Abstract
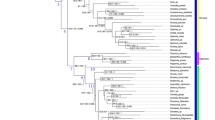
Despite previous efforts, the evolutionary history of the immigrans-tripunctata clade remains obscure in part due to its hypothesized origin through a rapid radiation. We performed a supermatrix analysis (3,243 base pairs) coupled with richness patterns, environmental phylogenetic signal and radiation tests in order to address phylogenetic relationships and macro-evolutionary hypotheses within this complex group of species. We propose a well-supported evolutionary scenario for the immigrans-tripunctata clade species, in which the tripunctata “radiation” was monophyletic and subdivided into three main lineages: the first including D. pallidipennis (pallidipennis group) imbedded among members of the tripunctata group; the second clustering the cardini and guarani groups; and the third grouping representatives from the tripunctata, calloptera and guaramunu groups. Therefore, we hypothesize that the tripunctata group encompasses a diphyletic taxon, with one clade including the pallidipennis group and the other showing a close affinity to the calloptera and guaramunu groups. Our results also suggest that niche evolution seems to have played a central role in the evolutionary history of the tripunctata species “radiation” allowing effective dispersion and diversification in the Neotropics, possibly in a southwards direction. Although the data as a whole support the notion that this occurred through rapid and successive speciation events, the radiation hypothesis remains to be further corroborated.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Control 19:716–723
Bächli G (2009) TaxoDros: the database on taxonomy of Drosophilidae, v.1.03, Database 2009/7. http://taxodros.unizh.ch/. Accessed on 27 Feb 2009
Blomberg SP, Garland T Jr (2002) Tempo and mode in evolution: phylogenetic inertia, adaptation and comparative methods. J Evol Biol 15:899–910
Böhning-Gaese K, Schuda MD, Helbig AJ (2003) Weak phylogenetic effects on ecological niches of Sylvia warblers. J Evol Biol 16:956–965
Brisson JA, Wilder J, Hollocher H (2006) Phylogenetic analysis of the cardini group of Drosophila with respect to changes in pigmentation. Evolution 60:1228–1247
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552
DaLage JL, Dergoat GJ, Maczkowiak F, Silvain JF, Cariou ML, Lachaise D (2007) A phylogeny of Drosophilidae using the Amyrel gene: questioning the Drosophila melanogaster species group boundaries. J Zoolog Syst Evol Res 45:47–63
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol 7:214
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Farris JS, Källersjö M, Kluge A, Bult C (1994) Testing significance of congruence. Cladistics 10:315–320
Farris JS, Källersjö M, Kluge A, Bult C (1995) Constructing a significance test for incongruence. Syst Biol 44:570–572
Frota-Pessoa O (1954) Revision of the tripunctata group of Drosophila with description of fifteen new species (Drosophilidae, Diptera). Arq Mus Paranaense X:253–304
Gottschalk MS (2008) Utilização de recursos tróficos por espécies Neotropicais de Drosophilidae (Diptera). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Hatadani LM, McInerney JO, Medeiros HF, Junqueira ACM, Azeredo-Espin AM, Klaczko LB (2009) Molecular phylogeny of the Drosophila tripunctata and closely related groups (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 51:595–600
Hawkins BA, Diniz-Filho JAF, Soeler SA (2005) Water links the historical and contemporary components of the Australian bird diversity gradient. J Biogeogr 32:1035–1042
Hawkins BA, Diniz-Filho JAF, Jaramillo CA, Soeller SA (2006) Post-Eocene climate change, niche conservatism, and the latitudinal diversity gradient of New World birds. J Biogeogr 33:770–780
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2004) The WordClim interpolated global terrestrial climate surfaces, version 1.3. http://biogeo.berkeley.edu/
Hijmans RJ, Guarino L, Jarvis A, O’Brien R, Mathur P, Bussink C, Cruz M, Barrantes I, Rojas E (2005a) Diva-GIS version 5.2. Manual. International Potato Center, Lima
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005b) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol 25:1965–1978
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MrBayes: bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Kastritsis CD (1969) The chromosomes of some species of the guarani group of Drosophila. J Heredity 60:50–57
Katoh T, Nakaya D, Tamura K, Aotsuka T (2007) Phylogeny of the Drosophila immigrans species group (Diptera: Drosophilidae) based on Adh and Gpdh sequences. Zoolog Sci 24:913–921
Kwiatowski J, Ayala FJ (1999) Phylogeny of Drosophila and related genera: conflict between molecular and anatomical analyses. Mol Phylogenet Evol 13:319–328
Lee MSY, Hugall AF (2003) Partitioned likelihood support and the evaluation of data set conflicts. Syst Biol 52:15–22
Losos JB (2008) Phylogenetic niche conservatism, phylogenetic signal and the relationships between phylogenetic relatedness and ecological similarity among species. Ecol Lett 11:995–1007
Löwenberg-Neto P, Carvalho CJB, Diniz-Filho JAF (2008) Spatial congruence between biotic history and species richness of Muscidae (Diptera, Insecta) in the Andean and Neotropical regions. J Zoolog Syst Evol Res 46:374–380
Malogolowkin C (1953) Sobre a genitália dos Drosofilídeos. IV. A genitália masculina do gênero Drosophila. Rev Brasil Biol 13:245–264
Mota NR, Robe LJ, Valente VLS, Budnik M, Loreto ELS (2008) Phylogeny of the Drosophila mesophragmatica group (Diptera, Drosophilidae): an example of Andean evolution. Zoolog Sci 25:526–532
Nylander JA (2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Center, Uppsala University
Pearman P, Guisan A, Broennimann O, Randin C (2008) Niche dynamics in space and time. Trends Ecol Evol 23:149–158
Perlman SJ, Spicer GS, Shoemaker DD, Jaenike J (2003) Associations between mycophagous Drosophila and their Howardula nematode parasites: a worldwide phylogenetic shuffle. Mol Ecol 12:237–249
Posada C, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Pybus OG, Harvey PH (2000) Testing macro-evolutionary models using incomplete molecular phylogenies. Proc R Soc Lond B 267:2267–2272
Pybus OG, Rambaut A (2002) GENIE: genealogy interval explorer. Department of Zoology. University of Oxford, Oxford
Rambaut A (2002) PhyloGen, version 1.0. Department of Zoology, University of Oxford, Oxford
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2007) Tracer v1.4. Available from http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer
Remsen J, DeSalle R (1998) Character congruence and multiple data partitions and the origin of the Hawaiian Drosophilidae. Mol Phylogenet Evol 9:225–235
Remsen J, O’Grady PO (2002) Phylogeny of Drosophilinae (Diptera: Drosopilidae) with comments on combined analysis and character support. Mol Phylogenet Evol 24:249–264
Robe LJ, Valente VLS, Budnik M, Loreto ELS (2005) Molecular phylogeny of the subgenus Drosophila (Diptera, Drosophilidae) with an emphasis on Neotropical species and groups: a nuclear versus mitochondrial gene approach. Mol Phylogenet Evol 36:623–640
Robe LJ, Loreto ELS, Valente VLS (2010) Radiation of the “Drosophila” subgenus (Drosophilidae, Diptera) in the Neotropics. J Zool Syst Evol Res. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0469.2009.00563.x
Rosenberg M (2009) PASSaGE: Pattern analysis, spatial statistics, and geographic exegesis. Center for evolutionary functional genomics/biodesign institute. Arizona State University
Russo CAM, Takezaki N, Nei M (1995) Molecular phylogeny and divergence times of Drosophilid species. Mol Biol Evol 12:391–404
Sassi AK, Heredia F, Loreto ELS, Valente VLS, Rohde C (2005) Transposable elements P and gypsy in natural populations of Drosophila willistoni. Genet Mol Biol 28:734–739
Shimodaira H, Hasegawa M (1999) Multiple comparisons of log-likelihoods with applications to phylogenetic inference. Mol Biol Evol 16:1114–1116
Sorenson MD, Franzosa EA (2007) TreeRot, version 3. Boston University, Boston
Staden R (1996) The Staden sequence analysis package. Mol Biotechnol 5:233–241
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Massachusetts
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tatarenkov A, Kwiatowski J, Sharecky D, Barrío E, Ayala FJ (1999) On the evolution of Dopa decarboxylase (Ddc) and Drosophila systematics. J Mol Evol 48:445–462
Tatarenkov A, Zurovcová M, Ayala FJ (2001) Ddc and Amd sequences resolve phylogenetic relationships of Drosophila. Mol Phylogenet Evol 20:321–325
Throckmorton LH (1975) The phylogeny, ecology and geography of Drosophila. In: King RC (ed) Handbook of genetics. Plenum, New York, pp 421–469
Val FC, Marques MD, Vilela CR (1981) Drosophilidae of neotropical region. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, Thompson JN (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 123–168
van der Linde K, Houle D (2008) A supertree analysis and literature review of the genus Drosophila and closely related genera (Diptera, Drosophilidae). Insect Syst Evol 39:241–267
Wiens JJ, Graham CH (2005) Niche Conservatism: integrating evolution, ecology and conservation biology. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 36:139–519
Wiens JJ, Graham CH, Moen DS, Smith SA, Reeder TW (2006) Evolutionary and ecological causes of the latitudinal diversity gradient in hylid frogs: treefrog trees unearth the roots of hight tropical diversity. Am Nat 168:579–596
Yotoko KSC, Medeiros HF, Solferini VN, Klaczko LB (2003) A molecular study of the systematics of the Drosophila tripunctata group and the tripunctata radiation. Mol Phylogenet Evol 28:614–619
Zachos J, Pagani H, Sloan L, Thomas E, Billups K (2001) Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 ma to present. Science 292:686–693
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the fly suppliers for making this study possible, to Dr. Nicolás Mega for the statistical assistance and to Mr. Félix Nonnemacher for English correction. We also thank the reviewers for the valuable comments and suggestions. This research was supported by the Brazilian agencies CAPES and CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robe, L.J., Valente, V.L.S. & Loreto, E.L.S. Phylogenetic relationships and macro-evolutionary patterns within the Drosophila tripunctata “radiation” (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Genetica 138, 725–735 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-010-9453-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-010-9453-0