Abstract
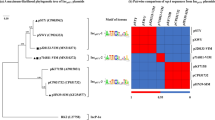
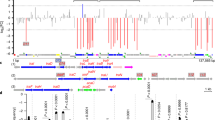
Plasmid pB4 is a conjugative antibiotic resistance plasmid, originally isolated from a microbial community growing in activated sludge, by means of an exogenous isolation method with Pseudomonas sp. B13 as recipient. We have determined the complete nucleotide sequence of pB4. The plasmid is 79,370 bp long and contains at least 81 complete coding regions. A suite of coding regions predicted to be involved in plasmid replication, plasmid maintenance, and conjugative transfer revealed significant similarity to the IncP-1β backbone of R751. Four resistance gene regions comprising mobile genetic elements are inserted in the IncP-1β backbone of pB4. The modular 'gene load' of pB4 includes (1) the novel transposon Tn5719 containing genes characteristic of chromate resistance determinants, (2) the transposon Tn5393c carrying the widespread streptomycin resistance gene pair strA-strB, (3) the β-lactam antibiotic resistance gene bla NPS-1 flanked by highly conserved sequences characteristic of integrons, and (4) a tripartite antibiotic resistance determinant comprising an efflux protein of the resistance-nodulation-division (RND) family, a periplasmic membrane fusion protein (MFP), and an outer membrane factor (OMF). The components of the RND-MFP-OMF efflux system showed the highest similarity to the products of the mexCD-oprJ determinant from the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosome. Functional analysis of the cloned resistance region from pB4 in Pseudomonas sp. B13 indicated that the RND-MFP-OMF efflux system conferred high-level resistance to erythromycin and roxithromycin resistance on the host strain. This is the first example of an RND-MFP-OMF-type antibiotic resistance determinant to be found in a plasmid genome. The global genetic organization of pB4 implies that its gene load might be disseminated between bacteria in different habitats by the combined action of the conjugation apparatus and the mobility of its component elements.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Berg T, Firth N, Apisiridej S, Hettiaratchi A, Leelaporn A, Skurray RA (1998) Complete nucleotide sequence of pSK41: evolution of staphylococcal conjugative multiresistance plasmids. J Bacteriol 180:4350–4359
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Cervantes C, Ohtake H, Chu L, Misra TK, Silver S (1990) Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the chromate resistance determinant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa plasmid pUM505. J Bacteriol 172:287–291
Cervantes C, Campos-Garcia J, Devars S, Gutierrez-Corona F, Loza-Tavera H, Torres-Guzman JC, Moreno-Sanchez R (2001) Interaction of chromium with microorganisms and plants. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:335–347
Chiou C-S, Jones AL (1993) Nucleotide sequence analysis of a transposon (Tn5393) carrying streptomycin resistance genes in Erwinia amylovora and other gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 175:732–740
Chiou C-S, Jones AL (1995) Expression and identification of the strA-strB gene pair from streptomycin-resistant Erwinia amylovora. Gene 152:47–51
Delcher AL, Harmon D, Kasif S, White O, Salzberg SL (1999) Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucleic Acids Res 27:4636–4641
Dodd IB, Egan JB (1990) Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 18:5019–5026
Dröge M, Pühler A, Selbitschka W (1999) Horizontal gene transfer among bacteria in terrestrial and aquatic habitats as assessed by microcosm and field studies. Biol Fertil Soils 29:221–245
Dröge M, Pühler A, Selbitschka W (2000) Phenotypic and molecular characterization of conjugative antibiotic resistance plasmids isolated from bacterial communities of activated sludge. Mol Gen Genet 263:471–482
Gotoh N, Kusumi T, Tsujimoto H, Wada T, Nishino T (1999) Topological analysis of an RND family transporter, MexD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett 458:32–36
Hall RM, Brown HJ, Brookes DE, Stokes HW (1994) Integrons found in different locations have identical 5′ ends but variable 3′ ends. J Bacteriol 176:6286–6294
Kurtz S, Choudhuri JV, Ohlebusch E, Schleiermacher C, Stoye J, Giegerich R (2001) REPuter: the manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4633–4642
L'Abée-Lund TM, Sørum H (2000) Functional Tn5393-like transposon in the R plasmid pRAS2 from the fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida subspecies salmonicida isolated in Norway. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5533–5535
Levesque RC, Jacoby GA (1988) Molecular structure and interrelationships of multiresistance β-lactamase transposons. Plasmid 19:21–29
Livermore DM, Jones CS (1986) Characterization of NPS-1, a novel plasmid-mediated β-lactamase, from two Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 29:99–103
Morita Y, Komori Y, Mima T, Kuroda T, Mizushima T, Tsuchiya T (2001) Construction of a series of mutants lacking all of the four major mex operons for multidrug efflux pumps or possessing each one of the operons from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: MexCD-OprJ is an inducible pump. FEMS Microbiol Lett 202:139–143
Myers EW, Miller W (1988) Optimal alignments in linear space. Comput Appl Biosci 4:11–17
Naas T, Nordmann P (1999) OXA-type β-lactamases. Curr Pharm Design 5:865–879
National Committee of Clinical Laboratory Standards (1997) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically: approved standards (4th edn). National Committee of Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Penn.
Nies A, Nies DH, Silver S (1990) Nucleotide sequence and expression of a plasmid-encoded chromate resistance determinant from Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Biol Chem 265:5648–5653
Pai H, Jacoby GA (2001) Sequences of the NPS-1 and TLE-1 β-lactamase genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:2947–2948
Pansegrau W, Lanka E, Barth PT, Figurski DH, Guiney DG, Haas D, Helinski DR, Schwab H, Stanisich VA, Thomas CM (1994) Complete nucleotide sequence of Birmingham IncPα plasmids: compilation and comparative analysis. J Mol Biol 239:623–663
Perreten V, Schwarz F, Cresta L, Boeglin M, Dasen G, Teuber M (1997) Antibiotic resistance spread in food. Nature 389:801–802
Poole K (2001a) Multidrug resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 4:500–508
Poole K (2001b) Multidrug efflux pumps and antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related organisms. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 3:255–264
Poole K, Gotoh N, Tsujimoto H, Zhao Q, Wada A, Yamasaki T, Neshat S, Yamagishi J, Li X-Z, Nishino T (1996) Overexpression of the mexC - mexD - oprJ efflux operon in nfxB -type multidrug-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 21:713–724
Prell J, Boesten B, Poole P, Priefer UB (2002) The Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae VF39 γ-aminobutyrate (GABA) aminotransferase gene ( gabT) is induced by GABA and highly expressed in bacteroids. Microbiology 148:615–623
Radström P, Sköld O, Swedeberg G, Flensburg J, Roy PH, Sundström L (1994) Transposon Tn5090 of plasmid R751, which carries an integron, is related to Tn7, Mu, and the retroelements. J Bacteriol 176:3257–3268
Recchia GD, Hall RM (1995) Gene cassettes: a new class of mobile elements. Microbiology 141:3015–3027
Reese MG, Harris NL, Eeckman FH (1996) Large scale sequencing specific neural networks for promoter and splice site recognition. In: Hunter L, Klein TE (eds) Biocomputing (Proceedings of the 1996 Pacific Symposium). World Scientific Publishing, Singapore
Rost B, Casadio R, Fariselli P, Sander C (1995) Prediction of helical transmembrane segments at 95% accuracy. Protein Sci 4:521–533
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd edn). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Schneiker S, Keller M, Dröge M, Lanka E, Pühler A, Selbitschka W (2001) The genetic organization and evolution of the broad host range mercury resistance plasmid pSB102 isolated from a microbial population residing in the rhizosphere of alfalfa. Nucleic Acids Res 29:5169–5181
Schwarz FV, Perreten V, Teuber M (2001) Sequence of the 50-kb conjugative multiresistance plasmid pRE25 from Enterococcus faecalis RE25. Plasmid 46:170–187
Séveno NA, Kallifidas D, Smalla K, van Elsas JD, Collard J-M, Karagouni AD, Wellington MH (2002) Occurrence and reservoirs of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Rev Med Microbiol 13:15–27
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in gram-negative bacteria. Biotechnology 1:784–794
Staden R (1996) The Staden sequence analysis package. Mol Biotechnol 5:233–241
Stover CK, et al (2000) Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406:959–964
Sundin GW (2000) Examination of base pair variants of the strA - strB streptomycin resistance genes from bacterial pathogens of humans, animals and plants. J Antimicrob Chemother 46:848–849
Sundin GW, Bender CL (1995) Expression of the strA - strB streptomycin resistance genes in Pseudomonas syringae and Xanthomonas campestris and characterization of IS6100 in X. campestris. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2891–2897
Sundin GW, Bender CL (1996) Dissemination of the strA - strB streptomycin-resistance genes among commensal and pathogenic bacteria from humans, animals, and plants. Mol Ecol 5:133–143
Tan Y-T, Tillet DJ, McKay IA (2000) Molecular strategies for overcoming antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Mol Medicine Today 6:309–314
Tauch A, Krieft S, Kalinowski J, Pühler A (2000) The 51,409-bp R-plasmid pTP10 from the multiresistant clinical isolate Corynebacterium striatum M82B is composed of DNA segments initially identified in soil bacteria and in plant, animal, and human pathogens. Mol Gen Genet 263:1–11
Teuber M (2001) Veterinary use and antibiotic resistance. Curr Opin Microbiol 4:493–499
Thorsted PB, Macartney DP, Akhtar P, Haines AS, Ali N, Davidson P, Stafford T, Pocklington MJ, Pansegrau W, Wilkins BM, Lanka E, Thomas CM (1998) Complete sequence of the IncPβ plasmid R751: implications for evolution and organization of the IncP backbone. J Mol Biol 282:969–990
Witte W (1998) Medical consequences of antibiotic use in agriculture. Science 279:996–997
Zgurskaya HI, Nikaido H (2000) Multidrug resistance mechanisms: drug efflux across two membranes. Mol Microbiol 37:219–225
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the sequencing team from IIT GmbH (Bielefeld, Germany) for DNA sequencing. This work was supported by BMBF grant 0312384.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Kondorosi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tauch, A., Schlüter, A., Bischoff, N. et al. The 79,370-bp conjugative plasmid pB4 consists of an IncP-1β backbone loaded with a chromate resistance transposon, the strA-strB streptomycin resistance gene pair, the oxacillinase gene bla NPS-1, and a tripartite antibiotic efflux system of the resistance-nodulation-division family. Mol Gen Genomics 268, 570–584 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-002-0785-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-002-0785-z