Abstract
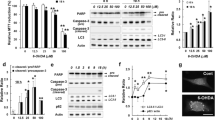
Caspase family has been recognized to be involved in dopaminergic (DA) neuronal death and to exert an unfavorable role in Parkinson’s disease (PD) pathology. Our previous study has revealed that caspase-1, as an important component of NLRP3 inflammasome, induces microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of PD. However, the role of caspase-1 in DA neuronal degeneration in the onset of PD remains unclear. Here, we showed that caspase-1 knockout ameliorated DA neuronal loss and dyskinesia in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine/probenecid (MPTP/p)-induced PD model mice. We further found that caspase-1 knockout decreased MPTP/p-induced caspase-7 cleavage, subsequently inhibited nuclear translocation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1), and reduced the release of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF). Consistently, we demonstrated that caspase-1 inhibitor suppressed caspase-7/PARP1/AIF-mediated apoptosis pathway by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+) stimulation in SH-SY5Y cells. Caspase-7 overexpression reduced the protective effects of caspase-1 inhibitor on SH-SY5Y cell apoptosis. Collectively, our results have revealed that caspase-1 regulates DA neuronal death in the pathogenesis of PD in mice via caspase-7/PARP1/AIF pathway. These findings will shed new insight into the potential of caspase-1 as a target for PD therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Connolly BS, Lang AE (2014) Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. Jama 311(16):1670–1683. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3654
Brichta L, Greengard P, Flajolet M (2013) Advances in the pharmacological treatment of Parkinson’s disease: targeting neurotransmitter systems. Trends Neurosci 36(9):543–554. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2013.06.003
Shulman JM, De Jager PL, Feany MB (2011) Parkinson’s disease: genetics and pathogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol 6:193–222. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130242
Perier C, Bove J, Vila M (2012) Mitochondria and programmed cell death in Parkinson’s disease: apoptosis and beyond. Antioxid Redox Signal 16(9):883–895. doi:10.1089/ars.2011.4074
Kulkarni VK, Deshmukh J, Banda NR, Banda VR (2012) Odontomas—silent tormentors of teeth eruption, shedding and occlusion. BMJ Case Reports. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007666
Arenas E (2014) Wnt signaling in midbrain dopaminergic neuron development and regenerative medicine for Parkinson’s disease. J Mol Cell Biol 6(1):42–53. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mju001
Kumar H, Kim IS, More SV, Kim BW, Bahk YY, Choi DK (2013) Gastrodin protects apoptotic dopaminergic neurons in a toxin-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern Med eCAM 2013:514095. doi:10.1155/2013/514095
Allen NE, Schwarzel AK, Canning CG (2013) Recurrent falls in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. Park Dis 2013:906274. doi:10.1155/2013/906274
Poreba M, Strozyk A, Salvesen GS, Drag M (2013) Caspase substrates and inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5(8):a008680. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a008680
Hyman BT, Yuan J (2012) Apoptotic and non-apoptotic roles of caspases in neuronal physiology and pathophysiology. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(6):395–406. doi:10.1038/nrn3228
Wu H, Che X, Zheng Q, Wu A, Pan K, Shao A, Wu Q, Zhang J, Hong Y (2014) Caspases: a molecular switch node in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Int J Biol Sci 10(9):1072–1083. doi:10.7150/ijbs.9719
Sollberger G, Strittmatter GE, Garstkiewicz M, Sand J, Beer HD (2014) Caspase-1: the inflammasome and beyond. Innate Immunity 20(2):115–125. doi:10.1177/1753425913484374
Collins LM, Toulouse A, Connor TJ, Nolan YM (2012) Contributions of central and systemic inflammation to the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 62(7):2154–2168. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.01.028
Denes A, Lopez-Castejon G, Brough D (2012) Caspase-1: is IL-1 just the tip of the ICEberg? Cell Death Dis 3:e338. doi:10.1038/cddis.2012.86
Wang L, Zhai YQ, Xu LL, Qiao C, Sun XL, Ding JH, Lu M, Hu G (2014) Metabolic inflammation exacerbates dopaminergic neuronal degeneration in response to acute MPTP challenge in type 2 diabetes mice. Exp Neurol 251:22–29. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.11.001
Lu M, Sun XL, Qiao C, Liu Y, Ding JH, Hu G (2014) Uncoupling protein 2 deficiency aggravates astrocytic endoplasmic reticulum stress and nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation. Neurobiol Aging 35(2):421–430. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.08.015
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Stutz A, Delekate A, Schwartz S, Vieira-Saecker A, Griep A, Axt D, Remus A, Tzeng TC, Gelpi E, Halle A, Korte M, Latz E, Golenbock DT (2013) NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 493(7434):674–678. doi:10.1038/nature11729
Kotas ME, Jurczak MJ, Annicelli C, Gillum MP, Cline GW, Shulman GI, Medzhitov R (2013) Role of caspase-1 in regulation of triglyceride metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(12):4810–4815. doi:10.1073/pnas.1301996110
Kole AJ, Annis RP, Deshmukh M (2013) Mature neurons: equipped for survival. Cell Death Dis 4:e689. doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.220
Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD, Van Damme P, Vanden Berghe T, Vanoverberghe I, Vandekerckhove J, Vandenabeele P, Gevaert K, Nunez G (2008) Targeted peptidecentric proteomics reveals caspase-7 as a substrate of the caspase-1 inflammasomes. Mole Cell Proteomics MCP 7(12):2350–2363. doi:10.1074/mcp.M800132-MCP200
Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD (2010) Caspase-7: a protease involved in apoptosis and inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42(1):21–24. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2009.09.013
Erener S, Petrilli V, Kassner I, Minotti R, Castillo R, Santoro R, Hassa PO, Tschopp J, Hottiger MO (2012) Inflammasome-activated caspase 7 cleaves PARP1 to enhance the expression of a subset of NF-kappaB target genes. Mol Cell 46(2):200–211. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.02.016
Forster JI, Koglsberger S, Trefois C, Boyd O, Baumuratov AS, Buck L, Balling R, Antony PM (2016) Characterization of differentiated SH-SY5Y as neuronal Screening model reveals increased oxidative vulnerability. J Biomol Screen. doi:10.1177/1087057115625190
Luk KC, Lee VM (2014) Modeling Lewy pathology propagation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(Suppl 1):S85–S87. doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(13)70022-1
Burguillos MA, Hajji N, Englund E, Persson A, Cenci AM, Machado A, Cano J, Joseph B, Venero JL (2011) Apoptosis-inducing factor mediates dopaminergic cell death in response to LPS-induced inflammatory stimulus: evidence in Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurobiol Dis 41(1):177–188. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2010.09.005
Kayagaki N, Wong MT, Stowe IB, Ramani SR, Gonzalez LC, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K, Zhang J, Lee WP, Muszynski A, Forsberg LS, Carlson RW, Dixit VM (2013) Noncanonical inflammasome activation by intracellular LPS independent of TLR4. Science 341(6151):1246–1249. doi:10.1126/science.1240248
Kamo N, Ke B, Ghaffari AA, Shen XD, Busuttil RW, Cheng G, Kupiec-Weglinski JW (2013) ASC/caspase-1/IL-1beta signaling triggers inflammatory responses by promoting HMGB1 induction in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Hepatology 58(1):351–362. doi:10.1002/hep.26320
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y, Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F, Shao F (2015) Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 526(7575):660–665. doi:10.1038/nature15514
Marino G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH, Kroemer G (2014) Self-consumption: the interplay of autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(2):81–94. doi:10.1038/nrm3735
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Ming Xiao (Nanjing Medical University) for the help with revising the manuscript. The work reported herein was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81473196), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20130039), and the key project of Natural Science Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province (No. 15KJA310002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 305 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, C., Zhang, LX., Sun, XY. et al. Caspase-1 Deficiency Alleviates Dopaminergic Neuronal Death via Inhibiting Caspase-7/AIF Pathway in MPTP/p Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 54, 4292–4302 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9980-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9980-5