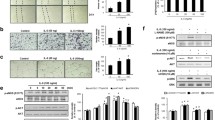
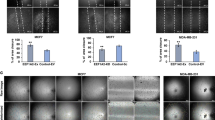
Abstract
Endothelial cell function is critical for angiogenic balance in both physiological and pathological conditions, such as wound healing and cancer, respectively. We report here that soluble heat shock protein beta-1 (HSPB1) is released primarily from endothelial cells (ECs), and plays a key role in regulating angiogenic balance via direct interaction with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). VEGF-mediated phosphorylation of intracellular HSPB1 inhibited the secretion of HSPB1 and their binding activity in ECs. Interestingly, co-culture of tumor ECs with tumor cells decreased HSPB1 secretion from tumor ECs, suggesting that inhibition of HSPB1 secretion allows VEGF to promote angiogenesis. Additionally, neutralization of HSPB1 in a primary mouse sarcoma model promoted tumor growth, indicating the anti-angiogenic role of soluble HSPB1. Overexpression of HSPB1 by HSPB1 adenovirus was sufficient to suppress lung metastases of CT26 colon carcinoma in vivo, while neutralization of HSPB1 promoted in vivo wound healing. While VEGF-induced regulation of angiogenesis has been studied extensively, these findings illustrate the key contribution of HSPB1-VEGF interactions in the balance between physiological and pathological angiogenesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9(6):669–676. doi:10.1038/nm0603-669
Chung AS, Ferrara N (2010) Targeting the tumor microenvironment with SRC kinase inhibition. Clin Cancer Res 16(3):775–777. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3081
Ferrara N, Gerber HP (2001) The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in angiogenesis. Acta Haematol 106(4):148–156
Folkman J (2003) Angiogenesis inhibitors: a new class of drugs. Cancer Biol Ther 2(4 Suppl 1):S127–133
Folkman J, Ryeom S (2005) Is oncogene addiction angiogenesis-dependent? Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 70:389–397. doi:10.1101/sqb.2005.70.042
Evans IM, Britton G, Zachary IC (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces heat shock protein (HSP) 27 serine 82 phosphorylation and endothelial tubulogenesis via protein kinase D and independent of p38 kinase. Cell Signal 20(7):1375–1384. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.03.002
Yancopoulos GD (2010) Clinical application of therapies targeting VEGF. Cell 143(1):13–16. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.028
Fernando NT, Koch M, Rothrock C, Gollogly LK, D’Amore PA, Ryeom S, Yoon SS (2008) Tumor escape from endogenous, extracellular matrix-associated angiogenesis inhibitors by up-regulation of multiple proangiogenic factors. Clin Cancer Res 14(5):1529–1539. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4126
Richter K, Haslbeck M, Buchner J (2010) The heat shock response: life on the verge of death. Mol Cell 40(2):253–266. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.10.006
Ousman SS, Tomooka BH, van Noort JM, Wawrousek EF, O’Connor KC, Hafler DA, Sobel RA, Robinson WH, Steinman L (2007) Protective and therapeutic role for alphaB-crystallin in autoimmune demyelination. Nature 448(7152):474–479. doi:10.1038/nature05935
Didelot C, Schmitt E, Brunet M, Maingret L, Parcellier A, Garrido C (2006) Heat shock proteins: endogenous modulators of apoptotic cell death. Mol Chaperones Health Dis 171–198
Kase S, He S, Sonoda S, Kitamura M, Spee C, Wawrousek E, Ryan SJ, Kannan R, Hinton DR (2010) AlphaB-crystallin regulation of angiogenesis by modulation of VEGF. Blood 115(16):3398–3406. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-01-197095
Dimberg A, Rylova S, Dieterich LC, Olsson AK, Schiller P, Wikner C, Bohman S, Botling J, Lukinius A, Wawrousek EF, Claesson-Welsh L (2008) AlphaB-crystallin promotes tumor angiogenesis by increasing vascular survival during tube morphogenesis. Blood 111(4):2015–2023. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-04-087841
Liao WC, Wu MS, Wang HP, Tien YW, Lin JT (2009) Serum heat shock protein 27 is increased in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Pancreas 38(4):422–426. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e318198281d
Huang Q, Ye J, Chen W, Wang L, Lin W, Lin J, Lin X (2010) Heat shock protein 27 is over-expressed in tumor tissues and increased in sera of patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin Chem Lab Med 48(2):263–269. doi:10.1515/CCLM.2010.043
Schmitt E, Gehrmann M, Brunet M, Multhoff G, Garrido C (2007) Intracellular and extracellular functions of heat shock proteins: repercussions in cancer therapy. J Leukoc Biol 81(1):15–27. doi:10.1189/jlb.0306167
Lee Y, Lee D, Cho C, Chung H, Bae S, Jhon G, Soh J, Jeoung D, Lee S, Lee Y (2005) HSP25 inhibits radiation-induced apoptosis through reduction of PKC¥ä-mediated ROS production. Oncogene 24(23):3715–3725
Lee YJ, Lee DH, Cho CK, Bae S, Jhon GJ, Lee SJ, Soh JW, Lee YS (2005) HSP25 inhibits protein kinase C delta-mediated cell death through direct interaction. J Biol Chem 280(18):18108–18119. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501131200
Ciocca DR, Oesterreich S, Chamness GC, McGuire WL, Fuqua SA (1993) Biological and clinical implications of heat shock protein 27,000 (Hsp27): a review. J Natl Cancer Inst 85(19):1558–1570
Geum D, Son GH, Kim K (2002) Phosphorylation-dependent cellular localization and thermoprotective role of heat shock protein 25 in hippocampal progenitor cells. J Biol Chem 277(22):19913–19921. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104396200
Lee YJ, Koch M, Karl D, Torres-Collado AX, Fernando NT, Rothrock C, Kuruppu D, Ryeom S, Iruela-Arispe ML, Yoon SS (2010) Variable inhibition of thrombospondin 1 against liver and lung metastases through differential activation of metalloproteinase ADAMTS1. Cancer Res 70(3):948–956. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3094
DuPage M, Dooley AL, Jacks T (2009) Conditional mouse lung cancer models using adenoviral or lentiviral delivery of Cre recombinase. Nat Protoc 4(7):1064–1072. doi:10.1038/nprot.2009.95
Kirsch DG, Dinulescu DM, Miller JB, Grimm J, Santiago PM, Young NP, Nielsen GP, Quade BJ, Chaber CJ, Schultz CP, Takeuchi O, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Korsmeyer SJ, Yoon SS, Hornicek FJ, Weissleder R, Jacks T (2007) A spatially and temporally restricted mouse model of soft tissue sarcoma. Nat Med 13(8):992–997. doi:10.1038/nm1602
Ryeom S, Baek KH, Rioth MJ, Lynch RC, Zaslavsky A, Birsner A, Yoon SS, McKeon F (2008) Targeted deletion of the calcineurin inhibitor DSCR1 suppresses tumor growth. Cancer Cell 13(5):420–431. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2008.02.018
Montrucchio G, Lupia E, Battaglia E, Del Sorbo L, Boccellino M, Biancone L, Emanuelli G, Camussi G (2000) Platelet-activating factor enhances vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell motility and neoangiogenesis in a murine matrigel model. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(1):80–88
Detwiller KY, Fernando NT, Segal NH, Ryeom SW, D’Amore PA, Yoon SS (2005) Analysis of hypoxia-related gene expression in sarcomas and effect of hypoxia on RNA interference of vascular endothelial cell growth factor A. Cancer Res 65(13):5881–5889. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4078
Roeckl W, Hecht D, Sztajer H, Waltenberger J, Yayon A, Weich HA (1998) Differential binding characteristics and cellular inhibition by soluble VEGF receptors 1 and 2. Exp Cell Res 241(1):161–170. doi:10.1006/excr.1998.4039
Goldman CK, Kendall RL, Cabrera G, Soroceanu L, Heike Y, Gillespie GY, Siegal GP, Mao X, Bett AJ, Huckle WR, Thomas KA, Curiel DT (1998) Paracrine expression of a native soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibits tumor growth, metastasis, and mortality rate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(15):8795–8800
Krepuska M, Szeberin Z, Sotonyi P, Sarkadi H, Fehervari M, Apor A, Rimely E, Prohaszka Z, Acsady G (2010) Serum level of soluble Hsp70 is associated with vascular calcification. Cell Stress Chaperones. doi:10.1007/s12192-010-0237-3
Rayner K, Chen YX, McNulty M, Simard T, Zhao X, Wells DJ, de Belleroche J, O’Brien ER (2008) Extracellular release of the atheroprotective heat shock protein 27 is mediated by estrogen and competitively inhibits acLDL binding to scavenger receptor-A. Circ Res 103(2):133–141. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.172155
Ciocca DR, Calderwood SK (2005) Heat shock proteins in cancer: diagnostic, prognostic, predictive, and treatment implications. Cell Stress Chaperones 10(2):86–103
Melle C, Ernst G, Escher N, Hartmann D, Schimmel B, Bleul A, Thieme H, Kaufmann R, Felix K, Friess HM, Settmacher U, Hommann M, Richter KK, Daffner W, Taubig H, Manger T, Claussen U, von Eggeling F (2007) Protein profiling of microdissected pancreas carcinoma and identification of HSP27 as a potential serum marker. Clin Chem 53(4):629–635. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2006.079194
Kim EH, Lee HJ, Lee DH, Bae S, Soh JW, Jeoung D, Kim J, Cho CK, Lee YJ, Lee YS (2007) Inhibition of heat shock protein 27-mediated resistance to DNA damaging agents by a novel PKC delta-V5 heptapeptide. Cancer Res 67(13):6333–6341. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4344
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285(21):1182–1186
Jain RK (2001) Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 7(9):987–989. doi:10.1038/nm0901-987
Wachsberger P, Burd R, Dicker AP (2003) Tumor response to ionizing radiation combined with antiangiogenesis or vascular targeting agents: exploring mechanisms of interaction. Clin Cancer Res 9(6):1957–1971
Dakappagari N, Neely L, Tangri S, Lundgren K, Hipolito L, Estrellado A, Burrows F, Zhang H (2010) An investigation into the potential use of serum Hsp70 as a novel tumour biomarker for Hsp90 inhibitors. Biomarkers 15(1):31–38. doi:10.3109/13547500903261347
Sreekumar PG, Kannan R, Kitamura M, Spee C, Barron E, Ryan SJ, Hinton DR (2010) AlphaB crystallin is apically secreted within exosomes by polarized human retinal pigment epithelium and provides neuroprotection to adjacent cells. PLoS One 5(10):e12578. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012578
Folkman J, Kalluri R (2004) Cancer without disease. Nature 427(6977):787. doi:10.1038/427787a
Feldman AL, Tamarkin L, Paciotti GF, Simpson BW, Linehan WM, Yang JC, Fogler WE, Turner EM, Alexander HR Jr, Libutti SK (2000) Serum endostatin levels are elevated and correlate with serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with stage IV clear cell renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6(12):4628–4634
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J (1997) Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 88(2):277–285
Zaslavsky A, Baek KH, Lynch RC, Short S, Grillo J, Folkman J, Italiano JE Jr, Ryeom S (2010) Platelet-derived thrombospondin-1 is a critical negative regulator and potential biomarker of angiogenesis. Blood 115(22):4605–4613. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-242065
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Sandra Ryeom (University of Pennsylvania Medical School) for helpful discussions and Dr. Christiana DelloRusso for assistance editing the manuscript. This work was supported by the Nuclear Research and Development Program (Grant No. M2AMA006), Basic Science Research Program (Grant No. R1A4A002), and Mid-career Researcher Program (Grat No. 2011-0013364) of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (MEST).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YJ., Lee, HJ., Choi, Sh. et al. Soluble HSPB1 regulates VEGF-mediated angiogenesis through their direct interaction. Angiogenesis 15, 229–242 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9255-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9255-3