Abstract
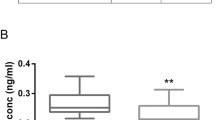
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is thought to be involved in the regulation of gastric and mesenteric blood flow, in the control of gastric acid secretion and in the modulation of intestinal motility, yet the precise physiological roles of CGRP remain to be elucidated. To further examine the role(s) of CGRP in gastrointestinal function, we examined mutant mice lacking αCGRP or βCGRP expression. Mutant mice did not demonstrate any overt phenotypic changes, yet exhibited a spontaneous, adult-onset colitis and increased colonic damage using a dextran sulfate sodium model of experimental colitis. Surprisingly, mice lacking βCGRP show no obvious alterations in CGRP immunoreactivity in the gut, accompanied by an increase in αCGRP messenger RNA expression, suggesting an adaptive mechanism to compensate for the lack of βCGRP. These data demonstrate that both αCGRP and βCGRP play a protective role in the generation of spontaneous colitis, supporting a role for both extrinsic and intrinsic CGRP-containing neurons.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wimalawansa SJ (1997) Amylin, calcitonin gene-related peptide, calcitonin, and adrenomedullin: a peptide superfamily. Crit Rev Neurobiol 11:167–239
Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES, Evans RM (1982) Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature 298:240–244
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod JJ, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature 304:129–135
Amara SG, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1984) Calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide transcription unit: tissue-specific expression involves selective use of alternative polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol 4:2151–2160
Rosenfeld MG, Amara SG, Evans RM (1984) Alternative RNA processing: determining neuronal phenotype. Science 225:1315–1320
Muff R, Born W, Lutz TA, Fischer JA (2004) Biological importance of the peptides of the calcitonin family as revealed by disruption and transfer of corresponding genes. Peptides 25:2027–2038
Thomas PM, Nasonkin I, Zhang H, Gagel RF, Cote GJ (2001) Structure of the mouse calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide alpha and beta genes. DNA Seq 12:131–135
Steenbergh PH, Hoppener JW, Zandberg J, Lips CJ, Jansz HS (1985) A second human calcitonin/CGRP gene. FEBS Lett 183:403–407
Amara SG, Arriza JL, Leff SE, Swanson LW, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1985) Expression in brain of a messenger RNA encoding a novel neuropeptide homologous to calcitonin gene-related peptide. Science 229:1094–1097
Mulderry PK, Ghatei MA, Spokes RA, Jones PM, Pierson AM, Hamid QA, Kanse S, Amara SG, Burrin JM, Legon S et al (1988) Differential expression of alpha-CGRP and beta-CGRP by primary sensory neurons and enteric autonomic neurons of the rat. Neuroscience 25:195–205
Sternini C, Anderson K (1992) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing neurons supplying the rat digestive system: differential distribution and expression pattern. Somatosens Mot Res 9:45–59
Schutz B, Mauer D, Salmon AM, Changeux JP, Zimmer A (2004) Analysis of the cellular expression pattern of beta-CGRP in alpha-CGRP-deficient mice. J Comp Neurol 476:32–43
Furness JB, Robbins HL, Xiao J, Stebbing MJ, Nurgali K (2004) Projections and chemistry of Dogiel type II neurons in the mouse colon. Cell Tissue Res 317:1–12
Gershon MD (2005) Nerves, reflexes, and the enteric nervous system: pathogenesis of the irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol 39:S184–193
Plourde V, St-Pierre S, Quirion R (1997) Calcitonin gene-related peptide in viscerosensitive response to colorectal distension in rats. Am J Physiol 273:G191–196
Grider JR (1994) CGRP as a transmitter in the sensory pathway mediating peristaltic reflex. Am J Physiol 266:G1139–1145
Grider JR (2003) Neurotransmitters mediating the intestinal peristaltic reflex in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:460–467
Cox HM (1995) Receptors for calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) in gastrointestinal epithelia. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 73:974–980
McCulloch CR, Cooke HJ (1989) Human alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide influences colonic secretion by acting on myenteric neurons. Regul Pept 24:87–96
Reinshagen M, Flamig G, Ernst S, Geerling I, Wong H, Walsh JH, Eysselein VE, Adler G (1998) Calcitonin gene-related peptide mediates the protective effect of sensory nerves in a model of colonic injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:657–661
Reinshagen M, Patel A, Sottili M, French S, Sternini C, Eysselein VE (1996) Action of sensory neurons in an experimental at colitis model of injury and repair. Am J Physiol 270:G79–86
Reinshagen M, Patel A, Sottili M, Nast C, Davis W, Mueller K, Eysselein V (1994) Protective function of extrinsic sensory neurons in acute rabbit experimental colitis. Gastroenterology 106:1208–1214
Domek MJ, Blackman EI, Kao J, Zhang XY, Iwata F, Seno K, Leung FW (1997) Functional ablation of afferent nerves aggravates dextran sulphate sodium-induced colonic damage in rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:698–702
Jurjus AR, Khoury NN, Reimund JM (2004) Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 50:81–92
Farrell RJ, Peppercorn MA (2002) Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 359:331–340
Shanahan F (2002) Crohn’s disease. Lancet 359:62–69
Kimball ES, Wallace NH, Schneider CR, D’Andrea MR, Hornby PJ (2004) Vanilloid receptor 1 antagonists attenuate disease severity in dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:811–818
Kihara N, de la Fuente SG, Fujino K, Takahashi T, Pappas TN, Mantyh CR (2003) Vanilloid receptor-1 containing primary sensory neurones mediate dextran sulphate sodium induced colitis in rats. Gut 52:713–719
Wimalawansa SJ (1996) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and its receptors: molecular genetics, physiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutic potentials. Endocr Rev 17:533–585
Dumont Y, Chabot JG, Quirion R (2004) Receptor autoradiography as mean to explore the possible functional relevance of neuropeptides: focus on new agonists and antagonists to study natriuretic peptides, neuropeptide Y and calcitonin gene-related peptides. Peptides 25:365–391
Tsien RY (1998) The green fluorescent protein. Annu Rev Biochem 67:509–544
Lu JT, Son YJ, Lee J, Jetton TL, Shiota M, Moscoso L, Niswender KD, Loewy AD, Magnuson MA, Sanes JR et al (1999) Mice lacking alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide exhibit normal cardiovascular regulation and neuromuscular development. Mol Cell Neurosci 14:99–120
Rosenblatt MI, Dickerson IM (1997) Endoproteolysis at tetrabasic amino acid sites in procalcitonin gene-related peptide by pituitary cell lines. Peptides 18:567–576
Emeson RB, Hedjran F, Yeakley JM, Guise JW, Rosenfeld MG (1989) Alternative production of calcitonin and CGRP mRNA is regulated at the calcitonin-specific splice acceptor. Nature 341:76–80
Rueter SM, Dawson TR, Emeson RB (1999) Regulation of alternative splicing by RNA editing. Nature 399:75–80
Feng Y, Sansam CL, Singh M, Emeson RB (2006) Altered RNA editing in mice lacking ADAR2 autoregulation. Mol Cell Biol 26:480–488
Park CM, Reid PE, Walker DC, MacPherson BR (1987) A simple, practical ‘swiss roll’ method of preparing tissues for paraffin or methacrylate embedding. J Microsc 145(Pt 1): 115–120
Dieleman LA, Palmen MJ, Akol H, Bloemena E, Pena AS, Meuwissen SG, Van Rees EP (1998) Chronic experimental colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) is characterized by Th1 and Th2 cytokines. Clin Exp Immunol 114:385–391
El Meskini R, Jin L, Marx R, Bruzzaniti A, Lee J, Emeson R, Mains R (2001) A signal sequence is sufficient for green fluorescent protein to be routed to regulated secretory granules. Endocrinology 142:864–873
Huang WY, Aramburu J, Douglas PS, Izumo S (2000) Transgenic expression of green fluorescence protein can cause dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat Med 6:482–483
Scacheri PC, Crabtree JS, Novotny EA, Garrett-Beal L, Chen A, Edgemon KA, Marx SJ, Spiegel AM, Chandrasekharappa SC, Collins FS (2001) Bidirectional transcriptional activity of PGK-neomycin and unexpected embryonic lethality in heterozygote chimeric knockout mice. Genesis 30:259–263
Kilby NJ, Snaith MR, Murray JA (1993) Site-specific recombinases: tools for genome engineering. Trends Genet 9:413–421
Noguchi K, Senba E, Morita Y, Sato M, Tohyama M (1990) Co-expression of alpha-CGRP and beta-CGRP mRNAs in the rat dorsal root ganglion cells. Neurosci Lett 108:1–5
Thompson RJ, Doran JF, Jackson P, Dhillon AP, Rode J (1983) PGP 9.5—a new marker for vertebrate neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res 278:224–228
Bowers MC, Katki KA, Rao A, Koehler M, Patel P, Spiekerman A, DiPette DJ, Supowit SC (2005) Role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in hypertension-induced renal damage. Hypertension 46:51–57
Oh-hashi Y, Shindo T, Kurihara Y, Imai T, Wang Y, Morita H, Imai Y, Kayaba Y, Nishimatsu H, Suematsu Y et al (2001) Elevated sympathetic nervous activity in mice deficient in alphaCGRP. Circ Res 89:983–990
Osinski MA, Bass P, Gaumnitz EA (1999) Peripheral and central actions of orphanin FQ (nociceptin) on murine colon. Am J Physiol 276:G125–131
Melgar S, Karlsson A, Michaelsson E (2005) Acute colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium progresses to chronicity in C57BL/6 but not in BALB/c mice: correlation between symptoms and inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288:G1328–1338
Kitajima S, Takuma S, Morimoto M (1999) Tissue distribution of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) in the acute phase of murine DSS-induced colitis. J Vet Med Sci 61:67–70
Ni J, Chen SF, Hollander D (1996) Effects of dextran sulphate sodium on intestinal epithelial cells and intestinal lymphocytes. Gut 39:234–241
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R (1990) A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 98:694–702
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G (1982) Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol 78:206–209
Sadlack B, Merz H, Schorle H, Schimpl A, Feller AC, Horak I (1993) Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell 75:253–261
Kuhn R, Lohler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Muller W (1993) Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75:263–274
Shull MM, Ormsby I, Kier AB, Pawlowski S, Diebold RJ, Yin M, Allen R, Sidman C, Proetzel G, Calvin D et al (1992) Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature 359:693–699
Mombaerts P, Mizoguchi E, Grusby MJ, Glimcher LH, Bhan AK, Tonegawa S (1993) Spontaneous development of inflammatory bowel disease in T cell receptor mutant mice. Cell 75:274–282
Rudolph U, Finegold MJ, Rich SS, Harriman GR, Srinivasan Y, Brabet P, Boulay G, Bradley A, Birnbaumer L (1995) Ulcerative colitis and adenocarcinoma of the colon in G alpha i2-deficient mice. Nat Genet 10:143–150
Maison SF, Emeson RB, Adams JC, Luebke AE, Liberman MC (2003) Loss of alpha CGRP reduces sound-evoked activity in the cochlear nerve. J Neurophysiol 90:2941–2949
Durham PL (2004) CGRP receptor antagonists: a new choice for acute treatment of migraine? Curr Opin Investig Drugs 5:731–735
Puel JL (1995) Chemical synaptic transmission in the cochlea. Prog Neurobiol 47:449–476
Li N, Lundeberg T, Yu LC (2001) Involvement of CGRP and CGRP1 receptor in nociception in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Brain Res 901:161–166
Yu LC, Weng XH, Wang JW, Lundeberg T (2003) Involvement of calcitonin gene-related peptide and its receptor in anti-nociception in the periaqueductal grey of rats. Neurosci Lett 349:1–4
Tache Y, Raybould H, Wei JY (1991) Central and peripheral actions of calcitonin gene-related peptide on gastric secretory and motor function. Adv Exp Med Biol 298:183–198
Tache Y (1992) Inhibition of gastric acid secretion and ulcers by calcitonin [correction of calciton] gene-related peptide. Ann N Y Acad Sci 657:240–247
Mulderry PK, Ghatei MA, Bishop AE, Allen YS, Polak JM, Bloom SR (1985) Distribution and chromatographic characterisation of CGRP-like immunoreactivity in the brain and gut of the rat. Regul Pept 12:133–143
Brain SD, MacIntyre I, Williams TJ (1986) A second form of human calcitonin gene-related peptide which is a potent vasodilator. Eur J Pharmacol 124:349–352
Beglinger C, Born W, Munch R, Kurtz A, Gutzwiller JP, Jager K, Fischer JA (1991) Distinct hemodynamic and gastric effects of human CGRP I and II in man. Peptides 12:1347–1351
Firth KF, Broughton Pipkin F (1989) Human alpha- and beta-calcitonin gene-related peptides are vasodilators in human chorionic plate vasculature. Am J Obstet Gynecol 161:1318–1319
Longmore J, Hogg JE, Hutson PH, Hill RG (1994) Effects of two truncated forms of human calcitonin-gene related peptide: implications for receptor classification. Eur J Pharmacol 265:53–59
Maggi CA, Giuliani S, Zagorodnyuk V (1996) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in the circular muscle of guinea-pig colon: role as inhibitory transmitter and mechanisms of relaxation. Regul Pept 61:27–36
Schworer H, Schmidt WE, Katsoulis S, Creutzfeldt W (1991) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) modulates cholinergic neurotransmission in the small intestine of man, pig and guinea-pig via presynaptic CGRP receptors. Regul Pept 36:345–358
Pan H, Gershon MD (2000) Activation of intrinsic afferent pathways in submucosal ganglia of the guinea pig small intestine. J Neurosci 20:3295–3309
Dennis T, Fournier A, St Pierre S, Quirion R (1989) Structure-activity profile of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and brain tissues. Evidence for receptor multiplicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:718–725
Poyner DR (1997) Molecular pharmacology of receptors for calcitonin-gene-related peptide, amylin and adrenomedullin. Biochem Soc Trans 25:1032–1036
Rossowski WJ, Jiang NY, Coy DH (1997) Adrenomedullin, amylin, calcitonin gene-related peptide and their fragments are potent inhibitors of gastric acid secretion in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 336:51–63
McLatchie LM, Fraser NJ, Main MJ, Wise A, Brown J, Thompson N, Solari R, Lee MG, Foord SM (1998) RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature 393:333–339
Conner AC, Simms J, Hay DL, Mahmoud K, Howitt SG, Wheatley M, Poyner DR (2004) Heterodimers and family-B GPCRs: RAMPs, CGRP and adrenomedullin. Biochem Soc Trans 32:843–846
Husmann K, Born W, Fischer JA, Muff R (2003) Three receptor-activity-modifying proteins define calcitonin gene-related peptide or adrenomedullin selectivity of the mouse calcitonin-like receptor in COS-7 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 66:2107–2115
Stucchi AF, Shofer S, Leeman S, Materne O, Beer E, McClung J, Shebani K, Moore F, O’Brien M, Becker JM (2000) NK-1 antagonist reduces colonic inflammation and oxidative stress in dextran sulfate-induced colitis in rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279:G1298–1306
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Morris HR, MacIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Dieleman LA, Ridwan BU, Tennyson GS, Beagley KW, Bucy RP, Elson CO (1994) Dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis occurs in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Gastroenterology 107:1643–1652
Xing L, Guo J, Wang X (2000) Induction and expression of beta-calcitonin gene-related peptide in rat T lymphocytes and its significance. J Immunol 165:4359–4366
Kneitz B, Herrmann T, Yonehara S, Schimpl A (1995) Normal clonal expansion but impaired Fas-mediated cell death and anergy induction in interleukin-2-deficient mice. Eur J Immunol 25:2572–2577
Hibi T, Ogata H, Sakuraba A (2002) Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol 37:409–417
Fernandez S, Knopf MA, Shankar G, McGillis JP (2003) Calcitonin gene-related peptide indirectly inhibits IL-7 responses in pre-B cells by induction of IL-6 and TNF-alpha in bone marrow. Cell Immunol 226:67–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, B.J., Washington, M.K., Kurre, U. et al. Protective Roles of α-Calcitonin and β-Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in Spontaneous and Experimentally Induced Colitis. Dig Dis Sci 53, 229–241 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-9848-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-9848-7