Abstract
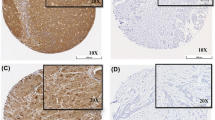
Appropriate mitochondrial functioning in normal cells depends on proper functioning of mitochondrial translocation machinery, of which translocase of the outer membrane of mitochondria (TOMM) plays important role. The aim of this study was to explore the expression of TOMM34 in invasive breast cancer (BC) with relevance to BC molecular subtypes and patients’ outcome. Gene expression data of 128 BC were analysed using artificial neuronal network (ANN) analysis to identify differentially expressed genes between BC with distant metastases and that without distant metastases. TOMM34 expression was assessed in a large series of BC (n = 1,061) with long-term follow-up using tissue microarray and immunohistochemistry. TOMM34 protein expression was quantitatively measured using the novel reverse phase protein microarray (RPPA) technique. ANN analysis revealed TOMM34 gene transcript as one of the top differentially expressed gene correlated with BC distant metastasis. Protein expression of TOMM34 was associated with features of aggressive behaviour including higher tumour grade, advanced nodal stage, larger tumour size and lymphovascular invasion. TOMM34 over-expression was significantly associated with shorter BC-specific survival and metastasis-free survival independent of standard prognostic parameters. TOMM34 protein expression was quantified by RPPA which showed that the mean expression values of TOMM34 were higher in samples demonstrating features of poor outcome. This study demonstrates at translational protein expression level that TOMM34 is a marker of poor prognosis in BC. Our findings underscore the role played by mitochondrial machinery in BC progression and warrant their validation on a prospective basis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng Y, Sun B, Li X, Zhang L, Niu Y, Xiao C, Ning L, Fang Z, Wang Y, Zhang L, Cheng J, Zhang W, Hao X (2007) Differentially expressed genes between primary cancer and paired lymph node metastases predict clinical outcome of node-positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 103:319–329
Weigel MT, Dowsett M (2010) Current and emerging biomarkers in breast cancer: prognosis and prediction. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:R245–R262
McBride HM, Neuspiel M, Wasiak S (2006) Mitochondria: more than just a powerhouse. Curr Biol 16:R551–R560
Cadenas E (2004) Mitochondrial free radical production and cell signaling. Mol Aspects Med 25:17–26
Carew JS, Huang P (2002) Mitochondrial defects in cancer. Mol Cancer 1:9
de Moura MB, dos Santos LS, Van Houten B (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Environ Mol Mutagen 51:391–405
Kroemer G (2006) Mitochondria in cancer. Oncogene 25:4630–4632
MacKenzie JA, Payne RM (2007) Mitochondrial protein import and human health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:509–523
Nuttall SD, Hanson BJ, Mori M, Hoogenraad NJ (1997) hTom34: a novel translocase for the import of proteins into human mitochondria. DNA Cell Biol 16:1067–1074
Chewawiwat N, Yano M, Terada K, Hoogenraad NJ, Mori M (1999) Characterization of the novel mitochondrial protein import component, Tom34, in mammalian cells. J Biochem 125:721–727
Shimokawa T, Matsushima S, Tsunoda T, Tahara H, Nakamura Y, Furukawa Y (2006) Identification of TOMM34, which shows elevated expression in the majority of human colon cancers, as a novel drug target. Int J Oncol 29:381–386
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2005) Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK). Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2:416–422
Abd El-Rehim DM, Ball G, Pinder SE, Rakha E, Paish C, Robertson JFR, Macmillan D, Blamey RW, Ellis IO (2005) High-throughput protein expression analysis using tissue microarray technology of a large well-characterised series identifies biologically distinct classes of breast cancer confirming recent cDNA expression analyses. Int J Cancer 116:340–350
Rakha EA, Elsheikh SE, Aleskandarany MA, Habashi HO, Green AR, Powe DG, El-Sayed ME, Benhasouna A, Brunet JS, Akslen LA, Evans AJ, Blamey R, Reis-Filho JS, Foulkes WD, Ellis IO (2009) Triple-negative breast cancer: distinguishing between basal and nonbasal subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 15:2302–2310
Naderi A, Teschendorff AE, Barbosa-Morais NL, Pinder SE, Green AR, Powe DG, Robertson JF, Aparicio S, Ellis IO, Brenton JD, Caldas C (2007) A gene-expression signature to predict survival in breast cancer across independent data sets. Oncogene 26:1507–1516
Zhang H, Rakha EA, Ball GR, Spiteri I, Aleskandarany M, Paish EC, Powe DG, Macmillan RD, Caldas C, Ellis IO, Green AR (2010) The proteins FABP7 and OATP2 are associated with the basal phenotype and patient outcome in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 121:41–51
McCarty KS Jr, Miller LS, Cox EB, Konrath J, McCarty KS Sr (1985) Estrogen receptor analyses. Correlation of biochemical and immunohistochemical methods using monoclonal antireceptor antibodies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 109:716–721
Nirmalan NJ, Harnden P, Selby PJ, Banks RE (2009) Development and validation of a novel protein extraction methodology for quantitation of protein expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues using western blotting. J Pathol 217:497–506
Rakha EA, Putti TC, El-Rehim DMA, Paish C, Green AR, Powe DG, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO (2006) Morphological and immunophenotypic analysis of breast carcinomas with basal and myoepithelial differentiation. J Pathol 208:495–506
Oyama T, Ishikawa Y, Hayashi M, Arihiro K, Horiguchi J (2007) The effects of fixation, processing and evaluation criteria on immunohistochemical detection of hormone receptors in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 14:182–188
Espina V, Wulfkuhle J, Calvert VS, Liotta LA, Petricoin EF (2008) Reverse phase protein microarrays for theranostics and patient-tailored therapy. Methods Mol Biol 441:113–128
Acknowledgments
M Aleskandarany, Ola H Negm and M AH Ahmed received the financial supports from the Ministry of High Education (Egypt).
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mohammed A. Aleskandarany and Ola H. Negm are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aleskandarany, M.A., Negm, O.H., Rakha, E.A. et al. TOMM34 expression in early invasive breast cancer: a biomarker associated with poor outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136, 419–427 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2249-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2249-4