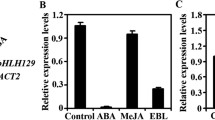
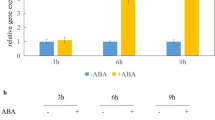
Abstract
The phytohormone ABA was known to play a vital role in modulating plant responses to drought stress. Here, we report that a nuclear-localized basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-type protein, AtAIB, positively regulates ABA response in Arabidopsis. The expression of AtAIB was transitorily induced by ABA and PEG, although its transcripts were accumulated in various organs. We provided evidence showing that AtAIB has transcriptional activation activity in yeast. Knockdown of AtAIB expression caused reduced sensitivity to ABA, whereas overexpression of this gene led to elevated sensitivity to ABA in cotyledon greening and seedling root growth. Furthermore, soil-grown plants overexpressing AtAIB showed increased drought tolerance. Taken together, these results suggested that AtAIB functions as a transcription activator involved in the regulation of ABA signaling in Arabidopsis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Urao T, Ito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 15:63–78
Abe H, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao T, Iwasaki T, Hosokawa D, Shinozaki K (1997) Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought- and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 9:1859–1868
Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Hom E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid M, Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301:653–657
Anderson JP, Badruzsaufari E, Schenk PM, Manners JM, Desmond OJ, Ehlert C, Maclean DJ, Ebert PR, Kazan K (2004) Antagonistic interaction between abscisic acid and jasmonate-ethylene signaling pathways modulates defense gene expression and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:3460–3479
Bechtold N, Pelletier G (1998) In planta Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants by vacuum infiltration. Methods Mol Biol 82:259–266
Bent AF, Kunkel BN, Dahlbeck D, Brown KL, Schmidt R, Giraudat J, Leung J, Staskawicz BJ (1994) RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265:1856–1860
Boter M, Ruiz-Rivero O, Abdeen A, Prat S (2004) Conserved MYC transcription factors play a key role in jasmonate signaling both in tomato and Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 18:1577–1591
Choi H, Hong J, Ha J, Kang J, Kim SY (2000) ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. J Biol Chem 275:1723–1730
Cutler S, Ghassemian M, Bonetta D, Cooney S, McCourt P (1996) A protein farnesyl transferase involved in abscisic acid signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Science 273:1239–1241
Duek PD, Fankhauser C (2005) bHLH class transcription factors take centre stage in phytochrome signalling. Trends Plant Sci 10:51–54
Ferre-D’Amare AR, Pognonec P, Roeder RG, Burley SK (1994) Structure and function of the b/HLH/Z domain of USF. EMBO J 13:180–189
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SS, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell 14(Suppl):S15–S45
Finkelstein RR, Lynch TJ (2000) The Arabidopsis abscisic acid response gene ABI5 encodes a basic leucine zipper transcription factor. Plant Cell 12:599–609
Finkelstein RR, Wang ML, Lynch TJ, Rao S, Goodman HM (1998) The Arabidopsis abscisic acid response locus ABI4 encodes an APETALA 2 domain protein. Plant Cell 10:1043–1054
Giraudat J, Hauge BM, Valon C, Smalle J, Parcy F, Goodman HM (1992) Isolation of the Arabidopsis ABI3 gene by positional cloning. Plant Cell 4:1251–1261
Gosti F, Beaudoin N, Serizet C, Webb AA, Vartanian N, Giraudat J (1999) ABI1 protein phosphatase 2C is a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 11:1897–1910
Guiltinan MJ, Marcotte WR Jr, Quatrano RS (1990) A plant leucine zipper protein that recognizes an abscisic acid response element. Science 250:267–271
Hobo T, Kowyama Y, Hattori T (1999) A bZIP factor, TRAB1, interacts with VP1 and mediates abscisic acid-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:15348–15353
Hugouvieux V, Kwak JM, Schroeder JI (2001) An mRNA cap binding protein, ABH1, modulates early abscisic acid signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Cell 106:477–487
Ingram J, Bartels D (1996) The molecular basis of dehydration tolerance in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:377–403
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Koornneef M, Reuling G, Karssen CM (1984) The isolation and characterization of abscisic acid -insensitive mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 61:377–383
Leung J, Giraudat J (1998) Abscisic acid signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:199–222
Leung J, Merlot S, Giraudat J (1997) The Arabidopsis ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE2 (ABI2) and ABI1 genes encode homologous protein phosphatases 2C involved in abscisic acid signal transduction. Plant Cell 9:759–771
Liu X, Yue Y, Li B, Nie Y, Li W, Wu WH, Ma L (2007) A G protein-coupled receptor is a plasma membrane receptor for the plant hormone abscisic acid. Science 315:1712–1716
Lopez-Molina L, Chua NH (2000) A null mutation in a bZIP factor confers ABA-insensitivity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 41:541–547
Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, Chua NH (2001) A postgermination developmental arrest checkpoint is mediated by abscisic acid and requires the ABI5 transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4782–4787
Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, Kinoshita N, Chua NH (2003) AFP is a novel negative regulator of ABA signaling that promotes ABI5 protein degradation. Genes Dev 17:410–418
Lorenzo O, Chico JM, Sanchez-Serrano JJ, Solano R (2004) JASMONATE-INSENSITIVE1 encodes a MYC transcription factor essential to discriminate between different jasmonate-regulated defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:1938–1950
McCourt P (1999) Genetic analysis of hormone signaling. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:219–243
Meyer K, Leube MP, Grill E (1994) A protein phosphatase 2C involved in ABA signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 264:1452–1455
Mundy J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Chua NH (1990) Nuclear proteins bind conserved elements in the abscisic acid-responsive promoter of a rice rab gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1406–1410
Murre C, McCaw PS, Baltimore D (1989) A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell 56:777–783
Razem FA, El-Kereamy A, Abrams SR, Hill RD (2006) The RNA-binding protein FCA is an abscisic acid receptor. Nature 439:290–294
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schiefelbein J (2003) Cell-fate specification in the epidermis: a common patterning mechanism in the root and shoot. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:74–78
Seki M, Ishida J, Narusaka M, Fujita M, Nanjo T, Umezawa T, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T, Satou M, Akiyama K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Carninci P, Kawai J, Hayashizaki Y, Shinozaki K (2002) Monitoring the expression pattern of around 7,000 Arabidopsis genes under ABA treatments using a full-length cDNA microarray. Funct Integr Genomics 2:282–291
Sheen J (1996) Ca2+-dependent protein kinases and stress signal transduction in plants. Science 274:1900–1902
Sheen J (1998) Mutational analysis of protein phosphatase 2C involved in abscisic acid signal transduction in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:975–980
Shen YY, Wang XF, Wu FQ, Du SY, Cao Z, Shang Y, Wang XL, Peng CC, Yu XC, Zhu SY, Fan RC, Xu YH, Zhang DP (2006) The Mg-chelatase H subunit is an abscisic acid receptor. Nature 443:823–826
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:217–223
Stone SL, Williams LA, Farmer LM, Vierstra RD, Callis J (2006) KEEP ON GOING, a RING E3 ligase essential for Arabidopsis growth and development, is involved in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 18:3415–3428
Toledo-Ortiz G, Huq E, Quail PH (2003) The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 15:1749–1770
Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11632–11637
Xiong L, Gong Z, Rock CD, Subramanian S, Guo Y, Xu W, Galbraith D, Zhu JK (2001a) Modulation of abscisic acid signal transduction and biosynthesis by an Sm-like protein in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 1:771–781
Xiong L, Lee B, Ishitani M, Lee H, Zhang C, Zhu JK (2001b) FIERY1 encoding an inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase is a negative regulator of abscisic acid and stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 15:1971–1984
Xiong L, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 14(Suppl):S165–S183
Yadav V, Mallappa C, Gangappa SN, Bhatia S, Chattopadhyay S (2005) A basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor in Arabidopsis, MYC2, acts as a repressor of blue light-mediated photomorphogenic growth. Plant Cell 17:1953–1966
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Zheng W, Zhai Q, Sun J, Li CB, Zhang L, Li H, Zhang X, Li S, Xu Y, Jiang H, Wu X, Li C (2006) Bestatin, an inhibitor of aminopeptidases, provides a chemical genetics approach to dissect jasmonate signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141:1400–1413
Acknowledgements
We thank the Arabidopsis Biological Resources Center for providing the T-DNA insertion mutant salk_087068. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of china (Grant No. 2006CB910604) and the national natural science foundation of china (Grant Nos. 30425033 and 30530440 to C. L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Sun, J., Xu, Y. et al. The bHLH-type transcription factor AtAIB positively regulates ABA response in Arabidopsis . Plant Mol Biol 65, 655–665 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9230-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9230-3