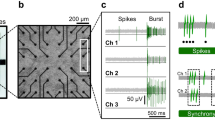
Abstract
Dissociated networks of neurons typically exhibit bursting behavior, whose features are strongly influenced by the age of the culture, by chemical/electrical stimulation or by environmental conditions. To help the experimenter in identifying the changes possibly induced by specific protocols, we developed a self-adapting method for detecting both bursts and network bursts from electrophysiological activity recorded by means of micro-electrode arrays. The algorithm is based on the computation of the logarithmic inter-spike interval histogram and automatically detects the best threshold to distinguish between inter- and intra-burst inter-spike intervals for each recording channel of the array. An analogous procedure is followed for the detection of network bursts, looking for sequences of closely spaced single-channel bursts. We tested our algorithm on recordings of spontaneous as well as chemically stimulated activity, comparing its performance to other methods available in the literature.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MEA:
-
Micro-electrode array
- BD:
-
Burst detection
- NBD:
-
Network burst detection
- DIV:
-
Days in vitro
- BIC:
-
Bicuculline
- APV:
-
D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid
- ISI:
-
Inter-spike interval
- logISIH:
-
Logarithmic inter-spike interval histogram
- ISIth:
-
Inter-spike interval threshold
- IBeI:
-
Inter-burst event interval
- logIBeIH:
-
Logarithmic inter-burst event interval histogram
- IBeIth:
-
Inter-burst event interval threshold
- newBD:
-
New burst detection algorithm
- SE:
-
Selinger’s algorithm
- CH:
-
Chiappalone’s algorithm
- WA:
-
Wagenaar’s algorithm
- GE:
-
Gourevitch-Eggermont’s algorithm
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
References
Barbieri, R., Quirk, M. C., Frank, L. M., Wilson, M. A., & Brown, E. N. (2001). Construction and analysis of non-Poisson stimulus-response models of neural spiking activity. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 105, 25–37.
Baruchi, I., Volman, V., Raichman, N., Shein, M., & Ben-Jacob, E. (2008). The emergence and properties of mutual synchronization in vitro coupled cortical networks. European Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 1825–1835.
Beggs, J. M., & Plenz, D. (2003). Neuronal avalanches in neocortical circuits. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23(35), 11167–11177.
Canepari, M., Bove, M., Maeda, E., Cappello, M., & Kawana, A. (1997). Experimental analysis of neuronal dynamics in cultured cortical networks and transitions between different patterns of activity. Biological Cybernetics, 77(2), 153–162.
Chao, Z. C., Bakkum, D. J., Potter, S. M. (2008). Shaping Embodied Neural Networks for Adaptive Goal-directed Behavior. PLOS Computational Biology, 4(3).
Chiappalone, M., Bove, M., Vato, A., Tedesco, M., & Martinoia, S. (2006). Dissociated cortical networks show spontaneously correlated activity patterns during in vitro development. Brain Research, 1093(1), 41–53.
Chiappalone, M., Massobrio, P., & Martinoia, S. (2008). Network plasticity in cortical assemblies. European Journal of Neuroscience, 28(1), 221–237.
Chiappalone, M., Novellino, A., Vajda, I., Vato, A., Martinoia, S., & van Pelt, J. (2005). Burst detection algorithms for the analysis of spatio-temporal patterns in cortical networks of neurons. Neurocomputing, 65–66, 653–662.
Cocatre-Zilgien, J. H., & Delcomyn, F. (1992). Identification of bursts in spike trains. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 41, 19–30.
Corner, M. A., Van Pelt, J., Wolters, P. S., Baker, R. E., & Nuytinck, R. H. (2002). Physiological effects of sustained blockade of excitatory synaptic transmission on spontaneously active developing neuronal networks—an inquiry into the reciprocal linkage between intrinsic biorhythms and neuroplasticity in early ontogeny. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 26, 127–185.
Cozzi, L., D’Angelo, P., & Sanguineti, V. (2006). Encoding of time-varying stimuli in population of cultured neurons. Biological Cybernetics, 94(5), 335–349.
Dayan, P., & Abbott, L. F. (2001). Theoretical neuroscience: Computational and mathematical modeling of neural systems. Cambridge: MIT.
Eytan, D., & Marom, S. (2006). Dynamics and effective topology underlying synchronization in networks of cortical neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(33), 8465–8476.
Gourevitch, B., & Eggermont, J. J. (2007). A nonparametric approach for detection of bursts in spike trains. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 160, 349–358.
Gramowski, A., Jugelt, K., Weiss, D. G., & Gross, G. W. (2004). Substance identification by quantitative characterization of oscillatory activity in murine spinal cord networks on microelectrode arrays. European Journal of Neuroscience, 19(10), 2815–2825.
Gross, G. W., Azzazy, H. M. E., Wu, M. C., & Rhodes, B. K. (1995). The use of neuronal networks on multielectrode arrays as biosensors. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 10, 553–567.
Habets, A. M., Van Dongen, A. M., Van Huizen, F., & Corner, M. A. (1987). Spontaneous neuronal firing patterns in fetal rat cortical networks during development in vitro: a quantitative analysis. Experimental Brain Research, 69(1), 43–52.
Ham, M. I., Bettencourt, L. M., McDaniel, F. D., & Gross, G. W. (2008). Spontaneous coordinated activity in cultured networks: analysis of multiple ignition sites, primary circuits, and burst phase delay distributions. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 24(3), 346–357.
Jimbo, Y., Tateno, Y., & Robinson, H. P. C. (1999). Simultaneous induction of pathway-specific potentiation and depression in networks of cortical neurons. Biophysical Journal, 76, 670–678.
Kamioka, H., Maeda, E., Jimbo, Y., Robinson, H. P. C., & Kawana, A. (1996). Spontaneous periodic synchronized bursting during formation of mature patterns of connections in cortical cultures. Neuroscience Letters, 206, 109–112.
Legendy, C. R., & Salcman, M. (1985). Bursts and recurrences of bursts in the spike trains of spontaneously active striate cortex neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 53(4), 926–939.
Maccione, A., Gandolfo, M., Massobrio, P., Novellino, A., Martinoia, S., & Chiappalone, M. (2009). A novel algorithm for precise identification of spikes in extracellularly recorded neuronal signals. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 177, 241–249.
Maeda, E., Robinson, H. P. C., & Kawana, A. (1995). The mechanism of generation and propagation of synchronized bursting in developing networks of cortical neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 15, 6834–6845.
Marom, S., & Shahaf, G. (2002). Development, learning and memory in large random networks of cortical neurons: lessons beyond anatomy. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics, 35(1), 63–87.
Metzner, W., Koch, C., Wessel, R., & Gabbiani, F. (1998). Feature extraction by burst-like patterns in multiple sensory maps. The Journal of Neuroscience, 18(6), 2283–2300.
Pasquale, V., Massobrio, P., Bologna, L. L., Chiappalone, M., & Martinoia, S. (2008). Self-organization and neuronal avalanches in networks of dissociated cortical neurons. Neuroscience, 153(4), 1354–1369.
Raichman, N., & Ben-Jacob, E. (2008). Identifying repeating motifs in the activation of synchronized bursts in cultured neuronal networks. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 170(1), 96–110.
Reinagel, P., Godwin, D., Sherman, S. M., & Koch, C. (1999). Encoding of visual information by LGN bursts. Journal of Neurophysiology, 81, 2558–2569.
Rolston, J. D., Wagenaar, D. A., & Potter, S. M. (2007). Precisely timed spatiotemporal patterns of neural activity in dissociated cortical cultures. Neuroscience, 148, 294–303.
Segev, R., Baruchi, I., Hulata, E., & Ben-Jacob, E. (2004). Hidden neuronal correlations in cultured networks. Physical Review Letters, 92(11), 1181021–1181024.
Selinger, J. V., Kulagina, N. V., O’Shaughnessy, T. J., Ma, W., & Pancrazio, J. J. (2007). Methods for characterizing interspike intervals and identifying bursts in neuronal activity. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 162, 64–71.
Shahaf, G., & Marom, S. (2001). Learning in networks of cortical neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 8782–8788.
Tam, D. C. (2002). An alternate burst analysis for detecting intra-burst firings based on inter-burst periods. Neurocomputing, 44–46, 1155–1159.
Turnbull, L., Dian, E., & Gross, G. W. (2005). The string method of burst identification in neuronal spike trains. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 145(1–2), 23–35.
Vajda, I., van Pelt, J., Wolters, P., Chiappalone, M., Martinoia, S., van Someren, E., et al. (2008). Low-frequency stimulation induces stable transitions in stereotypical activity in cortical networks. Biophysical Journal, 94, 5028–5039.
van Pelt, J., Corner, M. A., Wolters, P. S., Rutten, W. L. C., & Ramakers, G. J. A. (2004). Long-term stability and developmental changes in spontaneous network burst firing patterns in dissociated rat cerebral cortex cell cultures on multi-electrode arrays. Neuroscience Letters, 361(1–3), 86–89.
van Pelt, J., Vajda, I., Wolters, P. S., Corner, M. A., & Ramakers, G. J. A. (2005). Dynamics and plasticity in developing neural networks in vitro. Progress in Brain Research, 147, 171–188.
Wagenaar, D. A., DeMarse, T. B., Potter, S. M. (2005). MeaBench: A toolset for multi-electrode data acquisition and on-line analysis. 2nd Intl. IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, Washington, D.C., USA.
Wagenaar, D. A., Madhavan, R., Pine, J., & Potter, S. M. (2005). Controlling bursting in cortical cultures with closed-loop multi-electrode stimulation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(3), 680–688.
Wagenaar, D. A., Pine, J., Potter, S. M. (2006). An extremely rich repertoire of bursting patterns during the development of cortical cultures. BMC Neuroscience, 7(11).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Mariateresa Tedesco for excellent culture preparation and maintenance and for providing images for Fig. 1(a). The authors are very grateful to Dr Luca Leonardo Bologna, who provided the recordings of spontaneous activity during development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Action Editor: Rob Kass
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
S1
A self-adapting approach for the detection of bursts and network bursts in neuronal cultures (DOC 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasquale, V., Martinoia, S. & Chiappalone, M. A self-adapting approach for the detection of bursts and network bursts in neuronal cultures. J Comput Neurosci 29, 213–229 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-009-0175-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-009-0175-1