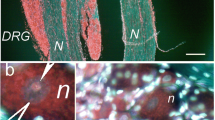
Abstract
FOXO3a, as a forkhead transcription factor, can control cell cycle through transcriptionally down-regulating p27kip1 level, which is a key regulator of the mammalian cell cycle and a good candidate to regulate multiple aspects of neurogenesis. To elucidate their expression and function in nervous system lesion and repair, we performed an acute sciatic nerve crush model and studied differential expressions of Foxo3a and p27kip1 in lumbar dorsal root ganglia. Temporally, Foxo3a protein level was reduced 1 day after injury, and following Foxo3a down-regulation, p27kip1 mRNA and protein levels were also decreased after injury. Spatially, decreased levels of Foxo3a and p27kip1 were predominant in neurons and glial cells, which were regenerating axons and largely proliferated after injury, respectively. Together with previous reports, we hypothesized decreased levels of Foxo3a and p27kip1 in lumbar dorsal root ganglia were implicated in axonal regeneration and the proliferation of glial cells after sciatic nerve injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DRG:
-
Dorsal root ganglia
- FOXO:
-
Forkhead box class O
- CDK2:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2
- PI3-K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- SGK:
-
Serum and glucocorticoid–induced kinase
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence system
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- NeuN:
-
Neuronal nuclei
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GAP-43:
-
Neuronal growth-associated protein-43
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcriptase PCR
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
References
Fawcett JW, Keynes RJ (1990) Peripheral nerve regeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci 13:43–60. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.13.1.43
Fu SY, Gordon T (1997) The cellular and molecular basis of peripheral nerve regeneration. Mol Neurobiol 14:67–116. doi:10.1007/BF02740621
Hokfelt T, Zhang X, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (1994) Messenger plasticity in primary sensory neurons following axotomy and its functional implications. Trends Neurosci 17:22–30. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(94)90031-0
Sgambato A, Cittadini A, Faraglia B, Weinstein IB (2000) Multiple functions of p27(Kip1) and its alterations in tumor cells: a review. J Cell Physiol 183:18–27. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(200004)183:1<18::AID-JCP3>3.0.CO;2-S
Fillies T, Woltering M, Brandt B, Van Diest JP, Werkmeister R, Joos U, Buerger H (2007) Cell cycle regulating proteins p21 and p27 inprognosis of oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oncol Rep 17:355–359
Miyazawa K, Himi T, Garcia V, Yamagishi H, Sato S, Ishizaki Y (2000) A role for p27/Kip1 inthe control of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation. J Neurosci 20:5756–5763
Carruthers S, Mason J, Papalopulu N (2003) Depletion of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27(Xic1) impairs neuronal differentiation and increases the number of ElrC(+) progenitor cells in Xenopus tropicalis. Mech Dev 120:607–616. doi:10.1016/S0925-4773(03)00010-8
Doetsch F, Verdugo JM, Caille I, Alvarez-Buylla A, Chao MV, Casaccia-Bonnefil P (2002) Lack of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 results in selective increase of transit-amplifying cells for adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci 22:2255–2264
Shen AG, Shi SX, Chen ML, Qin J, Gao SF, Cheng C (2007) Dynamic changes of p27(kip1) and Skp2 expression in injured rat sciatic nerve. Cell Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s10571-007-9167-8
Shen A, Liu YH, Zhao J, Qin J, Shi SX, Chen ML et al (2008) Temporal-spatial expressions of p27(kip1) and its phosphorylation on serine-10 after acute spinal cord injury in adult rat: Implications for post-traumatic glial proliferation. Neurochem Int 52:1266–1275. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2008.01.011
Burgering BM, Kops GJ (2002) Cell cycle and death control: long live forkheads. Trends Biochem Sci 27:352–360. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(02)02113-8
Tran H, Brunet A, Griffith EC, Greenberg ME (2003) The many forks in FOXO’s road. Sci STKE 2003:re5. doi:10.1126/stke.2003.172.re5
Dijkers PF, Medema RH, Pals C, Banerji L, Thomas NSB, Lam EWF et al (2000) Forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1 modulates cytokine-dependent transcriptional regulation of p27(kip1). Mol Cell Biol 20:9138–9148. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.24.9138-9148.2000
Medema RH, Kops GJ, Bos JL, Burgering BM (2000) AFX-like forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27 . Nature 404:782–787. doi:10.1038/35008115
Stahl M, Dijkers PF, Kops GJ, Lens SM, Coffer PJ, Burgering BM et al (2002) The forkhead transcription factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27kip1 and Bim in response to IL-2. J Immunol 168:5024–5031
Morris GF, Mathews MB (1989) Regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem 264:13856–13864
Farina V, Gadau S, Lepore G, Manca P, Zedda M (2004) Growth-associated protein expression in the frontal and occipital cortices of callosotomized rats. Funct Neurol 19:181–184
Cristino L, Pica A, Corte FD, Bentivoglio M (2000) Co-induction of nitric oxide synthase, bcl-2 and growth-associated protein-43 in spinal motoneurons during axon regeneration in the lizard tail. Neuroscience 101:451–458. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(00)00393-6
Chirwa S, Aduonum A, Pizarro J, Reasor J, Kawai Y, Gonzalez M et al (2005) Dopaminergic DA1 signaling couples growth-associated protein-43 and long-term potentiation in guinea pig hippocampus. Brain Res Bull 64:433–440. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2004.09.012
Van der Zee CE, Nielander HB, Vos JP, da Silva SL, Verhaagen J, Oestreicher AB et al (1989) Expression of growth-associated protein B-50 (GAP43) in dorsal root ganglia and sciatic nerve during regenerative sprouting. J Neurosci 9:3505–3512
Kenyon C, Chang J, Gensch E, Rudner A, Tabtiang R (1993) A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature 366:461–464. doi:10.1038/366461a0
Lin K, Dorman JB, Rodan A, Kenyon C (1997) Daf-16: an HNF-3/forkhead family member that can function to double the life-span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 278:1319–1322. doi:10.1126/science.278.5341.1319
Ogg S, Paradis S, Gottlieb S, Patterson GI, Lee L, Tissenbaum HA et al (1997) The forkhead transcription factor DAF-16 transduces insulin-like metabolic and longevity signals in C. elegans. Nature 389:994–999. doi:10.1038/40194
Asselin ML, David M, Biola-Vidamment A, Lecoeuche D, Zennaro MC, Bertoglio J et al (2004) GILZ, a new target for the transcription factor FoxO3, protects T lymphocytes from interleukin-2 withdrawal-induced apoptosis. Blood 104:215–223. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-12-4295
Samatar AA, Wang L, Mirza A, Koseoglu S, Liu S, Kumar CC (2002) Transforming growth factor-beta 2 is a transcriptional target for Akt/protein kinase B via forkhead transcription factor. J Biol Chem 277:28118–28126. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203686200
Tran H, Brunet A, Grenier JM, Datta SR, Fornace AJJ, DiStefano PS et al (2002) DNA repair pathway stimulated by the forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a through the Gadd45 protein. Science 296:530–534. doi:10.1126/science.1068712
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C, Calabria E, Picard A et al (2004) Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell 117:399–412. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00400-3
Shi SX, Cheng C, Zhao J, Chen ML, Qin J, Gao SF et al (2007) Expression of p27kip1 and Skp2 in the adult spinal cord following sciatic nerve injury. J Mol Neurosci 32:64–71. doi:10.1007/s12031-007-0015-6
Potente M, Fisslthaler B, Busse R, Fleming I (2003) 11, 12-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid-induced inhibition of FOXO factors promotes endothelial proliferation by down-regulating p27Kip1. J Biol Chem 278:29619–29625. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305385200
Abid MR, Guo S, Minami T, Spokes KC, Ueki K, Skurk C et al (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor activates PI3 K/Akt/forkhead signaling in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:294–300. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000110502.10593.06
Barthélémy C, Henderson CE, Pettmann B (2004) Foxo3a induces motoneuron death through the Fas pathway in cooperation with JNK. BMC Neurosci 5:48. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-5-48
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS et al (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80595-4
Gilley J, Coffer PJ, Ham J (2003) FOXO transcription factors directly activate bim gene expression and promote apoptosis in sympathetic neurons. J Cell Biol 162:613–622. doi:10.1083/jcb.200303026
Coqueret O (2003) New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment? Trends Cell Biol 13:65–70. doi:10.1016/S0962-8924(02)00043-0
Hu YY, Wang XY, Zeng L, Cai DY, Kanaga S, Stephen PG et al (2005) ERK phosphorylates p66shcA on Ser36 and subsequently regulates p27kip1 expression via the Akt-FOXO3a pathway: implication of p27kip1 in cell response to oxidative stress. Mol Biol Cell 16:3705–3718. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-04-0301
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China Grant (No. 30300099 and No. 30770488), Natural Scientific Foundation of Jiangsu Province Grant (No. BK2003035 and No. BK2006547), College and University Natural Scientific Research Programme of Jiangsu Province (No. 03KJB180109 and No. 04KJB320114), Technology Guidance Plan for Social Development of Jiangsu Province Grant (BS2004526), Health Project of Jiangsu Province (H200632), “Liu-Da-Ren-Cai-Gao-Feng” Financial Assistance of Jiangsu Province Grant (No. 2), Postgraduate Scientic Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. CX08S_026Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Youhua Wang and Yonghua Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Chen, Y. et al. Peripheral Nerve Injury Induces Down-Regulation of Foxo3a and p27kip1 in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia. Neurochem Res 34, 891–898 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9849-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9849-8