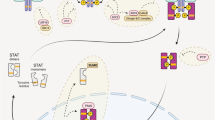
Abstract
The transcription factor, NF-κB (nuclear factor-κB) and associated regulatory factors make up a multi-component signaling pathway that regulates a wide range of biological processes, including cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, stress response, and death, as well as immunity and inflammation. Aberrant NF-κB pathway activity is known to be associated with a host of diseases, including immune deficiencies, inflammatory disorders, and cancer. Recent advances in our understanding of the inner workings of the NF-κB pathway have led to the development of new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of these diseases. In this review, we focus on the regulation of the NF-κB pathway by Bcl-3 (B cell leukemia-3), a nuclear member of the IκB (inhibitor of NF-κB) family. Both the regulation and the function of Bcl-3 will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nolan GP, Baltimore D. The inhibitory ankyrin and activator Rel proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992;2:211–20.
Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, Van Antwerp D, Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2723–35.
Lenardo MJ, Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989;58:227–9.
Crossen PE. Cytogenetic and molecular changes in chronic B-cell leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989;43:143–50.
Ohno H, Takimoto G, McKeithan TW. The candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 is related to genes implicated in cell lineage determination and cell cycle control. Cell. 1990;60:991–7.
Hatada EN, Nieters A, Wulczyn FG, Naumann M, Meyer R, Nucifora G, et al. The ankyrin repeat domains of the NF-kappa B precursor p105 and the protooncogene bcl-3 act as specific inhibitors of NF-kappa B DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:2489–93.
Wulczyn FG, Naumann M, Scheidereit C. Candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes a subunit-specific inhibitor of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1992;358:597–9.
Nolan GP, Fujita T, Bhatia K, Huppi C, Liou HC, Scott ML, et al. The bcl-3 proto-oncogene encodes a nuclear I kappa B-like molecule that preferentially interacts with NF-kappa B p50 and p52 in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:3557–66.
Naumann M, Wulczyn FG, Scheidereit C. The NF-kappa B precursor p105 and the proto-oncogene product Bcl-3 are I kappa B molecules and control nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1993;12:213–22.
Kerr LD, Duckett CS, Wamsley P, Zhang Q, Chiao P, Nabel G, et al. The proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes an I kappa B protein. Genes Dev. 1992;6:2352–63.
Inoue J, Takahara T, Akizawa T, Hino O. Bcl-3, a member of the I kappa B proteins, has distinct specificity towards the Rel family of proteins. Oncogene. 1993;8:2067–73.
Franzoso G, Bours V, Park S, Tomita-Yamaguchi M, Kelly K, Siebenlist U. The candidate oncoprotein Bcl-3 is an antagonist of p50/NF-kappa B-mediated inhibition. Nature. 1992;359:339–42.
Franzoso G, Bours V, Azarenko V, Park S, Tomita-Yamaguchi M, Kanno T, et al. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 can facilitate NF-kappa B-mediated transactivation by removing inhibiting p50 homodimers from select kappa B sites. EMBO J. 1993;12:3893–901.
Fujita T, Nolan GP, Liou HC, Scott ML, Baltimore D. The candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes a transcriptional coactivator that activates through NF-kappa B p50 homodimers. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1354–63.
Bours V, Franzoso G, Azarenko V, Park S, Kanno T, Brown K, et al. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly transactivates through kappa B motifs via association with DNA-binding p50B homodimers. Cell. 1993;72:729–39.
Watanabe N, Iwamura T, Shinoda T, Fujita T. Regulation of NFKB1 proteins by the candidate oncoprotein BCL-3: generation of NF-kappaB homodimers from the cytoplasmic pool of p50–p105 and nuclear translocation. EMBO J. 1997;16:3609–20.
Muhlbauer M, Chilton PM, Mitchell TC, Jobin C. Impaired Bcl3 up-regulation leads to enhanced lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin (IL)-23P19 gene expression in IL-10(-/-) mice. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:14182–9.
Kuwata H, Watanabe Y, Miyoshi H, Yamamoto M, Kaisho T, Takeda K, et al. IL-10-inducible Bcl-3 negatively regulates LPS-induced TNF-alpha production in macrophages. Blood. 2003;102:4123–9.
Caamano JH, Perez P, Lira SA, Bravo R. Constitutive expression of Bc1–3 in thymocytes increases the DNA binding of NF-kappaB1 (p50) homodimers in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:1342–8.
Carmody RJ, Ruan Q, Palmer S, Hilliard B, Chen YH. Negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling by NF-kappaB p50 ubiquitination blockade. Science. 2007;317:675–8.
Dechend R, Hirano F, Lehmann K, Heissmeyer V, Ansieau S, Wulczyn FG, et al. The Bcl-3 oncoprotein acts as a bridging factor between NF-kappaB/Rel and nuclear co-regulators. Oncogene. 1999;18:3316–23.
Wessells J, Baer M, Young HA, Claudio E, Brown K, Siebenlist U, et al. BCL-3 and NF-kappaB p50 attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:49995–50003.
Viatour P, Dejardin E, Warnier M, Lair F, Claudio E, Bureau F, et al. GSK3-mediated BCL-3 phosphorylation modulates its degradation and its oncogenicity. Mol Cell. 2004;16:35–45.
Zhong H, May MJ, Jimi E, Ghosh S. The phosphorylation status of nuclear NF-kappa B determines its association with CBP/p300 or HDAC-1. Mol Cell. 2002;9:625–36.
Leung TH, Hoffmann A, Baltimore D. One nucleotide in a kappaB site can determine cofactor specificity for NF-kappaB dimers. Cell. 2004;118:453–64.
McKeithan TW, Ohno H, Dickstein J, Hume E. Genomic structure of the candidate proto-oncogene BCL3. Genomics. 1994;24:120–6.
Richard M, Louahed J, Demoulin JB, Renauld JC. Interleukin-9 regulates NF-kappaB activity through BCL3 gene induction. Blood. 1999;93:4318–27.
Rebollo A, Dumoutier L, Renauld JC, Zaballos A, Ayllon V, Martinez AC. Bcl-3 expression promotes cell survival following interleukin-4 deprivation and is controlled by AP1 and AP1-like transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:3407–16.
Brasier AR, Lu M, Hai T, Lu Y, Boldogh I. NF-kappa B-inducible BCL-3 expression is an autoregulatory loop controlling nuclear p50/NF-kappa B1 residence. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:32080–93.
Ge B, Li O, Wilder P, Rizzino A, McKeithan TW. NF-kappa B regulates BCL3 transcription in T lymphocytes through an intronic enhancer. J Immunol. 2003;171:4210–8.
Corn RA, Aronica MA, Zhang F, Tong Y, Stanley SA, Kim SR, et al. T cell-intrinsic requirement for NF-kappa B induction in postdifferentiation IFN-gamma production and clonal expansion in a Th1 response. J Immunol. 2003;171:1816–24.
Jamaluddin M, Choudhary S, Wang S, Casola A, Huda R, Garofalo RP, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus-inducible BCL-3 expression antagonizes the STAT/IRF and NF-kappaB signaling pathways by inducing histone deacetylase 1 recruitment to the interleukin-8 promoter. J Virol. 2005;79:15302–13.
Beurel E, Jope RS. Differential regulation of STAT family members by glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:21934–44.
Kung CP, Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor through effects on Bcl-3 and STAT3. J Virol. 2008;82:5486–93.
Brocke-Heidrich K, Ge B, Cvijic H, Pfeifer G, Loffler D, Henze C, et al. BCL3 is induced by IL-6 via Stat3 binding to intronic enhancer HS4 and represses its own transcription. Oncogene. 2006;25:7297–304.
Feinman R, Koury J, Thames M, Barlogie B, Epstein J, Siegel DS. Role of NF-kappaB in the rescue of multiple myeloma cells from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis by bcl-2. Blood. 1999;93:3044–52.
Merika M, Thanos D. Enhanceosomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001;11:205–8.
Cheadle C, Fan J, Cho-Chung YS, Werner T, Ray J, Do L, et al. Control of gene expression during T cell activation: alternate regulation of mRNA transcription and mRNA stability. BMC Genomics. 2005;6:75.
Dai R, Phillips RA, Ahmed SA. Despite inhibition of nuclear localization of NF-kappa B p65, c-Rel, and RelB, 17-beta estradiol up-regulates NF-kappa B signaling in mouse splenocytes: the potential role of Bcl-3. J Immunol. 2007;179:1776–83.
Weyrich AS, Dixon DA, Pabla R, Elstad MR, McIntyre TM, Prescott SM, et al. Signal-dependent translation of a regulatory protein, Bcl-3, in activated human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:5556–61.
Piguet PF, Vesin C, Da Kan C. Activation of platelet caspases by TNF and its consequences for kinetics. Cytokine. 2002;18:222–30.
Bundy DL, McKeithan TW. Diverse effects of BCL3 phosphorylation on its modulation of NF-kappaB p52 homodimer binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:33132–9.
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V, Chariot A. Protein phosphorylation as a key mechanism for the regulation of BCL-3 activity. Cell Cycle. 2004;3:1498–501.
Freiman RN, Tjian R. Regulating the regulators: lysine modifications make their mark. Cell. 2003;112:11–7.
Conaway RC, Brower CS, Conaway JW. Emerging roles of ubiquitin in transcription regulation. Science. 2002;296:1254–8.
Massoumi R, Paus R. Cylindromatosis and the CYLD gene: new lessons on the molecular principles of epithelial growth control. Bioessays. 2007;29:1203–14.
Massoumi R, Chmielarska K, Hennecke K, Pfeifer A, Fassler R. Cyld inhibits tumor cell proliferation by blocking Bcl-3-dependent NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2006;125:665–77.
Ikeda F, Dikic I. CYLD in ubiquitin signaling and tumor pathogenesis. Cell. 2006;125:643–5.
Hovelmeyer N, Wunderlich FT, Massoumi R, Jakobsen CG, Song J, Worns MA, et al. Regulation of B cell homeostasis and activation by the tumor suppressor gene CYLD. J Exp Med. 2007;204:2615–27.
Zhang MY, Harhaj EW, Bell L, Sun SC, Miller BA. Bcl-3 expression and nuclear translocation are induced by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and erythropoietin in proliferating human erythroid precursors. Blood. 1998;92:1225–34.
Elliott SF, Coon CI, Hays E, Stadheim TA, Vincenti MP. Bcl-3 is an interleukin-1-responsive gene in chondrocytes and synovial fibroblasts that activates transcription of the matrix metalloproteinase 1 gene. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:3230–9.
Schwarz EM, Krimpenfort P, Berns A, Verma IM. Immunological defects in mice with a targeted disruption in Bcl-3. Genes Dev. 1997;11:187–97.
Franzoso G, Carlson L, Scharton-Kersten T, Shores EW, Epstein S, Grinberg A, et al. Critical roles for the Bcl-3 oncoprotein in T cell-mediated immunity, splenic microarchitecture, and germinal center reactions. Immunity. 1997;6:479–90.
Corn RA, Hunter C, Liou HC, Siebenlist U, Boothby MR. Opposing roles for RelB and Bcl-3 in regulation of T-box expressed in T cells, GATA-3, and Th effector differentiation. J Immunol. 2005;175:2102–10.
McKeithan TW, Takimoto GS, Ohno H, Bjorling VS, Morgan R, Hecht BK, et al. BCL3 rearrangements and t(14;19) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other B-cell malignancies: a molecular and cytogenetic study. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1997;20:64–72.
Cogswell PC, Guttridge DC, Funkhouser WK, Baldwin AS Jr. Selective activation of NF-kappa B subunits in human breast cancer: potential roles for NF-kappa B2/p52 and for Bcl-3. Oncogene. 2000;19:1123–31.
Thornburg NJ, Pathmanathan R, Raab-Traub N. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB p50 homodimer/Bcl-3 complexes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:8293–301.
Ong ST, Hackbarth ML, Degenstein LC, Baunoch DA, Anastasi J, McKeithan TW. Lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and altered immunoglobulin production in BCL3 transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1998;16:2333–43.
Rangelova, S, Kirschnek, S, Strasser, A, Hacker, G. FADD and the NF-kappaB family member Bcl-3 regulate complementary pathways to control T-cell survival and proliferation. Immunology. 2008 [Epub ahead of print].
Mitchell TC, Hildeman D, Kedl RM, Teague TK, Schaefer BC, White J, et al. Immunological adjuvants promote activated T cell survival via induction of Bcl-3. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:397–402.
Bauer A, Villunger A, Labi V, Fischer SF, Strasser A, Wagner H, et al. The NF-kappaB regulator Bcl-3 and the BH3-only proteins Bim and Puma control the death of activated T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:10979–84.
Westerheide SD, Mayo MW, Anest V, Hanson JL, Baldwin AS Jr. The putative oncoprotein Bcl-3 induces cyclin D1 to stimulate G(1) transition. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:8428–36.
Kashatus D, Cogswell P, Baldwin AS. Expression of the Bcl-3 proto-oncogene suppresses p53 activation. Genes Dev. 2006;20:225–35.