Abstract
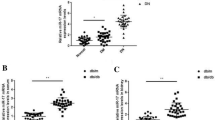
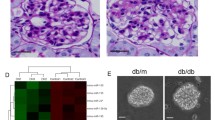
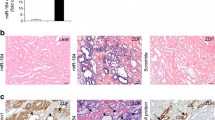
MicroRNAs (miRs) play important roles in initiation and progression of many pathologic processes. However, the roles of miRs in diabetic nephropathy remain unclear. This study was to determine whether miR-21 was involved in diabetic nephropathy and to explore the relationship between miR-21 and MMP9/TIMP1 expression in diabetic nephropathy. In situ hybridization studies showed that miR-21 was primarily localized and distributed in cortical glomerular and renal tubular cells in diabetic kk-ay kidney. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR demonstrated that the expression of miR-21 was significantly increased in kk-ay mice, compared with control C57BL mice. Interestingly, miR-21 expression positively correlated with urine albumin creatine ratio (ACR), TIMP1, collagen IV (ColIV), and fibronectin (FN); while negatively correlated with creatine clearance ratio (Ccr) and MMP-9 protein. Importantly, antagomir-21 not only ameliorated Ccr and ACR but also decreased TIMP1, ColIV, and FN proteins. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that miR-21 contributes to renal fibrosis by mediating MMP9/TIMP1 and that inhibition of miR-21 may be a novel target for diabetic nephropathy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rychlik, I., Miltenberger-Miltenyi, G., & Ritz, E. (1998). The drama of the continuous increase in end-stage renal failure in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 13(Suppl 8), 6–10.
Tervaert, T. W., Mooyaart, A. L., Amann, K., et al. (2010). Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 21, 556–563.
Mason, R. M., & Wahab, N. A. (2003). Extracellular matrix metabolism in diabetic nephropathy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 14, 1358–1373.
Ito, T., Tanimoto, M., Yamada, K., et al. (2006). Glomerular changes in the KK-Ay/Ta mouse: A possible model for human type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton), 11, 29–35.
Perron, M. P., & Provost, P. (2008). Protein interactions and complexes in human microRNA biogenesis and function. Frontiers in Bioscience, 13, 2537–2547.
Poy, M. N., Eliasson, L., Krutzfeldt, J., et al. (2004). A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature, 432, 226–230.
Kloosterman, W. P., Lagendijk, A. K., Ketting, R. F., et al. (2007). Targeted inhibition of miRNA maturation with morpholinos reveals a role for miR-375 in pancreatic islet development. PLoS Biology, 5, e203.
El Ouaamari, A., Baroukh, N., Martens, G. A., et al. (2008). miR-375 targets 3′-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 and regulates glucose-induced biological responses in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes, 57, 2708–2717.
Tang, X., Muniappan, L., Tang, G., et al. (2009). Identification of glucose-regulated miRNAs from pancreatic beta cells reveals a role for miR-30d in insulin transcription. RNA, 15, 287–293.
He, A., Zhu, L., Gupta, N., et al. (2007). Overexpression of micro ribonucleic acid 29, highly up-regulated in diabetic rats, leads to insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Molecular Endocrinology, 21, 2785–2794.
Qin, W., Chung, A. C., Huang, X. R., et al. (2011). TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling promotes renal fibrosis by inhibiting miR-29. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 22, 1462–1474.
Chung, A. C., Huang, X. R., Meng, X., et al. (2010). miR-192 mediates TGF-beta/Smad3-driven renal fibrosis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 21, 1317–1325.
Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Minto, A. W., et al. (2008). MicroRNA-377 is up-regulated and can lead to increased fibronectin production in diabetic nephropathy. FASEB Journal, 22, 4126–4135.
Zhang, Z., Luo, X., Ding, S., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-451 regulates p38 MAPK signaling by targeting of Ywhaz and suppresses the mesangial hypertrophy in early diabetic nephropathy. FEBS Letters, 586, 20–26.
Shantikumar, S., Caporali, A., & Emanueli, C. (2012). Role of microRNAs in diabetes and its cardiovascular complications. Cardiovascular Research, 93, 583–593.
Moriyama, T., Ohuchida, K., Mizumoto, K., et al. (2009). MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 8, 1067–1074.
Gabriely, G., Wurdinger, T., Kesari, S., et al. (2008). MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 28, 5369–5380.
Roy, S., Khanna, S., Hussain, S. R., et al. (2009). MicroRNA expression in response to murine myocardial infarction: miR-21 regulates fibroblast metalloprotease-2 via phosphatase and tensin homologue. Cardiovascular Research, 82, 21–29.
Meng, F., Henson, R., Wehbe-Janek, H., et al. (2007). MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology, 133, 647–658.
Li, H. Y., Hou, F. F., Zhang, X., et al. (2007). Advanced oxidation protein products accelerate renal fibrosis in a remnant kidney model. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 18, 528–538.
Miyazaki, T., Aoyama, I., Ise, M., et al. (2000). An oral sorbent reduces overload of indoxyl sulphate and gene expression of TGF-beta1 in uraemic rat kidneys. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 15, 1773–1781.
Nuovo, G. J. (2008). In situ detection of precursor and mature microRNAs in paraffin embedded, formalin fixed tissues and cell preparations. Methods, 2008(44), 39–46.
Schmittgen, T. D., Lee, E. J., Jiang, J., et al. (2008). Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA. Methods, 44, 31–38.
Pfaffl, M. W. (2001). A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Research, 2001(29), e45.
Viberti, G., & Wheeldon, N. M. (2002). Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A blood pressure-independent effect. Circulation, 106, 672–678.
Fioretto, P., & Mauer, M. (2010). Diabetic nephropathy: Diabetic nephropathy-challenges in pathologic classification. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 6, 508–510.
Krolewski, A. S., Canessa, M., Warram, J. H., et al. (1988). Predisposition to hypertension and susceptibility to renal disease in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine, 318, 140–145.
Ballard, D. J., Humphrey, L. L., Melton, L. J., 3rd, et al. (1988). Epidemiology of persistent proteinuria in type II diabetes mellitus. Population-based study in Rochester, Minnesota. Diabetes, 37, 405–412.
Krichevsky, A. M., & Gabriely, G. (2009). miR-21: A small multi-faceted RNA. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 13, 39–53.
Zarjou, A., Yang, S., Abraham, E., et al. (2011). Identification of a microRNA signature in renal fibrosis: Role of miR-21. American Journal of Physiology: Renal Physiology, 301, F793–F801.
Chau, B. N., Xin, C., Hartner, J., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-21 promotes fibrosis of the kidney by silencing metabolic pathways. Science Translational Medicine, 4, 121ra118.
Chen, S., Hong, S. W., Iglesias-de la Cruz, M. C., et al. (2001). The key role of the transforming growth factor-beta system in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Renal Failure, 2001(23), 471–481.
Davis, B. N., Hilyard, A. C., Lagna, G., et al. (2008). SMAD proteins control DROSHA-mediated microRNA maturation. Nature, 454, 56–61.
Zhang, Z., Peng, H., Chen, J., et al. (2009). MicroRNA-21 protects from mesangial cell proliferation induced by diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. FEBS Letters, 583, 2009–2014.
Snoek-van Beurden, P. A., & Von den Hoff, J. W. (2005). Zymographic techniques for the analysis of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. BioTechniques, 2005(38), 73–83.
Suminoe, A., Matsuzaki, A., Hattori, H., et al. (2007). Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and tissue inhibitor of MMP (TIMP) genes in blasts of infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia with organ involvement. Leukemia Research, 31, 1437–1440.
Bai, Y., Wang, L., Li, Y., et al. (2006). High ambient glucose levels modulates the production of MMP-9 and alpha5(IV) collagen by cultured podocytes. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 17, 57–68.
Liu, G., Friggeri, A., Yang, Y., et al. (2010). miR-21 mediates fibrogenic activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and lung fibrosis. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 207, 1589–1597.
Thum, T., Gross, C., Fiedler, J., et al. (2008). MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature, 456, 980–984.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the Major National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB518602), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81173238), and Scientific Research Project of Beijing Educational Committee (No. KZ201110025025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Gao, Y., Ma, M. et al. Effect of miR-21 on Renal Fibrosis by Regulating MMP-9 and TIMP1 in kk-ay Diabetic Nephropathy Mice. Cell Biochem Biophys 67, 537–546 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9539-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9539-2