Abstract
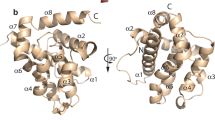
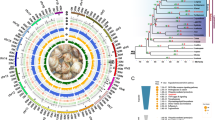
The expanding wealth of human, model and other organism’s genomic data has allowed the identification of a distinct gene family of apoptotic related genes. Most of these genes are currently unannotated or have been subsumed under two questionably related gene families in the past. For example the transmembrane Bax inhibitor 1 (BI1) motif family has been reported to play a role in apoptosis and to consist of at least seven mammalian protein genes, GRINA, BI1, Lfg/FAIM2, Ghitm, RESC1/Tmbim1, GAAP/Tmbim4, and Tmbm1b. However, a detailed sequence and phylogenetic analysis shows that only five of these form a clear and unique protein family. This now provides information for understanding and investigating the biological roles of these proteins across a wide range of tissues in model organisms. The evolutionary relationships among these genes provide a powerful prospective for extrapolating to human conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reimers K, Choi CYU, Mau-Thek E, Vogt PM (2006) Sequence analysis shows that Lifeguard belongs to a new evolutionarily conserved cytoprotective family. Int J Mol Med 18:729–734
Zhou J, Zhu T, Hu C et al (2008) Comparative genomics and function analysis on BI1 family. Comput Biol Chem 32:159–162
Pellicena-Palle A, Salz HK (1995) The putative Drosophila NMDARA1 gene is located on the second chromosome and is ubiquitously expressed in embryogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1261:301–303
Somia NV, Schmitt MJ, Vetter DE, Antwerp DV, Heinemann SF, Verma IM (1999) LFG: an anti-apoptotic gene that provides protection from Fas-mediated cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12667–12672
Schweitzer B, Taylor V, Welcher AA, McClelland M, Suter U (1998) Neural membrane protein 35 (NMP35): a novel member of a gene family which is highly expressed in the adult nervous system. Mol Cell Neurosci 11:260–273
Fernandez M, Segura MF, Sole C, Colino A, Comella JX, Cena V (2007) Lifeguard/neuronal membrane protein 35 regulates Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis in neurons via microdomain recruitment. J Neurochem 103:190–203
Chen JW, Cunningham MD, Galton N, Michaelis EK (1988) Immune labeling and purification of a 71-kDa glutamate-binding protein from brain synaptic membranes. Possible relationship of this protein to physiologic glutamate receptors. J Biol Chem 263:417–426
Eaton MJ, Chen JW, Kumar KN, Cong Y, Michaelis EK (1990) Immunochemical characterization of brain synaptic membrane glutamate-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 265:16195–16204
Kumar KN, Tilakaratne N, Johnson PS, Allen AE, Michaelis EK (1991) Cloning of cDNA for the glutamate-binding subunit of an NMDA receptor complex. Nature 354:70–73
Ly AM, Michaelis EK (1991) Solubilization, partial purification, and reconstitution of glutamate- and N-methyl-d-aspartate-activated cation channels from brain synaptic membranes. Biochemistry 30:4307–4316
Pal R, Eaton MJ, Islam S, Hake-Frendscho M, Kumar KN, Michaelis EK (1999) Immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization studies of the expression and distribution of three subunits of a complex with N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-like properties. Neuroscience 94:1291–1311
Mattson MP, Wang H, Michaelis EK (1991) Developmental expression, compartmentalization, and possible role in excitotoxicity of a putative NMDA receptor protein in cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 565:94–108
Bao X, Hui D, Naassila M, Michaelis EK (2001) Chronic ethanol exposure increases gene transcription of subunits of an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-like complex in cortical neurons in culture. Neurosci Lett 315:5–8
Bhave SV, Snell LD, Tabakoff B, Hoffman PL (1996) Mechanism of ethanol inhibition of NMDA receptor function in primary cultures of cerebral cortical cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 20:934–941
Chen X, Michaelis ML, Michaelis EK (1997) Effects of chronic ethanol treatment on the expression of calcium transport carriers and NMDA/glutamate receptor proteins in brain synaptic membranes. J Neurochem 69:1559–1569
Mattson MP, Kumar KN, Wang H, Cheng B, Michaelis EK (1993) Basic FGF regulates the expression of a functional 71 kDa NMDA receptor protein that mediates calcium influx and neurotoxicity in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 13:4575–4588
Hollmann M, Heinemann S (1994) Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 17:31–108
Szuchet S, Plachetzki DC, Eaton KS (2001) Oligodendrocyte transmembrane protein: a novel member of the glutamate-binding protein subfamily. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 283:900–907
Matsuda A, Suzuki Y, Honda G et al (2003) Large-scale identification and characterization of human genes that activate NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Oncogene 22:3307–3318
Aikawa H, Tomita H, Ishiguro S-i, Nishikawa S, Sugano E, Tamai M (2003) Increased expression of glutamate binding protein mRNA in rat retina after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Tohoku J Exp Med 199:25–33
Tachikawa K, Sasaki S, Maeda T, Nakajima K (2008) Identification of molecules preferentially expressed beneath the marginal zone in the developing cerebral cortex. Neurosci Res 60:135–146
Choi CYU, Reimers K, Allmeling C, Kall S, Choi Y-H, Vogt PM (2007) Inhibition of apoptosis by expression of antiapoptotic proteins in recombinant human keratinocytes. Cell Transpl 16:663–674
Beier CP, Wischhusen J, Gleichmann M et al (2005) FasL (CD95L/APO-1L) resistance of neurons mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt/protein kinase B-dependent expression of lifeguard/neuronal membrane protein 35. J Neurosci 25:6765–6774
Schweitzer B, Suter U, Taylor V (2002) Neural membrane protein 35/Lifeguard is localized at postsynaptic sites and in dendrites. Brain Res 107:47–56
Yoshisue H, Suzuki K, Kawabata A et al (2002) Large scale isolation of non-uniform shear stress-responsive genes from cultured human endothelial cells through the preparation of a subtracted cDNA library. Atherosclerosis 162:323–334
Zhao H, Ito A, Kimura SH et al (2006) RECS1 deficiency in mice induces susceptibility to cystic medial degeneration. Genes Genet Syst 81:41–50
Zhao H, Ito A, Sakai N, Matsuzawa Y, Yamashita S, Nojima H (2006) RECS1 is a negative regulator of matrix metalloproteinase-9 production and aged RECS1 knockout mice are prone to aortic dilation. Circ J 70:615–624
Gubser C, Bergamaschi D, Hollinshead M, Lu X, van Kuppeveld FJM, Smith GL (2007) A new inhibitor of apoptosis from vaccinia virus and eukaryotes. PLoS Pathog 3:e17
Van ‘t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ et al (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415:530–536
Lee S, Jo M, Lee J, Koh SS, Kim S (2007) Identification of novel universal housekeeping genes by statistical analysis of microarray data. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:226–231
He C, Zuo Z, Chen H et al (2007) Genome-wide detection of testis- and testicular cancer-specific alternative splicing. Carcinogenesis 28:2484–2490
Chae H-J, Ke N, Kim H-R et al (2003) Evolutionarily conserved cytoprotection provided by Bax Inhibitor-1 homologs from animals, plants, and yeast. Gene 323:101–113
Kleene KC (2005) Sexual selection, genetic conflict, selfish genes, and the atypical patterns of gene expression in spermatogenic cells. Dev Biol 277:16–26
Huckelhoven R (2004) BAX Inhibitor-1, an ancient cell death suppressor in animals and plants with prokaryotic relatives. Apoptosis 9:299–307
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305:567–580
Chintapalli VR, Wang J, Dow JAT (2007) Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nat Genet 39:715–720
Bingham J, Sudarsanam S (2000) Visualizing large hierarchical clusters in hyperbolic space. Bioinformatics 16:660–661
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Nancy Sands for her help with the manuscript. GG dedicates his efforts to the memory of his mentors Harvey R. Colten, Fred S. Rosen and Paul M. Gallop. He also thanks Olga A. Goldberger, Anatoly D. Altstein, Dmitry Leyfer, Juerg Straubhaar, Scott C. Mohr, Nelson A. Arango and Kerstin Reimers for their diverse input.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, L., Smith, T.F. & Goldberger, G. LFG: a candidate apoptosis regulatory gene family. Apoptosis 14, 1255–1265 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0402-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0402-2