Abstract
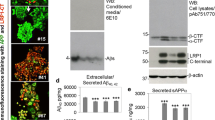
The clearance and degradation of extracellular Aβ is critical for regulating β-amyloid deposition, a major hallmark of brains of patients with Aβ in Alzheimer’s Disease. The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, LRP1, is a large endocytic receptor that significantly contributes to the balance between degradation and production of Aβ. An extracellular portion of the LRP, known as the cluster II region can bind to the secreted form of APP (sAPP-KPI). We show here that a GST fusion protein containing the cluster II region of LRP can be used as a ‘mini-receptor’ that specifically binds to sAPP-KPI from conditioned cultured medium. The binding between the GST-LRP-cluster II fusion protein and sAPP-KPI can be inhibited with the strong binding ligand of LRP1, called receptor-associated protein (RAP). Furthermore, a cell-based in vitro assay system has been developed to monitor the production of total Aβ and Aβ1–42 in the presence and absence of RAP in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines both deficient in LRP and expressing LRP. A 3-day treatment of the L2 (CHO cells deficient in LRP and overexpressing APP751) and L3 (CHO cells expressing LRP and overexpressing APP751) cell lines with RAP showed a decrease in total Aβ and, interestingly, also a decrease in the ratio of Aβ42/Aβtotal. This cell-based model system and LRP-cluster II mini-receptor will be very useful for screening novel compounds that can reduce Aβ accumulation by inhibiting binding of APP-KPI to LRP1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horn I. R., van den Berg B. M. M., van der Meijden P. Z., Pannekoek H., and van Zonneveld A.-J. (1997) Molecular analysis of ligand binding to the second cluster of complement-type repeats of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 13608–13613.
Kounnas M. Z., Moir R. D., Rebeck G. W., Bush A. I., Argraves W. S., Tanzi R. E., et al. (1995) LDL receptor-related protein, a multifunctional apoE receptor, binds secreted β-amyloid precursor protein and mediates its degradation. Cell 82, 331–340.
Moir R. D., Lynch T., Bush A. I., Whyte S., Henry A., Portbury S., et al. (1998) Relative increase in Alzheimer’s disease of soluble forms of cerebral Aβ amyloid protein precursor containing the Kunitz protease inhibitory domain. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5013–5019.
Tanzi R. E. (1999) Agenetic dichotomy model for the inheritance of Alzheimer’s disease and common age-related disorders. J. Clin. Invest. 104, 1175–1179.
Ulery P. G., Beers J., Mikhailenko I., Tanzi R. E., Rebeck G. W., Hyman B. T., and Strickland D. K. (2000) Modulation of β-amyloid precursor protein processing by the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7410–7415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goto, J.J., Tanzi, R.E. The role of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP1) in alzheimer’s Aβ generation. J Mol Neurosci 19, 37–41 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-002-0008-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-002-0008-4