventrolateral part | SolVL | 55–57 |
nucleus of the vertical limb of the diagonal band | VDB | 19–21 |
nucleus X | X | 48–52 |
nucleus Y | Y | 48 |
O | ||
obex | Obex | 57 |
octopus cell area, ventral cochlear nucleus | Oca | 47–49 |
oculomotor nerve | 3n | 36–37 |
oculomotor nucleus | 3N | 37–38 |
oculomotor nucleus, parvicellular part | 3PC | 36 |
olfactory nerve layer | ON | 1–8 |
olfactory tubercle | Tu | 16–23 |
olfactory ventricle (olfactory part of lateral ventricle) | OV | 1–16 |
olivary pretectal nucleus | OPT | 32–33 |
olivocerebellar tract | oc | 50–54 |
olivocochlear bundle | ocb | 46–47 |
optic chiasm | och | 21–25 |
optic nerve layer of the superior colliculus | Op | 33–40 |
optic tract | opt | 26–33 |
oriens layer of the hippocampus | Or | 27–36 |
oval paracentral thalamic nucleus | OPC | 29–31 |
P | ||
p1 periaqueductal gray | p1PAG | 32–34 |
p1 reticular formation | p1Rt | 32–35 |
paraabducens nucleus | Pa6 | 46–47 |
parabigeminal nucleus | PBG | 38–40 |
parabrachial pigmented nucleus of the ventral tegmental area | PBP | 33–37 |
paracentral thalamic nucleus | PC | 27–30 |
paracochlear glial substance | PCGS | 46 |
parafascicular thalamic nucleus | PF | 31–32 |
parafloccular sulcus | pfs | 44–50 |
paraflocculus | PFl | 43–50 |
parainterfascicular nucleus of the ventral tegmental area | PIF | 36–37 |
paralemniscal nucleus | PL | 40–42 |
paralemniscal nucleus, medial part | MPL | 41–42 |
paramedian lobule | PM | 49–56 |
paramedian raphe nucleus | PMnR | 39–42 |
paramedian sulcus | pms | 50–55 |
paranigral nucleus of the ventral tegmental area | PN | 36–37 |
parapyramidal nucleus | PPy | 49–50 |
pararubral nucleus | PaR | 35–38 |
parasolitary nucleus | PSol | 54–55 |
parastrial nucleus | PS | 23–24 |
parasubiculum | PaS | 35–42 |
parasubthalamic nucleus | PSTh | 32 |
paratenial thalamic nucleus | PT | 25–27 |
paraterete nucleus | PTe | 29–30 |
paratrigeminal nucleus | Pa5 | 54–57 |
paratrochlear nucleus | Pa4 | 40–41 |
paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, anterior parvicellular part | PaAP | 25–26 |
paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, medial magnocellular part | PaMM | 27–28 |
paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, medial parvicellular part | PaMP | 27 |
paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, posterior part | PaPo | 28 |
paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, ventral part | PaV | 27 |
paraventricular thalamic nucleus | PV | 27–28 |
paraventricular thalamic nucleus, anterior part | PVA | 25–26 |
paraventricular thalamic nucleus, posterior part | PVP | 29–31 |
paraxiphoid nucleus of thalamus | PaXi | 27–29 |
parietal cortex, posterior area | PtP | 28–31 |
parvicellular reticular nucleus | PCRt | 46–54 |
peduncular part of lateral hypothalamus | PLH | 26–33 |
pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus | PTg | 38–42 |
pericollicular tegmental area | Pta | 39–43 |
perifacial zone | P7 | 48–51 |
perifornical nucleus | PeF | 29–30 |
perifornical part of lateral hypothalamus | PeFLH | 29–32 |
perilemniscal nucleus, ventral part | PLV | 41–43 |
peripeduncular nucleus | PP | 33–35 |
perirhinal cortex | PRh | 28–42 |
peritrigeminal zone | P5 | 43–46 |
periventricular hypothalamic nucleus | Pe | 23–30 |
piriform cortex | Pir | 11–33 |
polymorph layer of the dentate gyrus | PoDG | 28–35 |
pontine nuclei | Pn | 39–42 |
pontine raphe nucleus | PnR | 43 |
pontine reticular nucleus, caudal part | PnC | 44–47 |
pontine reticular nucleus, oral part | PnO | 39–43 |
pontine reticular nucleus, ventral part | PnV | 45–47 |
posterior commissure | pc | 32–34 |
posterior hypothalamic area | PHA | 33 |
posterior hypothalamic area, dorsal part | PHD | 30–31 |
posterior hypothalamic nucleus | PH | 31–32 |
posterior intralaminar thalamic nucleus | PIL | 33–35 |
posterior limitans thalamic nucleus | PLi | 33–35 |
posterior pretectal nucleus | PPT | 33–35 |
posterior superior fissure | psf | 43–54 |
posterior thalamic nuclear group | Po | 28–33 |
posterior thalamic nuclear group, triangular part | PoT | 33–35 |
posterodorsal raphe nucleus | PDR | 39–42 |
posterodorsal tegmental nucleus | PDTg | 45 |
posterolateral cortical amygdaloid nucleus | PLCo | 27–29 |
posterolateral fissure | plf | 43–55 |
posteromedial cortical amygdaloid nucleus | PMCo | 29–33 |
posteromedian thalamic nucleus | PoMn | 31 |
postsubiculum | Post | 35–40 |
pre-Edinger–Westphal nucleus | PrEW | 34–35 |
precentral fissure | pcn | 43–46 |
precommissural nucleus | PrC | 31–33 |
preculminate fissure | pcuf | 43–47 |
precuneiform area | PrCnF | 38–41 |
prelimbic cortex | PrL | 9–18 |
premammillary nucleus, dorsal part | PMD | 33 |
premammillary nucleus, ventral part | PMV | 32–33 |
prepositus nucleus | Pr | 47–53 |
prepyramidal fissure | ppf | 51–56 |
prerubral field | PR | 31–34 |
presubiculum | PrS | 35–38 |
primary auditory cortex | Au1 | 28–33 |
primary auditory field | A1 | 29–33 |
primary fissure | prf | 43–50 |
primary motor cortex | M1 | 11–28 |
primary somatosensory cortex | S1 | 24–30 |
primary somatosensory cortex, barrel field | S1BF | 20–28 |
primary somatosensory cortex, dysgranular zone | S1DZ | 16–28 |
primary somatosensory cortex, forelimb region | S1FL | 15–24 |
primary somatosensory cortex, hindlimb region | S1HL | 20–26 |
primary somatosensory cortex, jaw region | S1J | 13–20 |
primary somatosensory cortex, oral dysgranular zone | S1DZO | 18–19 |
primary somatosensory cortex, shoulder region | S1Sh | 25–26 |
primary somatosensory cortex, trunk region | S1Tr | 27–28 |
primary somatosensory cortex, upper lip region | S1ULp | 18–28 |
primary visual cortex | V1 | 31–42 |
primary visual cortex, binocular area | V1B | 32–39 |
primary visual cortex, monocular area | V1M | 32–39 |
principal mammillary tract | pm | 33–34 |
principal sensory trigeminal nucleus, dorsomedial part | Pr5DM | 44–47 |
principal sensory trigeminal nucleus, ventrolateral part | Pr5VL | 43–47 |
pyramidal cell layer of the hippocampus | Py | 27–36 |
pyramidal decussation | pyx | 57–62 |
pyramidal tract | py | 43–58 |
R | ||
radiatum layer of the hippocampus | Rad | 28–36 |
raphe interpositus nucleus | RIP | 46–48 |
raphe magnus nucleus | RMg | 44–51 |
raphe obscurus nucleus | ROb | 50–58 |
raphe pallidus nucleus | RPa | 43–58 |
red nucleus, magnocellular part | RMC | 35–38 |
red nucleus, parvicellular part | RPC | 35–36 |
reticluostrial nucleus | RtSt | 26 |
reticular thalamic nucleus | Rt | 26–30 |
reticulotegmental nucleus of the pons | RtTg | 41–45 |
reticulotegmental nucleus of the pons, pericentral part | RtTgP | 41–42 |
retroambiguus nucleus | RAmb | 56–58 |
retrochiasmatic area | RCh | 27–28 |
retrochiasmatic area, lateral part | RChL | 27 |
retroethmoid nucleus | REth | 33 |
retrorubral field | RRF | 37–39 |
retrorubral nucleus | RR | 39–40 |
retrosplenial dysgranular cortex | RSD | 27–42 |
retrosplenial granular cortex | RSG | 40 |
retrosplenial granular cortex, a region | RSGa | 35–39 |
retrosplenial granular cortex, b region | RSGb | 32–39 |
retrosplenial granular cortex, c region | RSGc | 27–36 |
retrouniens area | RRe | 31 |
reuniens thalamic nucleus | Re | 26–30 |
rhabdoid nucleus | Rbd | 39 |
rhinal fissure | rf | 7–41 |
rhinal incisure | ri | 7–12 |
rhomboid thalamic nucleus | Rh | 27–30 |
rostral amygdalopiriform area | RAPir | 28–30 |
rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus | RI | 32–33 |
rostral linear nucleus of the raphe | RLi | 35–35 |
rostral periolivary nucleus | RPO | 44 |
rostral ventral respiratory group | RVRG | 53 |
rubrospinal tract | rs | 41–62 |
S | ||
sagulum nucleus | Sag | 41–43 |
scaphoid thalamic nucleus | Sc | 32 |
secondary auditory cortex, dorsal area | AuD | 28–36 |
secondary auditory cortex, ventral area | AuV | 28–36 |
secondary fissure | sf | 53–58 |
secondary motor cortex | M2 | 10–28 |
secondary somatosensory cortex | S2 | 18–28 |
secondary visual cortex, lateral area | V2L | 31–41 |
secondary visual cortex, medial area | V2M | 31–40 |
sensory root of the trigeminal nerve | s5 | 42–47 |
septofimbrial nucleus | SFi | 22–25 |
septohippocampal nucleus | SHi | 18–25 |
simple lobule | Sim | 43–49 |
simplex fissure | simf | 47–49 |
solitary nucleus, dorsolateral part | SolDL | 55–57 |
solitary nucleus, ventral part | SolV | 55–57 |
solitary tract | sol | 50–57 |
spherical cell area, ventral cochlear nucleus | Sca | 43–46 |
spinal trigeminal nucleus, caudal part | Sp5C | 55–62 |
spinal trigeminal nucleus, interpolar part | Sp5I | 49–56 |
spinal trigeminal nucleus, oral part | Sp5O | 48–51 |
spinal trigeminal tract | sp5 | 48–62 |
spinal vestibular nucleus | SpVe | 48–53 |
splenium of the corpus callosum | scc | 31–33 |
stratum lucidum of the hippocampus | SLu | 28–33 |
stria medullaris of the thalamus | sm | 25–30 |
stria terminalis | st | 23–31 |
strial part of the preoptic area | StA | 23 |
subbrachial nucleus | SubB | 36–38 |
subcoeruleus nucleus, alpha part | SubCA | 44 |
subcoeruleus nucleus, dorsal part | SubCD | 43–45 |
subcoeruleus nucleus, ventral part | SubCV | 43–45 |
subcommissural organ | SCO | 32–34 |
subfornical organ | SFO | 25 |
subgeniculate nucleus | SubG | 31–32 |
subiculum, transition area | STr | 37–38 |
subincertal nucleus | SubI | 29–30 |
sublenticular extended amygdala | EA | 26 |
sublenticular extended amygdala, central part | EAC | 25 |
submedius thalamic nucleus | Sub | 30 |
submedius thalamic nucleus, dorsal part | SubD | 28–29 |
submedius thalamic nucleus, ventral part | SubV | 28–29 |
subparafascicular thalamic nucleus | SPF | 31 |
subparafascicular thalamic nucleus, parvicellular part | SPFPC | 31–32 |
subparaventricular zone of the hypothalamus | SPa | 27–28 |
subpeduncular tegmental nucleus | SPTg | 40–42 |
substantia innominata, basal part | SIB | 21–24 |
substantia nigra, compact part | SNC | 33–38 |
substantia nigra, reticular part | SNR | 33–38 |
subthalamic nucleus | STh | 30–32 |
superficial gray layer of the superior colliculus | SuG | 33–41 |
superior cerebellar peduncle | scp | 41–49 |
superior medullary velum | SMV | 45–47 |
superior periolivary nucleus | SPN | 44–47 |
superior thalamic radiation | str | 31–32 |
superior vestibular nucleus | SuVe | 46–47 |
suprachiasmatic nucleus | SCh | 25 |
suprachiasmatic nucleus, dorsolateral part | SChDL | 26 |
suprachiasmatic nucleus, ventromedial part | SChVM | 26 |
suprageniculate thalamic nucleus | SG | 33–36 |
supragenual nucleus | SGe | 46 |
supramammillary decussation | sumx | 34 |
supramammillary nucleus, lateral part | SuML | 33–34 |
supramammillary nucleus, medial part | SuMM | 33–34 |
supraoculomotor cap | Su3C | 36–36 |
supraoculomotor periaqueductal gray | Su3 | 36–39 |
supraoptic decussation | sox | 26–32 |
supraoptic nucleus | SO | 23–27 |
supratrigeminal nucleus | Su5 | 43–45 |
T | ||
tectal gray | TG | 33–35 |
tectospinal tract | ts | 39–62 |
temporal association cortex | TeA | 37–39 |
terete hypothalamic nucleus | Te | 31 |
transverse fibers of the pons | tfp | 39 |
trapezoid body | tz | 43–49 |
triangular septal nucleus | TS | 24–25 |
trigeminal transition zone | 5Tr | 44–46 |
trigeminal-solitary transition zone | 5Sol | 48–55 |
trigeminothalamic tract | tth | 43–45 |
trochlear nerve | 4n | 41–44 |
trochlear nucleus | 4N | 39–40 |
trochlear nuclues shell region | 4Sh | 39–40 |
tuberal region of lateral hypothalamus | TuLH | 27–31 |
U | ||
uvular fissure | uf | 56–59 |
V | ||
vagus nerve | 10n | 52 |
ventral anterior thalamic nucleus | VA | 27 |
ventral cochlear nucleus, anterior part | VCA | 43–47 |
ventral cochlear nucleus, posterior part | VCP | 47–49 |
ventral endopiriform nucleus | VEn | 24–29 |
ventral geniculate nucleus | VG | 29–34 |
ventral geniculate nucleus, magnocellular part | VGMC | 31–32 |
ventral geniculate nucleus, parvicellular part | VGPC | 31–32 |
ventral hippocampal commissure | vhc | 25–27 |
ventral linear nucleus of the thalamus | VLi | 33 |
ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus | VNLL | 40 |
ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus, dorsal part | dVNLL | 41–42 |
ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus, ventral part | vVNLL | 41–43 |
ventral nucleus of the trapezoid body | VNTB | 43–47 |
ventral orbital cortex | VO | 9–16 |
ventral pallidum | VP | 16–25 |
ventral part of claustrum | VCl | 16–26 |
ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus, parvicellular part | VPPC | 31 |
ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus | VPL | 28–31 |
ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus | VPM | 28–32 |
ventral reuniens thalamic nucleus | VRe | 27–30 |
ventral spinocerebellar tract | vsc | 43–62 |
ventral subiculum | VS | 31–36 |
ventral tegmental area | VTA | 37–38 |
ventral tegmental area, rostral part | VTAR | 34–35 |
ventral tegmental decussation | vtgx | 35–37 |
ventral tegmental nucleus | VTg | 42 |
ventral tenia tecta | VTT | 11–16 |
ventral tuberomammillary nucleus | VTM | 33–34 |
ventrolateral hypothalamic nucleus | VLH | 27 |
ventrolateral hypothalamic tract | vlh | 27 |
ventrolateral periaqueductal gray | VLPAG | 37–42 |
ventrolateral preoptic nucleus | VLPO | 23–24 |
ventrolateral thalamic nucleus | VL | 27–30 |
ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus | VMH | 28–31 |
ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, central part | VMHC | 29–30 |
ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, dorsomedial part | VMHDM | 29–30 |
venalamic nucleus, ventrolateral part | VMHVL | 29–30 |
ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus shell | VMHSh | 28–31 |
ventromedial preoptic nucleus | VMPO | 23–24 |
ventromedial thalamic nucleus | VM | 27–30 |
vestibulocerebellar nucleus | VeCb | 46–49 |
vestibulocochlear nerve | 8n | 46–48 |
vestibulomesencephalic tract | veme | 46–48 |
vestibulospinal tract | vesp | 49 |
X | ||
xiphoid thalamic nucleus | Xi | 27–28 |
Z | ||
zona incerta | ZI | 28–29 |
zona incerta, caudal part | ZIC | 34–34 |
zona incerta, dorsal part | ZID | 30–33 |
zona incerta, rostral part | ZIR | 26–27 |
zona incerta, ventral part | ZIV | 30–33 |
zonal layer of the superior colliculus | Zo | 33–41 |
Index of abbreviations
The abbreviations are listed in alphabetical order followed by the name of the structure and the plate number(s) of occurrence
1 | layer 1 of cortex | 11–33 | |
2 | layer 2 of cortex | 11–33 | |
3 | layer 3 of cortex | 11–33 | |
4 | layer 4 of cortex | 14–16 | |
1Cb | 1st cerebellar lobule (lingula) | 46–48 | |
2Cb | 2nd cerebellar lobule | 43–46 | |
3Cb | 3rd cerebellar lobule | 43–49 | |
3n | oculomotor nerve | 36–37 | |
3N | oculomotor nucleus | 37–38 | |
3PC | oculomotor nucleus, parvicellular part | 36 | |
3V | 3rd ventricle | 23–34 | |
4Cb | 4th cerebellar lobule | 41–49 | |
4n | trochlear nerve | 41–44 | |
4N | trochlear nucleus | 39–40 | |
4Sh | trochlear nuclues shell region | 39–40 | |
4V | 4th ventricle | 43–54 | |
5ADi | motor trigeminal nucleus, anterior digastric part | 45–46 | |
5Cb | 5th cerebellar lobule | 42–50 | |
5N | motor trigeminal nucleus | 44–45 | |
5Sol | trigeminal-solitary transition zone | 48–55 | |
5Tr | trigeminal transition zone | 44–46 | |
5TT | motor trigeminal nucleus, tensor tympani part | 43–44 | |
6Cb | 6th cerebellar lobule | 46–54 | |
6n | abducens nerve | 46–47 | |
6N | abducens nucleus | 47 | |
7Cb | 7th cerebellar lobule | 51–56 | |
7DI | facial nucleus, dorsal intermediate subnucleus | 48–50 | |
7DL | facial nucleus, dorsolateral subnucleus | 48–50 | |
7DM | facial nucleus, dorsomedial subnucleus | 48–50 | |
7L | facial nucleus, lateral subnucleus | 49–51 | |
7n | facial nerve | 45–47 | |
7VI | facial nucleus, ventral intermediate subnucleus | 48–50 | |
7VM | facial nucleus, ventromedial subnucleus | 48–50 | |
8Cb | 8th cerebellar lobule | 51–58 | |
8n | vestibulocochlear nerve | 46–48 | |
9aCb | 9th cerebellar lobule, a | 52–59 | |
9bCb | 9th cerebellar lobule, b | 52–59 | |
9Cb | 9th cerebellar lobule | 50–51 | |
9cCb | 9th cerebellar lobule, c | 52–59 | |
9N | glossopharyngeal nerve nucleus | 62 | |
10Cb | 10th cerebellar lobule (nodule) | 50–55 | |
10N | dorsal motor nucleus of vagus | 53–58 | |
10n | vagus nerve | 52 | |
11N | accessory nerve nucleus | 60–62 | |
12GH | hypoglossal nucleus, geniohyoid part | 57–58 | |
12n | hypoglossal nerve | 53–58 | |
12N | hypoglossal nucleus | 51–58 | |
A | |||
A1 | primary auditory field | 29–33 | |
A11 | A11 dopamine cells | 30–31 | |
A13 | A13 dopamine cells | 28–29 | |
A5 | A5 noradrenaline cells | 44–47 | |
AA | anterior amygdaloid area | 24–26 | |
AAF | anterior auditory field | 28–29 | |
aca | anterior commissure, anterior part | 11–24 | |
AcbC | accumbens nucleus, core | 16–21 | |
AcbSh | accumbens nucleus, shell | 16–21 | |
acer | anterior cerebral artery | 23 | |
aci | anterior commissure, intrabulbar part | 1–10 | |
ACo | anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus | 24–28 | |
acp | anterior commissure, posterior part | 23–25 | |
AD | anterodorsal thalamic nucleus | 26–27 | |
af | amygdaloid fissure | 31–32 | |
AHA | anterior hypothalamic area, anterior part | 25–26 | |
AHC | anterior hypothalamic area, central part | 27–28 | |
AHi | amygdalohippocampal area | 29–33 | |
AHP | anterior hypothalamic area, posterior part | 28 | |
AI | agranular insular cortex | 11–27 | |
ALPO | anterolateral periolivary nucleus | 44 | |
alv | alveus of the hippocampus | 27–38 | |
AM | anteromedial thalamic nucleus | 25–28 | |
AmbC | ambiguus nucleus, compact part | 52 | |
AmbL | ambiguus nucleus, loose part | 55 | |
AmbSC | ambiguus nucleus, subcompact part | 53–54 | |
AMV | anteromedial thalamic nucleus, ventral part | 27 | |
AngT | angular thalamic nucleus | 28–28 | |
ANS | accessory neurosecretory nuclei | 27–28 | |
AOD | anterior olfactory nucleus, dorsal part | 8–12 | |
AOE | anterior olfactory nucleus, external part | 6–10 | |
AOL | anterior olfactory nucleus, lateral part | 6–12 | |
AOM | anterior olfactory nucleus, medial part | 9–13 | |
AOP | anterior olfactory nucleus, posterior part | 14–16 | |
AOV | anterior olfactory nucleus, ventral part | 8–11 | |
AOVP | anterior olfactory nucleus, ventroposterior part | 11–15 | |
AP | area postrema | 55–56 | |
APir | amygdalopiriform transition area | 30–35 | |
apmf | ansoparamedian fissure | 52–55 | |
APT | anterior pretectal nucleus | 35 | |
APTD | anterior pretectal nucleus, dorsal part | 31–34 | |
APTV | anterior pretectal nucleus, ventral part | 32–34 | |
Aq | aqueduct | 35–42 | |
Arc | arcuate hypothalamic nucleus | 27–33 | |
asc7 | ascending fibers of the facial nerve | 48 | |
ASt | amygdalostriatal transition area | 26–30 | |
ATg | anterior tegmental nucleus | 40–41 | |
Au1 | primary auditory cortex | 28–33 | |
AuD | secondary auditory cortex, dorsal area | 28–36 | |
AuV | secondary auditory cortex, ventral area | 28–36 | |
AV | anteroventral thalamic nucleus | 25 | |
AVDM | anterovent thalamic nucleus, dorsomedial part | 26–28 | |
AVPe | anteroventral periventricular nucleus | 23 | |
AVVL | anteroventral thalamic nucleus, ventrolateral part | 26–27 | |
B | |||
B | basal nucleus (Meynert) | 24–29 | |
BAC | bed nucleus of the anterior commissure | 24 | |
BAOT | bed nucleus of the accessory olfactory tract | 27 | |
Bar | Barrington’s nucleus | 43–44 | |
bic | brachium of the inferior colliculus | 36–40 | |
BIC | nucleus of the brachium of the inferior colliculus | 36–37 | |
BLA | basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, anterior part | 25–29 | |
BLP | basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, posterior part | 27–32 | |
BLV | basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventral part | 25–27 | |
BMA | basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, anterior part | 25–27 | |
BMP | basomedial amygdaloid nucleus, posterior part | 28–31 | |
Bo | Bötzinger complex | 52 | |
bsc | brachium of the superior colliculus | 33–35 | |
BV | blood vessel | 21 | |
C | |||
CA1 | field CA1 of the hippocampus | 28–36 | |
CA2 | field CA2 of the hippocampus | 28–32 | |
CA3 | field CA3 of the hippocampus | 27–34 | |
CAT | nucleus of the central acoustic tract | 43 | |
CB | cell bridges of the ventral striatum | 20–22 | |
cbw | cerebellar white matter | 43–57 | |
CC | central canal | 55–62 | |
cc | corpus callosum | 20–30 | |
CeC | central amygdaloid nucleus, capsular part | 26– | 29 |
CeCv | central cervical nucleus of the spinal cord | 56–62 | |
CeL | central amygdaloid nucleus, lateral division | 27–28 | |
CeM | central amygdaloid nucleus, medial division | 25–29 | |
CEnt | caudomedial entothinal cortex | 35–41 | |
CG | central gray | 43 | |
cg | cingulum | 17–34 | |
Cg1 | cingulate cortex, area 1 | 10–27 | |
Cg2 | cingulate cortex, area 2 | 19–27 | |
CGA | central gray, alpha part | 44–46 | |
CGB | central gray, beta part | 44–45 | |
CGG | central gray, gamma part | 46 | |
CGO | central gray, nucleus O | 44–45 | |
CGPn | central gray of the pons | 45 | |
chp | choroid plexus | 24–54 | |
CIC | central nucleus of the inferior colliculus | 39–42 | |
cic | commissure of the inferior colliculus | 42–43 | |
CL | centrolateral thalamic nucleus | 28–31 | |
Cl | claustrum | 12–27 | |
CLi | caudal linear nucleus of the raphe | 37–39 | |
cll | commissure of the lateral lemniscus | 41–42 | |
CM | central medial thalamic nucleus | 26–31 | |
CnF | cuneiform nucleus | 41–43 | |
Cop | copula of the pyramis | 49–57 | |
cp | cerebral peduncle | 28–39 | |
CPO | caudal periolivary nucleus | 48 | |
CPu | caudate putamen (striatum) | 17–30 | |
Crus1 | crus 1 of the ansiform lobule | 43–54 | |
Crus2 | crus 2 of the ansiform lobule | 49–55 | |
csc | commissure of the superior colliculus34–36 | ||
cst | commissural stria terminalis | 26–27 | |
cu | cuneate fasciculus | 53–62 | |
Cu | cuneate nucleus | 52–62 | |
CuR | cuneate nucleus, rotundus part | 55–56 | |
CVL | caudoventrolateral reticular nucleus | 52–53 | |
CxA | cortex-amygdala transition zone | 24–26 | |
D | |||
DA | dorsal hypothalamic area | 29–30 | |
das | dorsal acoustic stria | 49–50 | |
DCDp | dorsal cochlear nucleus, deep core | 49–50 | |
DCFu | dorsal cochlear nucleus, fusiform layer | 48–50 | |
DCIC | dorsal cortex of the inferior colliculus | 40–43 | |
DCl | dorsal part of claustrum | 16–26 | |
DCMo | dorsal cochlear nucleus, molecular layer | 48–50 | |
dcs | dorsal corticospinal tract | 60–62 | |
dcw | deep cerebral white matter | 29–39 | |
DEn | dorsal endopiriform nucleus | 12–32 | |
df | dorsal fornix | 26–27 | |
DG | dentate gyrus | 30 | |
dhc | dorsal hippocampal commissure | 28–38 | |
DI | dysgranular insular cortex | 13–27 | |
Dk | nucleus of Darkschewitsch | 33–35 | |
DLG | dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus | 29–33 | |
dlo | dorsal lateral olfactory tract | 5–12 | |
DLO | dorsolateral orbital cortex | 9–12 | |
DLPAG | dorsolateral periaqueductal gray | 36–42 | |
DLPO | dorsolateral periolivary nucleus | 44–47 | |
DM | dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus | 29–32 | |
DMC | dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, compact part | 31 | |
DMD | dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, dorsal part | 31 | |
DMIC | dorsomedial nucleus of the inferior colliculus | 41–43 | |
DMPAG | dorsomedial periaqueductal gray | 35–42 | |
DMSp5 | dorsomedial spinal trigeminal nucleus | 48–54 | |
DMTg | dorsomedial tegmental area | 43–45 | |
DMV | dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, ventral part | 31 | |
DNLL | dorsal nucleus of the lateral lemniscus | 41–42 | |
DP | dorsal peduncular cortex | 12–18 | |
DpG | deep gray layer of the superior colliculus | 33–41 | |
DPGi | dorsal paragigantocellular nucleus | 48–51 | |
DPO | dorsal periolivary nucleus | 45–47 | |
DpWh | deep white layer of the superior colliculus | 34–41 | |
DR | dorsal raphe nucleus | 37–38 | |
DRC | dorsal raphe nucleus, caudal part | 43–44 | |
DRD | dorsal raphe nucleus, dorsal part | 39–42 | |
DRL | dorsal raphe nucleus, lateral part | 39–41 | |
DRV | dorsal raphe nucleus, ventral part | 39–42 | |
DS | dorsal subiculum | 33–36 | |
dsc | dorsal spinocerebellar tract | 52–62 | |
DTg | dorsal tegmental nucleus | 44 | |
DTgC | dorsal tegmental nucleus, central part | 43 | |
DTgP | dorsal tegmental nucleus, pericentral part | 43 | |
dtgx | dorsal tegmental decussation | 36–37 | |
Dtr | dorsal transition zone | 12–15 | |
DTT | dorsal tenia tecta | 11–18 | |
dVNLL | ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus, dorsal part | 41–42 | |
E | |||
E | ependyma and subependymal layer | 1–23 | |
EA | sublenticular extended amygdala | 26 | |
EAC | sublenticular extended amygdala, central part | 25 | |
ec | external capsule | 19–30 | |
ECIC | external cortex of the inferior colliculus | 38–44 | |
Ect | ectorhinal cortex | 28–42 | |
ECu | external cuneate nucleus | 52–56 | |
eml | external medullary lamina | 28–30 | |
Ent | entorhinal cortex | 42 | |
EP | entopeduncular nucleus | 27–28 | |
EPl | external plexiform layer of the olfactory bulb | 1–9 | |
EPlA | external plexiform layer of the accessory olfactory bulb | 5–9 | |
Eth | ethmoid thalamic nucleus | 32 | |
EVe | nucleus of origin of efferents of the vestibular nerve | 47 | |
EW | Edinger–Westphal nucleus | 36–38 | |
F | |||
f | fornix | 23–32 | |
F | nucleus of the fields of Forel | 32–34 | |
FC | fasciola cinereum | 29–33 | |
fi | fimbria of the hippocampus | 22–30 | |
Fl | flocculus | 43–48 | |
fmi | forceps minor of the corpus callosum | 13–18 | |
fmj | forceps major of the corpus callosum | 34–39 | |
fr | fasciculus retroflexus | 27–36 | |
Fr3 | frontal cortex, area 3 | 11–17 | |
FrA | frontal association cortex | 7–9 | |
Fu | bed nucleus of stria terminalis, fusiform part | 23 | |
FVe | F cell group of the vestibular complex | 52 | |
G | |||
g7 | genu of the facial nerve | 46–48 | |
Gca | globular cell area, ventral cochlear nucleus | 46–49 | |
gcc | genu of the corpus callosum | 19 | |
Ge5 | gelatinous layer of the caudal spinal trigeminal nucleus | 57–62 | |
Gi | gigantocellular reticular nucleus | 47–54 | |
GI | granular insular cortex | 13–27 | |
GiA | gigantocellular reticular nucleus, alpha part | 48–51 | |
GiV | gigantocellular reticular nucleus, ventral part | 51–52 | |
Gl | glomerular layer of the olfactory bulb | 1–11 | |
GlA | glomerular layer of the accessory olfactory bulb | 5–10 | |
GP | globus pallidus | 24–29 | |
gr | gracile fasciculus | 54–62 | |
Gr | gracile nucleus | 54–62 | |
GrA | granule cell layer of the accessory olfactory bulb | 3–10 | |
GrC | granule cell layer of cochlear nuclei | 43–50 | |
GrDG | granular layer of the dentate gyrus | 27–36 | |
GrO | granular cell layer of the olfactory bulb | 1–10 | |
H | |||
hbc | habenular commissure | 31–32 | |
HDB | nucleus of the horizontal limb of the diagonal band | 20–25 | |
hif | hippocampal fissure | 30–34 | |
I | |||
I | intercalated nuclei of the amygdala | 23–29 | |
IAD | interanterodorsal thalamic nucleus | 26–27 | |
IAM | interanteromedial thalamic nucleus | 27 | |
IB | interstitial nucleus of the medulla | 57–62 | |
ic | internal capsule | 23–30 | |
icf | intercrural fissure | 49–54 | |
ICj | islands of Calleja | 16–22 | |
ICjM | islands of Calleja, major island | 20–21 | |
icp | inferior cerebellar peduncle (restiform body) | 46–53 | |
IEn | intermediate endopiriform nucleus | 12–24 | |
IF | interfascicular nucleus | 35–38 | |
IG | indusium griseum | 18–33 | |
IL | infralimbic cortex | 14–18 | |
IM | intercalated amygdaloid nucleus, main part | 26 | |
IMD | intermediodorsal thalamic nucleus | 28–30 | |
IMG | amygdaloid intramedullary gray | 27–28 | |
iml | internal medullary lamina | 26 | |
imvc | intermedioventral thalamic commissure | 29–30 | |
InC | interstitial nucleus of Cajal | 33–38 | |
InG | intermediate gray layer of the superior colliculus | 33–41 | |
INLL | intermediate nucleus of the lateral lemniscus | 40–42 | |
IntA | interposed cerebellar nucleus, anterior part | 47–49 | |
IntDL | interposed cerebellar nucleus, dorsolateral hump | 47–50 | |
IntDM | interposed cerebellar nucleus, dorsomedial crest | 48–50 | |
IntP | interposed cerebellar nucleus, posterior part | 49–50 | |
IntPPC | interposed cerebellar nucleus, posterior parvicellular part | 49–50 | |
InWh | intermediate white layer of the superior colliculus | 33–41 | |
IOA | inferior olive, subnucleus A of medial nucleus | 57–58 | |
IOB | inferior olive, subnucleus B of medial nucleus | 56–58 | |
IOBe | inferior olive, beta subnucleus | 56–58 | |
IOC | inferior olive, subnucleus C of medial nucleus | 56–58 | |
IOD | inferior olive, dorsal nucleus | 52–56 | |
IODM | inferior olive, dorsomedial cell group | 52–55 | |
IOK | inferior olive, cap of Kooy of the medial nucleus | 56–57 | |
IOM | inferior olive, medial nucleus | 52–55 | |
IOPr | inferior olive, principal nucleus | 52–56 | |
IPAC | interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure | 22–25 | |
IPC | interpeduncular nucleus, caudal subnucleus | 37–40 | |
IPD | interpeduncular nucleus, dorsal subnucleus | 38 | |
IPF | interpeduncular fossa | 36 | |
IPI | interpeduncular nucleus, intermediate subnucleus | 38–39 | |
IPl | internal plexiform layer of the olfactory bulb | 1–10 | |
IPL | interpeduncular nucleus, lateral subnucleus | 37–39 | |
IPR | interpeduncular nucleus, rostral subnucleus | 37–38 | |
IRt | intermediate reticular nucleus | 46–62 | |
isRt | isthmic reticular formation | 39–42 | |
IVF | interventricular foramen | 25 | |
K | |||
KF | Kölliker–Fuse nucleus | 43–44 | |
L | |||
La | lateral amygdaloid nucleus | 26–31 | |
LA | lateroanterior hypothalamic nucleus | 25–26 | |
LAcbSh | lateral accumbens shell | 19–21 | |
LaD | lateral amygdaloid nucleus, dorsal part | 27–30 | |
Lat | lateral (dentate) cerebellar nucleus | 46–49 | |
LatPC | lateral cerebellar nucleus, parvicellular part | 46–48 | |
LaV | lateral amygdaloid nucleus, ventral part | 27–30 | |
LC | locus coeruleus | 44–45 | |
Ld | lambdoid septal zone | 19–21 | |
LDDM | laterodorsal thalamic nucleus, dorsomedial part | 27–28 | |
LDTg | laterodorsal tegmental nucleus | 42–44 | |
LDTgV | laterodorsal tegmental nucleus, ventral part | 43 | |
LDVL | laterodorsal thalamic nucleus, ventrolateral part | 27–29 | |
LEnt | lateral entorhinal cortex | 29–41 | |
lfp | longitudinal fasciculus of the pons | 40–43 | |
LHb | lateral habenular nucleus | 28–31 | |
LHbL | lateral habenular nucleus, lateral part | 29–30 | |
LHbM | lateral habenular nucleus, medial part | 29–30 | |
Li | linear nucleus of the medulla | 51–53 | |
ll | lateral lemniscus | 39–43 | |
LM | lateral mammillary nucleus | 33–35 | |
LMol | lacunosum moleculare layer of the hippocampus | 29–36 | |
LNTB | lateral nucleus of the trapezoid body | 44–47 | |
lo | lateral olfactory tract | 5–25 | |
LO | lateral orbital cortex | 8–16 | |
LOT | nucleus of the lateral olfactory tract | 25–26 | |
LPAG | lateral periaqueductal gray | 35–42 | |
LPB | lateral parabrachial nucleus | 45 | |
LPBC | lateral parabrachial nucleus, central part | 43–44 | |
LPBCr | lateral parabrachial nucleus, crescent part | 44 | |
LPBI | lateral parabrachial nucleus, internal part | 43–45 | |
LPGi | lateral paragigantocellular nucleus | 51–53 | |
LPGiA | lateral paragigantocellular nucleus, alpha part | 48–50 | |
LPGiE | lateral paragigantocellular nucleus, external part | 48–50 | |
LPLC | lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, laterocaudal part | 32–33 | |
LPLR | lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, laterorostral part | 29–31 | |
LPMC | lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, mediocaudal part | 32–34 | |
LPMR | lateral posterior thalamic nucleus, mediorostral part | 29–32 | |
LPO | lateral preoptic area | 22–25 | |
LPtA | lateral parietal association cortex | 28–30 | |
LR4V | lateral recess of the 4th ventricle | 45–51 | |
LRt | lateral reticular nucleus | 54–59 | |
LRtPC | lateral reticular nucleus, parvicellular part | 56–58 | |
LRtS5 | lateral reticular nucleus, subtrigeminal part | 55–56 | |
LSD | lateral septal nucleus, dorsal part | 19–25 | |
LSI | lateral septal nucleus, intermediate part | 18–23 | |
LSO | lateral superior olive | 45–47 | |
LSS | lateral stripe of the striatum | 21–23 | |
LSV | lateral septal nucleus, ventral part | 19–23 | |
LT | lateral terminal nucleus of the accessory optic tract | 33 | |
LTer | lemina terminalis | 24 | |
Lth | lithoid nucleus | 33 | |
LV | lateral ventricle | 17–32 | |
LVe | lateral vestibular nucleus | 47–49 | |
LVPO | lateroventral periolivary nucleus | 44–47 | |
M | |||
M1 | primary motor cortex | 11–28 | |
M2 | secondary motor cortex | 10–28 | |
m5 | motor root of the trigeminal nerve | 43–45 | |
MA3 | medial accessory oculomotor nucleus | 34–35 | |
mcer | middle cerebral artery | 23 | |
mch | medial corticohypothalamic tract | 25 | |
MCLH | magnocellular nucleus of the lateral hypothalamus | 29 | |
mcp | middle cerebellar peduncle | 40–46 | |
MCPC | magnocellular nucleus of the posterior commissure | 33–34 | |
MCPO | magnocellular preoptic nucleus | 23–25 | |
MD | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus | 27 | |
MDC | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, central part | 28–30 | |
MdD | medullary reticular nucleus, dorsal part | 55–62 | |
MDL | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, lateral part | 28–30 | |
MDM | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, medial part | 28–30 | |
MdV | medullary reticular nucleus, ventral part | 55–62 | |
ME | median eminence | 30–32 | |
Me5 | mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus | 38–45 | |
me5 | mesencephalic trigeminal tract | 43–45 | |
MeAD | medial amygdaloid nucleus, anterodorsal part | 26–27 | |
MeAV | medial amygdaloid nucleus, anteroventral part | 27 | |
Med | medial (fastigial) cerebellar nucleus | 47–50 | |
MedDL | medial cerebellar nucleus, dorsolateral protuberance | 49–50 | |
MedL | medial cerebellar nucleus, lateral part | 49–50 | |
MEnt | medial entorhinal cortex | 34–41 | |
MePD | medial amygdaloid nucleus, posterodorsal part | 27–29 | |
MePV | medial amygdaloid nucleus, posteroventral part | 28–29 | |
mfb | medial forebrain bundle | 19–32 | |
MGD | medial geniculate nucleus, dorsal part | 33–36 | |
MGM | medial geniculate nucleus, medial part | 33–36 | |
MGV | medial geniculate nucleus, ventral part | 33–36 | |
MHb | medial habenular nucleus | 27–31 | |
Mi | mitral cell layer of the olfactory bulb | 1–10 | |
MiA | mitral cell layer of the accessory olfactory bulb | 5–9 | |
MiTg | microcellular tegmental nucleus | 38–39 | |
ml | medial lemniscus | 28–54 | |
ML | medial mammillary nucleus, lateral part | 34–36 | |
mlf | medial longitudinal fasciculus | 37–62 | |
mlx | medial lemniscal decussation | 56 | |
MM | medial mammillary nucleus, medial part | 34–35 | |
MnA | median accessory nucleus of the medulla | 59–62 | |
MnM | medial mammillary nucleus, median part | 34 | |
MnPO | median preoptic nucleus | 22–24 | |
MnR | median raphe nucleus | 39–43 | |
MNTB | medial nucleus of the trapezoid body | 43–47 | |
MO | medial orbital cortex | 8–14 | |
MoDG | molecular layer of the dentate gyrus | 27–37 | |
MoS | molecular layer of the subiculum | 37 | |
mp | mammillary peduncle | 35–36 | |
MPA | medial preoptic area | 22–25 | |
MPB | medial parabrachial nucleus | 43–45 | |
MPBE | medial parabrachial nucleus, external part | 44 | |
MPL | paralemniscal nucleus, medial part | 41–42 | |
MPO | medial preoptic nucleus | 24–25 | |
MPT | medial pretectal nucleus | 32 | |
MPtA | medial parietal association cortex | 28–30 | |
MRe | mammillary recess of the 3rd ventricle | 34 | |
mRt | mesencehalic reticular formation | 36–38 | |
MS | medial septal nucleus | 19–23 | |
MSO | medial superior olive | 44–47 | |
mt | mammillothalamic tract | 27–33 | |
MT | medial terminal nucleus of the accessory optic tract | 35 | |
mtg | mammillotegmental tract | 33 | |
MTu | medial tuberal nucleus | 29–31 | |
MVe | medial vestibular nucleus | 53 | |
MVeMC | medial vestibular nucleus, magnocellular part | 46–52 | |
MVePC | medial vestibular nucleus, parvicellular part | 46–52 | |
MVPO | medioventral periolivary nucleus | 44–47 | |
Mx | matrix region of the medulla | 50–59 | |
MZMG | marginal zone of the medial geniculate | 33–35 | |
N | |||
ns | nigrostriatal bundle | 27–33 | |
Nv | navicular nucleus of the basal forebrain | 17–18 | |
O | |||
Obex | obex | 57 | |
oc | olivocerebellar tract | 50–54 | |
Oca | octopus cell area, ventral cochlear nucleus | 47–49 | |
ocb | olivocochlear bundle | 46–47 | |
och | optic chiasm | 21–25 | |
ON | olfactory nerve layer | 1–8 | |
Op | optic nerve layer of the superior colliculus | 33–40 | |
OPC | oval paracentral thalamic nucleus | 29–31 | |
OPT | olivary pretectal nucleus | 32–33 | |
opt | optic tract | 26–33 | |
Or | oriens layer of the hippocampus | 27–36 | |
OT | nucleus of the optic tract | 32–35 | |
OV | olfactory ventricle (olfactory part of lateral ventricle) | 1–16 | |
P | |||
p1PAG | p1 periaqueductal gray | 32–34 | |
p1Rt | p1 reticular formation | 32–35 | |
P5 | peritrigeminal zone | 43–46 | |
P7 | perifacial zone | 48–51 | |
Pa4 | paratrochlear nucleus | 40–41 | |
Pa5 | paratrigeminal nucleus | 54–57 | |
Pa6 | paraabducens nucleus | 46–47 | |
PaAP | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, anterior parvicellular part | 25–26 | |
PaMM | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, medial magnocellular part | 27–28 | |
PaMP | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, medial parvicellular part | 27 | |
PaPo | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, posterior part | 28 | |
PaR | pararubral nucleus | 35–38 | |
PaS | parasubiculum | 35–42 | |
PaV | paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, ventral part | 27 | |
PaXi | paraxiphoid nucleus of thalamus | 27–29 | |
PBG | parabigeminal nucleus | 38–40 | |
PBP | parabrachial pigmented nucleus of the ventral tegmental area | 33–37 | |
PC | paracentral thalamic nucleus | 27–30 | |
pc | posterior commissure | 32–34 | |
PCGS | paracochlear glial substance | 46 | |
pcn | precentral fissure | 43–46 | |
PCom | nucleus of the posterior commissure | 33–34 | |
PCRt | parvicellular reticular nucleus | 46–54 | |
pcuf | preculminate fissure | 43–47 | |
PDR | posterodorsal raphe nucleus | 39–42 | |
PDTg | posterodorsal tegmental nucleus | 45 | |
Pe | periventricular hypothalamic nucleus | 23–30 | |
PeF | perifornical nucleus | 29–30 | |
PeFLH | perifornical part of lateral hypothalamus | 29–32 | |
PF | parafascicular thalamic nucleus | 31–32 | |
PFl | paraflocculus | 43–50 | |
pfs | parafloccular sulcus | 44–50 | |
PH | posterior hypothalamic nucleus | 31–32 | |
PHA | posterior hypothalamic area | 33 | |
PHD | posterior hypothalamic area, dorsal part | 30–31 | |
PIF | parainterfascicular nucleus of the ventral tegmental area | 36–37 | |
PIL | posterior intralaminar thalamic nucleus | 33–35 | |
Pir | piriform cortex | 11–33 | |
PL | paralemniscal nucleus | 40–42 | |
PLCo | posterolateral cortical amygdaloid nucleus | 27–29 | |
plf | posterolateral fissure | 43–55 | |
PLH | peduncular part of lateral hypothalamus | 26–33 | |
PLi | posterior limitans thalamic nucleus | 33–35 | |
PLV | perilemniscal nucleus, ventral part | 41–43 | |
PM | paramedian lobule | 49–56 | |
pm | principal mammillary tract | 33–34 | |
PMCo | posteromedial cortical amygdaloid nucleus | 29–33 | |
PMD | premammillary nucleus, dorsal part | 33 | |
PMnR | paramedian raphe nucleus | 39–42 | |
pms | paramedian sulcus | 50–55 | |
PMV | premammillary nucleus, ventral part | 32–33 | |
PN | paranigral nucleus of the ventral tegmental area | 36–37 | |
Pn | pontine nuclei | 39–42 | |
PnC | pontine reticular nucleus, caudal part | 44–47 | |
PnO | pontine reticular nucleus, oral part | 39–43 | |
PnR | pontine raphe nucleus | 43 | |
PnV | pontine reticular nucleus, ventral part | 45–47 | |
Po | posterior thalamic nuclear group | 28–33 | |
PoDG | polymorph layer of the dentate gyrus | 28–35 | |
PoMn | posteromedian thalamic nucleus | 31 | |
Post | postsubiculum | 35–40 | |
PoT | posterior thalamic nuclear group, triangular part | 33–35 | |
PP | peripeduncular nucleus | 33–35 | |
ppf | prepyramidal fissure | 51–56 | |
PPT | posterior pretectal nucleus | 33–35 | |
PPy | parapyramidal nucleus | 49–50 | |
Pr | prepositus nucleus | 47–53 | |
PR | prerubral field | 31–34 | |
Pr5DM | principal sensory trigeminal nucleus, dorsomedial part | 44–47 | |
Pr5VL | principal sensory trigeminal nucleus, ventrolateral part | 43–47 | |
PrC | precommissural nucleus | 31–33 | |
PrCnF | precuneiform area | 38–41 | |
PrEW | pre-Edinger–Westphal nucleus | 34–35 | |
prf | primary fissure | 43–50 | |
PRh | perirhinal cortex | 28–42 | |
PrL | prelimbic cortex | 9–18 | |
PrS | presubiculum | 35–38 | |
PS | parastrial nucleus | 23–24 | |
psf | posterior superior fissure | 43–54 | |
PSol | parasolitary nucleus | 54–55 | |
PSTh | parasubthalamic nucleus | 32 | |
PT | paratenial thalamic nucleus | 25–27 | |
Pta | pericollicular tegmental area | 39–43 | |
PTe | paraterete nucleus | 29–30 | |
PTg | pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus | 38–42 | |
PtP | parietal cortex, posterior area | 28–31 | |
PV | paraventricular thalamic nucleus | 27–28 | |
PVA | paraventricular thalamic nucleus, anterior part | 25–26 | |
PVP | paraventricular thalamic nucleus, posterior part | 29–31 | |
Py | pyramidal cell layer of the hippocampus | 27–36 | |
py | pyramidal tract | 43–58 | |
pyx | pyramidal decussation | 57–62 | |
R | |||
Rad | radiatum layer of the hippocampus | 28–36 | |
RAmb | retroambiguus nucleus | 56–58 | |
RAPir | rostral amygdalopiriform area | 28–30 | |
Rbd | rhabdoid nucleus | 39 | |
RCh | retrochiasmatic area | 27–28 | |
RChL | retrochiasmatic area, lateral part | 27 | |
Re | reuniens thalamic nucleus | 26–30 | |
REth | retroethmoid nucleus | 33 | |
rf | rhinal fissure | 7–41 | |
Rh | rhomboid thalamic nucleus | 27–30 | |
ri | rhinal incisure | 7–12 | |
RI | rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus | 32–33 | |
RIP | raphe interpositus nucleus | 46–48 | |
RLi | rostral linear nucleus of the raphe | 35–35 | |
RMC | red nucleus, magnocellular part | 35–38 | |
RMg | raphe magnus nucleus | 44–51 | |
Ro | nucleus of Roller | 52–56 | |
ROb | raphe obscurus nucleus | 50–58 | |
RPa | raphe pallidus nucleus | 43–58 | |
RPC | red nucleus, parvicellular part | 35–36 | |
RPO | rostral periolivary nucleus | 44 | |
RR | retrorubral nucleus | 39–40 | |
RRe | retrouniens area | 31 | |
RRF | retrorubral field | 37–39 | |
rs | rubrospinal tract | 41–62 | |
RSD | retrosplenial dysgranular cortex | 27–42 | |
RSG | retrosplenial granular cortex | 40 | |
RSGa | retrosplenial granular cortex, a region | 35–39 | |
RSGb | retrosplenial granular cortex, b region | 32–39 | |
RSGc | retrosplenial granular cortex, c region | 27–36 | |
Rt | reticular thalamic nucleus | 26–30 | |
RtSt | reticluostrial nucleus | 26 | |
RtTg | reticulotegmental nucleus of the pons | 41–45 | |
RtTgP | reticulotegmental nucleus of the pons, pericentral part | 41–42 | |
RVRG | rostral ventral respiratory group | 53 | |
S | |||
S1 | primary somatosensory cortex | 24–30 | |
S1BF | primary somatosensory cortex, barrel field | 20–28 | |
S1DZ | primary somatosensory cortex, dysgranular zone | 16–28 | |
S1DZO | primary somatosensory cortex, oral dysgranular zone | 18–19 | |
S1FL | primary somatosensory cortex, forelimb region | 15–24 | |
S1HL | primary somatosensory cortex, hindlimb region | 20–26 | |
S1J | primary somatosensory cortex, jaw region | 13–20 | |
S1Sh | primary somatosensory cortex, shoulder region | 25–26 | |
S1Tr | primary somatosensory cortex, trunk region | 27–28 | |
S1ULp | primary somatosensory cortex, upper lip region | 18–28 | |
S2 | secondary somatosensory cortex | 18–28 | |
s5 | sensory root of the trigeminal nerve | 42–47 | |
Sag | sagulum nucleus | 41–43 | |
Sc | scaphoid thalamic nucleus | 32 | |
Sca | spherical cell area, ventral cochlear nucleus | 43–46 | |
scc | splenium of the corpus callosum | 31–33 | |
SCh | suprachiasmatic nucleus | 25 | |
SChDL | suprachiasmatic nucleus, dorsolateral part | 26 | |
SChVM | suprachiasmatic nucleus, ventromedial part | 26 | |
SCO | subcommissural organ | 32–34 | |
scp | superior cerebellar peduncle | 41–49 | |
sf | secondary fissure | 53–58 | |
SFi | septofimbrial nucleus | 22–25 | |
SFO | subfornical organ | 25 | |
SG | suprageniculate thalamic nucleus | 33–36 | |
SGe | supragenual nucleus | 46 | |
SHi | septohippocampal nucleus | 18–25 | |
SIB | substantia innominata, basal part | 21–24 | |
Sim | simple lobule | 43–49 | |
simf | simplex fissure | 47–49 | |
SLu | stratum lucidum of the hippocampus | 28–33 | |
sm | stria medullaris of the thalamus | 25–30 | |
SMV | superior medullary velum | 45–47 | |
SNC | substantia nigra, compact part | 33–38 | |
SNR | substantia nigra, reticular part | 33–38 | |
SO | supraoptic nucleus | 23–27 | |
Sol | nucleus of the solitary tract | 49–50 | |
sol | solitary tract | 50–57 | |
SolC | nucleus of the solitary tract, commissural part | 55–62 | |
SolDL | solitary nucleus, dorsolateral part | 55–57 | |
SolM | nucleus of the solitary tract, medial part | 55–59 | |
SolV | solitary nucleus, ventral part | 55–57 | |
SolVL | nucleus of the solitary tract, ventrolateral part | 55–57 | |
sox | supraoptic decussation | 26–32 | |
sp5 | spinal trigeminal tract | 48–62 | |
Sp5C | spinal trigeminal nucleus, caudal part | 55–62 | |
Sp5I | spinal trigeminal nucleus, interpolar part | 49–56 | |
Sp5O | spinal trigeminal nucleus, oral part | 48–51 | |
SPa | subparaventricular zone of the hypothalamus | 27–28 | |
SPF | subparafascicular thalamic nucleus | 31 | |
SPFPC | subparafascicular thalamic nucleus, parvicellular part | 31–32 | |
SPN | superior periolivary nucleus | 44–47 | |
SPTg | subpeduncular tegmental nucleus | 40–42 | |
SpVe | spinal vestibular nucleus | 48–53 | |
ST | bed nucleus of the stria terminalis | 22 | |
st | stria terminalis | 23–31 | |
StA | strial part of the preoptic area | 23 | |
STh | subthalamic nucleus | 30–32 | |
STIA | bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, intraamygdaloid division | 28–29 | |
STLI | bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division, intermediate part | 24 | |
STLP | bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division, posterior part | 23–24 | |
STLV | bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, lateral division, ventral part | 23–24 | |
STMA | bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division, anterior part | 23–24 | |
STMP | bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division, posterior part | 25–26 | |
STMV | bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial division, ventral part | 23–24 | |
STr | subiculum, transition area | 37–38 | |
str | superior thalamic radiation | 31–32 | |
Su3 | supraoculomotor periaqueductal gray | 36–39 | |
Su3C | supraoculomotor cap | 36–36 | |
Su5 | supratrigeminal nucleus | 43–45 | |
Sub | submedius thalamic nucleus | 30 | |
SubB | subbrachial nucleus | 36–38 | |
SubCA | subcoeruleus nucleus, alpha part | 44 | |
SubCD | subcoeruleus nucleus, dorsal part | 43–45 | |
SubCV | subcoeruleus nucleus, ventral part | 43–45 | |
SubD | submedius thalamic nucleus, dorsal part | 28–29 | |
SubG | subgeniculate nucleus | 31–32 | |
SubI | subincertal nucleus | 29–30 | |
SubV | submedius thalamic nucleus, ventral part | 28–29 | |
SuG | superficial gray layer of the superior colliculus | 33–41 | |
SuML | supramammillary nucleus, lateral part | 33–34 | |
SuMM | supramammillary nucleus, medial part | 33–34 | |
sumx | supramammillary decussation | 34 | |
SuVe | superior vestibular nucleus | 46–47 | |
T | |||
Te | terete hypothalamic nucleus | 31 | |
TeA | temporal association cortex | 37–39 | |
tfp | transverse fibers of the pons | 39 | |
TG | tectal gray | 33–35 | |
ts | tectospinal tract | 39–62 | |
TS | triangular septal nucleus | 24–25 | |
tth | trigeminothalamic tract | 43–45 | |
Tu | olfactory tubercle | 16–23 | |
TuLH | tuberal region of lateral hypothalamus | 27–31 | |
tz | trapezoid body | 43–49 | |
tzx | decussation of the trapezoid body | 44–47 | |
U | |||
uf | uvular fissure | 56–59 | |
V | |||
V1 | primary visual cortex | 31–42 | |
V1B | primary visual cortex, binocular area | 32–39 | |
V1M | primary visual cortex, monocular area | 32–39 | |
V2L | secondary visual cortex, lateral area | 31–41 | |
V2M | secondary visual cortex, medial area | 31–40 | |
VA | ventral anterior thalamic nucleus | 27 | |
VCA | ventral cochlear nucleus, anterior part | 43–47 | |
VCl | ventral part of claustrum | 16–26 | |
VCP | ventral cochlear nucleus, posterior part | 47–49 | |
VDB | nucleus of the vertical limb of the diagonal band | 19–21 | |
VeCb | vestibulocerebellar nucleus | 46–49 | |
veme | vestibulomesencephalic tract | 46–48 | |
VEn | ventral endopiriform nucleus | 24–29 | |
vesp | vestibulospinal tract | 49 | |
VG | ventral geniculate nucleus | 29–34 | |
VGMC | ventral geniculate nucleus, magnocellular part | 31–32 | |
VGPC | ventral geniculate nucleus, parvicellular part | 31–32 | |
vhc | ventral hippocampal commissure | 25–27 | |
VL | ventrolateral thalamic nucleus | 27–30 | |
VLH | ventrolateral hypothalamic nucleus | 27 | |
vlh | ventrolateral hypothalamic tract | 27 | |
VLi | ventral linear nucleus of the thalamus | 33 | |
VLPAG | ventrolateral periaqueductal gray | 37–42 | |
VLPO | ventrolateral preoptic nucleus | 23–24 | |
VM | ventromedial thalamic nucleus | 27–30 | |
VMH | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus | 28–31 | |
VMHC | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, central part | 29–30 | |
VMHDM | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, dorsomedial part | 29–30 | |
VMHSh | ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus shell | 28–31 | |
VMHVL | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, ventrolateral part | 29–30 | |
VMPO | ventromedial preoptic nucleus | 23–24 | |
VNLL | ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus | 40 | |
VNTB | ventral nucleus of the trapezoid body | 43–47 | |
VO | ventral orbital cortex | 9–16 | |
VP | ventral pallidum | 16–25 | |
VPL | ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus | 28–31 | |
VPM | ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus | 28–32 | |
VPPC | ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus, parvicellular part | 31 | |
VRe | ventral reuniens thalamic nucleus | 27–30 | |
VS | ventral subiculum | 31–36 | |
vsc | ventral spinocerebellar tract | 43–62 | |
VTA | ventral tegmental area | 37–38 | |
VTAR | ventral tegmental area, rostral part | 34–35 | |
VTg | ventral tegmental nucleus | 42 | |
vtgx | ventral tegmental decussation | 35–37 | |
VTM | ventral tuberomammillary nucleus | 33–34 | |
VTT | ventral tenia tecta | 11–16 | |
vVNLL | ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus, ventral part | 41–43 | |
X | |||
X | nucleus X | 48–52 | |
Xi | xiphoid thalamic nucleus | 27–28 | |
xscp | decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle | 39–41 | |
Y | |||
Y | nucleus Y | 48 | |
Z | |||
ZI | zona incerta | 28–29 | |
ZIC | zona incerta, caudal part | 34–34 | |
ZID | zona incerta, dorsal part | 30–33 | |
ZIR | zona incerta, rostral part | 26–27 | |
ZIV | zona incerta, ventral part | 30–33 | |
Zo | zonal layer of the superior colliculus | 33–41 | |
























































































































































































































































.
References
Budinger E, Heil P, Scheich H (2000) Functional organization of auditory cortex in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). IV. Connections with anatomically characterized subcortical structures. Eur J Neurosci 12(7):2452–2474. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00143.x
Budinger E, Brosch M, Scheich H, Mylius J (2013) The subcortical auditory structures in the Mongolian gerbil: II. Frequency-related topography of the connections with cortical field AI. J Comp Neurol 521(12):2772–2797. doi:10.1002/cne.23314
Dong H-W (2008) Allen reference atlas: a digital color brain atlas of the C57BL/6 J male mouse. Wiley, Hoboken. doi:10.1111/j.1601-183X.2009.00552.x
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (2008) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Hong Kong. ISBN 0123742445
Gallyas F (1979) Silver staining of myelin by means of physical development. Neurol Res 1(2):203–209
Loskota WJ, Lomax P, Verity A (1974) A stereotaxic atlas of the mongolian gerbil brain (Meriones unguiculatus). Ann Arbor Science Publishers Inc, Ann Arbor, p 48106. ISBN 0-250-40040-5
Mylius J, Brosch M, Scheich H, Budinger E (2013) Subcortical auditory structures in the Mongolian gerbil: I. Golgi architecture. J Comp Neurol 521(6):1289–1321. doi:10.1002/cne.23232
Paxinos G (1995) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, Sydney. ISBN 0125476353
Paxinos G (2004) The rat nervous system. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego. ISBN 0080542614
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Hong Kong
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, San Diego. ISBN 978-0-12-547612-4
Paxinos G, Watson C, Carrive P, Kirkcaldie M, Ashwell KWS (2009) Chemoarchitectonic atlas of the rat brain. Academic Press, London. ISBN 0123742377
Radtke-Schuller S, Seeler S, Grothe B (2015) Restricted loss of olivocochlear but not vestibular efferent neurons in the senescent gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Front Aging Neurosci 7:4. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2015.00004
Schuller G, Radtke-Schuller S, Betz M (1986) A stereotaxic method for small animals using experimentally determined reference profiles. J Neurosci Methods 18(4):339–350
Swanson LW (1992) Brain maps: structure of the rat brain. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 0444814140
Swanson LW (2004) Brain maps III: structure of the rat brain. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 0126105820
Swanson LW (2015) Brain maps online: toward open access atlases and a pan-mammalian nomenclature. J Comp Neurol 523:2272–2276. doi:10.1002/cne.23788
Thiessen D, Goar S (1970) Stereotaxic atlas of the hypothalamus of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). J Comp Neurol 140(1):123–127. doi:10.1002/cne.901400108
Thiessen D, Yahr P (1977) The gerbil in behavioral investigations. University of Texas Press, Austin. ISBN 0-292-74190-4
Thomas O (1908) The Duke of Bedford’s zoological exploration in Eastern Asia. XI List of mammals from the Mongolian plateau. Proc Zool Soc Lond:104–110
Watson C, Paxinos G (2010) Chemoarchitectonic atlas of the mouse brain. Elsevier Academic Press, London. ISBN 9780123694973
Watson C, Paxinos G, Puelles L (2012) The mouse nervous system. Academic Press, London. ISBN 9780123694973
Zilles K (1985) The cortex of the rat. Springer, Heidelberg. ISBN 3642705758
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Anja Gürke, Sibylle Kerling, Karla Krautwald, Barbara Mosler and Gitta Ziegleder for their technical assistance and George Pollak for correcting the English version. The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding sources BMBF (German Federal Ministry of Education and Research; FKZ: EO 0901; IFB, German Center for Vertigo and Balance Disorders), DFG (German Research Foundation; SFB TRR31), GSN (Graduate School for Systemic Neurosciences Munich) and the Anatomical Institute of the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experiments were in agreement with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (2011) and the guidelines of the European Communities Council Directive (86/609/EEC) and approved by the animal care committee of Sachsen-Anhalt, Germany.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Radtke-Schuller, S., Schuller, G., Angenstein, F. et al. Brain atlas of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) in CT/MRI-aided stereotaxic coordinates. Brain Struct Funct 221 (Suppl 1), 1–272 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1259-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1259-0