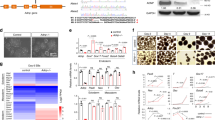
Abstract
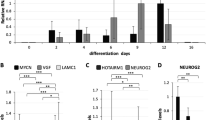
Complete deficiency in activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) results in neural tube closure defects and death at gestation day 9 in mice. ADNP-deficient embryos exhibit dramatic increases in gene transcripts associated with lipid metabolism coupled to reduction in organogenesis/neurogenesis-related transcripts. In the pluripotent teratocarcinoma cell line P19, ADNP was shown to interact with specific chromatin regions in the neurodifferentiated state, which was associated with binding to the heterochromatin protein 1 alpha. In this study, using P19 cells as a differentiation model, we showed that ADNP expression and cytoplasm/nucleus distribution is unique in neuronal-differentiated cells compared to cardiovascular and nondifferentiated pluripotent cells. ADNP-like immunohistochemical localization to the neuronal cytoplasm and neurites was shown in this study not only in the cellular model but also in the brain cerebral cortex and olfactory bulb. Small hairpin RNA ADNP downregulation was used to further investigate ADNP involvement in p19 neurodifferentiation. An approximately 80% robust reduction in ADNP led to a substantial reduction in embryoid body formation and a significant reduction (approximately 50%) in neurite numbers. These results position ADNP in direct association with neuronal cell differentiation and maturation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama, H., Sugiyama, A., Uzawa, K., Fujisawa, N., Tashiro, Y., & Tashiro, F. (2003). Implication of Trip15/CSN2 in early stage of neuronal differentiation of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Developmental Brain Research, 140, 45–56.
Baas, D., Bumsted, K. M., Martinez, J. A., Vaccarino, F. M., Wikler, K. C., & Barnstable, C. J. (2000). The subcellular localization of Otx2 is cell-type specific and developmentally regulated in the mouse retina. Molecular Brain Research, 78, 26–37.
Bassan, M., Zamostiano, R., Davidson, A., Pinhasov, A., Giladi, E., Perl, O., et al. (1999). Complete sequence of a novel protein containing a femtomolar-activity-dependent neuroprotective peptide. Journal of Neurochemistry, 72, 1283–1293.
Beni-Adani, L., Gozes, I., Cohen, Y., Assaf, Y., Steingart, R. A., Brenneman, D. E., et al. (2001). A peptide derived from activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) ameliorates injury response in closed head injury in mice. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 296, 57–63.
Borozdin, W., Graham, J. M., Jr., Bohm, D., Bamshad, M. J., Spranger, S., Burke, L., et al. (2007). Multigene deletions on chromosome 20q13.13-q13.2 including SALL4 result in an expanded phenotype of Okihiro syndrome plus developmental delay. Human Mutation, 28, 830.
Chen, S. Y., Charness, M. E., Wilkemeyer, M. F., & Sulik, K. K. (2005). Peptide-mediated protection from ethanol-induced neural tube defects. Developmental Neuroscience, 27, 13–19.
Divinski, I., Mittelman, L., & Gozes, I. (2004). A femtomolar acting octapeptide interacts with tubulin and protects astrocytes against zinc intoxication. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 28531–28538.
Divinski, I., Holtser-Cochav, M., Vulih-Schultzman, I., Steingart, R. A., & Gozes, I. (2006). Peptide neuroprotection through specific interaction with brain tubulin. Journal of Neurochemistry, 98, 973–984.
Furman, S., Steingart, R. A., Mandel, S., Hauser, J. M., Brenneman, D. E., & Gozes, I. (2004). Subcellular localization and secretion of activity-dependent neuroprotective protein in astrocytes. Neuron Glia Biology, 1, 193–199.
Furman, S., Hill, J. M., Vulih, I., Zaltzman, R., Hauser, J. M., Brenneman, D. E., et al. (2005). Sexual dimorphism of activity-dependent neuroprotective protein in the mouse arcuate nucleus. Neuroscience Letters, 373, 73–78.
Gozes, I. (2007). Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein: From gene to drug candidate. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 114, 146–154.
Gozes, I., & Barnstable, C. J. (1982). Monoclonal antibodies that recognize discrete forms of tubulin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 79, 2579–2583.
Gozes, I., & Divinski, I. (2004). The femtomolar-acting NAP interacts with microtubules: Novel aspects of astrocyte protection. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 6, S37–S41.
Gozes, I., Divinsky, I., Pilzer, I., Fridkin, M., Brenneman, D. E., & Spier, A. D. (2003). From vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) through activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) to NAP: A view of neuroprotection and cell division. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 20, 315–322.
Gozes, I., Morimoto, B. H., Tiong, J., Fox, A., Sutherland, K., Dangoor, D., et al. (2005b). NAP: Research and development of a peptide derived from activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP). CNS Drug Reviews, 11, 353–368.
Gozes, I., Zaltzman, R., Hauser, J., Brenneman, D. E., Shohami, E., & Hill, J. M. (2005a). The expression of activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) is regulated by brain damage and treatment of mice with the ADNP derived peptide, NAP, reduces the severity of traumatic head injury. Current Alzheimer Research, 2, 149–153.
Mandel, S., & Gozes, I. (2007) Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein constitutes a novel element in the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 34448–34456.
Mandel, S., Rechavi, G., & Gozes, I. (2007). Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) differentially interacts with chromatin to regulate genes essential for embryogenesis. Developments in Biologicals, 303, 814–824.
Matsuoka, Y., Gray, A. J., Hirata-Fukae, C., Minami, S. S., Waterhouse, E. G., Mattson, M. P., et al. (2007). Intranasal NAP administration reduces accumulation of amyloid peptide and tau hyperphosphorylation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease at early pathological stage. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 31, 165–170.
Nedelec, S., Foucher, I., Brunet, I., Bouillot, C., Prochiantz, A., & Trembleau, A. (2004). Emx2 homeodomain transcription factor interacts with eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) in the axons of olfactory sensory neurons. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 10815–10820.
Pascual, M., & Guerri, C. (2007). The peptide NAP promotes neuronal growth and differentiation through extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase and Akt pathways, and protects neurons co-cultured with astrocytes damaged by ethanol. Journal of Neurochemistry, in press.
Pinhasov, A., Mandel, S., Torchinsky, A., Torchinsky, A., Giladi, E., Pittel, Z., et al. (2003). Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein: A novel gene essential for brain formation. Developmental Brain Research, 144, 83–90.
Poggi, S. H., Vink, J., Goodwin, K., Hill, J. M., Brenneman, D. E., Pinhasov, A., et al. (2002). Differential expression of embryonic and maternal activity-dependent neuroprotective protein during mouse development. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 187, 973–976.
Sari, Y., & Gozes, I. (2006). Brain deficits associated with fetal alcohol exposure may be protected, in part, by peptides derived from activity-dependent neurotrophic factor and activity-dependent neuroprotective protein. Brain Research Reviews, 52, 107–118.
Sigalov, E., Fridkin, M., Brenneman, D. E., & Gozes, I. (2000). VIP-Related protection against lodoacetate toxicity in pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells: A model for ischemic/hypoxic injury. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 15, 147–154.
Smith-Swintosky, V. L., Gozes, I., Brenneman, D. E., D’Andrea, M. R., & Plata-Salaman, C. R. (2005). Activity-dependent neurotrophic factor-9 and NAP promote neurite outgrowth in rat hippocampal and cortical cultures. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 25, 225–238.
Steingart, R. A., & Gozes, I. (2006). Recombinant activity-dependent neuroprotective protein protects cells against oxidative stress. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 252, 148–153.
van der Heyden, M. A., & Defize, L. H. (2003). Twenty one years of P19 cells: What an embryonal carcinoma cell line taught us about cardiomyocyte differentiation. Cardiovascular Research, 58, 292–302.
Vulih-Shultzman, I., Pinhasov, A., Mandel, S., Grigoriadis, N., Touloumi, O., Pittel, Z., et al. (2007). Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein snippet NAP reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and enhances learning in a novel transgenic mouse model. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 323, 438–449.
Wilhelm, J. E., Hilton, M., Amos, Q., & Henzel, W. J. (2003). Cup is an eIF4E binding protein required for both the translational repression of oskar and the recruitment of Barentsz. Journal of Cell Biology, 163, 1197–1204.
Zaltzman, R., Alexandrovich, A., Beni, S. M., Trembovler, V., Shohami, E., & Gozes, I. (2004). Brain injury-dependent expression of activity-dependent neuroprotective protein. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 24, 181–187.
Zamostiano, R., Pinhasov, A., Gelber, E., et al. (2001). Cloning and characterization of the human activity-dependent neuroprotective protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 708–714.
Zusev, M., & Gozes, I. (2004). Differential regulation of activity-dependent neuroprotective protein in rat astrocytes by VIP and PACAP. Regulatory Peptides, 123, 33–41.
Acknowledgements
This work is in partial fulfillment of the Ph.D. thesis requirements of Mr. Shmuel Mandel. We thank Dr. Joanna M. Hill for her initial help with techniques in immunohistochemistry and Professor Colin Barnstable for the monoclonal anti-tubulin antibodies. Support was provided by the BSF, ISF and Allon Therapeutics Inc. Professor Gozes is the incumbent of the Lily and Avraham Gildor Chair for the Investigation of Growth Factors, and the Director of the Adams Super Center for Brain Studies, the Levie-Edersheim-Gitter Institute for Functional Brain Imaging and the Dr. Diana and Zelman Elton (Elbaum) Laboratory for Molecular Neuroendocrinology and Allon Therapeutics. Professor Illana Gozes serves as the Chief Scientific Officer of Allon Therapeutics. NAP is in phase II clinical trials for neuroprotection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandel, S., Spivak-Pohis, I. & Gozes, I. ADNP Differential Nucleus/Cytoplasm Localization in Neurons Suggests Multiple Roles in Neuronal Differentiation and Maintenance. J Mol Neurosci 35, 127–141 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-007-9013-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-007-9013-y