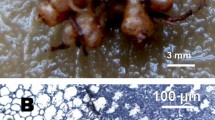
Abstract
The large sulphur bacteria, first discovered in the early nineteenth century, include some of the largest bacteria identified to date. Individual cells are often visible to the unaided eye and can reach 750 μm in diameter. The cells usually feature light-refracting inclusions of elemental sulphur and a large internal aqueous vacuole, which restricts the cytoplasm to the outermost periphery. In some taxa, it has been demonstrated that the vacuole can also serve for the storage of high millimolar concentrations of nitrate. Over the course of the past two centuries, a wide range of morphological variation within the family Beggiatoaceae has been found. However, representatives of this clade are frequently recalcitrant to current standard microbiological techniques, including 16S rRNA gene sequencing and culturing, and a reliable classification of these bacteria is often complicated. Here we present a summary of the efforts made and achievements accomplished in the past years, and give perspectives for investigating the heterogeneity and possible evolutionary developments in this extraordinary group of bacteria.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Barry JP, Nelson DC (1999) Phylogenetic affinity of a wide, vacuolate, nitrate-accumulating Beggiatoa sp. from Monterey Canyon, California, with Thioploca spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:270–277
Ahmad A, Kalanetra KM, Nelson DC (2006) Cultivated Beggiatoa spp. define the phylogenetic root of morphologically diverse, noncultured, vacuolate sulfur bacteria. Can J Microbiol 52:591–598
Angert ER (2005) Alternatives to binary fission in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:214–224
Angert ER, Northup DE, Reysenbach A-L, Peek AS, Goebel BM, Pace NR (1998) Molecular phylogenetic analysis of a bacterial community in Sulphur River, Parker Cave, Kentucky. Am Mineral 83:1583–1592
Aranda C, Paredes J, Valenzuela C, Lam P, Guillou L (2010) 16S rRNA gene-based molecular analysis of mat-forming and accompanying bacteria covering organically-enriched marine sediments underlying a salmon farm in Southern Chile (Calbuso Island). Gayana 74:125–135
Bailey JV, Joye SB, Kalanetra KM, Flood E, Corsetti FA (2007) Evidence of giant sulphur bacteria in neoproterozoic phosphorites. Nature 445:198–201
Bailey JV, Salman V, Rouse G, Schulz-Vogt HN, Levin L, Orphan V (2011) Dimorphism in methane seep dwelling ecotypes of the largest known bacteria. ISME J 5:1926–1935
Becking B (1934) Geobiologie of inleiding tot de milieukunde Diligentia Wetensch. Serie 18/19, van Stockum’s Gravenhange
Beutler M, Milucka J, Hinck S, Schreiber F, Brock J, Mussmann M, Schulz-Vogt HN, de Beer D (2012) Vacuolar respiration of nitrate coupled to energy conservation in filamentous Beggiatoaceae. Environ Microbiol 14:2911–2919
Brock TD (1974) Family IV. Leucotrichaceae Buchanan 1957. In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (eds) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th edn. The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, pp 118–119
Brock J, Rhiel E, Beutler M, Salman V, Schulz-Vogt HN (2012) Unusual polyphosphate inclusions observed in a marine Beggiatoa strain. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101:347–357
Buchanan RE (1957) Family III. Leucotrichaceae Buchanan. fam. nov. In: Breed RS, Murray EGD, Smith NR (eds) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 7th edn. The Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore, pp 850–851
Coleman ML, Sullivan MB, Martiny AC, Steglich C, Barry K, DeLong EF, Chisholm SW (2006) Genomic islands and the ecology and evolution of Prochlorococcus. Science 311:1768–1770
Crépeau V, Cambon-Bonavita MA, Lesongeur F, Randrianalivelo H, Sarradin PM, Sarrazin J, Godfroy A (2011) Diversity and function in microbial mats from the Lucky Strike hydrothermal vent field. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76:524–540
De Albuquerque JP, Keim CN, Lins U (2010) Comparative analysis of Beggiatoa from hypersaline and marine environments. Micron 41:507–517
DeLong EF, Preston CM, Mincer T, Rich V, Hallam SJ, Frigaard N-U, Martinez A, Sullivan MB, Edwards R, Rodriguez Brito B, Chisholm SW, Karl DM (2006) Community genomics among stratified microbial assemblages in the ocean’s interior. Science 311:496–503
Edgcomb VP, Kysela DT, Teske A, de Vera Gomez A, Sogin ML (2002) Benthic eukaryotic diversity in the Guaymas Basin hydrothermal vent environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7658–7662
Fossing H, Gallardo VA, Jørgensen BB, Hüttel M, Nielsen LP, Schulz H, Canfield DE, Forster S, Glud RN, Gundersen JK, Küver J, Ramsing NB, Teske A, Thamdrup B, Ulloa O (1995) Concentration and transport of nitrate by the mat-forming sulphur bacterium Thioploca. Nature 374:713–715
Fuhrman JA, Steele JA, Hewson I, Schwalbach MS, Brown MV, Green JL, Brown JH (2008) A latitudinal diversity gradient in planktonic marine bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:7774–7778
Gallardo VA (1977) Large benthic microbial communities in sulfide biota under Peru–Chile subsurface countercurrent. Nature 268:331–332
Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T (2005) Family I. Thiotrichaceae fam. nov. In: Garrity GM, Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, Vol 2, part B. Springer, New York, pp 131–179
Gillan DC, Speksnijder AGCL, Zwart G, De Ridder C (1998) Genetic diversity of the biofilm covering Montacuta ferruginosa (Mollusca, Bivalvia) as evaluated by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis and cloning of PCR-amplified gene fragments coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3464–3472
Girnth A-C, Grünke S, Lichtschlag A, Felden J, Knittel K, Wenzhöfer F, De Beer D, Boetius A (2011) A novel, mat-forming Thiomargarita population associated with a sulfidic fluid flow from a deep-sea mud volcano. Environ Microbiol 13:495–505
Goffredi SK, Orphan VJ (2010) Bacterial community shifts in taxa and diversity in response to localized organic loading in the deep sea. Environ Microbiol 12:344–363
Grünke S, Felden J, Lichtschlag A, Girnth A-C, de Beer D, Wenzhöfer F, Boetius A (2011) Niche differentiation among mat-forming, sulfide-oxidizing bacteria at cold seeps of the Nile Deep Sea Fan (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Geobiology 9:330–348
Grünke S, Lichtschlag A, de Beer D, Felden J, Salman V, Ramette A, Schulz-Vogt HN, Boetius A (2012) Mats of psychrophilic thiotrophic bacteria associated with cold seeps of the Barents Sea. Biogeosciences 9:2947–2960
Head IM, Gray ND, Howarth R, Pickup RW, Clarke KJ, Jones JG (2000) Achromatium oxaliferum—understanding the unmistakable. In: Schink B (ed) Advances in microbial ecology. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York, pp 1–40
Heijs SK, Damste JSS, Forney LJ (2005) Characterization of a deep-sea microbial mat from an active cold seep at the Milano mud volcano in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:47–56
Hinck S, Mussmann M, Salman V, Neu TR, Lenk S, de Beer D, Jonkers HM (2011) Vacuolated Beggiatoa-like filaments from different hypersaline environments form a novel genus. Environ Microbiol 12:3194–3205
Hinze G (1903) Thiophysa volutans, ein neues Schwefelbakterium. Ber Dtsch Bot Ges (Heft 6) 21:309–316
Hoffmann L, Komárek J, Kaštovský J (2005) System of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacteria)—state in 2004. Algol Stud 117:95–115
Høgsund S, Nielsen JL, Nielsen LP (2010) Distribution, ecology and molecular identification of Thioploca spp. from Danish brackish water sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:110–120
Jørgensen BB, Gallardo VA (1999) Thioploca spp.: filamentous sulfur bacteria with nitrate vacuoles. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 28:301–313
Jørgensen BB, Dunker R, Grünke S, Roy H (2010) Filamentous sulfur bacteria, Beggiatoa spp., in arctic marine sediments (Svalbard, 79 degrees N). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:500–513
Kalanetra KM, Nelson DC (2010) Vacuolate-attached filaments: highly productive Ridgeia piscesae epibionts at the Juan de Fuca hydrothermal vents. Mar Biol 157:791–800
Kalanetra KM, Huston SL, Nelson DC (2004) Novel, attached, sulfur-oxidizing bacteria at shallow hydrothermal vents possess vacuoles not involved in respiratory nitrate accumulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7487–7496
Kalanetra KM, Joye SB, Sunseri NR, Nelson DC (2005) Novel vacuolate sulfur bacteria from the Gulf of Mexico reproduce by reductive division in three dimensions. Environ Microbiol 7:1451–1460
Kamp A, Roy H, Schulz-Vogt HN (2008) Video-supported analysis of Beggiatoa filament growth, breakage, and movement. Microbiol Ecol 56:484–491
Kojima H, Fukui M (2003) Phylogenetic analysis of Beggiatoa spp. from organic rich sediment of Tokyo Bay, Japan. Water Res 37:3216–3223
Kojima H, Teske A, Fukui M (2003) Morphological and phylogenetic characterizations of freshwater Thioploca species from Lake Biwa, Japan, and Lake Constance, Germany. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:390–398
Komarek J (2006) Cyanobacterial taxonomy: current problems and prospects for the integration of traditional and molecular approaches. Algae 21:349–375
Komarek J (2010) Recent changes (2008) in cyanobacteria taxonomy based on a combination of molecular background with phenotype and ecological consequences (genus and species concept). Hydrobiologia 639:245–259
Komarek J, Anagnostidis K (1998) Cyanoprokaryota. In: Ettl H, Gartner G, Heynig H, Mollenhauer D (eds) Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 19/1. Gustav Fischer, Jena-Stuttgart-Lübeck-Ulm, pp 1–548
Lane DJ, Harrison AP Jr, Stahl D, Pace B, Giovannoni SJ, Olsen GJ, Pace NR (1992) Evolutionary relationships among sulfur- and iron-oxidizing eubacteria. J Bacteriol 174:269–278
Lapage SP, Sneath PHA, Lessel EF, Skerman VBD, Seeliger HPR, Clark WA (1992) International code of nomenclature of bacteria: bacteriological code. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Larkin JM, Henk MC (1996) Filamentous sulfide-oxidizing bacteria at hydrocarbon seeps of the Gulf of Mexico. Microsc Res Tech 33:23–31
Larkin JM, Shinabarger DL (1983) Characterization of Thiothrix nivea. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:841–846
Lauterborn R (1907) Eine neue Gattung der Schwefelbakterien (Thioploca schmidlei nov. gen. nov. spec.). Ber Dtsch Bot Ges 25:238–242
Leadbetter ER (1974) Family II. Beggiatoaceae. In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (eds) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th edn. The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, pp 112–116
López-García P, Duperron S, Philippot P, Foriel J, Susini J, Moreira D (2003) Bacterial diversity in hydrothermal sediment and epsilonproteobacterial dominance in experimental microcolonizers at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Environ Microbiol 5:961–976
Macalady JL, Dattagupta S, Schaperdoth I, Jones DS, Druschel GK, Eastman D (2008) Niche differentiation among sulfur-oxidizing bacterial populations in cave waters. ISME J 2:590–601
MacGregor BJ, Biddle JF, Teske A (2013a) Mobile elements in a single-filament orange Guaymas Basin Beggiatoa sp. genome: evidence for genetic exchange with cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. doi:10.1128/AEM.03821-12
MacGregor BJ, Biddle JF, Siebert JR, Staunton E, Hegg EL, Matthysse AG, Teske A (2013b) Why orange Guaymas Basin Beggiatoa spp. are orange: single-filament-genome-enabled identification of an abundant octaheme cytochrome with hydroxylamine oxidase, hydrazine oxidase, and nitrite reductase activities. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1183–1190
Maier S, Gallardo VA (1984) Nutritional characteristics of two marine thioplocas determined by autoradiography. Arch Microbiol 139:218–220
Martiny JBH, Bohannan BJ, Brown JH, Colwell RK, Fuhrman JA, Green JL, Horner-Devine MC, Kane M, Krumins JA, Kuske CR, Morin PJ, Naeem S, Ovreas L, Reysenbach A-L, Smith VH, Staley JT (2006) Microbial biogeography: putting mircoorganisms on the map. Nat Microbiol Rev 4:102–112
McHatton SC, Barry JP, Jannasch HW, Nelson DC (1996) High nitrate concentrations in vacuolate, autotrophic marine Beggiatoa spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:954–958
McKay LJ, MacGregor BJ, Biddle JF, Albert DB, Mendlovitz HP, Hoer DR, Lipp JS, Lloyd KG, Teske AP (2012) Spatial heterogeneity and underlying geochemistry of phylogenetically diverse orange and white Beggiatoa mats in Guaymas Basin hydrothermal sediments. Deep Sea Res I 67:21–31
Mussmann M, Schulz HN, Strotmann B, Kjaer T, Nielsen LP, Rosello-Mora RA, Amann RI, Jørgensen BB (2003) Phylogeny and distribution of nitrate-storing Beggiatoa spp. in coastal marine sediments. Environ Microbiol 5:523–533
Mussmann M, Hu FZ, Richter M, De Beer D, Preisler A, Jørgensen BB, Huntemann M, Glöckner FO, Amann R, Koopman WJH, Lasken RS, Janto B, Hogg J, Stoodley P, Boissy R, Ehrlich GD (2007) Insights into the genome of large sulfur bacteria revealed by analysis of single filaments. PLoS Biol 5:1923–1937
Nelson WC, Jannasch HW (1983) Chemoautotrophic growth of a marine Beggiatoa in sulfide-gradient cultures. Arch Microbiol 136:262–269
Nelson DC, Waterbury JB, Jannasch HW (1982) Nitrogen-fixation and nitrate utilization by marine and freshwater Beggiatoa. Arch Microbiol 133:172–177
Nelson WC, Revsbech NP, Jørgensen BB (1986) Microoxic–anoxic niche of Beggiatoa spp.: microelectrode survey of marine and freshwater strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:161–168
Nelson DC, Wirsen CO, Jannasch HW (1989) Characterization of large, autotrophic Beggiatoa spp. abundant at hydrothermal vents of the Guaymas Basin. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:2909–2917
Oerstedt AS (1844) De regionibus marinis. Elementa topographiae historiconaturalis freti Oeresund. PhD thesis, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen
Otte S, Kuenen G, Nielsen LP, Paerl HW, Zopfi J, Schulz HN, Teske A, Strotmann B, Gallardo VA, Jørgensen BB (1999) Nitrogen, carbon, and sulfur metabolism in natural Thioploca samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3148–3157
Pace NR, Olsen GJ, Woese CR (1986) Ribosomal RNA phylogeny and the primary lines of evolutionary descent. Cell 45:325–326
Peplies J, Kottmann R, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO (2008) A standard operating procedure for phylogenetic inference (SOPPI) using (rRNA) marker genes. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:251–257
Rabenhorst L (1865) Flora europaca algarum aquae dulcis submannae. Section II. Kummer, Leipzig: 94
Roa R, Gallardo VA, Ernst B, Baltazar M, Cañete JI, Enríquez-Briones S (1995) Nursery ground, age structure and abundance of juvenile squat lobster Pleuroncodes monodon on the continental shelf off central Chile. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 116:47–54
Salman V, Amann R, Girnth A-C, Polerecky L, Bailey J, Høgslund S, Jessen G, Pantoja S, Schulz-Vogt HN (2011) A single-cell sequencing approach to the classification of large, vacuolated sulfur bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:243–259
Salman V, Amann R, Shub DA, Schulz-Vogt HN (2012) Multiple self-splicing introns in the 16S rRNA genes of giant sulfur bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:4203–4208
Sanchez-Baracaldo P, Haydes PK, Blank CE (2005) Morphological and habitat evolution in the Cyanobacteria using a compartmentalization approach. Geobiology 3:145–165
Saravanakumar C, Dineshkumar N, Alavandi SV, Salman V, Poornima M, Kalaimani N (2012) Enrichment and identification of large filamentous sulfur bacteria related to Beggiatoa species from brackishwater ecosystems of Tamil Nadu, Southeast coast of India. Syst Appl Microbiol 35:396–403
Sayama M, Risgaard-Petersen N, Nielsen LP, Fossing H, Christensen PB (2005) Impact of bacterial NO3 − transport on sediment biogeochemistry. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7575–7577
Schattenhofer M, Fuchs BM, Amann R, Zubkov MV, Tarran GA, Pernthaler J (2009) Latitudinal distribution of prokaryotic picoplankton populations in the Atlantic Ocean. Environ Microbiol 11:2078–2093
Schewiakoff W (1892) Über einen neuen bacterienähnlichen Organismus des Süsswassers. Habilitation thesis, University Heidelberg, Heidelberg
Schulz HN (2006) The genus Thiomargarita. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes, 3 edn. Springer, New York, pp 1156–1163
Schulz HN, De Beer D (2002) Uptake rates of oxygen and sulfide measured with individual Thiomargarita namibiensis cells by using microelectrodes. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5746–5749
Schulz HN, Jørgensen BB (2001) Big bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:105–137
Schulz HN, Schulz HD (2005) Large sulfur bacteria and the formation of phosphorite. Science 307:416–418
Schulz HN, Jørgensen BB, Fossing HA, Ramsing NB (1996) Community structure of filamentous, sheath-building sulfur bacteria, Thioploca spp., off the coast of Chile. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1855–1862
Schulz HN, Brinkhoff T, Ferdelman TG, Marine MH, Teske A, Jørgensen BB (1999) Dense populations of a giant sulfur bacterium in Namibian shelf sediments. Science 284:493–495
Schwedt A, Kreutzmann A-C, Polerecky L, Schulz-Vogt HN (2012) Sulfur respiration in a marine chemolithoautotrophic Beggiatoa strain. Front Microbiol 2:276
Sekar R, Mills DK, Remily ER, Voss JD, Richardson LL (2006) Microbial communities in the surface mucopolysaccharide layer and the black band microbial mat of black band-diseased Siderastrea siderea. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5963–5973
Selje N, Simon M, Brinkhoff T (2004) A newly discovered Roseobacter cluster in temperate and polar oceans. Nature 427:445–448
Soutar A, Crill PA (1977) Sedimentation and climatic patterns in the Santa Barbara Basin during 19th and 20th centuries. Geol Soc Am Bull 88:1161–1172
Stevens H, Ulloa O (2008) Bacterial diversity in the oxygen minimum zone of the eastern tropical South Pacific. Environ Microbiol 10:1244–1259
Strohl WR (1989) Family I. Beggiatoaceae. In: Staley JT, Bryant MP, Pfennig N, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 3, 1st edn. The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, pp 2089–2106
Strohl WR, Larkin JM (1978) Enumeration, isolation, and characterization of Beggiatoa from freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 36:755–770
Strohl WR, Cannon GC, Shively JM, Gude H, Hook LA, Lane CM, Larkin JM (1981) Heterotrophic carbon metabolism by Beggiatoa alba. J Bacteriol 148:572–583
Summit M, Baross JA (1998) Thermophilic subseafloor microorganisms from the 1996 North Gorda Ridge eruption. Deep Sea Res II 45:2751–2766
Teske A, Ramsing NB, Küver J, Fossing H (1995) Phylogeny of Thioploca and related filamentous sulfide-oxidizing bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 18:517–526
Teske A, Sogin ML, Nielsen LP, Jannasch HW (1999) Phylogenetic position of a large marine Beggiatoa. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:39–44
Trevisan V (1842) Prospetto della Flora Euganea. Coi Tipi del Seminario, Padua
Van Niel CB (1948) Family A. Achromatiaceae Massart. In: Breed RS, Murray EGD, Hitchens AP (eds) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 6th edn. The Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore, pp 997–999
Vaucher JP (1803) Histoire des conferves d′eau douce, contenant leurs différents modes de reproduction, et la description de leurs principales espèces: Paschoud, Geneva
Waterbury JB, Stanier RW (1978) Patterns of growth and development in pleurocapsalean cyanobacteria. Microbiol Rev 42:2–44
West GS, Griffiths BM (1909) Hillhousia mirabilis, a giant sulphur bacterium. Proc R Soc Lond B 81:398–405
Williams LA, Reimers C (1983) Role of bacterial mats in oxygen-deficient marine basins and coastal upwelling regimes: preliminary report. Geology 11:267–269
Winogradsky SN (1887) Über Schwefelbacterien. Bot Zeitung 45:489–610
Winogradsky SN (1888) Beiträge zur Morphologie und Physiologie der Bacterien, Heft 1. Zur Morphologie und Physiologie der Schwefelbacterien: Leipzig, pp 1–120
Wirsen CO, Brinkhoff T, Küver J, Muyzer G, Molyneaux S, Jannasch HW (1998) Comparison of a new Thiomicrospira strain from the mid-atlantic ridge with known hydrothermal vent isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4057–4059
Yarza P, Richter M, Peplies J, Euzeby J, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO, Rosello-Mora R (2008) The all-species living tree project: a 16S rRNA-based phylogenetic tree of all sequenced type strains. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:241–250
Acknowledgments
We warmly thank Joe Morton for providing the illustrations of different types of large sulphur bacteria. Thank you also to Barbara MacGregor, Anne-Christin Kreutzmann and Heide Schulz-Vogt for reviewing the manuscript and providing valuable comments for its improvement. This study was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SA 2505/1-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salman, V., Bailey, J.V. & Teske, A. Phylogenetic and morphologic complexity of giant sulphur bacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 104, 169–186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9952-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9952-y