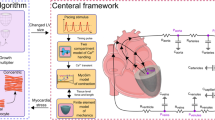
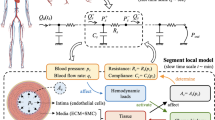
Abstract
We propose a multiphysical mathematical model by fully coupling lipid deposition, monocytes/macrophages recruitment and angiogenesis to investigate the pathophysiological responses of an atherosclerotic plaque to the dynamic changes in the microenvironment. The time evolutions of cellular (endothelial cells, macrophages, smooth muscle cells, etc.) and acellular components (low density lipoprotein, proinflammatory cytokines, extravascular plasma concentration, etc.) within the plaque microenvironment are assessed quantitatively. The thickening of the intima, the distributions of the lipid and inflammatory factors, and the intraplaque hemorrhage show a qualitative consistency with the MRI and histology data. Models with and without angiogenesis are compared to demonstrate the important role of neovasculature in the accumulation of blood-borne components in the atherosclerotic lesion by extravasation from the leaky vessel wall, leading to the formation of a lipid core and an inflammatory microenvironment, which eventually promotes plaque destabilization. This model can serve as a theoretical platform for the investigation of the pathological mechanisms of plaque progression and may contribute to the optimal design of atherosclerosis treatment strategies, such as lipid-lowering or anti-angiogenetic therapies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alimohamadi H. Numerical simulation of porosity effect on blood flow pattern and atherosclerotic plaques temperature. Int. J. Technol. Enhanc. Emerg. Eng. Res. 2:44–49, 2014.
Anlamlert, W., Y. Lenbury, and J. Bell. Modeling fibrous cap formation in atherosclerotic plaque development: stability and oscillatory behavior. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017:195, 2017.
Barrett, S. R. H., M. P. F. Sutcliffe, S. Howarth, Z. Y. Li, and J. H. Gillard. Experimental measurement of the mechanical properties of carotid atherothrombotic plaque fibrous cap. J. Biomech. 42:1650–1655, 2009.
Brown, A. J., Z. Z. Teng, P. C. Evans, J. H. Gillard, H. Samady, and M. R. Bennett. Role of biomechanical forces in the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 13:210–220, 2016.
Cai, Y., S. Xu, J. Wu, and Q. Long. Coupled modelling of tumour angiogenesis, tumour growth and blood perfusion. J. Theor. Biol. 279:90–101, 2011.
Chalmers, A. D., A. Cohen, C. A. Bursill, and M. R. Myerscough. Bifurcation and dynamics in a mathematical model of early atherosclerosis: how acute inflammation drives lesion development. J. Math. Biol. 71:1451–1480, 2015.
Chien, S. Molecular and mechanical bases of focal lipid accumulation in arterial wall. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 83:131–151, 2003.
Cobbold, C. A., J. A. Sherratt, and S. R. J. Maxwell. Lipoprotein oxidation and its significance for atherosclerosis: a mathematical approach. Bull. Math. Biol. 64:65–95, 2002.
de Vries, M. R., and P. H. A. Quax. Plaque angiogenesis and its relation to inflammation and atherosclerotic plaque destabilization. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 27:499–506, 2016.
Dolan, J. M., J. Kolega, and H. Meng. High wall shear stress and spatial gradients in vascular pathology: a review. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 41:1411–1427, 2013.
Dolan, J. M., F. J. Sim, H. Meng, and J. Kolega. Endothelial cells express a unique transcriptional profile under very high wall shear stress known to induce expansive arterial remodeling. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 302:C1109–C1118, 2012.
Doran, A. C., N. Meller, and C. A. McNamara. Role of smooth muscle cells in the initiation and early progression of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28:812–819, 2008.
El Khatib, N., S. Genieys, B. Kazmierczak, and V. Volpert. Reaction-diffusion model of atherosclerosis development. J. Math. Biol. 65:349–374, 2012.
Fok, P. W. Mathematical model of intimal thickening in atherosclerosis: vessel stenosis as a free boundary problem. J. Theor. Biol. 314:23–33, 2012.
Fong, G. H. Potential contributions of intimal and plaque hypoxia to atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 17:510, 2015.
Friedman, A., and W. R. Hao. A mathematical model of atherosclerosis with reverse cholesterol transport and associated risk factors. Bull. Math. Biol. 77:758–781, 2015.
Gao, H., Q. Long, M. Graves, J. H. Gillard, and Z. Y. Li. Carotid arterial plaque stress analysis using fluid-structure interactive simulation based on in vivo magnetic resonance images of four patients. J. Biomech. 42:1416–1423, 2009.
Goodman, M. E., X. Y. Luo, and N. A. Hill. A mathematical model on the feedback between wall shear stress and intimal hyperplasia. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 08:1640011, 2016.
Groh, L., S. T. Keating, L. A. B. Joosten, M. G. Netea, and N. P. Riksen. Monocyte and macrophage immunometabolism in atherosclerosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 40:203–214, 2018.
Grootaert, M. O. J., M. Moulis, L. Roth, W. Martinet, C. Vindis, M. R. Bennett, and G. R. Y. De Meyer. Vascular smooth muscle cell death, autophagy and senescence in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 114:622–634, 2018.
Guo, M. Y., Y. Cai, X. K. Yao, and Z. Y. Li. Mathematical modeling of atherosclerotic plaque destabilization: role of neovascularization and intraplaque hemorrhage. J. Theor. Biol. 450:53–65, 2018.
Hansson, G. K., P. Libby, and I. Tabas. Inflammation and plaque vulnerability. J. Intern. Med. 278:483–493, 2015.
Harrington, J. R. The role of MCP-1 in atherosclerosis. Stem Cells 18:65–66, 2000.
Hidalgo, A., L. Tello, and E. F. Toro. Numerical and analytical study of an atherosclerosis inflammatory disease model. J. Math. Biol. 68:1785–1814, 2014.
Inoue, M., H. Itoh, M. Ueda, T. Naruko, A. Kojima, R. Komatsu, K. Doi, Y. Ogawa, N. Tamura, K. Takaya, T. Igaki, J. Yamashita, T. H. Chun, K. Masatsugu, A. E. Becker, and K. Nakao. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in human coronary atherosclerotic lesions—possible pathophysiological significance of VEGF in progression of atherosclerosis. Circulation 98:2108–2116, 1998.
Jain, R. K., A. V. Finn, F. D. Kolodgie, H. K. Gold, and R. Virmani. Antiangiogenic therapy for normalization of atherosclerotic plaque vasculature: a potential strategy for plaque stabilization. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 4:491–502, 2007.
Koshiba, N., J. Ando, M. Chen, and T. Hisada. Multiphysics simulation of blood flow and LDL transport in a porohyperelastic arterial wall model. J. Biomech. Eng.-Trans. Asme 129:374–385, 2007.
Kwak, B. R., M. Back, M. L. Bochaton-Piallat, G. Caligiuri, M. J. A. P. Daemens, P. F. Davies, I. E. Hoefer, P. Holvoet, H. Jo, R. Krams, S. Lehoux, C. Monaco, S. Steffens, R. Virmani, C. Weber, J. J. Wentzel, and P. C. Evans. Biomechanical factors in atherosclerosis: mechanisms and clinical implications. Eur. Heart J. 35(3013–3020):3020a–3020d, 2014.
Ley, K., Y. I. Miller, and C. C. Hedrick. Monocyte and macrophage dynamics during atherogenesis. Arterioscler., Thromb., Vasc. Biol. 31:1506–1516, 2011.
Li, Z. Y., S. P. Howarth, T. Tang, and J. H. Gillard. How critical is fibrous cap thickness to carotid plaque stability? A flow-plaque interaction model. Stroke: J. Cereb. Circ. 37:1195–1199, 2006.
Li, Z. Y., S. Howarth, R. A. Trivedi, J. M. Ukingim, M. J. Graves, A. Brown, L. Q. Wang, and J. H. Gillard. Stress analysis of carotid plaque rupture based on in vivo high resolution MRI. J. Biomech. 39:2611–2622, 2006.
Michel J. B., R. Virmani, E. Arbustini and G. Pasterkamp. Intraplaque haemorrhages as the trigger of plaque vulnerability. European Heart Journal 32: 1977–1985, 1985a, 1985b, 1985c, 2011.
Moore, K. J., F. J. Sheedy, and E. A. Fisher. Macrophages in atherosclerosis: a dynamic balance. Nat. Rev.: Immunol. 13:709–721, 2013.
Olgac, U., V. Kurtcuoglu, and D. Poulikakos. Computational modeling of coupled blood-wall mass transport of LDL: effects of local wall shear stress. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 294:H909–919, 2008.
Parma, L., F. Baganha, P. H. A. Quax, and M. R. de Vries. Plaque angiogenesis and intraplaque hemorrhage in atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 816:107–115, 2017.
Rai, S., D. E. Thaler, P. Salehi, N. Madan, and L. Y. Leung. More to atherosclerosis than stenosis: symptomatic carotid artery with intraplaque hemorrhage. Stroke 48:e104–e107, 2017.
Roustaei, M., M. R. Nikmaneshi, and B. Firoozabadi. Simulation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) permeation into multilayer coronary arterial wall: Interactive effects of wall shear stress and fluid-structure interaction in hypertension. J. Biomech. 67:114–122, 2018.
Silva, T., A. Sequeira, R. F. Santos, and J. Tiago. Mathematical modeling of atherosclerotic plaque formation coupled with a non-newtonian model of blood flow. Conf. Pap. Math. 1–14:2013, 2013.
Silvestre-Roig, C., M. P. de Winther, C. Weber, M. J. Daemen, E. Lutgens, and O. Soehnlein. Atherosclerotic plaque destabilization mechanisms, models, and therapeutic strategies. Circ. Res. 114:214–226, 2014.
Teng, Z. Z., U. Sadat, A. J. Brown, and J. H. Gillard. Plaque hemorrhage in carotid artery disease: pathogenesis, clinical and biomechanical considerations. J. Biomech. 47:847–858, 2014.
Tiago, J. Existence, uniqueness, stability and asymptotic behavior of solutions for a mathematical model of atherosclerosis. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst.-Ser. S 9:343–362, 2016.
Timmins, L. H., D. S. Molony, P. Eshtehardi, M. C. McDaniel, J. N. Oshinski, D. P. Giddens, and H. Samady. Oscillatory wall shear stress is a dominant flow characteristic affecting lesion progression patterns and plaque vulnerability in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Royal Soc. Interface 14:20160927, 2017.
Wiesner, P., M. Tafelmeier, D. Chittka, S. H. Choi, L. Zhang, Y. S. Byun, F. Almazan, X. Yang, N. Iqbal, P. Chowdhury, A. Maisel, J. L. Witztum, T. M. Handel, S. Tsimikas, and Y. I. Miller. MCP-1 binds to oxidized LDL and is carried by lipoprotein(a) in human plasma. J. Lipid Res. 54:1877–1883, 2013.
Yilmaz, A., B. Lipfert, I. Cicha, K. Schubert, M. Klein, D. Raithel, W. G. Daniel, and C. D. Garlichs. Accumulation of immune cells and high expression of chemokines/chemokine receptors in the upstream shoulder of atherosclerotic carotid plaques. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 82:245–255, 2007.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) Grant Number [2013CB733800], the National Nature Science Foundation of China Grant Numbers (11422222, 11302050, 11772093), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the National Demonstration Center for Experimental Biomedical Engineering Education (Southeast University), and ARC Grant Number (FT140101152).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest regarding to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Debra T. Auguste oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, M., Cai, Y., He, C. et al. Coupled Modeling of Lipid Deposition, Inflammatory Response and Intraplaque Angiogenesis in Atherosclerotic Plaque. Ann Biomed Eng 47, 439–452 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-02173-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-02173-1