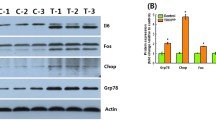
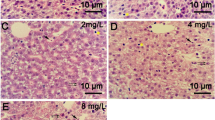
Abstract
Naphthalene has been used worldwide as a commercial insecticide for decades, which when detected in the environment can have various negative effects on non-target organism, such as hepatotoxicity. However, the molecular mechanisms of how naphthalene acts to affect the liver in zebrafish (Danio rerio) remains unknown. In this study, we evaluated the potential toxic effects of naphthalene on livers in female adult zebrafish over a 21-day subacute exposure. Global hepatic gene expression was examined by microarrays and the results indicated the regulated genes were associated significantly with vital hepatic injury pathways and GO categories upon naphthalene exposure, such as disruptions in lipid metabolism, inflammatory response, and the carcinogenic processes. According to our observations of liver histology, nuclear enlargement as a potential indicator of cancers and hepatic lipometabolic disorder precisely were supported. The 96 h acute naphthalene tests on Tg(lysC:DsRed) and LiPan lines larvae revealed recruitment of neutrophils by the liver, as well as decreased liver size, which further confirmed hepatic inflammation response to naphthalene exposure. Thus, these findings advance the field of ecotoxicology by unveiling a new role of naphthalene as a leading cause of liver damage and provide potential biomarker-genes for environmental naphthalene monitoring.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batterman S et al. (2012) Sources, concentrations, and risks of naphthalene in indoor and outdoor air. Indoor Air 22:266–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0668.2011.00760.x
Beltran AL et al. (2014) Clinicopathological characteristics and outcome of nested carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Virchows Arch 465:199–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1601-y
Berg JM., Tymoczko JL, Stryer L (2011) Biochemistry, Seventh Edition
Beyer J, Jabari S, Rau TT, Neuhuber W, Brehmer A, (2013) Substance P- and choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivities in somatostatin-containing, human submucosal neurons. Histochem Cell Biol 140:157
Briggs KJ et al. (2016) Paracrine induction of HIF by glutamate in breast cancer: EglN1 senses cysteine. Cell 166:126–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.042
Bromberg JF,Wrzeszczynska MH,Devgan G,Zhao Y,Pestell RG,Albanese C,Darnell JE,(1999) Stat3 as an Oncogene Cell 98:295–303.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81959-5
Brown KW, Donnelly KC (1988) An estimation of the risk associated with the organic-constituents of hazardous and municipal waste landfill leachates. Hazard Waste Hazard Mater 5:1–30. https://doi.org/10.1089/hwm.1988.5.1
Burns CG MD, Grande EJ, Rottbauer W, MacRae CA, Fishman MC (2005) Highthroughput assay for small molecules that modulate zebrafish embryonic heart rate. Nat Chem Biol 1(5):263–264
Carlson P, Van Beneden RJ (2014) Arsenic exposure alters expression of cell cycle and lipid metabolism genes in the liver of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 153:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.10.006
Chakraborty AK, Weiss A (2014) Insights into the initiation of TCR signaling. Nat Immunol 15:798–807. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2940
Chaturvedi P et al. (2013) Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent breast cancer-mesenchymal stem cell bidirectional signaling promotes metastasis. J Clin Invest 123:189–205. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64993
Chen X et al. (2014) XBP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer by controlling the HIF1alpha pathway. Nature 508:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13119
Collin G, Höke H (2000) Naphthalene and Hydronaphthalenes. Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.KGaA
Dennison JB et al. (2013) Lactate dehydrogenase B: a metabolic marker of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:3703–3713. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0623
Field HA, Ober EA, Roeser T, Stainier DYR (2003) Formation of the digestive system in zebrafish. I. liver morphogenesis. Dev Biol 253:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-1606(02)00017-9
Floyel T et al. (2014) CTSH regulates beta-cell function and disease progression in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:10305–10310. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1402571111
Friedman SE, Grendell JH, McQuaid KR (2003) Current diagnosis & treatment in gastroenterology. Lang Medical Books/McGraw-Hill, New York
G.Kaelin Jr. W, J.Ratcliffe P (2008) Oxygen sensing by metazoans: the central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol Cell 30:393–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.04.009
Galus M et al. (2013) Chronic, low concentration exposure to pharmaceuticals impacts multiple organ systems in zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 132-133:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.12.021
Gioacchini G, Giorgini E, Olivotto I, Maradonna F, Merrifield DL, Carnevali O (2014) The influence of probiotics on zebrafish Danio rerio innate immunity and hepatic stress. Zebrafish 11:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2013.0932
Gonzalez P, Baudrimont M, Boudou A, Bourdineaud JP (2006) Comparative effects of direct cadmium contamination on gene expression in gills, liver, skeletal muscles and brain of the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Biometals 19:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-005-5670-x
Hoffmann JL, Thomason RG, Lee DM, Brill JL, Price BB, Carr GJ, Versteeg DJ (2008) Hepatic gene expression profiling using GeneChips in zebrafish exposed to 17alpha-methyldihydrotestosterone. Aquat Toxicol 87:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.01.012
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Huang X, Zhou L, Gong Z (2012) Liver tumor models in transgenic zebrafish: an alternative in vivo approach to study hepatocarcinogenes. Future Oncol 8:21–28. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.11.137
Jelski W, Szmitkowski M (2008) Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) in the cancer diseases. Clin Chim Acta 395:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2008.05.001
Jeon H et al. (2011) Comparative analysis of the role of small G proteins in cell migration and cell death: cytoprotective and promigratory effects of Ral. A Exp Cell Res 317:2007–2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.05.021
Kendziorski CM, Zhang Y, Lan H, Attie AD (2003) The efficiency of pooling mRNA in microarray experiments. Biostatistics 4:465–477. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/4.3.465
Kirchheiner J, Roots I, Goldammer M, Rosenkranz B, Brockmoller J (2005) Effect of genetic polymorphisms in cytochromep450 (CYP) 2C9 and CYP2C8 on the pharmacokinetics of oral antidiabetic drugs: clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:1209–1225. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200544120-00002
Kusunoki J, Kanatani A, Moller DE (2006) Modulation of fatty acid metabolism as a potential approach to the treatment of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Endocrine 29:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1385/endo:29:1:91
Labrousse AM et al. (2011) Frustrated phagocytosis on micro-patterned immune complexes to characterize lysosome movements in live macrophages. Front Immunol 2:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2011.00051
Liu C et al. (2016) Acute exposure to tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCIPP) causes hepatic inflammation and leads to hepatotoxicity in zebrafish. Sci Rep 6:19045. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19045
Longo N, Amat di San Filippo C, Pasquali M (2006) Disorders of carnitine transport and the carnitine cycle. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 142C:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.30087
Martin TD, Der CJ (2012) Differential involvement of RalA and RalB in colorectal cancer. Small GTPases 3:126–130. https://doi.org/10.4161/sgtp.19571
Menke AL, Spitsbergen JM, Wolterbeek AP, Woutersen RA (2011) Normal anatomy and histology of the adult zebrafish. Toxicol Pathol 39:759–775. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623311409597
Moller AM, Hermsen C, Floehr T, Lamoree MH, Segner H (2014) Tissue-specific metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): a comparison between the liver and immune organs. Drug Metab Dispos: Biol fate Chem 42:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.113.053777
Montagner M et al. (2012) SHARP1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis by promoting degradation of hypoxia-inducible factors. Nature 487:380–384. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11207
Mukherjee A, Khuda-Bukhsh AR (2015) Quercetin down-regulates IL-6/STAT-3 signals to induce mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in a nonsmall- cell lung-cancer cell line, A549. J Pharmacopunct 18:19–26. https://doi.org/10.3831/KPI.2015.18.002
Neurath MF, Finotto S (2011) IL-6 signaling in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 22:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.02.003
North TE et al. (2010) PGE2-regulated wnt signaling and N-acetylcysteine are synergistically hepatoprotective in zebrafish acetaminophen injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:17315–17320. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008209107
Orton RJ, Sturm OE, Vyshemirsky V, Calder M, Gilbert DR, Kolch W (2005) Computational modelling of the receptor-tyrosine-kinase-activated MAPK pathway. Biochem J 392:249–261. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20050908
Palanikumar L, Kumaraguru AK, Ramakritinan CM (2013) Biochemical and genotoxic response of naphthalene to fingerlings of milkfish Chanos chanos. Ecotoxicology 22:1111–1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1098-1
Pandit A, Sachdeva T, Bafna P (2012) Drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Rev J Appl Pharm Sci 2:233–243. https://doi.org/10.7324/japs.2012.2541
Pearson WH, Olla BL (1980) Threshold for detection of naphthalene and other behavioral responses by the blue crab. Callinectes sapidus Estuaries 3:224–229
Pereira TS, Beltrami LS, Rocha JA, Broto FP, Comellas LR, Salvadori DM, Vargas VM (2013) Toxicogenetic monitoring in urban cities exposed to different airborne contaminants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 90:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.12.029
Pramfalk C, Angelin B, Eriksson M, Parini P (2007) Cholesterol regulates ACAT2 gene expression and enzyme activity in human hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 364:402–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.10.028
Rahmanpour S, Farzaneh Ghorghani N, Lotfi Ashtiyani SM (2014) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) in four fish species from different trophic levels in the Persian Gulf. Environ Monit Assess 186:7047–7053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3909-0
Ramachandran R, Kakar S (2009) Histological patterns in drug-induced liver disease. J Clin Pathol 62:481–492. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2008.058248
Reddy PS, Katyayani RV, Fingerman M (1996) Cadmium and naphthalene-induced hyperglycemia in the fiddler crab, uca pugilator: differential modes of action on the neuroendocrine system. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56:425–431
Rodriguez EF, Dacic S, Pantanowitz L, Khalbuss WE, Monaco SE (2015) Cytopathology of pulmonary adenocarcinoma with a single histological pattern using the proposed International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society (IASLC/ATS/ERS) classification Cancer cytopathology https://doi.org/10.1002/cncy.21532
SA B (2003) Complement and autoimmunity. Biomed Pharmacother 57:269–273
Shi X, Du Y, Lam PK, Wu RS, Zhou B (2008) Developmental toxicity and alteration of gene expression in zebrafish embryos exposed to PFOS. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 230:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2008.01.043
Tsuruda LS, Lame MW, Jones AD (1995) Formation of epoxide and quinone protein adducts in B6C3F1 mice treated with naphthalene, sulfate conjugate of 1,4-dihydroxynaphthalene and 1,4-naphthoquinone. Arch Toxicol 69:362–367
Ung CY et al. (2011) Existence of inverted profile in chemically responsive molecular pathways in the zebrafish liver. PLoS ONE 6:e27819. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027819
Van dOR, Beyer J, Vermeulen NP (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environmental toxicology and pharmacology 13:57–149
Vijayavel K, Gomathi RD, Durgabhavani K, Balasubramanian MP (2004) Sublethal effect of naphthalene on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in the edible marine crab Scylla serrata. Mar Pollut Bull 48:429–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.08.017
Viravaidya K, Sin A, Shuler ML (2004) Development of a microscale cell culture analog to probe naphthalene toxicity. Biotechnol Prog 20:316–323
Vliegenthart AD, Tucker CS, Del Pozo J, Dear JW (2014) Zebrafish as model organisms for studying drug-induced liver injury. Br J Clin Pharmacol 78:1217–1227. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12408
Watts C (2012) The endosome-lysosome pathway and information generation in the immune system. Biochim Et Biophys Acta 1824:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.07.006
Wright CS, Zhao Q, Rastinejad F (2003) Structural analysis of lipid complexes of GM2-activator protein. J Mol Biol 331:951–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00794-0
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R (2009) STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 9:798–809. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2734
Z. Feng K-JL (2015) Identification of genes and pathways associated with osteoarthritis by bioinformatics analyses. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:736–744
Zhang X, Li C, Gong Z (2014) Development of a convenient in vivo hepatotoxin assay using a transgenic zebrafish line with liver-specific DsRed expression. PLoS ONE 9:e91874. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091874
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
All the authors of this manuscript accept that the paper is submitted for publication in the Ecotoxicology journal and report that this paper has not been published or accepted for publication in another journal, and it is not under consideration at another journal.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Sheng, L., Gong, Z. et al. Investigation of the molecular mechanisms of hepatic injury upon naphthalene exposure in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicology 27, 650–660 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1943-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1943-3