Abstract
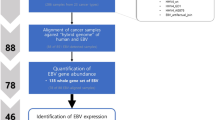
The latent expression pattern of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) has been extensively investigated, and the expression of several lytic genes in NPC has been reported. However, comprehensive information through EBV transcriptome analysis in NPC is limited. We performed paired-end RNA-seq to systematically and comprehensively characterize the expression of EBV genes in NPC tissue and C666-1 NPC cell line, which consistently carries EBV. In addition to the transcripts restricted to type II latency infection, the type III latency EBNA3s genes and a substantial number of lytic genes, such as BZLF1, BRLF1, and BMRF1, were detected through RNA-seq and were further verified in C666-1 cells and NPC tissue through realtime PCR.We also performed clustering analysis to classify NPC patient groups in terms of EBV gene expression, which presented two subtypes of NPC samples. Results revealed interesting patterns of EBV gene expression in NPC patients. This clustering was correlated with many signaling pathways, such as those related to heterotrimeric G-protein signaling, inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling, ribosomes, protein metabolism, influenza infection, and ECM-receptor interaction. Our combined findings suggested that the expression of EBV genes in NPC is restricted not only to type II latency genes but also to type III latency and lytic genes. This study provided further insights into the potential role of EBV in the development of NPC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer, 2004; 4(10): 757–768
Decaussin G, Sbih-Lammali F, de Turenne-Tessier M, Bouguermouh A, Ooka T. Expression of BARF1 gene encoded by Epstein- Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsies. Cancer Res, 2000; 60(19): 5584–5588
Pattle SB, Farrell PJ. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2006; 6(11): 1193–1205
Xu ZJ, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zou XN, Chen WQ. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China in 2009. Chin J Cancer, 2013; 32(8): 453–460
Wei KR, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Liang ZH, Ou ZX, Chen WQ. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China in 2010. Chin J Cancer, 2014; 33(8): 381–387
Dong JQ, Li MZ, Liu ZG, Zhong Q, Xiong D, Xu LH, Du Y, Xia YF, Zeng MS. Establishment and characterization of a novel nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (SUNE2) from a Cantonese patient. Chin J Cancer, 2012; 31(1): 36–44
Busson P, Keryer C, Ooka T, Corbex M. EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinomas: from epidemiology to virus-targeting strategies. Trends Microbiol, 2004; 12(8): 356–360
Deyrup AT. Epstein-Barr virus-associated epithelial and mesenchymal neoplasms. Hum Pathol, 2008; 39(4): 473–483
Tao Q, Chan AT. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic developments. Expert Rev Mol Med, 2007; 9(12): 1–24
Cabras G, Decaussin G, Zeng Y, Djennaoui D, Melouli H, Broully P, Bouguermouh AM, Ooka T. Epstein-Barr virus encoded BALF1 gene is transcribed in Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines and in nasopharyngeal carcinoma’s biopsies. J Clin Virol, 2005; 34(1): 26–34
Martel-Renoir D, Grunewald V, Touitou R, Schwaab G, Joab I. Qualitative analysis of the expression of Epstein-Barr virus lytic genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsies. J Gen Virol, 1995; 76 (Pt 6): 1401–1408
Sbih-Lammali F, Berger F, Busson P, Ooka T. Expression of the DNase encoded by the BGLF5 gene of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma epithelial cells. Virology, 1996; 222(1): 64–74
Lin Z, Xu G, Deng N, Taylor C, Zhu D, Flemington EK. Quantitative and qualitative RNA-Seq-based evaluation of Epstein-Barr virus transcription in type I latency Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. J Virol, 2010; 84(24): 13053–13058
Li C, Chen RS, Hung SK, Lee YT, Yen CY, Lai YW, Teng RH, Huang JY, Tang YC, Tung CP, Wei TT, Shieh B, Liu ST. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus infection and gene expression in human tumors by microarray analysis. J Virol Methods, 2006; 133(2): 158–166
Feng L, Liu H, Liu Y, Lu Z, Guo G, Guo S, Zheng H, Gao Y, Cheng S, Wang J, Zhang K, Zhang Y. Power of deep sequencing and agilent microarray for gene expression profiling study. Mol Biotechnol, 2010; 45(2): 101–110
Haas BJ, Zody MC. Advancing RNA-Seq analysis. Nat Biotechnol, 2010; 28(5): 421–423
Zhu JY, Pfuhl T, Motsch N, Barth S, Nicholls J, Grässer F, Meister G. Identification of novel Epstein-Barr virus microRNA genes from nasopharyngeal carcinomas. J Virol, 2009; 83(7): 3333–3341
Chen SJ, Chen GH, Chen YH, Liu CY, Chang KP, Chang YS, Chen HC. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus miRNAome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by deep sequencing. PLoS ONE, 2010; 5(9): e12745
Strong MJ, Xu G, Coco J, Baribault C, Vinay DS, Lacey MR, Strong AL, Lehman TA, Seddon MB, Lin Z, Concha M, Baddoo M, Ferris M, Swan KF, Sullivan DE, Burow ME, Taylor CM, Flemington EK. Differences in gastric carcinoma microenvironment stratify according to EBV infection intensity: implications for possible immune adjuvant therapy. PLoS Pathog, 2013; 9(5): e1003341
Hui AB, Cheung ST, Fong Y, Lo KW, Huang DP. Characterization of a new EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line. Cancer Genet Cytogenet, 1998; 101(2): 83–88
Cheung ST, Huang DP, Hui AB, Lo KW, Ko CW, Tsang YS, Wong N, Whitney BM, Lee JC. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (C666-1) consistently harbouring Epstein-Barr virus. Int J Cancer, 1999; 83(1): 121–126
Bernasconi M, Berger C, Sigrist JA, Bonanomi A, Sobek J, Niggli FK, Nadal D. Quantitative profiling of housekeeping and Epstein- Barr virus gene transcription in Burkitt lymphoma cell lines using an oligonucleotide microarray. Virol J, 2006; 3(1): 43
Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc, 2009; 4(1): 44–57
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet, 2000; 25(1): 25–29
Al-Mozaini M, Bodelon G, Karstegl CE, Jin B, Al-Ahdal M, Farrell PJ. Epstein-Barr virus BART gene expression. J Gen Virol, 2009; 90 (Pt 2): 307–316
Miller G, El-Guindy A, Countryman J, Ye J, Gradoville L. Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human γ herpesviruses. Adv Cancer Res, 2007, 97: 81–109
Zhang Q, Hong Y, Dorsky D, Holley-Guthrie E, Zalani S, Elshiekh NA, Kiehl A, Le T, Kenney S. Functional and physical interactions between the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) proteins BZLF1 and BMRF1: effects on EBV transcription and lytic replication. J Virol, 1996; 70(8): 5131–5142
Jung YJ, Choi H, Kim H, Lee SK. MicroRNA miR-BART20-5p stabilizes Epstein-Barr virus latency by directly targeting BZLF1 and BRLF1. J Virol, 2014; 88(16): 9027–9037
Wille CK, Nawandar DM, Panfil AR, Ko MM, Hagemeier SR, Kenney SC. Viral genome methylation differentially affects the ability of BZLF1 versus BRLF1 to activate Epstein-Barr virus lytic gene expression and viral replication. J Virol, 2013; 87(2): 935–950
Fung LF, Lo AK, Yuen PW, Liu Y, Wang XH, Tsao SW. Differential gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Life Sci, 2000; 67(8): 923–936
Bell AI, Groves K, Kelly GL, Croom-Carter D, Hui E, Chan AT, Rickinson AB. Analysis of Epstein-Barr virus latency gene expression in endemic Burkitt’s lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumour cells by using quantitative real-time PCR assays. J Gen Virol, 2006; 87(Pt 10): 2885–2890
Clarke PA, Sharp NA, Clemens MJ. Expression of genes for the Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs EBER-1 and EBER-2 in Daudi Burkitt’s lymphoma cells: effects of interferon treatment. J Gen Virol, 1992; 73(Pt 12): 3169–3175
Houmani JL, Davis CI, Ruf IK. Growth-promoting properties of Epstein-Barr virus EBER-1 RNA correlate with ribosomal protein L22 binding. J Virol, 2009; 83(19): 9844–9853
Wu Y, Maruo S, Yajima M, Kanda T, Takada K. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded RNA 2 (EBER2) but not EBER1 plays a critical role in EBV-induced B-cell growth transformation. J Virol, 2007; 81(20): 11236–11245
Cheung ST, Huang DP, Hui AB, Lo KW, Ko CW, Tsang YS, Wong N, Whitney BM, Lee JC. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (C666-1) consistently harbouring Epstein-Barr virus. Int J Cancer, 1999; 83(1): 121–126
Sengupta S, den Boon JA, Chen IH, Newton MA, Dahl DB, Chen M, Cheng YJ, Westra WH, Chen CJ, Hildesheim A, Sugden B, Ahlquist P. Genome-wide expression profiling reveals EBVassociated inhibition of MHC class I expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res, 2006; 66(16): 7999–8006
Nikitin PA, Yan CM, Forte E, Bocedi A, Tourigny JP, White RE, Allday MJ, Patel A, Dave SS, Kim W, Hu K, Guo J, Tainter D, Rusyn E, Luftig MA. An ATM/Chk2-mediated DNA damageresponsive signaling pathway suppresses Epstein-Barr virus transformation of primary human B cells. Cell Host Microbe, 2010; 8(6): 510–522
Gao Y, Smith PR, Karran L, Lu QL, Griffin BE. Induction of an exceptionally high-level, nontranslated, Epstein-Barr virus-encoded polyadenylated transcript in the Burkitt’s lymphoma line Daudi. J Virol, 1997; 71(1): 84–94
Xue SA, Griffin BE. Complexities associated with expression of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lytic origins of DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res, 2007; 35(10): 3391–3406
Feng P, Ren EC, Liu D, Chan SH, Hu H. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus lytic gene BRLF1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: potential use in diagnosis. J Gen Virol, 2000; 81(Pt 10): 2417–2423
Tanner JE, Wei MX, Alfieri C, Ahmad A, Taylor P, Ooka T, Menezes J. Antibody and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses against the BamHI A rightward open-reading frame-1 protein of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in EBV-associated disorders. J Infect Dis, 1997; 175(1): 38–46
Hitt MM, Allday MJ, Hara T, Karran L, Jones MD, Busson P, Tursz T, Ernberg I, Griffin BE. EBV gene expression in an NPC-related tumour. EMBO J, 1989; 8(9): 2639–2651
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, L., Lin, Z., Wu, Y. et al. Comprehensive profiling of EBV gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through paired-end transcriptome sequencing. Front. Med. 10, 61–75 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-016-0436-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-016-0436-0