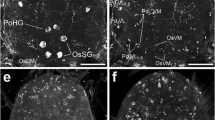
Abstract
Neuropeptides are crucial regulators of development and various physiological functions but little is known about their identity, expression and function in vectors of pathogens causing serious diseases, such as ticks. Therefore, we have used antibodies against multiple insect and crustacean neuropeptides to reveal the presence of these bioactive molecules in peptidergic neurons and cells of the ixodid tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus. These antibodies have detected 15 different immunoreactive compounds expressed in specific central and peripheral neurons associated with the synganglion. Most central neurons arborize in distinct areas of the neuropile or the putative neurohaemal periganglionic sheath of the synganglion. Several large identified neurons in the synganglion project multiple processes through peripheral nerves to form elaborate axonal arborizations on the surface of salivary glands or to terminate in the lateral segmental organs (LSO). Additional neuropeptide immunoreactivity has been observed in intrinsic secretory cells of the LSO. We have also identified two novel clusters of peripheral neurons embedded in the cheliceral and paraspiracular nerves. These neurons project branching axons into the synganglion and into the periphery. Our study has thus revealed a complex network of central and peripheral peptidergic neurons, putative neurohaemal and neuromodulatory structures and endocrine cells in the tick comparable with those found in insect and crustacean neuroendocrine systems. Strong specific staining with a large variety of antibodies also indicates that the tick nervous system and adjacent secretory organs are rich sources of diverse neuropeptides related to those identified in insects, crustaceans or even vertebrates.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali DW (1997) The aminergic and peptidergic innervation of insect salivary glands. J Exp Biol 200:1941–1949
Anastasi A, Erspamer V (1963) The isolation and amino acid sequence of eleidosin, the active endecapeptide of the posterior salivary glands of Eledone. Arch Biochem Biophys 101:56–65
Balashov YS (1998) Iksodovyje kleshchi - parazity i perenoschiki infektsij (in English: Ixodid ticks – parasites and vectors of diseases). Nauka, Sankt-Peterburg
Bendena WG, Donly BC, Tobe SS (1999) Allatostatins: a growing family of neuropeptides with structural and functional diversity. Ann NY Acad Sci 897:311–329
Binnington KC (1978) Sequential changes in salivary gland structure during attachment and feeding of the catle tick, Boophilus microplus. Int J Parasitol 8:97–115
Binnington KC (1981) Ultrastructural evidence for the endocrine nature of the lateral organs of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. Tissue Cell 13:475–490
Binnington KC (1987) Histology and ultrastructure of the acarine synganglion. In: Gupta AP (ed) Arthropod brain. Its evolution, development, structure, and functions. Wiley, New York, pp 95–109
Binnington KC, Tatchell RJ (1973) The nervous system and neurosecretory cells of Boophilus microplus (Acarina, Ixodidae). Z Wiss Zool 185:193–206
Champagne DE, Ribeiro J (1994) Sialokinin I and II. Vasodilatory tachykinins from the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:138–142
Chang ES, Kaufman WR (2005) Endocrinology of Crustacea and Chelicerata. In: Gilbert LI, Iatrou K, Gill SS (eds) Comprehensive molecular insect science, vol 3. Elsevier Pergamon, Amsterdam-Tokyo, pp 805–842
Chow YS, Wang CH (1974) Neurosecretory cells and their ultrastructures of Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille) (Acarina, Ixodidae). Acta Arachnol 25:53–67
Chow YS, Lin SH, Wang CH (1972) An ultrastructural and electrophysiological study of the brain of the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille). Chin Biosci I:83–92
Colombani J, Bianchini L, Layalle S, Pondeville E, Dauphin-Villemant C, Antoniewski C, Carre C, Noselli S, Leopold P (2005) Antagonistic actions of ecdysone and insulins determine final size in Drosophila. Science 310:667–670
Coons LB, Alberti G (1999) The Acari-ticks. In: Harrison FW, Foelix R (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 8B. Chelicerate Arthropoda. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 267–514
Coons LB, Roshdy MA (1973) Fine structure of the salivary glands of unfed male Dermacentor variabilis (Say) (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae). J Parasitol 59:900–912
Coons LB, Roshdy MA, Axtell RC (1974) Fine structure of the central nervous system of Dermacentor variabilis (Say), Amblyomma americanum (L.), and Argas arboreus Kaiser, Hoogstraal, and Kohls (Ixodoidea). J Parasitol 60:687–698
Coons LB, Lessman CA, Ward MA, Berg RH, Lamoreaux WJ (1994) Evidence of a myoepithelial cell in tick salivary glands. Int J Parasitol 24:551–562
Dai L, Žitňan D, Adams ME (2007) Strategic expression of ion transport peptide gene products in central and peripheral neurons of insects. J Comp Neurol 500:353–367
Davis HH, Dotson EM, Oliver JH Jr (1994) Localization of insulin-like immunoreactivity in the synganglion of nymphal and adult Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp Appl Acarol 18:111–122
Davis NT, Homberg U, Dircksen H, Levine RB, Hildebrand JG (1993) Crustacean cardioactive peptide-immunoreactive neurons in the hawkmoth Manduca sexta and changes in their immunoreactivity during postembryonic development. J Comp Neurol 338:612–627
Davis NT, Veenstra JA, Feyereisen R, Hildebrand JG (1997) Allatostatin-like-immunoreactive neurons of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta, and isolation and identification of a new neuropeptide related to cockroach allatostatins. J Comp Neurol 385:265–284
Dircksen H, Heyn U (1998) Crustacean hyperglycemic hormone-like peptides in crab and locust peripheral intrinsic neurosecretory cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 839:392–394
Dircksen H, Böcking D, Heyn U, Mandel C, Chung JS, Baggerman G, Verhaert P, Daufeldt S, Plösch T, Jaros PP, Waelkens E, Keller R, Webster SG (2001) Crustacean hyperglycemic hormone (CHH)-like peptides and CHH-precursor related peptides from pericardial organ neurosecretory cells in the shore crab, Carcinus maenas, are putatively spliced and modified products of multiple genes. Biochem J 356:159–170
Duve H, Johnsen AH, Sewell JC, Scott AG, Orchard I, Rehfeld JF, Thorpe A (1992) Isolation, structure, and activity of -Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 neuropeptides (designated calliFMRFamides) from the blowfly Calliphora vomitoria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:2326–2330
El Shoura SM (1989) Ultrastructure of the lateral organs in larval Argas (Persicargas) arboreus (Ixodoidea: Argasidae). Exp Appl Acarol 7:231–237
Gäde G, Hoffmann KH (2005) Neuropeptides regulating development and reproduction in insects. Physiol Entomol 30:103–121
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Spencer AN (1984) FMRFamide immunoreactivity in the nervous system of the medusa Polyorchis penicillatus. J Comp Neurol 230:361–371
Hill CA, Wikel SK (2005) The Ixodes scapularis genome project: an opportunity for advancing tick research. Trends Parasitol 21:151–153
Holmes SP, He H, Chen AC, Ivie GV, Pietrantonio PV (2000) Cloning and transcriptional expression of a leucokinin-like peptide receptor from the southern cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Insect Mol Biol 9:457–465
Holmes SP, Barhoumit R, Nachman RJ, Pietrantonio PV (2003) Functional analysis of a G protein-coupled receptor from the southern cattle tick Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) identifies it as the first arthropod myokinin receptor. Insect Mol Biol 12:27–38
Iwami M (2000) Bombyxin: an insect brain peptide that belongs to the insulin family. Zool Sci 17:1035–1044
Kaufman WR (1983) The function of tick salivary glands. In: Harris KF (ed) Current topics in vector research. Praeger Scientific, New York, pp 215–247
Kaufman WR, Sloley BD, Tatchell RJ, Zbitnew GL, Diefenbach TJ, Goldberg JI (1999) Quantification and cellular localization of dopamine in the salivary gland of the ixodid tick Amblyomma hebraeum. Exp Appl Acarol 23:251–265
Kim Y-J, Žitňan D, Cho K-H, Mizoguchi A, Schooley D, Adams ME (2006) Central peptidergic ensembles associated with organization of an innate behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14211–14216
Krolak JM, Ownby CL, Sauer JR (1982) Alveolar structure of salivary glands of the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum (L.): unfed females. J Parasitol 68:61–82
Lamoreaux WJ, Needham GR, Coons LB (1994) Fluid secretion by isolated tick salivary glands depends on an intact cytoskeleton. Int J Parasitol 24:563–567
Lamoreaux WJ, Needham GR, Coons LB (2000) Evidence that dilation of isolated salivary ducts from the tick Dermacentor variabilis (Say) is mediated by nitric oxide. J Insect Physiol 46:959–964
Lees K, Bowman AS (2007) Tick neurobiology: recent advances and the post-genomic era. Invert Neurosci 7:183–198
Liang JG, Zhang J, Lai R, Rees HH (2005) An opioid peptide from synganglia of the tick, Amblyomma testindinarium. Peptides 26:603–606
Lomas LO, Turner PC, Rees HH (1997) A novel neuropeptide-endocrine interaction controlling ecdysteroid production in ixodid ticks. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 264:589–596
Lu D, Lee KY, Horodyski FM, Witten JL (2002) Molecular characterization and cell-specific expression of a Manduca sexta FLRFamide gene. J Comp Neurol 446:377–396
Marzouk AS, Mohamed FSA, Khalil GM (1985) Neurohemal-endocrine organs in the camel tick, Hyalomma dromedarii (Acari: Ixodoidea: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 22:385–391
Megaw MWJ (1977) The innervation of the salivary gland of the tick, Boophilus microplus. Cell Tissue Res 184:551–558
Megaw MWJ, Beadle DJ (1979) Structure and function of the salivary glands of the tick Boophilus microplus Canestrini (Acarina: hodidae). Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 8:67–83
Mizoguchi A, Ishizaki H, Nagasawa H, Kataoka H, Isogai A, Tamura S, Suzuki A, Fujino M, Kitada C (1987) A monoclonal antibody against a synthetic fragment of bombyxin (4K-prothoracicotropic hormone) from the silkmoth, Bombyx mori; characterization and immunohistochemistry. Mol Cell Endocrinol 51:227–235
Mizoguchi A, Oka T, Kataoka H, Nagasawa H, Suzuki A, Ishizaki H (1990) Immunohistochemical localization of prothoracicotropic hormone-producing neurosecretory cells in the brain of Bombyx mori. Dev Growth Differ 32:591–598
Nässel DR, Cantera R, Karlsson A (1992) Neurons in the cockroach nervous system reacting with antisera to the neuropeptide leucokinin I. J Comp Neurol 322:45–67
Nässel DR, Shiga S, Mohrherr CJ, Rao KR (1993) Pigment-dispersing hormone-like peptide in the nervous system of the flies Phormia and Drosophila: immunocytochemistry and partial characterization. J Comp Neurol 331:183–198
Neupert S, Predel R, Russell WK, Davies R, Pietrantonio PV, Nachman RJ (2005) Identification of tick periviscerokinin, the first neurohormone of Ixodidae: single cell analysis by means of MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:1860–1864
Obenchain FD (1974) Neurosecretory system of the American dog tick, Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae). I. Diversity of cell types. J Morphol 142:433–446
Obenchain FD, Oliver JH Jr (1975) Neurosecretory system of the American dog tick, Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae). II. Distribution of secretory cell types, axonal pathways and putative neurohemal-neuroendocrine associations; comparative histological and anatomical implications. J Morphol 145:269–294
Obenchain FD, Oliver JH Jr (1976) Peripheral nervous system of the ticks, Amblyomma tuberculatum Marx and Argas radiatus Railliet (Acari: Ixodoidea). J Parasitol 62:811–817
Panfilova IM (1978) Lateral”nye organy Ixodes persulcatus (Parasitiformes, Ixodidae) (in English: lateral organs in Ixodes persulcatus (Parasitiformes, Ixodidae). Zool Zh 57:190–196
Park JH, Helfrich-Förster C, Lee G, Liu L, Rosbash M, Hall JC (2000) Differential regulation of circadian pacemaker output by separate clock genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3608–3613
Persson MG, Eklund MB, Dircksen H, Muren JE, Nässel DR (2001) Pigment-dispersing factor in the locust abdominal ganglia may have roles as circulating neurohormone and central neuromodulator. J Neurobiol 48:19–41
Pound MJ, Oliver JH Jr (1982) Synganglial and neurosecretory morphology of female Ornithodoros parkeri (Cooley) (Acari: Argasidae). J Morphol 173:159–177
Prullage JB, Pound JM, Meola SM (1992) Synganglial morphology and neurosecretory centers of adult Amblyomma americanum (L.) (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 29:1023–1034
Rees HH (2004) Hormonal control of tick development and reproduction. Parasitology 129:S127–S143
Roller L, Tanaka Y, Tanaka S (2003) Corazonin and corazonin-like substances in the central nervous system of the pterygote and apterygote insects. Cell Tissue Res 312:393–406
Roller L, Yamanaka N, Watanabe K, Daubnerová I, Žitňan D, Kataoka H, Tanaka Y (2008) The unique evolution of neuropeptide genes in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol (in press)
Roshdy MA, Shoukrey NM, Coons LB (1973) The subgenus Persicargas (Ixodoidea: Argasidae: Argas). 17. A neurohemal organ in A. (P.) arboreus Kaiser, Hoogstraal and Kohls. J Parasitol 59:530–544
Saito Y (1960) Studies on ixodid ticks. Part IV. The internal anatomy in each stage of Haemaphysalis flava Neuman, 1897. Acta Med Biol 8:189–239
Schoofs L, Vanden Broeck J, De Loof A (1993) The myotropic peptides of Locusta migratoria: structures, distribution, functions and receptors. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 23:859–881
Šimo L, Park Y (2008) Genomics and proteomics of neuropeptides in the black-legged tick Ixodes scapularis. Second Annual Arthropod Genomics Symposium, April 10–13, 2008, Kansas City
Slovák M, Labuda M, Marley SE (2002) Mass laboratory rearing of Dermacentor reticulatus ticks (Acarina, Ixodidae). Biologia (Bratislava) 57:261–266
Sonenshine DE (1991) Biology of ticks, vol 1. Oxford University Press, New York Oxford
Stangier J, Hilbich C, Dircksen H, Keller R (1988) Distribution of a novel cardioactive neuropeptide (CCAP) in the nervous system of the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Peptides 4:795–800
Stay B, Chan KK, Woodhead AP (1992) Allatostatin-immunoreactive neurons projecting to the corpora allata of adult Diploptera punctata. Cell Tissue Res 270:15–23
Szlendak E, Oliver JH Jr (1992) Anatomy of synganglia, including their neurosecretory regions, in unfed, virgin female Ixodes scapularis Say (Acari: Ixodidae). J Morphol 213:349–364
Taneja-Bageshwar S, Strey A, Zubrzak P, Pietrantonio PV, Nachman RJ (2006) Comparative structure-activity analysis of insect kinin core analogs on recombinant kinin receptors from southern cattle tick Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) and mosquito Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 62:128–140
White K, Hurteau T, Punsal P (1986) Neuropeptide FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in Drosophila. Wilhem Roux’s Arch 142:131–182
Yamanaka N, Žitňan D, Kim Y-J, Adams ME, Hua Y-J, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M, Suzuki A, Satake H, Mizoguchi A, Asaoka K, Tanaka Y, Kataoka H (2006) Regulation of insect steroid hormone biosynthesis by innervating peptidergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:8622–8627
Zhu XX, Oliver JH Jr (1991) Immunocytochemical localization of an insulin like substance in the synganglion of the tick Ornithodoros parkeri (Acari: Argasidae). Exp Appl Acarol 13:153–159
Zhu XX, Oliver JH Jr (2001) Cockroach allatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the synganglion of the American dog tick Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp Appl Acarol 25:1005–1013
Zhu XX, Zhang WY, Oliver JH Jr (1995) Immunocytochemical mapping of FMRFamide-like peptides in the argasid tick Ornithodoros parkeri and the ixodid tick Dermacentor variabilis. Exp Appl Acarol 19:1–9
Žitňan D, Adams ME (2005) Neuroendocrine regulation of insect ecdysis. In: Gilbert LI, Iatrou K, Gill SS (eds) Comprehensive molecular insect science, vol 3. Elsevier Pergamon, Amsterdam-Tokyo, pp 1–60
Žitňan D, Sehnal F, Bryant P (1993) Neurons producing specific neuropeptides in the central nervous system of normal and pupariation-delayed Drosophila. Dev Biol 155:682–693
Žitňan D, Kingan TG, Kramer SJ, Beckage NE (1995) Accumulation of neuropeptides in the cerebral neurosecretory system of Manduca sexta larvae parasitized by the braconid wasp Cotesia congregata. J Comp Neurol 356:83–100
Žitňan D, Ross LS, Žitňanová I, Hermesman JL, Gill SS, Adams MA (1999) Steroid induction of a peptide hormone gene leads to orchestration of a defined behavioral sequence. Neuron 23:523–535
Žitňan D, Hollar L, Spalovská I, Takáč P, Žitňanová I, Gill SS, Adams ME (2002) Molecular cloning and function of ecdysis-triggering hormones in the silkworm Bombyx mori. J Exp Biol 205:3459–3473
Žitňanová I, Adams ME, Žitňan D (2001) Dual ecdysteroid action on the epitracheal glands and central nervous system preceding ecdysis of Manduca sexta. J Exp Biol 204:3483–3495
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs. M.E. Adams, H. Dircksen, C.J.P. Grimmelikhuijzen, D. Kodrík, A. Mizoguchi, D.R. Nässel, L. Schoofs and Y. Tanaka for providing antibodies to AKH, corazonin, bombyxin, PTTH, ITP, MIP, BMS, leucokinin, tachykinin and PDF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Slovak grant agencies: Agentúra na podporu výskumu a vývoja (APVV-51-039105) and Vedecká grantová agentúra (VEGA 2-6090-26 and 2/6155/26).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šimo, L., Slovák, M., Park, Y. et al. Identification of a complex peptidergic neuroendocrine network in the hard tick, Rhipicephalus appendiculatus . Cell Tissue Res 335, 639–655 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0731-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0731-4