Abstract
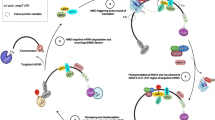
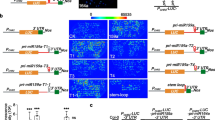
Nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) is a quality control mechanism that identifies and degrades aberrant mRNAs containing premature termination codons (PTC). NMD also regulates the expression of many wild-type genes. In plants, NMD identifies a stop codon as a PTC and initiates the rapid degradation of the transcript if the 3′untranslated region (UTR) is unusually long or if it harbors an intron. Approximately 20% of plant transcripts have an upstream ORF (uORF) in the 5′UTR. In theory, if a uORF is translated, the 3′UTR downstream of the uORF will be long and harbor introns, thus these transcripts might be degraded by NMD. Therefore, if uORFs can trigger NMD, uORF containing transcripts would be a major group of NMD regulated wild-type plant mRNAs. The aim of this study was to clarify whether plant uORFs could activate NMD. Here we demonstrate that plant uORFs induce NMD in a size-dependent manner, a 50 amino acid (aa) long uORF triggered NMD efficiently, whereas similar but shorter (31 and 15 aa long) uORFs failed to activate NMD response. We have found that only ~2% of annotated Arabidopsis genes contain a first uORF that is longer than 35 aa, thus we propose that NMD regulates only a small fraction of uORF containing transcripts. However, as mRNAs having uORF that is longer than the critical size are strongly overrepresented within the up-regulated transcripts of NMD deficient plants, it is likely that this subset of natural NMD targets induces NMD because of containing a relatively long translatable uORF.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NMD:
-
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
- uORF:
-
Upstream ORF
- VIGS:
-
Virus-induced gene silencing
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- EJC:
-
Exon-junction complex
- eRF:
-
Eukaryotic releasing factor
References
Arciga-Reyes L, Wootton L, Kieffer M, Davies B (2006) UPF1 is required for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) and RNAi in Arabidopsis. Plant J 47:480–489
Belostotsky DA, Sieburth LE (2009) Kill the messenger: mRNA decay and plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:96–102
Cao D, Parker R (2003) Computational modeling and experimental analysis of nonsense-mediated decay in yeast. Cell 113:533–545
Chiba Y, Green P (2009) mRNA degradation machinery in plants. J Plant Biol 52:114–124
Churbanov A, Rogozin IB, Babenko VN, Ali H, Koonin EV (2005) Evolutionary conservation suggests a regulatory function of AUG triplets in 5′-UTRs of eukaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res 33:5512–5520
Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk A, Piontek P, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Jarmolowski A (2008) The nuclear cap-binding protein complex is not essential for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) in plants. Acta Biochim Pol 55:825–828
Eberle AB, Lykke-Andersen S, Muhlemann O, Jensen TH (2009) SMG6 promotes endonucleolytic cleavage of nonsense mRNA in human cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:49–55
Fukuhara N, Ebert J, Unterholzner L, Lindner D, Izaurralde E, Conti E (2005) SMG7 is a 14-3-3-like adaptor in the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway. Mol Cell 17:537–547
Gatfield D, Izaurralde E (2004) Nonsense-mediated messenger RNA decay is initiated by endonucleolytic cleavage in Drosophila. Nature 429:575–578
Hagan KW, Ruiz-Echevarria MJ, Quan Y, Peltz SW (1995) Characterization of cis-acting sequences and decay intermediates involved in nonsense-mediated mRNA turnover. Mol Cell Biol 15:809–823
Hayden CA, Bosco G (2008) Comparative genomic analysis of novel conserved peptide upstream open reading frames in Drosophila melanogaster and other dipteran species. BMC Genomics 9:61
Hayden CA, Jorgensen RA (2007) Identification of novel conserved peptide uORF homology groups in Arabidopsis and rice reveals ancient eukaryotic origin of select groups and preferential association with transcription factor-encoding genes. BMC Biol 5:32
Hayes CS, Bose B, Sauer RT (2002) Proline residues at the C terminus of nascent chains induce SsrA tagging during translation termination. J Biol Chem 277:33825–33832
Hori K, Watanabe Y (2005) UPF3 suppresses aberrant spliced mRNA in Arabidopsis. Plant J 43:530–540
Hori K, Watanabe Y (2007) Context analysis of termination codons in mRNA that are recognized by plant NMD. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1072–1078
Hosoda N, Kim YK, Lejeune F, Maquat LE (2005) CBP80 promotes interaction of Upf1 with Upf2 during nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in mammalian cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:893–901
Huntzinger E, Kashima I, Fauser M, Sauliere J, Izaurralde E (2008) SMG6 is the catalytic endonuclease that cleaves mRNAs containing nonsense codons in metazoan. Rna 14:2609–2617
Ishigaki Y, Li X, Serin G, Maquat LE (2001) Evidence for a pioneer round of mRNA translation: mRNAs subject to nonsense-mediated decay in mammalian cells are bound by CBP80 and CBP20. Cell 106:607–617
Isken O, Maquat LE (2008) The multiple lives of NMD factors: balancing roles in gene and genome regulation. Nat Rev Genet 9:699–712
Kashima I, Yamashita A, Izumi N, Kataoka N, Morishita R, Hoshino S, Ohno M, Dreyfuss G, Ohno S (2006) Binding of a novel SMG-1-Upf1-eRF1-eRF3 complex (SURF) to the exon junction complex triggers Upf1 phosphorylation and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes Dev 20:355–367
Kawaguchi R, Bailey-Serres J (2005) mRNA sequence features that contribute to translational regulation in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 33:955–965
Kerenyi Z, Merai Z, Hiripi L, Benkovics A, Gyula P, Lacomme C, Barta E, Nagy F, Silhavy D (2008) Inter-kingdom conservation of mechanism of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. EMBO J 27:1585–1595
Kertesz S, Kerenyi Z, Merai Z, Bartos I, Palfy T, Barta E, Silhavy D (2006) Both introns and long 3′-UTRs operate as cis-acting elements to trigger nonsense-mediated decay in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 34:6147–6157
Kozak M (2002) Pushing the limits of the scanning mechanism for initiation of translation. Gene 299:1–34
Kozak M (2005) Regulation of translation via mRNA structure in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Gene 361:13–37
Kurihara Y, Matsui A, Hanada K, Kawashima M, Ishida J, Morosawa T, Tanaka M, Kaminuma E, Mochizuki Y, Matsushima A, Toyoda T, Shinozaki K, Seki M (2009) Genome-wide suppression of aberrant mRNA-like noncoding RNAs by NMD in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2453–2458
Le Hir H, Izaurralde E, Maquat LE, Moore MJ (2000) The spliceosome deposits multiple proteins 20–24 nucleotides upstream of mRNA exon–exon junctions. EMBO J 19:6860–6869
Le Hir H, Gatfield D, Izaurralde E, Moore MJ (2001) The exon–exon junction complex provides a binding platform for factors involved in mRNA export and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. EMBO J 20:4987–4997
Lee MH, Schedl T (2004) Translation repression by GLD-1 protects its mRNA targets from nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in C. elegans. Genes Dev 18:1047–1059
Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2002) Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J 31:777–786
Mango SE (2001) Stop making nonSense: the C. elegans smg genes. Trends Genet 17:646–653
Mendell JT, Sharifi NA, Meyers JL, Martinez-Murillo F, Dietz HC (2004) Nonsense surveillance regulates expression of diverse classes of mammalian transcripts and mutes genomic noise. Nat Genet 36:1073–1078
Mitchell P, Tollervey D (2003) An NMD pathway in yeast involving accelerated deadenylation and exosome-mediated 3′–>5′ degradation. Mol Cell 11:1405–1413
Muhlemann O (2008) Recognition of nonsense mRNA: towards a unified model. Biochem Soc Trans 36:497–501
Neu-Yilik G, Kulozik AE (2008) NMD: multitasking between mRNA surveillance and modulation of gene expression. Adv Genet 62:185–243
Ratcliff F, Martin-Hernandez AM, Baulcombe DC (2001) Technical advance. Tobacco rattle virus as a vector for analysis of gene function by silencing. Plant J 25:237–245
Rebbapragada I, Lykke-Andersen J (2009) Execution of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: what defines a substrate? Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:394–402
Ruiz-Echevarria MJ, Peltz SW (2000) The RNA binding protein Pub1 modulates the stability of transcripts containing upstream open reading frames. Cell 101:741–751
Sachs MS, Geballe AP (2006) Downstream control of upstream open reading frames. Genes Dev 20:915–921
Schoning JC, Streitner C, Meyer IM, Gao Y, Staiger D (2008) Reciprocal regulation of glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins via an interlocked feedback loop coupling alternative splicing to nonsense-mediated decay in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 36:6977–6987
Schwartz AM, Komarova TV, Skulachev MV, Zvereva AS, Dorokhov Iu L, Atabekov JG (2006) Stability of plant mRNAs depends on the length of the 3′-untranslated region. Biochemistry (Mosc) 71:1377–1384
Shyu AB, Wilkinson MF, van Hoof A (2008) Messenger RNA regulation: to translate or to degrade. EMBO J 27:471–481
Silhavy D, Molnar A, Lucioli A, Szittya G, Hornyik C, Tavazza M, Burgyan J (2002) A viral protein suppresses RNA silencing and binds silencing-generated, 21- to 25-nucleotide double-stranded RNAs. EMBO J 21:3070–3080
Silva AL, Romao L (2009) The mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway: to decay or not to decay! Which players make the decision? FEBS Lett 583:499–505
Silva AL, Pereira FJ, Morgado A, Kong J, Martins R, Faustino P, Liebhaber SA, Romao L (2006) The canonical UPF1-dependent nonsense-mediated mRNA decay is inhibited in transcripts carrying a short open reading frame independent of sequence context. Rna 12:2160–2170
Silva AL, Ribeiro P, Inacio A, Liebhaber SA, Romao L (2008) Proximity of the poly(A)-binding protein to a premature termination codon inhibits mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Rna 14:563–576
Tran MK, Schultz CJ, Baumann U (2008) Conserved upstream open reading frames in higher plants. BMC Genomics 9:361
Valentine T, Shaw J, Blok VC, Phillips MS, Oparka KJ, Lacomme C (2004) Efficient virus-induced gene silencing in roots using a modified tobacco rattle virus vector. Plant Physiol 136:3999–4009
Wachter A, Tunc-Ozdemir M, Grove BC, Green PJ, Shintani DK, Breaker RR (2007) Riboswitch control of gene expression in plants by splicing and alternative 3′ end processing of mRNAs. Plant Cell 19:3437–3450
Wu J, Kang JH, Hettenhausen C, Baldwin IT (2007) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) silences the accumulation of aberrant trypsin proteinase inhibitor mRNA in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant J 51:693–706
Yoine M, Ohto MA, Onai K, Mita S, Nakamura K (2006) The lba1 mutation of UPF1 RNA helicase involved in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay causes pleiotropic phenotypic changes and altered sugar signalling in Arabidopsis. Plant J 46:49–62
Zhang J, Maquat LE (1997) Evidence that translation reinitiation abrogates nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in mammalian cells. EMBO J 16:826–833
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to C. Lacomme (University of Edinburgh), D. Baulcombe (University of Cambridge) and S. P. Dinesh-Kumar (Yale University) for TRV vectors. This research was supported by grants from the OTKA (K60102 and C77086) and from the National Office for Research and Technology (4/064/2004, “Búzakalász”). We thank E. Barta (University of Debrecen) for his help with bioinformatical studies. D. Silhavy was supported by the Bolyai János Scholarship. T. Nyikó and Zs. Mérai are graduate students of ELTE “Classical and Molecular Genetics” PhD program. A. Hangyáné Benkovics is a graduate student of Corvinus University of Budapest (“Program of Viticulture” at the Doctoral School of Horticulture).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tünde Nyikó and Boglárka Sonkoly contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nyikó, T., Sonkoly, B., Mérai, Z. et al. Plant upstream ORFs can trigger nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in a size-dependent manner. Plant Mol Biol 71, 367 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9528-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9528-4