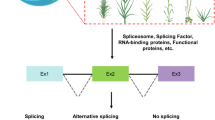
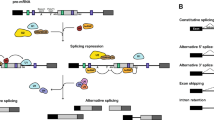
Abstract
Alternative splicing, which generates multiple transcripts from the same gene and potentially different protein isoforms, is a key posttranscriptional regulatory mechanism for expanding proteomic diversity and functional complexity in higher eukaryotes. The most recent estimates, based on whole transcriptome sequencing, indicate that about 95 % of human and 60 % of Arabidopsis multi-exon genes undergo alternative splicing, suggesting important roles for this mechanism in biological processes. However, while the misregulation of alternative splicing has been associated with many human diseases, its biological relevance in plant systems is just beginning to unfold. We review here the few plant genes for which the production of multiple splice isoforms has been reported to have a clear in vivo functional impact. These case studies implicate alternative splicing in the control of a wide range of physiological and developmental processes, including photosynthetic and starch metabolism, hormone signaling, seed germination, root growth and flowering, as well as in biotic and abiotic stress responses. Future functional characterization of alternative splicing events and identification of the transcripts targeted by major regulators of this versatile means of modulating gene expression should uncover the breadth of its physiological significance in higher plants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali GS, Reddy AS (2006) ATP, phosphorylation and transcription regulate the mobility of plant splicing factors. J Cell Sci 119:3527–3538
Ali GS, Reddy AS (2008) Regulation of alternative splicing of pre-mRNAs by stresses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 326:257–275
Ali GS, Golovkin M, Reddy AS (2003) Nuclear localization and in vivo dynamics of a plant-specific serine/arginine-rich protein. Plant J 36:883–893
Ali GS, Palusa SG, Golovkin M, Prasad J, Manley JL, Reddy AS (2007) Regulation of plant developmental processes by a novel splicing factor. PLoS One 2:e471
Ali GS, Prasad KV, Hanumappa M, Reddy AS (2008) Analyses of in vivo interaction and mobility of two spliceosomal proteins using FRAP and BiFC. PLoS One 3:e1953
Avanci NC, Luche DD, Goldman GH, Goldman MH (2010) Jasmonates are phytohormones with multiple functions, including plant defense and reproduction. Genet Mol Res 9:484–505
Barbazuk WB, Fu Y, McGinnis KM (2008) Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing in plants: opportunities and challenges. Genome Res 18:1381–1392
Barta A, Kalyna M, Lorkovic ZJ (2008) Plant SR proteins and their functions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 326:83–102
Blencowe BJ (2006) Alternative splicing: new insights from global analyses. Cell 126:37–47
Braverman N, Dodt G, Gould SJ, Valle D (1998) An Isoform of Pex5p, the human PTS1 receptor, is required for the import of PTS2 proteins into peroxisomes. Hum Mol Genet 7:1195–1205
Brett D, Pospisil H, Valcarcel J, Reich J, Bork P (2002) Alternative splicing and genome complexity. Nat Genet 30:29–30
Brown L-A, Baker A (2008) Shuttles and cycles: transport of proteins into the peroxisome matrix (Review). Mol Membr Biol 25:363–375
Campbell MA, Haas BJ, Hamilton JP, Mount SM, Buell CR (2006) Comprehensive analysis of alternative splicing in rice and comparative analyses with Arabidopsis. BMC Genomics 7:327
Carvalho RF, Carvalho SD, Duque P (2010) The plant-specific SR45 protein negatively regulates glucose and ABA signaling during early seedling development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 154:772–783
Carvalho SD, Saraiva R, Maia TM, Abreu IA, Duque P (2012) XBAT35, a novel Arabidopsis RING E3 ligase exhibiting dual targeting of its splice isoforms, is involved in ethylene-mediated regulation of apical hook curvature. Mol Plant. doi:10.1093/mp/sss048
Castillon A, Shen H, Huq E (2007) Phytochrome Interacting Factors: central players in phytochrome-mediated light signaling networks. Trends Plant Sci 12:514–521
Cheong JJ, Choi YD (2003) Methyl jasmonate as a vital substance in plants. Trends Genet 19:409–413
Chung HS, Howe GA (2009) A critical role for the TIFY motif in repression of jasmonate signaling by a stabilized splice variant of the JASMONATE ZIM-domain protein JAZ10 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:131–145
Chung HS, Niu Y, Browse J, Howe GA (2009) Top hits in contemporary JAZ: an update on jasmonate signaling. Phytochemistry 70:1547–1559
Chung HS, Cooke TF, Depew CL, Patel LC, Ogawa N, Kobayashi Y, Howe GA (2010) Alternative splicing expands the repertoire of dominant JAZ repressors of jasmonate signaling. Plant J 63:613–622
Costanzo S, Jia Y (2009) Alternatively spliced transcripts of Pi-ta blast resistance gene in Oryza sativa. Plant Sci 177:468–478
Crafts-Brandner SJ, Van De Loo FJ, Salvucci ME (1997) The two forms of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase differ in sensitivity to elevated temperature. Plant Physiol 114:439–444
Deridder BP, Shybut ME, Dyle MC, Kremling KA, Shapiro MB (2012) Changes at the 3'-untranslated region stabilize Rubisco activase transcript levels during heat stress in Arabidopsis. Planta 236:463–476
Dinesh-Kumar SP, Baker BJ (2000) Alternatively spliced N resistance gene transcripts: their possible role in tobacco mosaic virus resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:1908–1913
Duque P (2011) A role for SR proteins in plant stress responses. Plant Signal Behav 6:49–54
Feller U, Crafts-Brandner SJ, Salvucci ME (1998) Moderately high temperatures inhibit ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) Activase-Mediated Activation of Rubisco. Plant Physiol 116:539–546
Filichkin SA, Priest HD, Givan SA, Shen R, Bryant DW, Fox SE, Wong WK, Mockler TC (2010) Genome-wide mapping of alternative splicing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Res 20:45–58
Franklin KA, Lee SH, Patel D, Kumar SV, Spartz AK, Gu C, Ye S, Yu P, Breen G, Cohen JD, Wigge PA, Gray WM (2011) Phytochrome-interacting factor 4 (PIF4) regulates auxin biosynthesis at high temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:20231–20235
Fu Y, Bannach O, Chen H, Teune JH, Schmitz A, Steger G, Xiong L, Barbazuk WB (2009) Alternative splicing of anciently exonized 5S rRNA regulates plant transcription factor TFIIIA. Genome Res 19:913–921
Gassmann W (2008) Alternative splicing in plant defense. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 326:219–233
Gassmann W, Hinsch ME, Staskawicz BJ (1999) The Arabidopsis RPS4 bacterial-resistance gene is a member of the TIR-NBS-LRR family of disease-resistance genes. Plant J 20:265–277
Golovkin M, Reddy AS (1999) An SC35-like protein and a novel serine/arginine-rich protein interact with Arabidopsis U1-70K protein. J Biol Chem 274:36428–36438
Haas BJ, Delcher AL, Mount SM, Wortman JR, Smith RK Jr, Hannick LI, Maiti R, Ronning CM, Rusch DB, Town CD, Salzberg SL, White O (2003) Improving the Arabidopsis genome annotation using maximal transcript alignment assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res 31:5654–5666
Hazen SP, Naef F, Quisel T, Gendron JM, Chen H, Ecker JR, Borevitz JO, Kay SA (2009) Exploring the transcriptional landscape of plant circadian rhythms using genome tiling arrays. Genome Biol 10:R17
Hinsch M, Staskawicz B (1996) Identification of a new Arabidopsis disease resistance locus, RPs4, and cloning of the corresponding avirulence gene, avrRps4, from Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9:55–61
Hu J, Baker A, Bartel B, Linka N, Mullen RT, Reumann S, Zolman BK (2012) Plant peroxisomes: biogenesis and function. Plant Cell 24:2279–2303
Hughes TA (2006) Regulation of gene expression by alternative untranslated regions. Trends in Genet 22:119–122
Iida K, Seki M, Sakurai T, Satou M, Akiyama K, Toyoda T, Konagaya A, Shinozaki K (2004) Genome-wide analysis of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in Arabidopsis thaliana based on full-length cDNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32:5096–5103
Jordan T, Schornack S, Lahaye T (2002) Alternative splicing of transcripts encoding Toll-like plant resistance proteins—what's the functional relevance to innate immunity? Trends Plant Sci 7:392–398
Kalyna M, Simpson CG, Syed NH, Lewandowska D, Marquez Y, Kusenda B, Marshall J, Fuller J, Cardle L, McNicol J, Dinh HQ, Barta A, Brown JW (2012) Alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated decay modulate expression of important regulatory genes in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 40:2454–2469
Kazan K (2003) Alternative splicing and proteome diversity in plants: the tip of the iceberg has just emerged. Trends Plant Sci 8:468–471
Kazan K, Manners JM (2008) Jasmonate signaling: toward an integrated view. Plant Physiol 146:1459–1468
Kikuchi S, Satoh K, Nagata T, Kawagashira N, Doi K, Kishimoto N, Yazaki J, Ishikawa M, Yamada H, Ooka H, Hotta I, Kojima K, Namiki T, Ohneda E, Yahagi W, Suzuki K, Li CJ, Ohtsuki K, Shishiki T, Otomo Y, Murakami K, Iida Y, Sugano S, Fujimura T, Suzuki Y, Tsunoda Y, Kurosaki T, Kodama T, Masuda H, Kobayashi M, Xie Q, Lu M, Narikawa R, Sugiyama A, Mizuno K, Yokomizo S, Niikura J, Ikeda R, Ishibiki J, Kawamata M, Yoshimura A, Miura J, Kusumegi T, Oka M, Ryu R, Ueda M, Matsubara K, Kawai J, Carninci P, Adachi J, Aizawa K, Arakawa T, Fukuda S, Hara A, Hashizume W, Hayatsu N, Imotani K, Ishii Y, Itoh M, Kagawa I, Kondo S, Konno H, Miyazaki A, Osato N, Ota Y, Saito R, Sasaki D, Sato K, Shibata K, Shinagawa A, Shiraki T, Yoshino M, Hayashizaki Y, Yasunishi A (2003) Collection, mapping, and annotation of over 28,000 cDNA clones from japonica rice. Science 301:376–379
Kim E, Magen A, Ast G (2007) Different levels of alternative splicing among eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:125–131
Kim E, Goren A, Ast G (2008) Alternative splicing: current perspectives. Bioessays 30:38–47
Kim SH, Kwon SI, Saha D, Anyanwu NC, Gassmann W (2009) Resistance to the Pseudomonas syringae effector HopA1 is governed by the TIR-NBS-LRR protein RPS6 and is enhanced by mutations in SRFR1. Plant Physiol 150:1723–1732
Kobza J, Edwards GE (1987) Influences of leaf temperature on photosynthetic carbon metabolism in wheat. Plant Physiol 83:69–74
Koini MA, Alvey L, Allen T, Tilley CA, Harberd NP, Whitelam GC, Franklin KA (2009) High temperature-mediated adaptations in plant architecture require the bHLH transcription factor PIF4. Curr Biol 19:408–413
Koncz C, Dejong F, Villacorta N, Szakonyi D, Koncz Z (2012) The spliceosome-activating complex: molecular mechanisms underlying the function of a pleiotropic regulator. Front Plant Sci 3:9
Krasensky J, Jonak C (2012) Drought, salt, and temperature stress-induced metabolic rearrangements and regulatory networks. J Exp Bot 63:1593–1608
Law RD, Crafts-Brandner SJ (1999) Inhibition and acclimation of photosynthesis to heat stress is closely correlated with activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase. Plant Physiol 120:173–182
Lee JR, Jang HH, Park JH, Jung JH, Lee SS, Park SK, Chi YH, Moon JC, Lee YM, Kim SY, Kim J-Y, Yun D-J, Cho MJ, Lee KO, Lee SY (2006) Cloning of two splice variants of the rice PTS1 receptor, OsPex5pL and OsPex5pS, and their functional characterization using pex5-deficient yeast and Arabidopsis. Plant J 47:457–466
Long JC, Caceres JF (2009) The SR protein family of splicing factors: master regulators of gene expression. Biochem J 417:15–27
Lu T, Lu G, Fan D, Zhu C, Li W, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhao Y, Guo Y, Huang X, Han B (2010) Function annotation of the rice transcriptome at single-nucleotide resolution by RNA-seq. Genome Res 20:1238–1249
Macknight R, Bancroft I, Page T, Lister C, Schmidt R, Love K, Westphal L, Murphy G, Sherson S, Cobbett C, Dean C (1997) FCA, a gene controlling flowering time in Arabidopsis, encodes a protein containing RNA-binding domains. Cell 89:737–745
Macknight R, Duroux M, Laurie R, Dijkwel P, Simpson G, Dean C (2002) Functional significance of the alternative transcript processing of the Arabidopsis floral promoter FCA. Plant Cell 14:877–888
Mao DD, Tian LF, Li LG, Chen J, Deng PY, Li DP, Luan S (2008) AtMGT7: an Arabidopsis gene encoding a low-affinity magnesium transporter. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1530–1538
Marquez Y, Brown JW, Simpson C, Barta A, Kalyna M (2012) Transcriptome survey reveals increased complexity of the alternative splicing landscape in Arabidopsis. Genome Res 22:1184–1195
Nagasaki H, Arita M, Nishizawa T, Suwa M, Gotoh O (2005) Species-specific variation of alternative splicing and transcriptional initiation in six eukaryotes. Gene 364:53–62
Ner-Gaon H, Fluhr R (2006) Whole-genome microarray in Arabidopsis facilitates global analysis of retained introns. DNA Res 13:111–121
Ner-Gaon H, Halachmi R, Savaldi-Goldstein S, Rubin E, Ophir R, Fluhr R (2004) Intron retention is a major phenomenon in alternative splicing in Arabidopsis. Plant J 39:877–885
Nicholson P, Yepiskoposyan H, Metze S, Zamudio Orozco R, Kleinschmidt N, Muhlemann O (2010) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human cells: mechanistic insights, functions beyond quality control and the double-life of NMD factors. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:677–700
Nilsen TW, Graveley BR (2010) Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature 463:457–463
Palusa SG, Ali GS, Reddy AS (2007) Alternative splicing of pre-mRNAs of Arabidopsis serine/arginine-rich proteins: regulation by hormones and stresses. Plant J 49:1091–1107
Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ, Blencowe BJ (2008) Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat Genet 40:1413–1415
Penfield S, Josse EM, Halliday KJ (2010) A role for an alternative splice variant of PIF6 in the control of Arabidopsis primary seed dormancy. Plant Mol Biol 73:89–95
Portis AR Jr (2003) Rubisco activase—Rubisco's catalytic chaperone. Photosynth Res 75:11–27
Quesada V, Macknight R, Dean C, Simpson GG (2003) Autoregulation of FCA pre-mRNA processing controls Arabidopsis flowering time. EMBO J 22:3142–3152
Reddy ASN (2001) Nuclear Pre-mRNA splicing in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 20:523–571
Reddy AS (2007) Alternative splicing of pre-messenger RNAs in plants in the genomic era. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:267–294
Robert-Seilaniantz A, Grant M, Jones JD (2011) Hormone crosstalk in plant disease and defense: more than just jasmonate-salicylate antagonism. Annu Rev Phytopathol 49:317–343
Ru Y, Wang BB, Brendel V (2008) Spliceosomal proteins in plants. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 326:1–15
Salvucci ME, Werneke JM, Ogren WL, Portis AR (1987) Purification and species distribution of rubisco activase. Plant Physiol 84:930–936
Salvucci ME, DeRidder BP, Portis AR Jr (2006) Effect of activase level and isoform on the thermotolerance of photosynthesis in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 57:3793–3799
Sanchez SE, Petrillo E, Beckwith EJ, Zhang X, Rugnone ML, Hernando CE, Cuevas JC, Godoy Herz MA, Depetris-Chauvin A, Simpson CG, Brown JW, Cerdan PD, Borevitz JO, Mas P, Ceriani MF, Kornblihtt AR, Yanovsky MJ (2010) A methyl transferase links the circadian clock to the regulation of alternative splicing. Nature 468:112–116
Sanchez SE, Petrillo E, Kornblihtt AR, Yanovsky MJ (2011) Alternative splicing at the right time. RNA Biol 8:954–959
Schmidt A, Baumann N, Schwarzkopf A, Frommer WB, Desimone M (2006) Comparative studies on Ureide Permeases in Arabidopsis thaliana and analysis of two alternative splice variants of AtUPS5. Planta 224:1329–1340
Schmucker D, Clemens JC, Shu H, Worby CA, Xiao J, Muda M, Dixon JE, Zipursky SL (2000) Drosophila Dscam is an axon guidance receptor exhibiting extraordinary molecular diversity. Cell 101:671–684
Seo PJ, Kim MJ, Ryu JY, Jeong EY, Park CM (2011) Two splice variants of the IDD14 transcription factor competitively form nonfunctional heterodimers which may regulate starch metabolism. Nat Commun 2:303
Shen JB, Orozco EM Jr, Ogren WL (1991) Expression of the two isoforms of spinach ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activase and essentiality of the conserved lysine in the consensus nucleotide-binding domain. J Biol Chem 266:8963–8968
Shepard PJ, Hertel KJ (2009) The SR protein family. Genome Biol 10:242
Simpson GG (2004) The autonomous pathway: epigenetic and post-transcriptional gene regulation in the control of Arabidopsis flowering time. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:570–574
Simpson GG, Dijkwel PP, Quesada V, Henderson I, Dean C (2003) FY is an RNA 3' end-processing factor that interacts with FCA to control the Arabidopsis floral transition. Cell 113:777–787
Smalle J, Vierstra RD (2004) The ubiquitin 26S proteasome proteolytic pathway. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:555–590
Staal J, Dixelius C (2008) RLM3, a potential adaptor between specific TIR-NB-LRR receptors and DZC proteins. Commun Integr Biol 1:59–61
Staal J, Kaliff M, Dewaele E, Persson M, Dixelius C (2008) RLM3, a TIR domain encoding gene involved in broad-range immunity of Arabidopsis to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant J 55:188–200
Stamm S, Ben-Ari S, Rafalska I, Tang Y, Zhang Z, Toiber D, Thanaraj TA, Soreq H (2005) Function of alternative splicing. Gene 344:1–20
Stone SL, Hauksdottir H, Troy A, Herschleb J, Kraft E, Callis J (2005) Functional analysis of the RING-type ubiquitin ligase family of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 137:13–30
Szymanski M, Barciszewska MZ, Erdmann VA, Barciszewski J (2003) 5S rRNA: structure and interactions. Biochem J 371:641–651
To KY, Suen DF, Chen SC (1999) Molecular characterization of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase in rice leaves. Planta 209:66–76
Wahl MC, Will CL, Luhrmann R (2009) The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell 136:701–718
Wang BB, Brendel V (2006) Genomewide comparative analysis of alternative splicing in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:7175–7180
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Zhang L, Mayr C, Kingsmore SF, Schroth GP, Burge CB (2008) Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 456:470–476
Wang D, Lu Q, Li X, Jiang Q, Wu J, Jiang D (2009) Relationship between Rubisco activase isoform levels and photosynthetic rate in different leaf positions of rice plant. Photosynthetica 47:621–629
Wang D, Li XF, Zhou ZJ, Feng XP, Yang WJ, Jiang DA (2010) Two Rubisco activase isoforms may play different roles in photosynthetic heat acclimation in the rice plant. Physiol Plant 139:55–67
Ward AJ, Cooper TA (2010) The pathobiology of splicing. J Pathol 220:152–163
Weis E (1981) The temperature-sensitivity of dark-inactivation and light-activation of the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate car‚òêylase in spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Lett 129:197–200
Werneke JM, Chatfield JM, Ogren WL (1989) Alternative mRNA splicing generates the two ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase polypeptides in spinach and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1:815–825
Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B (1994) The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: similarity to toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 78:1101–1115
Woodward AW, Bartel B (2005) The Arabidopsis peroxisomal targeting signal type 2 receptor PEX7 Is necessary for peroxisome function and dependent on PEX5. Mol Biol Cell 16:573–583
Yamori W, Suzuki K, Noguchi K, Nakai M, Terashima I (2006) Effects of Rubisco kinetics and Rubisco activation state on the temperature dependence of the photosynthetic rate in spinach leaves from contrasting growth temperatures. Plant Cell Environ 29:1659–1670
Yan Y, Stolz S, Chetelat A, Reymond P, Pagni M, Dubugnon L, Farmer EE (2007) A downstream mediator in the growth repression limb of the jasmonate pathway. Plant Cell 19:2470–2483
Zhang XC, Gassmann W (2003) RPS4-mediated disease resistance requires the combined presence of RPS4 transcripts with full-length and truncated open reading frames. Plant Cell 15:2333–2342
Zhang XC, Gassmann W (2007) Alternative splicing and mRNA levels of the disease resistance gene RPS4 are induced during defense responses. Plant Physiol 145:1577–1587
Zhang XN, Mount SM (2009) Two alternatively spliced isoforms of the Arabidopsis SR45 protein have distinct roles during normal plant development. Plant Physiol 150:1450–1458
Zhang N, Portis AR Jr (1999) Mechanism of light regulation of Rubisco: a specific role for the larger Rubisco activase isoform involving reductive activation by thioredoxin-f. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:9438–9443
Zhang N, Kallis RP, Ewy RG, Portis AR Jr (2002) Light modulation of Rubisco in Arabidopsis requires a capacity for redox regulation of the larger Rubisco activase isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:3330–3334
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (Grant PTDC/AGR-PRO/119058/2010 as well as Postdoctoral Fellowship SFRH/BPD/80073/2011 awarded to R.F.C.). P.D. is supported by Programa Ciência (QREN/MCTES).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: David Robinson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvalho, R.F., Feijão, C.V. & Duque, P. On the physiological significance of alternative splicing events in higher plants. Protoplasma 250, 639–650 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-012-0448-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-012-0448-9