Abstract
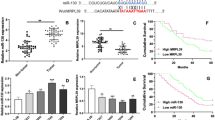
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide. P21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4) has been identified as an oncogenic protein in a variety of cancers. However, the contribution and regulation of PAK4 in HCC remain poorly understood. In the present study, we found that inhibition of PAK4 expression by specific shRNA significantly attenuated HCC cell proliferation. Moreover, we show that microRNA-433 (miRNA-433) could directly target PAK4 through the miRNA-433 binding sequence at the 3′-UTR of PAK4 mRNA, and inhibit PAK4 protein expression. We further show that miRNA-433 expression was downregulated in HCC tissues and cell culture as well, which inversely correlated with PAK4 expression levels. Overexpression of miRNA-433 significantly suppressed the proliferation of HepG2 cells, while this effect was partially rescued by forced expression of PAK4 through restoring PI3K/AKT signaling in HepG2 cells. These findings will shed light on the roles and mechanisms of miRNA-433 in regulating HCC proliferation, and may benefit future development of therapeutics targeting miRNA-433 and PAK4 in HCC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249. doi:10.3322/caac.20006
Wysocki PJ (2010) Targeted therapy of hepatocellular cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19:265–274. doi:10.1517/13543780903514110
Bokoch GM (2003) Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 72:743–781. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161742
Callow MG, Clairvoyant F, Zhu S, Schryver B, Whyte DB, Bischoff JR, Jallal B, Smeal T (2002) Requirement for PAK4 in the anchorage-independent growth of human cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem 277:550–558. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105732200
Zhang HJ, Siu MK, Yeung MC, Jiang LL, Mak VC, Ngan HY, Wong OG, Zhang HQ, Cheung AN (2011) Overexpressed PAK4 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of choriocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 32:765–771. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgr033
Ahmed T, Shea K, Masters JR, Jones GE, Wells CM (2008) A PAK4-LIMK1 pathway drives prostate cancer cell migration downstream of HGF. Cell Signal 20:1320–1328. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.02.021
Kesanakurti D, Chetty C, Rajasekhar Maddirela D, Gujrati M, Rao JS (2012) Functional cooperativity by direct interaction between PAK4 and MMP-2 in the regulation of anoikis resistance, migration and invasion in glioma. Cell Death Dis 3:e445. doi:10.1038/cddis.2012.182
Li Q, Ding C, Chen C, Zhang Z, Xiao H, Xie F, Lei L, Chen Y, Mao B, Jiang M, Li J, Wang D, Wang G (2014) miR-224 promotion of cell migration and invasion by targeting homeobox D 10 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:835–842. doi:10.1111/jgh.12429
Wahid F, Shehzad A, Khan T, Kim YY (2010) MicroRNAs: synthesis, mechanism, function, and recent clinical trials. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:1231–1243. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.06.013
Schickel R, Boyerinas B, Park SM, Peter ME (2008) MicroRNAs: key players in the immune system, differentiation, tumorigenesis and cell death. Oncogene 27:5959–5974. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.274
Trang P, Weidhaas JB, Slack FJ (2008) MicroRNAs as potential cancer therapeutics. Oncogene 27(Suppl. 2):S52–S57. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.353
Gu H, Guo X, Zou L, Zhu H, Zhang J (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-372 associates with tumor progression and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 375:23–30. doi:10.1007/s11010-012-1521-6
Zhou Q, Lui VW, Yeo W (2011) Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol 7:1149–1167. doi:10.2217/fon.11.95
Paliouras GN, Naujokas MA, Park M (2009) Pak4, a novel Gab1 binding partner, modulates cell migration and invasion by the Met receptor. Mol Cell Biol 29:3018–3032. doi:10.1128/MCB.01286-08
Ahn HK, Jang J, Lee J, Se Hoon P, Park JO, Park YS, Lim HY, Kim KM, Kang WK (2011) P21-activated kinase 4 overexpression in metastatic gastric cancer patients. Transl Oncol 4:345–349. doi:10.1593/tlo.11145
Zhang J, Wang J, Guo Q, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Peng H, Cheng M, Zhao D, Li F (2012) LCH-7749944, a novel and potent p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and invasion in human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett 317:24–32. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.11.007
Mak GW, Chan MM, Leong VY, Lee JM, Yau TO, Ng IO, Ching YP (2011) Overexpression of a novel activator of PAK4, the CDK5 kinase-associated protein CDK5RAP3, promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Res 71:2949–2958. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4046
Hou J, Lin L, Zhou W, Wang Z, Ding G, Dong Q, Qin L, Wu X, Zheng Y, Yang Y, Tian W, Zhang Q, Wang C, Zhuang SM, Zheng L, Liang A, Tao W, Cao X (2011) Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 19:232–243. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.001
Krell J, Frampton AE, Stebbing J (2013) MicroRNAs in the cancer clinic. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 5:204–213
Yang Z, Tsuchiya H, Zhang Y, Hartnett ME, Wang L (2013) MicroRNA-433 inhibits liver cancer cell migration by repressing the protein expression and function of cAMP response element-binding protein. J Biol Chem 288:28893–28899. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.502682
Luo H, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Ning B, Guo J, Nie N, Liu B, Wu X (2009) Down-regulated miR-9 and miR-433 in human gastric carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 28:82
Simon D, Laloo B, Barillot M, Barnetche T, Blanchard C, Rooryck C, Marche M, Burgelin I, Coupry I, Chassaing N, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Lacombe D, Grosset C, Arveiler B (2010) A mutation in the 3′-UTR of the HDAC6 gene abolishing the post-transcriptional regulation mediated by hsa-miR-433 is linked to a new form of dominant X-linked chondrodysplasia. Hum Mol Genet 19:2015–2027
Zhang Y, Li Z, Yang M, Wang D, Yu L, Guo C, Guo X, Lin N (2013) Identification of GRB2 and GAB1 coexpression as an unfavorable prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma by a combination of expression profile and network analysis. PLoS One 8:e85170. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085170PONE-D-13-39700
Ding G, Liu HD, Huang Q, Liang HX, Ding ZH, Liao ZJ, Huang G (2013) HDAC6 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting P53 transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett 587:880–886
Guo LH, Li H, Wang F, Yu J, He JS (2013) The tumor suppressor roles of miR-433 and miR-127 in gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14:14171–14184
Lin X, Rice KL, Buzzai M, Hexner E, Costa FF, Kilpivaara O, Mullally A, Soares MB, Ebert BL, Levine R, Licht JD (2013) miR-433 is aberrantly expressed in myeloproliferative neoplasms and suppresses hematopoietic cell growth and differentiation. Leukemia 27:344–352
Torella D, Iaconetti C, Catalucci D, Ellison GM, Leone A, Waring CD, Bochicchio A, Vicinanza C, Aquila I, Curcio A, Condorelli GIndolfi C (2011) MicroRNA-133 controls vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch in vitro and vascular remodeling in vivo. Circ Res 109:880–893
Gao S, Wassler M, Zhang L, Li Y, Wang J, Zhang Y, Shelat H, Williams J, Geng YJ (2014) MicroRNA-133a regulates insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in murine atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 232:171–179
Fu X, Feng J, Zeng D, Ding Y, Yu C, Yang B (2014) PAK4 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells via PI3K/Akt- and MEK/Erk-dependent pathways. Biosci Rep 34(2):59–67
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the The China Scholarship Council (No. 201306370138) and the Science & Technology Department of Hunan Province (2012FJ4133).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, J., Chen, LZ., Li, ZZ. et al. MicroRNA-433 inhibits cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting p21 activated kinase (PAK4). Mol Cell Biochem 399, 77–86 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2234-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2234-9