Abstract
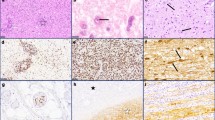
The initial stages of Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis in mice were immunohistochemically characterized following the first 8 h post-intranasal inoculation. The events found after 8 h were: (1) amebas in contact with the mucous layer of the olfactory epithelium, (2) numerous parasites eliminated by extensive shedding of the mucous layer, and (3) many organisms reaching the nasal epithelium. In contrast to other works, we observed that after 24 h, amebas invaded the epithelium, without evidence of the disruption of the nasal mucosa. In addition some trophozoites invading through the respiratory epithelium were observed, suggesting an additional invasion route. The inflammatory response detected was scarce until 30 h post-inoculation. After 96 h, the inflammatory response was severe in the olfactory bulb and brain, and the tissue damage great. Consequently, an inflammatory reaction may enhance tissue damage but apparently does not destroy amebas which seem to proliferate in the olfactory bulb.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldape K, Huizinga H, Bouvier J, McKerrow J (1994) Naegleria fowleri: characterization of a secreted histolytic cysteine protease. Exp Parasitol 78:230–241
Belley A, Keller K, Gottke M, Chadee K, Goettke M (1999) Intestinal mucins in colonization and host defense against pathogens. Am J Trop Med Hyg 60:10–15
Carter RF (1972) Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. An appraisal of present knowledge. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 66:193–213
Chadee K, Petri WAJr, Innes DJ, Ravdin JI (1987) Rat and human colonic mucins bind to and inhibit adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest 80:1245–1254
Chadee K, Johnson ML, Orozco E, Petri WA Jr, Ravdin JI (1988) Binding and internalization of rat colonic mucins by the galactose/N-acetyl-D-galactosamine adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis 158:398–406
Deplancke B, Gaskins HR (2001) Microbial modulation of innate defense: goblet cells and the intestinal mucus layer. Am J Clin Nutr 73:1131S–1141S.
Duma RJ, Rosenblum WI, McGehee RF, Jones MM, Nelson EC (1971) Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis caused by Naegleria. Two new cases, response to amphotericine B, and a review. Ann Intern Med 74:923–931
Eisen D, Franson RC (1987) Acid-active neuraminidases in the growth media from cultures of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri and in sonicates of rabbit alveolar macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta 19:369–372
Ferrante A (1989) Augmentation of the neutrophil response to Naegleria fowleri by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect Immun 57:3110–3115
Ferrante A, Mocatta TJ (1984) Human neutrophils require activation by mononuclear leucocyte conditioned medium to kill the pathogenic free-living amoeba, Naegleria fowleri. Clin Exp Immunol 56:559–566
Ferrante A, Carter RF, Lopez AF, Rowan-Kelly B, Hill NL, Vadas MA (1988) Depression of immunity to Naegleria fowleri in mice by selective depletion of neutrophils with a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun 56:2286–2291
Ferrante A, Hill NL, Goh DH, Kumaratilake L (1989) Altered neutrophils in mice immune to experimental Naegleria amoebic meningoencephalitis. Immunol Lett 22:301–305
Fulford DE, Marciano-Cabral F (1986) Cytolytic activity of Naegleria fowleri cell-free extract. J Protozool 33:498–502
Imai S, Fujita K (2004) Molecules of parasites as immunomodulatory drugs. Curr Top Med Chem 4:539–552
Jarolim KL, McCosh JK, Howard MJ, John DT (2000) A light microscopy study of the migration of Naegleria fowleri from the nasal submucosa to the central nervous system during the early stage of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in mice. J Parasitol 86:50–55
John DT (1993) Opportunistically pathogenic free-living amebas. In: Kreier JP, Baker JR (eds) Parasitic protozoa. Academic Press, New York, pp 143–244
Martinez AJ (1985) Free-living amebas: natural history, prevention diagnosis, pathology, and treatment of disease. CRC, Boca Raton, Fla., pp 1–156
Martinez AJ, Visvesvara G (1997) Free-living, amphizoic and opportunistic amebas. Brain Pathol 7:583–598
Martinez AJ, Duma RJ, Nelson EC, Moretta FL (1973) Experimental Naegleria meningoencephalitis in mice. Penetration of the olfactory mucosal epithelium by Naegleria and pathologic changes produced: a light and electron microscopy study. Lab Invest 29:121–133
Olomu N, Martinez AJ, Lamarco KL, Nerad TA, Saha AK, Das S, Glew RH (1986) Demonstration of various acid hydrolases and preliminary characterization of acid phosphatase in Naegleria fowleri. J Protozool 33:317–321
Singh BN, Das SR (1970) Studies on pathogenic and non-pathogenic small free-living amebas and the bearing of nuclear division on the classification of the order Amoebida. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 259:435–476
Thong YH, Ferrante A, Rowan-Kelly B (1983) Site of expression of immunity to Naegleria fowleri in immunized mice. Parasite Immunol 5:67–76
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by COFAA, IPN, CONACyT 34834 and 43102 and UNAM DGAPA PAPIIT IN207800 and IN213903 grants. Saul Rojas Hernandez was supported by a doctoral fellowship from the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) and Consejo Mexiquense de Ciencia y Tecnología. (COMECYT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rojas-Hernández, S., Jarillo-Luna, A., Rodríguez-Monroy, M. et al. Immunohistochemical characterization of the initial stages of Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis in mice. Parasitol Res 94, 31–36 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1177-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1177-6