Abstract
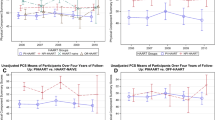
Background: Studies have shown the detrimental effect of HIV disease on quality of life (QOL). Changes in QOL related to the use of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) have been inconsistent and it is unknown how QOL after HAART compares to pre-infection levels. Objective: The objective of this study was to determine the impacts of becoming HIV infected and using HAART on QOL within individuals followed in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS). Methods: Using the standard Medical Outcome Study SF-36 form, QOL data were collected pre-seroconversion, post-seroconversion but before HAART initiation, and after HAART initiation for 68 seroconverters. The QOL physical health summary score (PHS) and mental health summary score (MHS) were used as outcomes. The effects of HIV infection and HAART use on QOL summary scores were determined using random effects mixed linear models after controlling for possible confounders. The clinical significance of QOL change was assessed using the Cohen’s effect size method. Results: Compared to pre-seroconversion values, the PHS decreased after seroconversion (mean difference (diff) = −1.62; 95% confidence interval (CI): [−3.20, −0.03]) and after HAART initiation (diff = −4.20; 95% CI: [−5.86, −2.54]) with small to medium effect sizes. The score remained significantly lower than prior to HIV infection (diff = −6.16; 95% CI: [−8.09, −4.23]) after being on HAART for more than 4 years. The MHS did not significantly differ upon seroconversion (diff = −1.16; 95% CI: [−3.32, 1.00]). After using HAART for more than 4 years, the MHS was significantly greater than prior to HIV infection (diff = 2.93; 95% CI: [0.31, 5.55]) with a small effect size. Conclusion: The QOL of participants has been dynamic over the HIV disease course. HIV infection deteriorated physical but not mental QOL. In this group, although the PHS following HAART has remained lower than that prior to infection, HAART has enhanced mental health functioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ART:
-
antiretroviral therapy
- CESD:
-
Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression scale
- CI:
-
confidence interval
- Diff:
-
difference
- HAART:
-
highly active antiretroviral therapy
- HIV:
-
human immunodeficiency virus
- MACS:
-
Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study
- MHS:
-
mental health summary score
- NNRTI:
-
non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
- NRTI:
-
nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
- PHS:
-
physical health summary score
- PI:
-
protease inhibitor
- QOL:
-
quality of life
- SF-36:
-
short form-36
References
AW Wu WC Mathews LT Brysk et al. (1990) ArticleTitleQuality of life in a placebo-controlled trial of zidovudine in patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 3 IssueID7 683–690 Occurrence Handle2191113 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3c3nvVOisg%3D%3D
RD Hays WE Cunningham CD Sherbourne et al. (2000) ArticleTitleHealth-related quality of life in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection in the United States: Results from the HIV Cost and Services Utilization Study Am J Med 108 IssueID9 714–722 Occurrence Handle10924648 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvhs1ektQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9343(00)00387-9
AW Wu HR Rubin WC Mathews et al. (1991) ArticleTitleA health status questionnaire using 30 items from the Medical Outcomes Study. Preliminary validation in persons with early HIV infection Med Care 29 IssueID8 786–798 Occurrence Handle1875745 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3Mzkt1altA%3D%3D
A Burgess M Dayer J Catalan D Hawkins B Gazzard (1993) ArticleTitleThe reliability and validity of two HIV-specific health-related Quality-of-Life measures: A preliminary analysis AIDS 7 IssueID7 1001–1008 Occurrence Handle8357546 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3szmtlansg%3D%3D
MA Fischl DD Richman MH Grieco et al. (1987) ArticleTitleThe efficacy of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial N Engl J Med 317 IssueID4 185–191 Occurrence Handle3299089 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s3lvVSrsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM198707233170401
WR Lenderking RD Gelber DJ Cotton et al. (1994) ArticleTitleEvaluation of the quality of life associated with zidovudine treatment in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection. The AIDS Clinical Trials Group N Engl J Med 330 IssueID11 738–743 Occurrence Handle7906386 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2c7ltVGntA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199403173301102
SM Hammer KE Squires MD Hughes et al. (1997) ArticleTitleA controlled trial of two nucleoside analogues plus indinavir in persons with human immunodeficiency virus infection and CD4 cell counts of 200 per cubic millimeter or less. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 320 Study Team N Engl J Med 337 IssueID11 725–733 Occurrence Handle9287227 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmt1yit7o%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199709113371101
R Detels A Munoz G McFarlane et al. (1998) ArticleTitleEffectiveness of potent antiretroviral therapy on time to AIDS and death in men with known HIV infection duration. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study Investigators JAMA 280 IssueID17 1497–1503 Occurrence Handle9809730 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FisFKjsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.280.17.1497
S Low-Beer K Chan E Wood et al. (2000) ArticleTitleHealth related quality of life among persons with HIV after the use of protease inhibitors Qual Life Res 9 IssueID8 941–949 Occurrence Handle11284213 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3ivVCgug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008985728271
DS Saunders RW Burgoyne (2002) ArticleTitleEvaluating health-related wellbeing outcomes among outpatient adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection in the HAART era Int J STD AIDS 13 IssueID10 683–690 Occurrence Handle12396538 Occurrence Handle10.1258/095646202760326435
P Carrieri B Spire S Duran et al. (2003) ArticleTitleHealth-related quality of life after 1 year of highly active antiretroviral therapy J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 32 IssueID1 38–47 Occurrence Handle12514412
PT Nieuwkerk EH Gisolf R Colebunders AW Wu SA Danner MA Sprangers (2000) ArticleTitleQuality of life in asymptomatic- and symptomatic HIV infected patients in a trial of ritonavir/saquinavir therapy. The Prometheus Study Group AIDS 14 IssueID2 181–187 Occurrence Handle10708289 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7ntVGrsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002030-200001280-00014
CJ Gill JL Griffith D Jacobson S Skinner SL Gorbach IB Wilson (2002) ArticleTitleRelationship of HIV viral loads, CD4 counts, and HAART use to health-related quality of life J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 30 IssueID5 485–492 Occurrence Handle12154339
RA Kaslow DG Ostrow R Detels JP Phair BF Polk CR Rinaldo SuffixJr. (1987) ArticleTitleThe Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study: Rationale, organization, and selected characteristics of the participants Am J Epidemiol 126 IssueID2 310–318 Occurrence Handle3300281 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s3mslGgtg%3D%3D
R Detels JP Phair AJ Saah et al. (1992) ArticleTitleRecent scientific contributions to understanding HIV/AIDS from the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study J Epidemiol [Jpn] 2 IssueID2 s11–s19
JV Giorgi HL Cheng JB Margolick et al. (1990) ArticleTitleQuality control in the flow cytometric measurement of T-lymphocyte subsets: The multicenter AIDS cohort study experience. The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study Group Clin Immunol Immunopathol 55 IssueID2 173–186 Occurrence Handle1969782 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3c3htl2mtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0090-1229(90)90096-9
LS Radloff (1977) ArticleTitleThe CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population Appl Psychol Meas 1 385–401
N Breslan (1984) ArticleTitleDepressive symptoms, major depression, and generalized anxiety: A comparison of self-reports on CES-D and results from diagnostic interviews Psychiatry Res 15 219–229 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0165-1781(85)90079-4
ME Kantz WJ Harris K Levitsky JE Ware SuffixJr. AR Davies (1992) ArticleTitleMethods for assessing condition-specific and generic functional status outcomes after total knee replacement Med Care 30 IssueID5 Suppl MS240–MS252 Occurrence Handle1583936 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK383mtFSrsA%3D%3D
CA McHorney JE Ware SuffixJr. JF Lu CD Sherbourne (1994) ArticleTitleThe MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): III. Tests of data quality, scaling assumptions, and reliability across diverse patient groups Med Care 32 IssueID1 40–66 Occurrence Handle8277801 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2c7gsVeltQ%3D%3D
JE Ware SuffixJr. M Kosinski MS Bayliss CA McHorney WH Rogers A Raczek (1995) ArticleTitleComparison of methods for the scoring and statistical analysis of SF-36 health profile and summary measures: summary of results from the Medical Outcomes Study Med Care 33 IssueID4 Suppl AS264–AS279 Occurrence Handle7723455
JE Ware M Kosinski (2001) ArticleTitleInterpreting SF-36 summary health measures: A response Qual Life Res 10 IssueID5 405–413 Occurrence Handle11763203 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FjsVelsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1012588218728
DHHS/Henry J. Kaiser, Family Foundation Panel on Clinical ractices for the Treatment of HIV infection. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-infected adults and adolescents. April 2005 revision. Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov. 2005
X Li JB Margolick CS Conover et al. (2005) ArticleTitleInterruption and discontinuation of highly active antiretroviral therapy in the multicenter AIDS cohort study J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 38 IssueID3 320–328 Occurrence Handle15735452 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhslaks7k%3D
J Piette TJ Wachtel V Mor K Mayer (1995) ArticleTitleThe impact of age on the quality of life in persons with HIV infection J Aging Health 7 IssueID2 163–178 Occurrence Handle10165953 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28jhvVSlsg%3D%3D
EG Bing RD Hays LP Jacobson et al. (2000) ArticleTitleHealth-related quality of life among people with HIV disease: Results from the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study Qual Life Res 9 IssueID1 55–63 Occurrence Handle10981206 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvlsFahtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008919227665
AH Miners CA Sabin A Mocroft M Youle M Fisher M Johnson (2001) ArticleTitleHealth-related quality of life in individuals infected with HIV in the era of HAART HIV Clin Trials 2 IssueID6 484–492 Occurrence Handle11742437 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MjgtV2ruw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1310/48ET-TT7G-35RA-D4C3
L Ahdieh SJ Gange R Greenblatt et al. (2000) ArticleTitleSelection by indication of potent antiretroviral therapy use in a large cohort of women infected with human immunodeficiency virus Am J Epidemiol 152 IssueID10 923–933 Occurrence Handle11092434 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FmvVeqtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1093/aje/152.10.923
TE Yamashita JP Phair A Munoz et al. (2001) ArticleTitleImmunologic and virologic response to highly active antiretroviral therapy in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study AIDS 15 IssueID6 735–746 Occurrence Handle11371688 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXktVSgsbk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002030-200104130-00009
J. Cohen (1969) Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences Academic Press London
PR Rosenbaum DB Rubin (1983) ArticleTitleThe central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects Biometrika 70 41–55 Occurrence Handle10.2307/2335942
GR Norman JA Sloan KW Wyrwich (2003) ArticleTitleInterpretation of changes in health-related quality of life: The remarkable universality of half a standard deviation Med Care 41 IssueID5 582–592 Occurrence Handle12719681 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005650-200305000-00004
C Cohen DA Revicki A Nabulsi PW Sarocco P Jiang (1998) ArticleTitleA randomized trial of the effect of ritonavir in maintaining quality of life in advanced HIV disease. Advanced HIV Disease Ritonavir Study Group AIDS 12 IssueID12 1495–1502 Occurrence Handle9727571 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlvVCntrs%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002030-199812000-00012
DA Revicki C Swartz AW Wu R Haubrich AC Collier (1999) ArticleTitleQuality of life outcomes of saquinavir, zalcitabine and combination saquinavir plus zalcitabine therapy for adults with advanced HIV infection with CD4 counts between 50 and 300 cells/mm3 Antivir Ther 4 IssueID1 35–44 Occurrence Handle10682127 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXisFOjtr0%3D
F Arpinelli G Visona R Bruno CG De G Apolone (2000) ArticleTitleHealth-related quality of life in asymptomatic patients with HIV. Evaluation of the SF-36 health survey in Italian patients Pharmacoeconomics 18 IssueID1 63–72 Occurrence Handle11010605 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2Fgs1ersw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.2165/00019053-200018010-00007
DE Ostrow KJ Fox JS Chmiel et al. (2002) ArticleTitleAttitudes towards highly active antiretroviral therapy are associated with sexual risk taking among HIV-infected and uninfected homosexual men AIDS 16 IssueID5 775–780 Occurrence Handle11964534 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002030-200203290-00013
KP Weinfurt RJ Willke HA Glick WW Freimuth KA Schulman (2000) ArticleTitleRelationship between CD4 count, viral burden, and quality of life over time in HIV-1-infected patients Med Care 38 IssueID4 404–410 Occurrence Handle10752972 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3hsVKntA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005650-200004000-00007
SA Call JC Klapow KE Stewart et al. (2000) ArticleTitleHealth-related quality of life and virologic outcomes in an HIV clinic Qual Life Res 9 IssueID9 977–985 Occurrence Handle11332226 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3ovVagtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1016668802328
NH Dukers J Spaargaren RB Geskus J Beijnen RA Coutinho HS Fennema (2002) ArticleTitleHIV incidence on the increase among homosexual men attending an Amsterdam sexually transmitted disease clinic: Using a novel approach for detecting recent infections AIDS 16 IssueID10 F19–F24 Occurrence Handle12131206 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002030-200207050-00001
G Samsa D Edelman ML Rothman GR Williams J Lipscomb D Matchar (1999) ArticleTitleDetermining clinically important differences in health status measures: a general approach with illustration to the Health Utilities Index Mark II Pharmacoeconomics 15 IssueID2 141–155 Occurrence Handle10351188 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3isFyitg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.2165/00019053-199915020-00003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Ostrow, D., Detels, R. et al. Impacts of HIV infection and HAART use on quality of life. Qual Life Res 15, 941–949 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-005-5913-x
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-005-5913-x